Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5: Malaysian Bond Market
Uploaded by
Pablo Ekskoba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views4 pagesThe Government of Malaysia issues marketable bonds to finance its working capital and development expenditure. Bank Negara Malaysia acts as a banker and financial advisor to governments. Khazanah Nasional Berhad act as the national asset management company Re-energize the Malaysian financial sector by buying non-performing loans (NPLs) from financial institutions and maximize their recovery value.
Original Description:
Original Title
Maf 630 Chapter 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Government of Malaysia issues marketable bonds to finance its working capital and development expenditure. Bank Negara Malaysia acts as a banker and financial advisor to governments. Khazanah Nasional Berhad act as the national asset management company Re-energize the Malaysian financial sector by buying non-performing loans (NPLs) from financial institutions and maximize their recovery value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views4 pagesChapter 5: Malaysian Bond Market
Uploaded by
Pablo EkskobaThe Government of Malaysia issues marketable bonds to finance its working capital and development expenditure. Bank Negara Malaysia acts as a banker and financial advisor to governments. Khazanah Nasional Berhad act as the national asset management company Re-energize the Malaysian financial sector by buying non-performing loans (NPLs) from financial institutions and maximize their recovery value.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
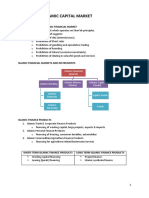
CHAPTER 5: MALAYSIAN BOND MARKET
NEEDS FOR A STRONG DOMESTIC BOND MARKET
Investors demand large amount of finance for manufacturing activities, infrastructure
improvements and provision of services
Change in economic structure from labour intensive to capital intensive
Long-term institutional investors need funds for portfolio diversification and liability
management purposes
WHO ARE THE ISSUERS?
1. Government of Malaysia
Government issues marketable bonds to finance its working capital and development
expenditure
Malaysian Treasury Bills (MTB) is one of the common short-term securities the
government issues for their working capital.
For development expenditure, the government issues interest-bearing long-term bonds
in the domestic capital market
2. Bank Negara Malaysia
Objectives of Bank Negara Malaysia:
To issue currency and keep reserves safeguarding the value of currency
To act as a banker and financial advisor to governments
To promote monetary stability and a sound financial structure
To promote reliable, efficient and smooth operation of national
payments and settlement systems
To ensure national payment and settlement systems policy is directed to
the advantages of Malaysia
To influence the credit situation to advantage of country
The central bank issues bonds to manage liquidity in both the conventional and Islamic
financial markets
Bank Negara provides temporary advances to the government to cover any deficit in the
budget revenue
Examples of securities issued by Bank Negara are:
Bank Negara Monetary Notes
Sukuk BNM Issues
Merdeka Savings Bonds
3. Quasi-government Institutions
Khazanah Nasional Berhad
It is the investment holding arm of the Government of Malaysia.
Khazanahs main long-term objective is to promote economic growth and
make strategic investments on behalf of the government which would
contribute towards nation building
Pengurusan Danaharta Nasional Berhad
Public company wholly owned by the Malaysian government.
Act as the national asset management company
Re-energize the Malaysian financial sector by buying non-performing loans
(NPLs) from financial institutions and maximize their recovery value
Danamodal
Special purpose company incorporated by Bank Negara Malaysia
Recapitalize and strengthen Malaysias banking institutions
Promote stability in the local banking industry
4. Cagamas Berhad
The National Mortgage Corporation which is a leading securitization house
Promote development of the private debt securities market
Promotes secondary mortgage market in Malaysia
Issues debt securities to finance the purchase of government servants housing loans
Examples of Cagamas issues are:
Cagamas Fixed Rate Bonds
Cagamas Floating Rate Bonds
Cagamas Notes
Sanadat Mudharabah Cagamas
5. Multilateral Development Banks
MDBs grant financing for technical assistance, advisory services or project preparation
Provide financial support and professional advice to the developing countries in terms of
economic and social development activities Interest rate on CDs is fixed over their stated
maturity.
Sources to raise funds:
MDBs borrow development funds from international capital markets and re-lend
to the governments of developing countries in the form of long-term loans.
