Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F3 Chapter 9 - Stars and Galaxies PDF
Uploaded by
Susan SuanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F3 Chapter 9 - Stars and Galaxies PDF
Uploaded by
Susan SuanCopyright:
Available Formats
Intensive
SCIENCE INTENSIVE PROGRAMME FOR FROM 3
CHAPTER 9 : STARS AND GALAXIES
FOR
FOR
FORM
FOR FORM
FORM 333 SMK SUNGAI PASIR , O8OOO SUNGAI PETANI , KEDAH DARULAMAN.
WWW.SMKSP.COM TEL : 04-421 1764 FAX : 422 0203 LAMAN WEB : WWW.SMKSP.COM
SCIENCE
SCIENCE
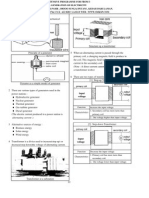
1 The Sun is the centre of our Solar System.
(2)
(3)
Solar System
2 The Sun is actually a star because it release heat and
light energy through nuclear reaction.
Solar flares :
A strong explosion of gases that happen suddenly
for few minute / hours in the chromosphere.
Solar flares released charged particles and emit
rays (like X-rays and gamma rays)
Sunspots :
Are dark spots on the surface of the Sun's
photosphere with lower temperature which exist
in groups and have various sizes. It can occurs for
a period of few hours to several months.
The area arround a sunspot has a strong magnetic
field.
3 Structure of the Sun :
(1)
(a)
(b)
(2)
(a)
5 The effects of the phenomena that occurs at the Sun
atmosphere :
(1) Influence the weather and climate on Earth.
(2) Disturbance to the communications system.
(3) Produced Aurora lights.
Sun's core :
Consists of hydrogen and helium gases.
Nuclear reaction occurs in the core.
Sun's atmosphere :
Consists of three layers ;
(1) Corona : Outer most layer which only
visible during eclipse of the Sun.
(2)
6 The Universe is defined as all of outer space and
everything in it. The Universe contains thousand of
millions of galaxies.
Temperature is about 1.5 million 0 C
Chromosphere : Bright red layer which
only visible during eclipse of the Sun.
7 Galaxies are classified according to shapes :
Shapes
Types and Examples
(1) Elliptical galaxies
0
(3)
Temperature is between 10,000-50,000 C
Photosphere : compact layer of gas seen
to be shining with yellow light from Earth.
Galaxy M87 in Virgo
Temperature is about 6000 0 C
(2) Spiral galaxies
Milky Way , Andromeda
4 Phenomena that occurs at the Sun's atmosphere ;
(1) Prominence :
an explosion of hot gas that shoots out from the
Sun's chromosphere with shiny bright light which
can take place for a short period or several weeks
Prominences cause flow of wind called Solar
Wind which consists of charged particles.
(3) Irregular galaxies
Magellanic Cloud
27
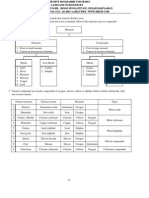
8 Birth and death of a Star :
(1) A Star is born from a nebula ( a large cloud of dust and gases such as hydrogen and helium)
(2) Strong garvitational force cause the particles in Nebula shrink and compressed to from a core.
(3) When the temperature in the core become very high, nuclear reaction occurs and the hydrogen is turned into
Helium. A lot of heat and light energy are released. The core shines and a star is born.
(4) A Star will die when all the hydrogen gas in its core is used up in nuclear reactions.
Nebula
Medium-sized Star
Large Star
Super-large Star
Red Giant
Red Giant
Red Giant
White Dwarf
Super Giant
Super Giant
Black Dwarf
Supernova
Supernova
Neutron Star
Black Hole
( Very small Star )
9 Stars are classified according to their characteristics :
(1) Size
(2) Brightness
(3) Colour and temperature.
