Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SPM Mathematics Revision: Standard Form, Number Bases, Polygons & Circles
Uploaded by
Dk HardianaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SPM Mathematics Revision: Standard Form, Number Bases, Polygons & Circles
Uploaded by
Dk HardianaCopyright:
Available Formats
[ SM. ST.
PETER TELIPOK ]
(A)
1
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
Standard Form 3 4 marks
Round off 0.0368 correct to two significant figures
A.
0.03
C.
0.036
B.
0.04
D.
0.037
[2003, No.1]
6.27 104 =
A.
0.0000627
C.
62700
B.
0.000627
D.
6270000
[2003, No.2]
1.8 105 + 88000 =
A.
2.68 105
C.
1.06 105
B.
2.68 109
D.
1.06 109
[2003, No.3]
The area of a rectangular nursery plot is 7.2 km 2. Its width is 2400 m. The length, in m, of the nursery
plot is
A.
3 103
C.
4.8 103
B.
3 104
D.
4.8 104
[2003, No.4]
Express 0.0000203 in standard form.
A.
2.03 105
C.
203 107
B.
2.03 105
D.
203 107
[2004, No.1]
4.86 10 2
(3 10 3 ) 2
A.
1.62 103
C.
5.4 103
B.
1.62 104
D.
5.4 104
[2004, No.2]
4.21 107 2.6 108 =
A.
1.61 108
B. 1.61 107
No.3]
8
0.08
B. 0.081
No.4]
D.
3.95 107
[2004,
C.
0.0810
D.
0.0811
[2004,
Round off 70615 correct to three significant figures.
A.
10
3.95 108
Round off 0.08108 correct to three significant figures.
A.
C.
70600
C.
70620
B. 70610
No.1]
D.
70700
[2005,
Express 7.564 106 as a single number.
A.
0.007564
C.
0.000007564
B.
0.00007564
D.
0.0000007564
[2005, No.2]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
11
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
0.03
=
5000000
A.
6 108
C.
5.4 108
B.
6 109
D.
5.4 109
[2005, No.3]
12
Round off 50941 correct to three significant figures.
A.
509
C.
50940
B.
510
D.
50900
[2006, No.1]
13
Express 351000 in standard form.
A.
3.51 103
C.
3.51 103
B.
3.51 105
D.
3.51 105
[2006, No.2]
14
0.0000025 1.3 107 =
A.
1.2 106
C.
2.37 106
B.
1.2 107
D.
2.37 107
[2006, No.3]
15
A rectangular floor has a width of 2400 cm and a length of 3000 cm. The floor will be covered with tiles.
Each tile is a square of side 20 cm. Calculate the number of tiles required to cover the floor fully.
A.
1.8 104
C.
3.6 104
B.
1.8 108
D.
3.6 108
[2006, No.4]
16
Round off 30106 correct to three significant figures.
A.
30000
C.
30110
B.
30100
D.
30200
[2007, No.1]
17
Express 1.205 104 as a single number.
A.
1205
C.
1205000
B.
12050
D.
12050000
[2007, No.2]
18
0.0078 6 105 =
A.
183 103
C.
7.74 103
B.
1.83 105
D.
7.74 105
[2007, No.3]
19
Round off 0.6782 correct to two significant figures.
A.
0.60
C.
0.68
B.
0.67
D.
0.70
[2008, No.1]
20
Express 0.0000101 in standard form.
A.
1.01 106
C.
1.01 105
B.
1.01 105
D.
1.01 106
[2008, No.2]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
21
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
3.1 1015 + 6.2 1014 =
A.
3.72 1014
C.
3.72 1015
B.
6.51 1014
D.
6.51 1015
[2008, No.3]
22
The diagram shows an empty tank, which is a cuboid, with length 800 cm, width 500 cm and height 300 cm.
A worker fills up 80% of the tank with water. Calculate the volume, in cm3, of water in the tank.
