Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PLL Ac
Uploaded by
ShashankOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PLL Ac
Uploaded by
ShashankCopyright:
Available Formats
Phase locked loop
2014
B M S COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(Autonomous Institution under Visvesvaraya Technological University, Belgaum)
Report On
Open End Experiment
Phase locked loop
Submitted in partial fulfilment for the award of degree in
Bachelor of Engineering in Telecommunication Engineering
By
Student Name
USN
SANDEEP KUMAR S
1BM12TE044
SHASHANK K R
1BM12TE050
2014 - 2015
Department of Telecommunication Engineering
B.M SREENIVASAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Bull Temple Road, Basavanagudi, Bangalore - 560019
DEPARTMENT OF
TELECOMMUNICATION,BMSCE
Phase locked loop
2014
PHASE LOCKED LOOP
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that
generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an
input signal. It is an electronic circuit with a voltage- or currentdriven oscillator that is constantly adjusted to match in phase (and
thus lock on) the frequency of an input signal.
COMPONENTS
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF A PLL
The basic PLL block diagram is given above. It consists of 4 main parts1. Phase detector - It detects and compares the input frequency and
the VCO frequency. It generates a DC voltage which is proportional
to the phase difference between the 2 frequencies. There are
different circuits employed for this purpose - eg. Double-balanced
mixer, edge triggered, and monolithic phase detectors.
2. Low pass filter - It removes the high frequency components
(including noise) in the output of the phase detector. It controls
dynamic characteristics of the PLL, such as capture and lock ranges,
bandwidth and transient response.
3. Voltage controlled oscillator - It generates an output frequency that
is directly proportional to the input voltage.
DEPARTMENT OF
TELECOMMUNICATION,BMSCE
Phase locked loop
2014
4. Feedback path - Feedback is required to supply the output of the
VCO back to the phase detector.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
1. Before input is applied, the PLL is in free running mode.
2. The phase detector, or comparator compares the input frequency fIN
with the feedback frequency fOUT. The output is proportional to that
phase difference between fIN and fOUT.
3. The output of the phase detector is supplied to the low pass filter,
which removes the high frequency noise and produces a DC level.
4. The above DC level is given as input to the VCO (voltage controlled
oscillator).
5. The output of the VCO is directly proportional to the input dc level.
The VCO frequency is compared with the input frequency fIN and
adjusted till it is equal to the input frequency. This is the capture
mode of the PLL.
6. When the VCO frequency becomes equal to the input frequency, it is
in the phase locked state.
MONOLITHIC (IC) PLLs
For this experiment, we make use the IC565, which is a monolithic PLL
manufactured by Signetics Corporation. It is available in either a 14 pin
DIP package or a 10 pin metal can.
DEPARTMENT OF
TELECOMMUNICATION,BMSCE
Phase locked loop
2014
The important characteristics of this IC are 1. Operating frequency range: 0.001 Hz to 500 kHz
2. Operating voltage range: +/- 6 V to +/- 12 V
3. Input level for tracking: 10 mV to 3 V (peak-to-peak)
4. Input impedance: 10 k
5. Output sink/source current: 1 mA/10 mA
6. Drift in VCO center frequency: 300 ppm/ C
7. Drift in VCO center frequency with supply voltage: 1.5 %/V
DESIGN
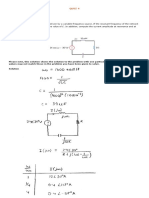
Centre frequency of PLL fOUT = 1.2/4R1C1 Hz i)
Lock frequency fL = +/- 8fOUT/V Hz, where V = +V - (-V) volts (supply
voltages) ii)
DEPARTMENT OF
TELECOMMUNICATION,BMSCE
Phase locked loop
2014
Capture frequency fC = +/- [fL/(2*3.6*1000*C2)]1/2 Hz ..
iii)
From the above circuit diagram,
R1 = 12 k
C1 = 0.01 F
C2 = 10 F
Substituting the above values in equations i, ii, iii, we get the
theoretical values
fOUT = 2.5 kHz, fL = +/- 1 kHz, fC = +/- 66.85 Hz
DEPARTMENT OF
TELECOMMUNICATION,BMSCE
Phase locked loop
2014
We obtain the practical relationship between the 3 frequency
parameters
Where fOUT = 4.1 kHz, fL = 1.5 to 6.2 kHz, fC = 3.5 to 4.7 kHz
APPLICATIONS OF PLL
1. Frequency multiplier - In this application, a frequency divider is
inserted between the VCO and the phase detector. Since the
output of the divider is locked to the input frequency fIN, the VCO
is running at a multiple of the input frequency. Desired amount of
multiplication N can be obtained by inserting a divide-by-N
network in the feedback loop.