10 Constellation is a group of stars that form a certain pattern in the sky.
Orion
Ursa Major
Southern Cross
28
You might also like
- WB Science F2 (Exp Note) 1st PDFDocument11 pagesWB Science F2 (Exp Note) 1st PDFSusan SuanNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 7Document8 pagesf1 Chapter 7NurAnnyss AzizNo ratings yet
- Land and Its ResourcesDocument18 pagesLand and Its ResourcesnanteniNo ratings yet
- Expressnotes Scienceform3Document15 pagesExpressnotes Scienceform3Xenia SeahNo ratings yet
- ExpressNotes SC (F1) 1st PDFDocument12 pagesExpressNotes SC (F1) 1st PDFSusan SuanNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 1Document7 pagesf1 Chapter 1Nurul AzuwinNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 5Document7 pagesf1 Chapter 5NurAnnyss AzizNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 PDFDocument7 pagesBab 2 PDFSusan SuanNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 7 - ElectricityDocument4 pagesF3 Chapter 7 - ElectricityArrow BlackNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 8 - Generation of ElectricityDocument5 pagesF3 Chapter 8 - Generation of ElectricityAnnysse SophielleaNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 10 - Space ExplorationDocument1 pageF3 Chapter 10 - Space ExplorationNasruddin Amir100% (1)
- f1 Chapter 4Document7 pagesf1 Chapter 4NurAnnyss AzizNo ratings yet
- For Form 3Document1 pageFor Form 3Shu85No ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 6 - Land and Its ResourcesDocument6 pagesF3 Chapter 6 - Land and Its ResourcesArif Mosh XI0% (1)
- F3 Chapter 2 - Blood CirculationDocument2 pagesF3 Chapter 2 - Blood CirculationJessica StewartNo ratings yet
- Skema Set B BI PT3 2014Document4 pagesSkema Set B BI PT3 2014bdy3372No ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 3 - ExcretionDocument2 pagesF3 Chapter 3 - ExcretionMona MohtarNo ratings yet
- For Form 3Document1 pageFor Form 3Shu85No ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 4 - ReproductionDocument6 pagesF3 Chapter 4 - ReproductionMona MohtarNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 1 - RespirationDocument1 pageF3 Chapter 1 - Respirationzalifah74No ratings yet
- Modul Set ADocument9 pagesModul Set AZuraihan Yusof75% (16)
- Mark Scheme SECTION A: Error Identification (20 Marks) Identification of Errors (A) Correction of Errors (B) TotalDocument6 pagesMark Scheme SECTION A: Error Identification (20 Marks) Identification of Errors (A) Correction of Errors (B) TotalAnnie ChengNo ratings yet
- Modul Set BDocument10 pagesModul Set BZuraihan Yusof100% (4)
- Kertas Ujian Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4 KSSR Kertas 1Document3 pagesKertas Ujian Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4 KSSR Kertas 1Susan SuanNo ratings yet
- PT3 Kelantan BI PDFDocument13 pagesPT3 Kelantan BI PDFSusan SuanNo ratings yet
- (10 Marks) (Time Suggested: 15 Minutes) : Sulit 014/2 Section ADocument8 pages(10 Marks) (Time Suggested: 15 Minutes) : Sulit 014/2 Section AwisNo ratings yet
- Moral Revision 2013Document2 pagesMoral Revision 2013Susan SuanNo ratings yet
- BI K1, 2 Form 2 PAT 2012 SelangorDocument0 pagesBI K1, 2 Form 2 PAT 2012 Selangorainishi88No ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFDocument4 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFFarah Sofea Razali91% (11)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 6 Uniform Circular MotionDocument83 pages6 Uniform Circular MotionRamachandranPerumal0% (1)
- (Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Document12 pages(Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Resonance Eduventures100% (1)
- Additive ManufacturingDocument20 pagesAdditive Manufacturingjoeborderline100% (1)
- Metal FormingDocument13 pagesMetal Formingabdsu75No ratings yet