A.
1.2 106
C.
9.6 107
B.
1.2 108
D.
9.6 109
[2008, No.4]
23
Round off 8157 correct to three significant figures.
A.
815
C.
8150
B.
816
D.
8160
[J 2008, No.1]
24
State 4.06 104 as a single number.
A.
4060
C.
406000
B.
40600
D.
40600000
[J 2008, No.2]
25
6.1 105 1.2 104 =
A.
4.90 104
C.
4.90 105
B.
5.98 104
D.
5.98 105
[J 2008, No.3]
26
The diagram shows a rectangle representing an agricultural zone and a square representing an industrial zone.
Calculate the area, in cm2, of the agricultural zone.
A.
1.84 108
C.
4 107
B.
1.84 107
D.
4 106
[J 2008, No.4]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(B)
27
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
Number Bases 2 mark
Express 110101012 as a number in base eight.
A.
6518
C.
3258
B.
6258
D.
2218
[2003, No.5]
28
111012 + 11102 =
A.
1000112
C.
1011112
B.
1110012
D.
1010112
[2003, No.6]
29
Express 53 + 3 as a number in base five.
A.
1035
C.
10035
B.
3035
D.
30035
[2004, No.5]
30
110112 + 1112 =
A.
1000102
C.
1100112
B.
1011002
D.
1111012
[2004, No.6]
31
1100012 10112 =
A.
1001002
C.
11110102
B.
1001102
D.
1111002
[2005, No.4]
32
What is the value of the digit 2, in base ten, in the number 32415 ?
A.
25
C.
200
B.
50
D.
250
[2005, No.5]
33
What is the value of the digit 2, in base ten, in the number 12035 ?
A.
10
C.
200
B.
50
D.
250
[2006, No.5]
34
110012 1012 =
A.
10012
B.
11012
C.
D.
100002
101002
[2006, No.6]
35
1100102 111012 =
A.
1011012
C.
1001012
B.
110002
D.
101012
[2007, No.5]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
36
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
Given 3 53 + 4 52 + 5y = 34205, find the value of y.
A.
C.
B.
D.
4
[2007, No.6]
37
101012 112 =
A.
100002
C.
101002
B.
100102
D.
101102
[2008, No.5]
38
Express 2048 as a number in base five.
A.
10125
B.
13045
C.
D.
21015
40315
[2008, No.6]
39
Convert 3248 to a number in base two.
A.
1000010112
C.
110011002
B.
1000100112
D.
110101002
[J 2008, No.5]
40
101002 11112 =
A.
1012
C.
10012
B.
1112
D.
10112
[J 2008, No.6]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(C)
41
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
Polygons 1 2 marks
In the diagram, PQRSTU is a regular hexagon. PUT and QPW are straight lines.
The value of x + y =
A.
69
C.
76
B.
72
D.
86
[2003, No.7]
42
In the diagram, PWQ is an isosceles triangle. PQR, PWV and STU are straight lines.
The value of x + y =
A.
240
C.
300
B.
280
D.
380
[2003, No.8]
43
In the diagram, GHJKL is a regular pentagon. FGH and FMJ are straight lines.
The value of x + y =
A.
57
C.
36
B.
42
D.
21
[2004, No.7]
44
The diagram shows a pentagon PQRST. Straight line PQ is parallel to straight line UTS.
Find the value of x + y.
A.
216
C.
250
B.
222
D.
260
[2005, No.6]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
45
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
The diagram shows a rhombus PQRS.
Find the value of z.
A.
15
C.
60
B.
45
D.
75
[2005, No.7]
46
In the diagram, PQRST is a regular pentagon and PSUV is a parallelogram. STU is a straight line.
Find the value of x.
A.
36
C.
108
B.
72
D.
144
[2006, No.7]
47
In the diagram, MNPQRSTU is a regular octagon and TUVW is a straight line.
Find the value of x.
A.
65
C.