2. Frequency shift keying (FSK) modulator
DEPARTMENT OF
TELECOMMUNICATION,BMSCE
Phase locked loop
2014
3. Demodulation of FM The most important application of PLL is in
the demodulation of FM waves. The output of the low-pass filter
is directly proportional to the original modulating signal.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
PO3 Ability to design solutions for systems/sub-systems that meet
desired specifications
PO5 Ability to design, formulate and conduct experiments using
electronic components,
electronic instruments and/or modern
engineering tools to demonstrate concepts
PO9 Ability to function effectively as an individual, and as a member/
leader in a team
PO10 Ability to communicate effectively, write reports and make
effective presentation
PO12 Ability to engage in independent learning and continuously
upgrade knowledge
COURSE OUTCOMES
CO5, CO6
REFERENCES
Communication systems Simon Haykin
Op-amps and LICs - Ramakant A. Gayakwad
DEPARTMENT OF
TELECOMMUNICATION,BMSCE
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Fdocuments - in Low Power Vlsi Design PPT 250 259Document10 pagesFdocuments - in Low Power Vlsi Design PPT 250 259B VasuNo ratings yet
- Minor Project SynopsisDocument3 pagesMinor Project SynopsisChanchal Kumar0% (2)
- Lab Report 3: Electric Circuit Analysis I E E E - 121Document8 pagesLab Report 3: Electric Circuit Analysis I E E E - 121HaiderNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Circuits: Half-Wave Rectifier (HWR)Document18 pagesRectifier Circuits: Half-Wave Rectifier (HWR)Md ArifNo ratings yet
- EEE301 Project Tic Tac Toe ReportDocument7 pagesEEE301 Project Tic Tac Toe ReportKasshaf Ahmad100% (1)
- EE309 Notes 20 PDFDocument3 pagesEE309 Notes 20 PDFHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Presentation1 Final Presentation Parking SensorDocument12 pagesMini Project Presentation1 Final Presentation Parking SensorChethan ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2.linear Integrated Circuits Lab PDFDocument104 pages2.linear Integrated Circuits Lab PDFSAMPATH KUMAR.J MCE-LECT/ECENo ratings yet
- Manual de Pinagem, Circuitos Básicos de Testes e CaracterísticasDocument339 pagesManual de Pinagem, Circuitos Básicos de Testes e Característicasmarcelo vintageNo ratings yet
- 25 Input Voltage: 50 Igbt ResultDocument3 pages25 Input Voltage: 50 Igbt ResultEdwin KevynNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument4 pagesProject ProposalSushrut BhatNo ratings yet
- Ultra Sonic DectorDocument2 pagesUltra Sonic DectorSAMO SAMARANo ratings yet
- EE103 Exp9 TOSHIT - 2101CB59Document5 pagesEE103 Exp9 TOSHIT - 2101CB59Rahul PalNo ratings yet
- Static CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsDocument19 pagesStatic CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsAbhijna MaiyaNo ratings yet
- Physics 30 - Digital ElectronicsDocument30 pagesPhysics 30 - Digital ElectronicsHakim Abbas0% (1)
- Class Activity STI AnswerDocument3 pagesClass Activity STI AnswerBien MedinaNo ratings yet
- B.E Electronics & Communication Engineering / Telecommunication Engineering (Common To Electronics & Communication and Telecommunication Engineering)Document3 pagesB.E Electronics & Communication Engineering / Telecommunication Engineering (Common To Electronics & Communication and Telecommunication Engineering)mabhatNo ratings yet
- Pin-Pointer Metal Detector - "PETRAPIN-A07" Rev.1Document15 pagesPin-Pointer Metal Detector - "PETRAPIN-A07" Rev.1eu1mister6002100% (1)
- CS1403 Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument2 pagesCS1403 Linear Integrated CircuitsMohamed Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Microelectronics Journal: A Low-Power Comparator With A Wide Input VCM RangeDocument13 pagesMicroelectronics Journal: A Low-Power Comparator With A Wide Input VCM Rangesavani1979No ratings yet
- CMOS OTA (Output Transconductance Amplifier) (Analog Devices Wiki)Document4 pagesCMOS OTA (Output Transconductance Amplifier) (Analog Devices Wiki)qqazertyNo ratings yet
- Network Theory SolutionsDocument159 pagesNetwork Theory SolutionsSrijan DwivediNo ratings yet
- IP9001 4-Ch Motor Drive Ic For Portable CDP: DescriptionsDocument32 pagesIP9001 4-Ch Motor Drive Ic For Portable CDP: DescriptionsvetchboyNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 3: Group #: - 1Document12 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 3: Group #: - 1Jomar RosalesNo ratings yet
- 74HC4351Document18 pages74HC4351mahbub_32No ratings yet
- EE103 - Compiled Quizes PDFDocument25 pagesEE103 - Compiled Quizes PDFJacob PopcornsNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Edn Design Ideas 2002Document198 pagesVdocuments - MX Edn Design Ideas 2002ciccioNo ratings yet
- Lect8 SpiceDocument27 pagesLect8 SpiceishantNo ratings yet
- HFIC Chapter 9 HF Mixer Switch Modulator DesignDocument48 pagesHFIC Chapter 9 HF Mixer Switch Modulator DesignAnonymous 39lpTJiNo ratings yet
- Low Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFDocument1 pageLow Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFShrivlsi RamNo ratings yet