Professional Documents
Culture Documents
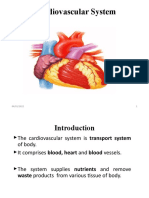
Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Beatrice Del RosarioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Beatrice Del RosarioCopyright:
Available Formats
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Two system of branching tubes of
the circulatory system that
encloses circulating fluids would
be blood-vascular system and
the lymphatic system.
BLOOD VASULAR SYSTEM
Branching tubes: lymphatic
vessels and open spaces:
lymphatic sinuses
Lymphatic sinuses: beneath the
skin and between the muscles
Lymph glands has the
lymphocytes which are a variety
of white blood corpuscles
Tonsils, thymus and spleen
belong the lymph glands
Fluid: lymph
A closed system
Made up of blood vessels
arteries, veins and capillaries
BLOOD AND BLOOD VESSELS
and the heart
Heart: contractile muscular organ
Arises from the mesoderm
that is situated in the median
mesenchyme cells and the
ventral portion of the body
patches are called the blood
Arteries: carry blood AWAY from
corpuscles
the heart and have thicker walls
Somatic vessels and splanchnic
Veins: carry blood TOWARDS
vessels
the heart and are made up of
VITELLINE VEINS: earliest blood
thinner walls
vessel to form on the surface of
1. Systemic veins flow
the yolk sac
directly into the right side of
the heart
HEART
2. Pulmonary veins flow from
the lungs into the left side of
Ventral mesentery
the heart
Dorsal and ventral mesocardia
3. Portal veins this no longer
Anterior region of the heart:
returns to the heart which flow
Ventral aorta
through
a
system
of
Aortic arches: pair of branches
capillaries
that
are
which encircle the pharynx
reconnected
to
the
Dorsal aortae (dorsal part of the
systemic veins
body)
Capillaries: attached to the ends
Caudal artery (dorsal artery
of the arteries and the front of the
which extends up to the tail
veins
region)
Carries blood which is color red
Affarent branchical vessels
and plasma which is colorless
from the aorta to the branchial
and the corpuscles
bars
(SEEN
IN
CYCLOSTOMES)
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Efferent branchial vessels or
An open system
epibranchial vessels from the
branchial bars to the aorta (SEEN
IN CYCLOSTOMES)
TRANSVERSE
SEPTUMbridges the splanchnic and
somatic mesoderm
Anterior and posterior cardinal
veins
DUCT OF CUVIER OR THE
COMMON CARDINAL VEIN
passes each side of the heart
through the transverse septum
LATERAL
OR
VENTRAL
ABDOMINAL VEINS enter the
heart along with the common
cardinal vein
Two vitelline veins
1. subintestinal
vein
mesentery of the gut and
constitutes the chief vein of
the digestive tract
2. caudal vein this continues
up to the tail as the caudal
vein
1.
Median
visceral
or
splanchnic branches (digestive
tract)
2. Lateral visceral branches
(urogenital system)
3. Parietal visceral branches
(body wall)
PORTAL SYSTEM
Part of the VENOUS system
1. Hepatic portal system (liver)
2. Renal portal system (kidney)
HEPATIC PORTAL SYSTEM
- transverse system is posterior
end of the heart
a. hepatic vein Hepatic portal
vein
b. mesenteric vein
RENAL PORTAL SYSTEM
a. subcardinal vein
b. renal portal vein
HEART
S-shaped
4 chambers
1. Sinus venosus thin walled
chambered and at the anterior
region of the heart
2. Atrium thin- walled and is
laterally (atrium has atrial
appendages which are the
flaps of the atrium)
3. Ventricle thick walled
4. Conus
arteriosusmost
anterior portion and is anterior
to the ventral aorta
INTERVENTRICULAR SEPTUM:
divides the ventricle into the left
and right compartments
Sinus venosus is now part of
the RIGHT ATRIUM
CONUS ARTERIOSUS split
into two: systemic aorta and
pulmonary trunk
Systemic aorta: connects with the
LEFT VENTRICLE
Pulmonary trunk: connects with
the RIGHT VENTRICLE
Muscular contaction begins
with the sinus venosus
Sinoatrial mode: beating of the
heart
CIRCULATION OF BLOOD
Right auricle or atrium to
the right ventricle via the
tricuspid valve.