80
B.
70
D.
90
[2007, No.6]
48
In the diagram, PQRW is a rhombus and VWP is a straight line.
Find the value of x + y.
A.
160
C.
220
B.
170
D.
230
[2007, No.7]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
49
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
The diagram shows a regular pentagon PQRST and an equilateral triangle TUV. PUQ is a straight line.
Find the value of x.
A.
47
C.
60
B.
49
D.
71
[2008, No.7]
50
In the diagram, PQRST is a regular polygon. PUT is a straight line. VP = VU.
Find the value of x.
A.
36
C.
60
B.
54
D.
72
[J 2008, No.7]
51
In the diagram, PQRTX is a pentagon which is symmetrical about the straight line QWV. RTV is a straight
line. SRVU is part of a regular hexagon.
Find the value of x.
A.
130
C.
144
B.
132
D.
145
[J 2008, No.8]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(D)
52
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
Circles 1 mark
In the diagram, RST is a tangent to the circle with centre O.
The value of y
A.
45
C.
70
B.
60
D.
125
[2003, No.9]
53
In the diagram, JK is a tangent to the circle KLM at K and JML is a straight line.
The value of x is
A.
15
C.
60
B.
45
D.
75
[2004, No.8]
54
In the diagram, TPS is a tangent to the circle PQR at P.
The length of arc PR is equal to the length of arc QR. Find the value of x.
A.
22
C.
44
B.
34
D.
88
[2005, No.8]
55
In the diagram, QRT is a tangent to the circle with centre O, at R. PUS, OPQ and OUR are straight lines.
Find the value of x.
A.
40
C.
50
B.
45
D.
65
[2006, No.8]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
56
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
10
The diagram shows a circle, PFQ, centre O. EFG is a tangent to the circle at F.
Find the value of x.
A.
32
C.
61
B.
48
D.
74
[2007, No.8]
57
In the diagram, JKL is a tangent to the circle centre O at K and JNM is a straight line.
Find the value of x.
A.
45
C.
15
B.
25
D.
5
[2008, No.8]
58
In the diagram, URT is the tangent to the circle PQRS at point R. PQR is an equilateral triangle and
URS = 20.
Find the value of x.
A.
30
C.
40
B.
35
D.
45
[J 2008, No.9]
59
In the diagram, O is the centre of a circle. TQU is the tangent to the circle at point Q. PSR is a straight line
and OPS = 10.
Find the value of x.
A.
18
C.
28
B.
22
D.
33
[J 2008, No.10]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(E)
60
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
11
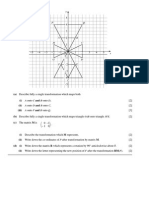
Transformations 2 3 marks
The diagram shows five triangles drawn on a square grid.
Considering the four triangles, A, B, C, and D, which of these is the image of H under a rotaion of 180
about the centre O ?
[2003, No.16]
61
The diagram shows seven points on a square grid. Q is the image of P under a reflection.
The axis of reflection is the straight line that joins H and
A.
C.
B.
D.
N
[2003, No.17]
62
h
In the diagram, N is the image of M under a translation . The distance of MN is 5 units.
k
h
The translasi
k
is
A.
C.
4
3
B.
D.
3
4
[2003, No.18]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
63
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
12
The diagram shows two squares, R and S, drawn on a square grids.
S is the image of R under an enlargement. Which of the point, A, B, C, or D, is the centre of the
enlargement ?
[2004, No.9]
64
The diagram shows points plotted on a Cartesian plane.
Which of the points, A, B, C, or D, is the image of point K under a clockwise rotation of 90 about the
centre (3, 1) ?
[2004, No.10]
65
The diagram shows four triangles drawn on square grids ?
Which of the triangles are similar ?
A.
I and II only
C.
I, II and IV only
B.
III and IV only
D.
I, II, III and IV
[2005, No.9]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
66
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
13
The diagram shows two triangles, R and S, drawn on square grids.