The MDBs use money donated by governments of other countries to finance
very long-term loans. The borrowing countries pay interest well below market
interest rates.
BOND INVESTORS
1. Employees Provident
Fund
2. Pension Funds
3. Unit Trusts
4. Insurance Companies
5. Asset Management
Companies
A national social security organization operating through a
provident fund scheme in Malaysia
A scheme designed with conservative investment
strategies
Manages contributors funds and assets to obtain good
returns for members
Diversify risk through investment portfolio
Managed by professional fund managers
Easy access to liquidity
Convenience and affordable investment amounts
Issue unit-linked bonds which are collective investment
funds similar to unit trusts
A central disposition agency which takes loans from all
financial institutions
2
6. Discount Houses
7. Commercial Banks
8. Islamic Banks
9. Investment Banks
10. Securities Companies
11. Finance Companies
12. Merchant Banks
Includes the business of receiving and utilizing deposits
and other funds for investment purposes
Financial intermediaries which transfer deposits by
making loans
Pool funds from numerous sources and lend these funds
to large number of borrowers
Banks which are governed by Shariah law
Provide Shariah-compliant products and services
Regarded as excellent proxies for capital market
Provide wide range of service areas: (i) advisory, (ii) fundraising and (iii) equities trading
Provide online stock broking services, trading, corporate
finance and market economic analysis
Offer investment research and advisory services
Provide additional services: (i) institutional dealings, (ii)
retail support services and (iii) futures dealing
Provide credit to individuals and businesses
Buy the time-sales contracts of merchants for the
purchase of consumer goods and services
Financial intermediaries which involve in transferring
capital to those interested in borrowing funds
Activities of merchant banks include: (i) mergers and
acquisitions and (ii) restructuring and reorganization
DEBT SECURITIES PRODUCTS
Fixed rate bond.
Hybrid bonds.
Floating rate notes.
Variable rate notes.
Medium-term note programmes.
Commercial mortgage-backed securities.
Asset-backed securities.
Securitized products.
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT SECURITIES
Malaysian Treasury Bills
Malaysian Islamic Treasury Bills
Malaysian Government Securities
Government Investment Issues
CORPORATE BONDS
Fixed coupon bearing bonds:
1. Straight bonds
2. Bonds with detachable warrants
3. Floaters
4. Asset-backed securities
5. Convertible bonds
6. Callable bonds
3
TYPES OF ISLAMIC BONDS
1. Debt-based bonds
2. Asset-based bonds
3. Equity-based bonds
COMPARISON BETWEEN ISLAMIC AND CONVENTIONAL BONDS
ITEMS
Issuance process
Structure types
Issuers
Investors
ISLAMIC BONDS
Must be approved by Shariah scholars
and Securities Commission
Asset, equity and debt based
Government, semi-government and
private sector
Both conventional and Islamic investors
CONVENTIONAL BONDS
Must be approved by Securities
Commission only
Debt based only
Government, semi-government and
private sector
Only conventional investors
BANK NEGARA MALAYSIA SUKUK IJARAH
Sukuk which is based on Ijarah or sale-and-lease-back concept
MERDEKA SAVINGS BONDS
Shariah-compliant and scripless bonds which are offered to Malaysian citizens aged 56 years and
above and individuals who have retires on medical grounds
MALAYSIAN ISLAMIC TREASURY BILLS
A short term securities issued on a weekly basis with an original maturity of one year
BANK NEGARA MONETARY NOTES
Islamic securities issued for the purpose of managing liquidity in Islamic financial market
BOND PRICING AGENCIES
1. Rating Agency Malaysia Berhad
2. Malaysian Rating Corporation Berhad
3. Standard & Poors
4. Moodys
You might also like
- Final PPTDocument141 pagesFinal PPTJanhvi ShahNo ratings yet
- 9th Edit OBLICON - CASE DIGEST - MIDTERM 1B PDFDocument429 pages9th Edit OBLICON - CASE DIGEST - MIDTERM 1B PDFjenifer Mendoza100% (1)