Right ventricle to the lungs
via the pulmonary trunk
Lungs to the left auricle via
the pulmonary vein
Left auricle to the left
ventricle via the mitral
valve or bicuspid valve
Exits via the systemic
aorta
Conus arteriosus splits into
the pulmonary and the aorta
Two auricles and two ventricles
and are separated by a septum
Double circulation
Left part: aortic arch
Renal portal system fuses with
the POSTCAVAL VEIN
ONLY HAS THE HEPATIC
PORTAL SYSTEM
Sinus venosus is merged with
the RIGHT AURICLE
HEART
CAT CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Sinus venosus and
arteriosus are absent
conus
The heart is covered with the
pericardial sac
2 ventricles: RIGHT AND LEFT
Ventricle: thick walled
1. apex (posterior part)
2. base (anterior part and is
broad)
- groove
which
separated the two
ventricles
contains
branches
of
the
coronary artery and
vein (surface of the
ventricles)
- left ventricle is larger
than the right ventricle
and the left ventricle
includes the APEX
2 atriums or auricles: LEFT AND
RIGHT
- auricles have lobes
which
are
called
appendages
- Between two arteries
would
be
the
pulmonary
artery
(arch to the left then
disappears) (anterior
to the arteries)
STRUCTURE OF THE HEART
blood from the ventricle
back to the auricle
Aorta and the arch of the aorta dorsal to the pulmonary artery
2 AURICLES
2 VENTRICLES
PULMONARY VEINS ENTER
THE LEFT AURICLE
INTERAURICULAR SEPTUM
LARGE
AURICOULOVENTRICULAR
OPENINGS (FLOOR OF THE
ARTERIES)
CORONARY SINUS IPENS UP
TO THE RIGHT AURICLE
PULMONARY ARTERY (RIGHT
VENTRICLE)
VENOUS SYSTEM
RIGHT VENTRICLE
TRABECULAE CARNAE
PAPILLARY MUSCLES
CHORDAE TENDINAE
FLAPS:
TRICUSPID
VALVE
Tricuspid valve: guards
the
right
auriculoventricular
opening and prevents
the blood from flowing
back from the ventricle
to the auricle
Three-pocket
shape:
SEMILUNAR VALVES
INTERVENTRICULAR
SEPTUM: separates the
two ventricles
BICUSPID AND MITRAL
VALVE
(LEFT
VENTRICLE)
Bicuspid valve: guards
the
left
auriculoventricular
opening and prevents
the regurgitation of the
The two systemic veins of the
cat: postcaval and precaval
veins
PRECAVAL VEIN (anterior vena
cava or descending vena cava)
anterior margin of the RIGHT
AURICLE
Coronary
sinus
LEFT
AURICLE runs to the dorsal
side of the heart between the
auricles and ventricles
SINUS enters to the right
auricle
AZYGOS VEIN
Pressing the RIGHT lung to the
left INTERCOSTAL VEINS
(anterior intercostal veins and
posterior intercostal veins)
Intercostal veins are along the
POSTERIOR border of the ribs
ANTERIOR TO THE PRECAVAL
VEIN
TWO INTERNAL MAMMARY
VEINS from the midventral wall
of the chest
- diaphragm, chest wall and
pericardium
Running through the abdomen
SUPERIOR EPIGASTRIC VEINS
INNOMINATE
VEIN
OR
BRANCHIOCEPHALIC VEIN 2nd rib
VERTEBRAL VEIN
- thymus gland and
adjacent muscles
- traced to the cervical
vertebrae
COSTOCERVICAL VEIN
- from the muscles of
the back
- inner muscles of the
first two ribs
SUBCLAVIAN VEIN
EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
AXILLARY VEIN
- pectoral musle
- insertion: humerus
SUBSCAPULAR VEIN
- proximal part of the
upper arm to the
dorsal side of humerus
- upper
arm
and
shoulder
- beginning is in the
trapezius muscles
POSTERIOR
CIRCUMFLEX
VEIN
- external surface of the upper
arm
VENTRAL THORACIC VEIN
- medial portions of the pectoral
muscles
LONG THORACIC VEIN
THORACODORSAL VEIN
- longissimus dorsi
BRACHIAL VEIN
- inner surface of the
upper arm
- nerves and brachial
artery
INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
- neck
- carotid artery and
vagus nerve
TRANSVERSE
SCAPULAR
VEIN
- shoulder
CEPHALIC VEIN
- arm
- superficial vein of the
forelimb
ANTERIOR FACIAL VEIN
- face,
jaws,