S is the image of R under a clockwise rotation of 90. Which of the point, A, B, C, or D, is the centre
of the rotation ?
[2005, No.10]
67
The diagram shows five triangles drawn on square grids.
Which of the triangles, A, B, C, or D, is not an image of triangle P under a rotation ?
[2006, No.9]
68
In the diagram, the square UVWX is the image of the square STUR under an enlargement.
The centre of the enlargement and its scale factor are
Centre of Enlargement
Scale Factor
A.
1
3
C.
1
3
D.
3
[2006, No.10]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
69
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
14
The diagram shows four quadrilaterals, W, X, Y and Z, drawn on square grids.
All the quadrilaterals are rotated 90 about the centre O. Which of the following is the correct rotation ?
Quadrilateral
Direction of rotation
Image
A.
Clockwise
B.
Anticlockwise
C.
Anticlockwise
D.
Anticlockwise
W
[2007, No.9]
70
The diagram shows two squares, PQRS and KLMN, drawn on square grids.
PQRS is the image of KLMN under an enlargement with centre O. Find the scale factor of the enlargement.
A.
1
3
C.
B.
1
2
D.
3
[2007, No.10]
71
In the diagram, pentagon N is the image of pentagon M under a clockwise rotation of 90.
Which of the points A, B, C or D, is the centre of the rotation ?
[2008, No.9]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
72
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
15
The diagram shows five quadrilaterals, P, A, B, C and D, drawn on square grids.
Which of the quadrilaterals A, B, C or D, is the image of quadrilateral P under an enlargement ?
[2008, No.10]
73
The diagram shows two polygons, PQRST and UVWXY, draw on square grids. UVWXY is the image of
PQRST under an enlargement.
What is the centre and the scale factor of the enlargement ?
Centre of Enlargement
Scale Factor
A.
C.
D.
2
[J 2008, No.11]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(F)
74
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
16
Trigonometry 2 3 marks
In the diagram, GHEK is a straight line and GH = HE.
Find the value of tan x.
A.
5
12
B.
12
13
C.
D.
13
12
12
5
[2003, No.11]
75
Which one of the following graphs represent y = sin x ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2003, No.12]
76
In the diagram, PRS is a straight line.
The value of cos x is
A.
7
24
C.
7
24
B.
24
25
D.
24
25
[2004, No.11]
77
The diagram shows the graph y = sin x.
The value of p is
A.
90
C.
270
B.
180
D.
360
[2004, No.12]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
78
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
17
In the diagram, JKL is a straight line.
It is given that cos x =
5
and tan y = 2. Calculate the length, in cm, of JKL.
13
A.
22
C.
44
B.
29
D.
58
[2004, No.13]
79
It is given that cos = 0.7721 and 180 360, find the values of .
A.
219 27
C.
309 27
B.
230 33
D.
320 33
[2005, No.11]
80
In the diagram, QRS is a straight line.
What is the value of cos ?
A.
4
5
C.
3
5
B.
3
5
D.
4
5
[2005, No.12]
81
Which of the following graphs represents y = cos 2x ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2005, No.13]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
82
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
18
In the diagram, S is the midpoint of straight line QST.
The value of cos x is
A.
4
3
C.
3
4
B.
4
5
D.
3
5
[2006, No.11]
83
In the diagram, MPQ is a right angled triangle.
It is given that QN = 13 cm, MP = 24 cm and N is the midpoint of MNP. Find the value of tan y.
A.
5
13
C.
5
12
B.
12
13
D.
13
12
[2006, No.12]
84
Which of the following graphs represents the grapah of y = cos x for 0 x 180 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2006, No.13]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
85
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
19
In the diagram, USR and VQTS are straight lines.
It is given that TS = 29 cm, PQ = 13 cm, QR = 16 cm and sin x =
A.
12
5
C.
5
12
B.