- Bank - A Financial Institution Licensed To Receive Deposits and Make Loans. Banks May AlsoDocument3 pagesBank - A Financial Institution Licensed To Receive Deposits and Make Loans. Banks May AlsoKyle PanlaquiNo ratings yet
- A Study On Credit AppraisalDocument83 pagesA Study On Credit AppraisalMallik ArjunNo ratings yet
- Black Derman Toy ModelDocument4 pagesBlack Derman Toy ModelLore-Anne A. CadsawanNo ratings yet
- Innovative Financial Instrument - FinalDocument6 pagesInnovative Financial Instrument - FinalRinse JohnNo ratings yet
- The Practice of Investor RelationsDocument14 pagesThe Practice of Investor RelationsLang Mensilang100% (1)
- Government Accounting ReviewDocument6 pagesGovernment Accounting ReviewErwinPaulM.SaritaNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Marine VesselsDocument41 pagesValuation of Marine VesselsReza Babakhani100% (1)
- 15 Pacific Rehouse v. CADocument1 page15 Pacific Rehouse v. CAMiguel SanchezNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02Document35 pagesManagement of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02suma100% (4)
- Depository & Non-Depository Institutions of BDDocument22 pagesDepository & Non-Depository Institutions of BDProbortok Somaj80% (5)
- Non Banking Financial InstitutionDocument5 pagesNon Banking Financial InstitutionRehan BalochNo ratings yet
- Financial and Regulatory Institutions: Assignment No. 2Document12 pagesFinancial and Regulatory Institutions: Assignment No. 2Saad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Bank Management Summary - Chapter OneDocument6 pagesBank Management Summary - Chapter Oneabshir sugoowNo ratings yet
- FMI - Chap 2Document35 pagesFMI - Chap 2alioNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and ServicesDocument12 pagesFinancial Markets and Servicessrilekha thamalampudiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - History and Development of Islamic Banking SystemDocument44 pagesChapter 1 - History and Development of Islamic Banking SystemHaniZahirahHalimNo ratings yet
- Individual Project Paper - G1918762 PDFDocument9 pagesIndividual Project Paper - G1918762 PDFHANISNo ratings yet
- Soft Copy of Project... 2Document21 pagesSoft Copy of Project... 2Jahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Non Bank Financial IntermediariesDocument53 pagesNon Bank Financial IntermediariesPuviin Varman100% (1)
- Planning, Organizing, Directing and Controlling: Estimation of Capital RequirementsDocument4 pagesPlanning, Organizing, Directing and Controlling: Estimation of Capital RequirementsJG ElbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document22 pagesChapter 7trevorsum123No ratings yet
- DPF10013 - Chapter 5Document19 pagesDPF10013 - Chapter 5严钧龄No ratings yet
- Topic 7 - BWFF3033 - FMI Capital Market DebtDocument36 pagesTopic 7 - BWFF3033 - FMI Capital Market Debtzikril94No ratings yet
- FMI Class - Chap 2Document29 pagesFMI Class - Chap 2ruman mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Fin 642 Report UpdatedDocument18 pagesFin 642 Report UpdatedMahmudulHasanRakibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1structre of Malaysian FinancialDocument19 pagesChapter 1structre of Malaysian FinancialdipanajnNo ratings yet
- Banking and FinanceDocument6 pagesBanking and FinanceLubna MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Assignment On NBFI Sector in BangladeshDocument10 pagesAssignment On NBFI Sector in BangladeshFarhan Ashraf SaadNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument38 pagesMerchant BankingBhargavKevadiyaNo ratings yet
- Economics Write UpDocument5 pagesEconomics Write UpHsfhrhfhfcu N3jddjejfjfrjNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Financial Management and Services For Cie 2 ExamDocument12 pagesPresentation of Financial Management and Services For Cie 2 ExamAarti .k.ahir8210No ratings yet
- Unit - II: Merchant BankingDocument38 pagesUnit - II: Merchant BankingashishNo ratings yet