submaxillary
and
lymph glands
- angular vein from the
eye
POSTERIOR FACIAL VEIN
- from the parotid gland
- posterior auricular vein
from pinna and back
of the head
TRANSVERSE VEIN
- connects the anterior
and posterior facial
veins
- across the ventral side
of the throat
ANGULAR VEIN
POSTERIOR AURICULAR VEIN
FROM THE POSTCAVAL VEIN
Also called the vena cava
posterior or the inferior and
ascending vena cava
Enters the RIGHT AURICLE
FROM BEHIND
Passes through the RIGHT
MEDIAN LOBE OF THE
LIVER
PHRENIC VEINS
HEPATIC VEINS
- from the liver
RIGHT
ADRENOLUMBAR
VEIN
RIGHT AND LEFT ADRENAL
GLAND
RIGHT AND LEFT RENAL
VEIN
- from kidney to the postcaval
vein
RIGHT
AND
LEFT
ADRENOLUMBAL VEIN
RIGHT
AND
LEFTAORTA AND ITS BRANCHES
INTERNAL
SPERMATIC
Large trunk: Aorta
VEIN
Dorsal to the pulmonary
- male cats
artery (from the left ventricle)
- traced to the scrotum
Right and left CORONARY
LEFT AND RIGHT OVARIAN
ARTERIES are from the
VEIN
base of the aorta
- female cats
LEFT
CORONARY
ILIOLUMBAR VEINS
ARTERY:
between
the
POSTCAVAL
pulmonary artery and left
auricle ventral and left side
Formed dorsal to the
of the heart
forking of the aorta by the
RIGHT
CORONARY
union
of
two
large
ARTERY groove between
COMMON ILIAC VEINS
the right auricle and right
SACRAL AND
CAUDAL
ventricle and brnaches to the
VEINS
right and dorsal surfaces of
ILIAC: INTERNAL ILIAC OR
the heart
HYPOGASTRIC
AND
ARCH OF THE AORTA
EXTERNAL ILIAC
neck, head and forelimbs
MIDDLE HAEMORRHOIDAL
- there are two in the CAT
VEIN
DEEP FEMORAL VEIN
EXTERNAL
SPERMATICARTERIAL SYSTEM
VEIN
BRANCHIOCEPHALIC OR
INFERIOR
EPIGASTRIC
INNOMINATE
ARTERY
VEIN
(RIGHT SIDE)
FEMORAL VEIN
SUBCLAVIAN
ARTERY
(LEFT SIDE)
PULMONARY VEINS
Lung region
Lungs and to the left auricle
Carries oxygenated blood
PULMONARY ARTERIES
RIGHT
AND
LEFT
PULMONARY ARTERIES
Extends from the base of the
RIGHT VENTRICLE forward
and between the auricles
Carries deoxygenated blood
Three branches in the CAT
FROM THE SUBCLAVIAN
ARTERY
1. RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN
2. RIGHT
COMMON
CAROTID
3. LEFT
COMMON
CAROTID
LEVEL OF THE FIRST RIB
1. INTERNAL MAMMARY
2. VERTEBRAL
3. COSTOCERVICAL AXIS
4. THYROCERVICAL AXIS
INTERNAL MAMMARY
SUPERIOR
EPIGASTRIC
ARTERY
- abdominal wall
COSTOCOCERVICAL
ARTERY
VERTEBRAL ARTERY
SUPERIOR INTERCOSTAL
ARTERY
- intercostal branches
- supplying
deep
muscles of the back
TRANSVERSE ARTERY OF
THE NECK
- serratus ventralis and
the
rhomboideus
muscles
THYROCERVICAL AXIS
DEEP CERVICAL ARTERY
TRANSVERSE SCAPULAR
ARTERY
- neck
SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY OR
AXILLARY ARTERY
- first rib into the axilla
VENTRAL
THORACIC
ARTERY
- medial ends of the
pectoral muscles
LONG THORACIC ARTERY
- posteriorly alongside
the middle pectoral
muscles
- latissimus dorsi
- arm
SUBSCAPULAR ARTERY
THORACODORSAL
ARTERY
- thoracic artery
- latissimus dorsi
COMMON CAROTID ARTERY
Arise
from
the
branchiocephalic
and
immediately diverge
Pass anterior in the neck
and one to each side of the
trachea
SUPERIOR
THYROID
ARTERY
INTERNAL
CAROTID
ARTERY
- dorsally with nerves and
enters the skull by a foramen
through the tympanic bulla
OCCIPITAL ARTERY
EXTERNAL
CAROTID
ARTERY
- jaw
- all parts of the head
LINGUAL ARTERY
- tongue
INTERNAL
MAXILLARY
ARTERY
- masseter
- lower and upper lips
- jaw
THE THORACIC AORTA
Arterial
ligament
or
ligament of Botallus
connection between the
pulmonary and aorta
Aorta that courses along
the thorax
Within the MEDIASTINUM
INTERCOSTAL ARTERIES
BRONCHIAL ARTERIES
ESOPHAGEAL ARTERIES
THORACIC ARTERIES
Thoracic duct
THE ABDOMINAL AORTA
Beneath the DIAPHRAGM
region
Posterior to the diaphragm:
celiac
and
superior
mesenteric arteries
Dorsal aorta
1.