5
12
D.
12
5
8
. Find the value of tan y.
17
[2007, No.11]
86
In the diagram, O is the origin and JOK is a straight line on a Cartesian plane.
The value of cos is
A.
4
5
C.
3
5
B.
3
5
D.
4
5
[2007, No.12]
87
Which of the following graphs represents the y = sin x for 0 x 180 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2007, No.13]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
88
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
20
The diagram shows a right-angled triangle PQR.
Given sin x =
A.
B.
1
, find the value of h.
2
k
tan 30
k tan 30
C.
D.
k
cos 60
k cos 30
[2008, No.11]
89
Given that tan x =
3
, where 180 x 360, find the value of cos x.
4
A.
4
5
C.
3
5
B.
3
5
D.
4
5
[2008, No.12]
90
Which of the following represents the graph of y = tan x for 0 x 360 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2008, No.13]
91
In the diagram, RTU is a right-angled triangle. RST and TUV are straight line.
It is given that RS = 28 cm, TU = 15 cm and tan RUV =
A.
23
C.
17
B.
22.63
D.
15.73
12
. Find the length, in cm, of SU.
5
[J 2008, No.12]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
92
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
Given that sin x =
A.
B.
1
2
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
21
, where 90 x 270, find the value of 3 cos x.
C.
D.
[J 2008, No.13]
93
Which graph represents y = cos x for 0 x 360 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[J 2008, No.14]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(G)
94
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
22
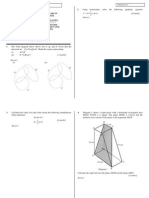
Lines and Planes in 3 Dimensions 1 mark
The diagram shows a right prism with an isosceles triangle PQR as its horizontal base. M and N are the
midpoint of SU and RQ, respectively.
Name the angle between the plane PQR and the plane PUS.
A.
UPT
C.
QPN
B.
NPT
D.
MPN
[2003, No.13]
95
The diagram shows a cube with a horizontal base PQRS.
Name the angle between the line QV and the plane QUR.
A.
VUR
C.
VQU
B.
VUQ
D.
VQR
[2004, No.14]
96
The diagram shows a right pyramid with a quadrilateral base EFGH.
What is the angle between the line VF and the base EFGH ?
A.
VFE
C.
FVH
B.
VFH
D.
FVE
[2005, No.14]
97
The diagram shows a cuboid with a horizontal base TUVW.
Name the angle between the plane PQWT and the plane SRWT.
A.
QTR
C.
QWR
B.
QTS
D.
QWS
[2006, No.14]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
98
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
23
The diagram shows a pyramid with its rectangle base QRST.
Vertex P is vertically above T. Name the angle between the plane PTS and the plane PTQ.
A.
PQT
C.
SPQ
B.
PST
D.
STQ
[2007, No.14]
99
The diagram shows a right-angled triangular prism with the horizontal base QSTV.
What is the angle between the plane STU and the base QSTV ?
A.
TUV
C.
USV
B.
UTV
D.
SUV
[2008, No.14]
100 The diagram shows a cuboid with horizontal base TUVW.
What is the angle between the plane SVW and the plane PQRS ?
A.
QSW
C.
QSV
B.
RSW
D.
PSV
[J 2008, No.15]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(H)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
24
Angles of Elevation and Depression 1 2 marks
101 In the diagram, TS and UV are two vertical poles standing on horizontal ground.
The angle of elevation of V from S is 42. Calculate the value of h.
A.
10.4
C.
14.1
B.
12.0
D.
17.9
[2003, No.10]
102 In the diagram, MN and POR are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane.
The angle of elevation of point P from point M is
A.
MPQ
C.
PMR
B.
PMQ
D.
PNR
[2004, No.15]
103 In the diagram, PQ and QR are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane.
The angle of depression of peak P from peak R is 34. Calculate the height, in m, of the pole PQ.
A.
4.65
C.