- Unit - II: Merchant BankingDocument39 pagesUnit - II: Merchant BankingashishNo ratings yet
- The Role of Financial Market and Institution in The Economic Development of BangladeshDocument11 pagesThe Role of Financial Market and Institution in The Economic Development of Bangladeshbleeding_heart120567% (12)
- Meaning of Finance: Information Has Been Collected From The WebsiteDocument93 pagesMeaning of Finance: Information Has Been Collected From The WebsiteShobhit GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Markets "Final Project": Submitted byDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Financial Markets "Final Project": Submitted byHafsa ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Financial Institutions and Their Operations LectureDocument147 pagesChapter Two Financial Institutions and Their Operations LectureAbdiNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document13 pagesPresentation 1ashwin6950No ratings yet
- Structure of Indian Financial SystemDocument24 pagesStructure of Indian Financial SystemRaj SodhaNo ratings yet
- Word Files NITDocument7 pagesWord Files NITapi-3700469No ratings yet
- Financial Market in Pakistan: Financial Markets and Their Roles: Commercial BanksDocument5 pagesFinancial Market in Pakistan: Financial Markets and Their Roles: Commercial BanksAnamMalikNo ratings yet
- The Role of Financial Intermediaries in Pakistan Economy With A Few Local Examples of Banks and Other Institutions.Document4 pagesThe Role of Financial Intermediaries in Pakistan Economy With A Few Local Examples of Banks and Other Institutions.aqibNo ratings yet
- Important Questions BankingDocument21 pagesImportant Questions BankingAshutosh AgalNo ratings yet
- Shivam - Kumar - MFS AssignmentDocument8 pagesShivam - Kumar - MFS AssignmentShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument6 pagesGroup 4 PresentationeranyigiNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument34 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionscr7milamkbNo ratings yet
- Financial Intermediaries and Players Philippines Financial Intermediaries and PlayersDocument9 pagesFinancial Intermediaries and Players Philippines Financial Intermediaries and PlayersLeo-Alyssa Gregorio-CorporalNo ratings yet
- CH 1 FIIMDocument28 pagesCH 1 FIIMMulata KahsayNo ratings yet
- Final Project of Fin 433Document43 pagesFinal Project of Fin 433UpomaAhmedNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report.................. Docx132Document37 pagesSummer Internship Report.................. Docx132Rashmin TomarNo ratings yet
- CH 1 FIIMDocument28 pagesCH 1 FIIMKume MezgebuNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Financial Services 1 PDFDocument6 pagesUnit1 Financial Services 1 PDFRoshan SinghNo ratings yet
- Fund Mobilization of Commercial BanksDocument3 pagesFund Mobilization of Commercial BanksSidra SidNo ratings yet
- FIM Group Assignmen FinalDocument9 pagesFIM Group Assignmen FinalEndeg KelkayNo ratings yet
- MBFS Financial SystemDocument40 pagesMBFS Financial SystemNagendra Basetti100% (1)
- Dbfi304 Financial ServicesDocument12 pagesDbfi304 Financial Servicesvikash rajNo ratings yet
- Management of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02Document31 pagesManagement of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02aimanbatool24No ratings yet
- Commercial BanksDocument28 pagesCommercial BanksHarshita MarmatNo ratings yet
- Report On Lankabangla Finance Limited by TowhidulDocument31 pagesReport On Lankabangla Finance Limited by TowhidulTowhidul Alam Pavel55% (11)
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument32 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationSaad MajeedNo ratings yet
- MB18FM02 Managing Banks and Financial InstitutionsDocument29 pagesMB18FM02 Managing Banks and Financial Institutionsdaniel rajkumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 AnswersDocument7 pagesTutorial 5 Answerskung siew houngNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 - Tutorial 2 An Overview of Fin Mkts & InstnsDocument4 pagesWEEK 2 - Tutorial 2 An Overview of Fin Mkts & Instnsweikang120503No ratings yet