Median
visceral
branches digestive
tract
2.
Lateral
visceral
branches kidneys
and
reproductive
organs
3.
Somatic branches
body wall
COELIC ARTERY
passes through the
stomach
- Three branches
COELIC ARTERY
1. HEPATIC ARTERY
- left end of the
pancreas, and to the
dorsal side of the
lesser curvature to the
hepato-duodenal
ligament
2. LEFT
GASTRIC
ARTERY
OR
CORONARY ARTERY
3. SPLENIC ARTERY
- omentum, spleen
and forks
SUPERIOR
MESENTERIC ARTERY
- greater part of the
intestine
MIDDLE COLIC ARTERY
POSTERIOR
PANCREATICODUODEN
AL ARTERY
pancreas
and
duodenum
ILEOCOLIC ARTERY
caecum
posterior part of the
ileum
RIGHT
COLIC:
ascending colon
DORSAL AORTA
Adrenal glands
ADRENOLUMBAR
ARTERY
RENAL ARTERY
PHRENIC ARTERY
INTERNAL SPERMATIC
ARTERIES
OVARIAN ARTERIES
LUMBAR ARTERIES
LEFT COLIC ARTERY
SUPERIOR
HAEMORRHOIDAL
ARTERY
EXTERNAL
ILIAC
ARTERIES
INTERNAL
ILIAC
ARTERIES
MEDIAN SACRAL OR
CAUDAL ARTERY
EXTERNAL ILIAC
DEEP
FEMORAL
ARTERIES
(thigh
region)
EXTERNAL SPERMATIC
ARTERY
INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC
ARTERY
INTERNAL ILIAC
UMBILICAL ARTERY
MIDDLE
HAEMORRHOIDAL
ARTERY
UTERINE
ARTERY
(FEMALE CATS)
- passes through the pancreas
a.
middle
gastroepiploic
vein
(omentum and stomach)
b. pancreatic vein (pancreas)
c. right splenic vein (spleen) and left
splenic vein (omentum and stomach)
HEPATIC PORTAL SYSTEM
Attached to the liver
Dorsal to the common bile duct:
Hepatic portal vein or the portal
vein
Ligament:
Hepato-duodenal
ligament
Small veins that enter the
PORTAL VEIN
1. Coronary vein
- from the stomach and lies in
the curve between the pylorus
stomach
- formed from the lesser
curvature of the stomach
- both sides of the stomach
2.Anterior
pancreaticoduodenal vein
- pancreas and duodenum
3. Right gastoepiploic vein
- pyloric region
greater curvature of the stomach
adjacent to the greater omentum
4.Gastrosplenic vein
Superior mesenteric vein
-
pancreas
and
duodenum
posterior
pancreaticoduodenal
vein
Inferior mesenteric vein
-
descending colon and
rectum
converges
intestinal
branches from small
intestine, caecum and
ascending colon
You might also like
- Clinical Epidemiology SGD 1Document6 pagesClinical Epidemiology SGD 1Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CMBDocument8 pagesChapter 8 CMBBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EmbryoDocument6 pagesChapter 4 EmbryoBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Formal ReportDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Formal ReportBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- HW2Document1 pageHW2Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- CMB Lab 1 9 1Document19 pagesCMB Lab 1 9 1rexartooz100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - GeneticsDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - GeneticsBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- CMBDocument4 pagesCMBBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation ReviewerDocument9 pagesArt Appreciation ReviewerBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- CMB 2Document6 pagesCMB 2Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 3bio2 Minutes 1Document3 pages3bio2 Minutes 1Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Art App 2Document5 pagesArt App 2Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- CMB Lab 1 9 1Document19 pagesCMB Lab 1 9 1rexartooz100% (1)
- GENETICS LABORATORY EXERCISESDocument8 pagesGENETICS LABORATORY EXERCISESBeatrice Del Rosario100% (2)
- UST College of Science Freshmen Elections ProposalDocument8 pagesUST College of Science Freshmen Elections ProposalBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EmbryoDocument7 pagesChapter 3 EmbryoBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- El Fili PaperDocument7 pagesEl Fili PaperBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- SCL HW#1Document3 pagesSCL HW#1Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Formulas: T-TestDocument1 pageExperiment 1 Formulas: T-TestBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Roadtrip PlaylistDocument1 pageRoadtrip PlaylistBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Etar Topic 8Document67 pagesEtar Topic 8Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Fieldwork-Things To BringDocument2 pagesFieldwork-Things To BringBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- (BIO 203 L) Exercise 2 Winogradsky (Preliminary)Document5 