11.51
B.
8.42
D.
13.82
[2004, No.16]
104 The diagram shows two vertical poles, PS and QR, on a horizontal plane.
The angle of depression of vertex Q from vertex P is 42. Calculate the angle of elevation of vertex Q from S.
A.
32
C.
57 59
B.
41 59
D.
68 11
[2005, No.15]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
25
105 In the diagram, PQ and TR are two two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. S is a point on TR such that
PQ = SR.
The angle of depression of P from T is
A.
TPS
C.
PTS
B.
RPT
D.
QTS
[2006, No.15]
106 In the diagram, JK is a vertical flag pole. KL is horizontal.
The angle of elevation of J from L is 42. The height, in m, of the flag pole is
A.
23.42
C.
31.51
B.
26.01
D.
38.87
[2006, No.16]
107 In the diagram, PQ and RS are two vertical poles on a horizontal plane. The height of RS is twice the height of
PQ. The angle of depression of P from vertex R is 53.
Calculate the height, in m, of RS.
A.
15.07
C.
30.14
B.
26.54
D.
53.08
[2007, No.15]
108 The diagram shows two vertical flagpoles on a horizontal plane. P, Q, R, S and T are five points on the
poles such that QR = ST.
Name the angle of elevation of point P from point S.
A.
QSP
C.
RSP
B.
QPS
D.
RTP
[2008, No.15]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
26
109 The diagram shows a tower PQ. The points P, R and S lie on a horizontal plane.
The angle of depression of R from Q is 45. Find the angle of elevation of Q from S
A.
22 37
C.
54 47
B.
35 13
D.
67 23
[2008, No.16]
110 In the diagram, Q and S are two points on a horizontal plane. R is the top of a vertical flagpole SR.
The angle of elevation of R from Q is 52. The distance between Q and S is 14 m. Calculate the height, in
cm, of flagpole SR.
A.
10.94
C.
15.59
B.
11.03
D.
17.92
[J 2008, No.16]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(I)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
27
Bearing 1mark
111 In the diagram, E lies to the north of G.
The bearing of G from F is
A.
110
C.
290
B.
250
D.
310
[2003, No.14]
112 Points P, Q and R lie on horizontal plane. P is due south of Q. The bearing of R from Q is 150 and the
bearing of P from R is 300. Which of the follwoing diagrams shows the posititon of P, Q and R ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2004, No.18]
113 The diagram shows the positions of points P and Q.
Find the bearing of point P from point Q.
A.
035
C.
125
B.
055
D.
215
[2005, No.16]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
28
114 Point M and N lie on a horizontal plane. The bearing of M from N is 060. Which of the following diagrams
shows the positions of M and N.
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2006, No.17]
115 The diagram shows three points, P, Q and R, on a horizontal plane.
It is given that Q lies due north of P and the bearing of R is from Q is 075. Find the bearing of P from R.
A.
049
C.
229
B.
101
D.
281
[2007, No.16]
116 The diagram shows three points, P, Q and R on a horizontal plane.
It is given that P is due north of Q. Find the bearing of R from P.
A.
052
C.
104
B.
076
D.
128
[2008, No.17]
117 Point P and point Q lie on a horizontal plane. The bearing of P from Q is 220 . Which diagram shows the
location of P and Q ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[J 2008, No.17]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(J)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
29
Earth as a Sphere 1 2 marks
118 In the diagram, N is the North Pole, S is the South Pole and NOS is the axis of the earth.
Considering the four points A, B, C and D, which of these is (40N, 0E) ?
[2003, No.15]
119 P (15N, 10W), Q and R are three points on the earths surface. Q is due south of P. The difference in
latitude between P and Q is 50. R is due west of Q. The difference in longitude between Q and R is 70 .
The position of R is
A.
(65N, 60E)
C.
(35S, 60E)
B.
(65N, 80W)
D.