- Applications of Solar Energy PDFDocument42 pagesApplications of Solar Energy PDFpallav guptaNo ratings yet
- Permanent WayDocument7 pagesPermanent Wayaishwarya mundraNo ratings yet
- 2 Manual de Proteccin Catdica Cathodic Protection HandbooDocument59 pages2 Manual de Proteccin Catdica Cathodic Protection Handboogoyote100% (1)
- Johor-Answer P2-Trial SPM 2007Document8 pagesJohor-Answer P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- Phy-153 Course OutlineDocument26 pagesPhy-153 Course OutlinealdricNo ratings yet
- 6 - Pressuremeter PDFDocument71 pages6 - Pressuremeter PDFjenvarmatNo ratings yet
- 2011121503-3-Wannate 8221enDocument2 pages2011121503-3-Wannate 8221en8612106535No ratings yet
- Note CHP 1-Material Science 281 Uitm Em110Document59 pagesNote CHP 1-Material Science 281 Uitm Em110bino_rye100% (3)
- AxaxxDocument19 pagesAxaxxkara_25No ratings yet
- Melamine Formaldehyde Curing Studies andDocument7 pagesMelamine Formaldehyde Curing Studies andtahera aqeelNo ratings yet
- Simulation work on Fractional Order PIλ Control Strategy for speed control of DC motor based on stability boundary locus methodDocument7 pagesSimulation work on Fractional Order PIλ Control Strategy for speed control of DC motor based on stability boundary locus methodseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - How Lenses Are Edged - 2007 - System For Ophthalmic DispensingDocument16 pagesChapter 24 - How Lenses Are Edged - 2007 - System For Ophthalmic DispensingsNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Aperture Focussing Technique For Testing The Defects in Concrete Using LS DynaDocument27 pagesSynthetic Aperture Focussing Technique For Testing The Defects in Concrete Using LS DynaAnishu RahmanNo ratings yet
- Enter Your Response (As An Integer) Using The Virtual Keyboard in The Box Provided BelowDocument102 pagesEnter Your Response (As An Integer) Using The Virtual Keyboard in The Box Provided BelowCharlie GoyalNo ratings yet
- Save Money, Go Solar: Top 5 Reasons To Go Solar Special Incentives AvailableDocument3 pagesSave Money, Go Solar: Top 5 Reasons To Go Solar Special Incentives AvailableMaogageoffreyNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - HeatDocument13 pagesElasticity - HeatHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- A4-P 4.0 enDocument32 pagesA4-P 4.0 enmkpqNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Lalitha Sahasranamam: (Where Spirituality Guides Science)Document9 pagesExploring The Lalitha Sahasranamam: (Where Spirituality Guides Science)ShraddhamritaChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Low Stress Mechanical Properties of Woven Silk Fabrics (Part-1)Document6 pagesLow Stress Mechanical Properties of Woven Silk Fabrics (Part-1)Mohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Full Lab Report #8Document13 pagesFull Lab Report #8Joe Morrison100% (2)
- Sleeperwall 1Document6 pagesSleeperwall 1John SmithNo ratings yet
- Chemical Physics: Manish Chopra, Niharendu ChoudhuryDocument11 pagesChemical Physics: Manish Chopra, Niharendu ChoudhuryasdikaNo ratings yet
- 2 Signals and Systems: Part I: Solutions To Recommended ProblemsDocument9 pages2 Signals and Systems: Part I: Solutions To Recommended ProblemssamibdzNo ratings yet
- Agar Extraction Process For Gracilaria CliftoniiDocument7 pagesAgar Extraction Process For Gracilaria CliftoniiAdaNo ratings yet
- Code - Bright. Constitutive Laws: Mechanical Constitutive Models Hydraulic and Thermal Constitutive ModelsDocument34 pagesCode - Bright. Constitutive Laws: Mechanical Constitutive Models Hydraulic and Thermal Constitutive ModelsJonathan TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- InggrissinkholeDocument2 pagesInggrissinkholeRika Rika SilvianaNo ratings yet