pages(BIO 203 L) Exercise 2 Winogradsky (Preliminary)Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- ECOLOGY Lab Exercise 4Document6 pagesECOLOGY Lab Exercise 4Beatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- PGC Debate - OppositionDocument3 pagesPGC Debate - OppositionBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EmbryoDocument6 pagesChapter 4 EmbryoBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Phenotype: GeneticsDocument1 pagePhenotype: GeneticsBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Complete List of Cat Muscle RegionsDocument1 pageComplete List of Cat Muscle RegionsBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 CompanaDocument4 pagesChapter 7 CompanaBeatrice Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Aortic Valve DiseaseDocument63 pagesAortic Valve DiseaseFaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument29 pagesMitral Stenosisrameshbmc100% (4)
- WBI01 01 Que 20180109Document24 pagesWBI01 01 Que 20180109Bekhiet AhmedNo ratings yet
- PathofBloodFlowHumanBodySystemsCirculatorySystemActivityMSLS13 PDFDocument4 pagesPathofBloodFlowHumanBodySystemsCirculatorySystemActivityMSLS13 PDFOliveenNo ratings yet
- 2014 ImatDocument25 pages2014 ImatNoorNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure and SoundDocument45 pagesBlood Pressure and SoundRamanathan SunderNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Ultrasound Imaging ProtocolDocument152 pagesCardiac Ultrasound Imaging Protocolbashir019No ratings yet
- Cvs ExaminationDocument50 pagesCvs ExaminationBanmeetNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument164 pagesCirculation and Gas ExchangeZuliyanto ZakariaNo ratings yet
- B F C C 18: ODY Luids AND IrculationDocument12 pagesB F C C 18: ODY Luids AND Irculation07 mathsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument42 pagesAnatomy of The HeartMae Rose Charlene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Biology Drawing Skills Handbook PDFDocument20 pagesBiology Drawing Skills Handbook PDFAna SantosNo ratings yet
- The Heart Is A Muscular Pump That Moves The Blood Through Two PathwaysDocument3 pagesThe Heart Is A Muscular Pump That Moves The Blood Through Two Pathwaysdaija paulNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Q1 WK1 2 The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument42 pagesSCIENCE 9 Q1 WK1 2 The Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDanielle SibayNo ratings yet
- Systema-Cardiovasculare-2014-by-OBD (Anat)Document72 pagesSystema-Cardiovasculare-2014-by-OBD (Anat)intan kaniaNo ratings yet
- Isolated Congenital Aortic Valve DiseaseDocument24 pagesIsolated Congenital Aortic Valve DiseaseOlga GoryachevaNo ratings yet
- Crocodiles - Biology, Husbandry and DiseasesDocument352 pagesCrocodiles - Biology, Husbandry and DiseasesElma Bibiam Naranjo Estepa83% (12)
- Anatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesAnatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemRafael Quieta Claro Jr.No ratings yet
- Magic Book DR Nikita 2.0 OnlineDocument263 pagesMagic Book DR Nikita 2.0 OnlineDinesh MorNo ratings yet
- Nclex Notes 1Document17 pagesNclex Notes 1itokumo100% (2)
- MullaDocument40 pagesMullaRijy LoranceNo ratings yet
- ValvularHeartDisease Notes S5w4Document6 pagesValvularHeartDisease Notes S5w4razzletothedazzleNo ratings yet
- CVS Examination EditedDocument134 pagesCVS Examination EditedThilak JayalathNo ratings yet
- Heart Valve Disease Treatment Guide - Cleveland ClinicDocument12 pagesHeart Valve Disease Treatment Guide - Cleveland ClinicGuillermo CenturionNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3 - HCVDDocument12 pagesCase Study 3 - HCVDJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Essential care considerations for common pediatric and medical conditionsDocument97 pagesEssential care considerations for common pediatric and medical conditionsMary Aurine FullanteNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument47 pagesCardiovascular SystemAtnasiya GadisaNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker learning essentialsDocument46 pagesPacemaker learning essentialsDeepak BhatNo ratings yet
- G5 Advanced Operation Manual PDFDocument133 pagesG5 Advanced Operation Manual PDFmhdNo ratings yet
- Practical Checklist PD CVS OnlyDocument6 pagesPractical Checklist PD CVS OnlyardiandawoodNo ratings yet