- 205 Finance Market & Banking OperationsDocument10 pages205 Finance Market & Banking Operationsxonline022No ratings yet
- Maf 630 Chapter 11Document6 pagesMaf 630 Chapter 11Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- MAF 680 Chapter 7 - Futures Derivatives (New)Document89 pagesMAF 680 Chapter 7 - Futures Derivatives (New)Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Maf 630 CHAPTER 7Document3 pagesMaf 630 CHAPTER 7Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Maf 630 Chapter 6Document5 pagesMaf 630 Chapter 6Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Stock Valuation Methods and Efficient Market HypothesisDocument5 pagesChapter 3: Stock Valuation Methods and Efficient Market HypothesisPablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Maf 630 Chapter 8Document4 pagesMaf 630 Chapter 8Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Maf 630 Chapter 1Document3 pagesMaf 630 Chapter 1Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Maf 630 Chapter 4Document2 pagesMaf 630 Chapter 4Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Suggested Solution FAR450 - JUNE 2012 Solution 1ADocument8 pagesSuggested Solution FAR450 - JUNE 2012 Solution 1APablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Solution Far450 - Jun 2014Document7 pagesSolution Far450 - Jun 2014Pablo EkskobaNo ratings yet
- Example:: Basis Assets LiabilitiesDocument23 pagesExample:: Basis Assets LiabilitiesAmbika Prasad ChandaNo ratings yet
- Magic Formula in The Brazilian Stock MarketDocument51 pagesMagic Formula in The Brazilian Stock Marketdeni_2013No ratings yet
- SIP Report 2021Document42 pagesSIP Report 2021Dhrupal TripathiNo ratings yet
- 100 Women in Hedge Funds - Fireside Chat With Saba Capital's Boaz WeinsteinDocument2 pages100 Women in Hedge Funds - Fireside Chat With Saba Capital's Boaz WeinsteingneymanNo ratings yet
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument14 pagesReserve Bank of IndiaJAYANTHI BNo ratings yet
- Foreign Portfolio Investment in IndiaDocument27 pagesForeign Portfolio Investment in IndiaSiddharth ShindeNo ratings yet
- H53H54Document1 pageH53H54MinamPeruNo ratings yet
- Option MomentumDocument63 pagesOption Momentumyeongloh100% (1)
- A View From The Trenches: Toronto, Sunday, May 5, 2013Document8 pagesA View From The Trenches: Toronto, Sunday, May 5, 2013dan4everNo ratings yet
- WP5 EpsteinDocument26 pagesWP5 EpsteinererereretrterNo ratings yet
- PS 1Document4 pagesPS 1BlackRoseNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Financial Management: Dividend - MeaningDocument4 pagesAssignment: Financial Management: Dividend - MeaningSiddhant gudwaniNo ratings yet
- 002 MAS FS Analysis Rev00 PDFDocument5 pages002 MAS FS Analysis Rev00 PDFCyvee Joy Hongayo OcheaNo ratings yet
- Futures and Options Trading: Pradiptarathi Panda Assistant Professor, NismDocument43 pagesFutures and Options Trading: Pradiptarathi Panda Assistant Professor, NismMaunil OzaNo ratings yet
- Business Finance - Horizontal AnalysisDocument2 pagesBusiness Finance - Horizontal AnalysisAnon0% (1)
- StocksDocument15 pagesStocksmayko-angeles-3102No ratings yet
- LegalForce's Opposition To Keker Van Nest & Peters Termination by UpCounselDocument129 pagesLegalForce's Opposition To Keker Van Nest & Peters Termination by UpCounselRaj AbhyankerNo ratings yet
- CIR Vs PAL - ConstructionDocument8 pagesCIR Vs PAL - ConstructionEvan NervezaNo ratings yet
- Edited For Final SubmissionDocument47 pagesEdited For Final SubmissionMedina Pangilinan0% (1)
- Surrender FormDocument2 pagesSurrender Formvi_sharNo ratings yet
- Kaveri Seed Company LimitedDocument27 pagesKaveri Seed Company LimitedAgarwal SaranshNo ratings yet
- Arkwright - Water Frame RulesDocument36 pagesArkwright - Water Frame RulestobymaoNo ratings yet
- Stock Exchange of IndiaDocument23 pagesStock Exchange of IndiaAnirudh UbhanNo ratings yet