(35S, 80W)
[2004, No.17]
120 In the diagram, N is the North Pole, S is the South Pole, NOS is the axis of the earth and PR is a diameter of
the parallels of latitude.
Find the position of point R.
A.
(40N, 70W)
C.
(40N, 110W)
B.
(40N, 70E)
D.
(40N, 110E)
[2005, No.17]
121 The diagram shows the position of five towns, A, B, C, D and X, on the surface of the earth.
Which of the town, A, B, C or D, is located east of X with difference in longitude of 40 ?
[2005, No.18]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
30
122 In the diagram, N is the North Pole, S is the South Pole and O is the centre of the earth. R is the centre of the
circle of latitude 30N.
The position of point P is
A.
(15S, 20E)
C.
(45S, 20E)
B.
(15S, 140E)
D.
(45S, 140E)
[2006, No.18]
123 In the diagram, N is the North Pole, S is the South Pole and NOS is the axis of the earth.
Find the position of point Q.
A.
(38N, 15E)
C.
(52N, 15E)
B.
(38N, 65E)
D.
(52S, 65E)
[2007, No.17]
124 P and Q are two points on the Equator and O is the centre of the earth. Q lies due east of P. The longitude of P
is 40W and POQ = 125. Find the longitude of Q.
A.
55E
C.
140E
B.
85E
D.
165E
[2007, No.18]
125 In the diagram, NOS is the axis of the earth. PQ is a diameter of the parallel of latitude.
Find the longitude of P.
A.
10W
C.
170W
B.
10E
D.
170E
[2008, No.18]
126 P and Q are two points on the surface of the earth and the latitude of P is 55 N. Given that Q is located 15
south of P, find the latitude of Q.
A.
40S
C.
70S
B.
40N
D.
70N
[J 2008, No.18]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(K)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
31
Algebraic Expressions 1 mark
127 (3p m) (p + 2m) =
A.
3p2 + 5pm 2m2
C.
3p2 + 7pm 2m2
B.
3p2 5pm + 2m2
D.
3p2 7pm + 2m2
[2003, No.19]
128 3x (x 2y) (3x y)2 =
A.
6x2 + y2
C.
6x2 6xy + y2
B.
6x2 y2
D.
3x2 9xy y2
[2004, No.20]
129 (3h + 4) (2h 5) =
A.
6h2 7h + 20
C.
6h2 23h + 20
B.
6h2 7h 20
D.
6h2 23h 20
[2005, No.19]
130 3x2 x (1 x) =
A.
2x2 1
C.
4x2 1
B.
2x2 x
D.
4x2 x
[2006, No.19]
131 Simplify (3n2 + mn)
A.
B.
m
n
m
n2
m
2
n ( m 3n)
C.
D.
m2
n2
3m 2
4n
[2006, No.20]
132 (2x y)2 x (x y) =
A.
3x2 3xy + y2
C.
3x2 + xy y2
B.
3x2 5xy + y2
D.
3x2 5xy y2
[2007, No.19]
133 5pq 2 (1 pq) =
A.
3pq 2
C.
6pq 2
B.
4pq 2
D.
7pq 2
[2008, No.19]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
(L)
Algebraic Fractions 1 mark
134
h3
2h
=
3h
h
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
A.
2h 3
3h
C.
2h 3
3h
B.
2h 1
3h
D.
4h 3
3h
32
[2003, No.21]
135 Express
A.
B.
2
4n
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
3n
9n 2
7n 4
C.
9n
5n 4
D.
9n
n2
9n 2
n2
9n 2
[2004, No.19]
136 Express
p
1 p
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
3m
m
pm 3m p
A.
3m
pm 3m p
B.
3m
C.
4p 3
3m
D.
2 3
3m
[2005, No.20]
137 Express
A.
B.
p3
p
p2
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
p
3 p p2
p
3 p p2
p2
C.
D.
3 p p2
p
3 p p2
p2
[2007, No.21]
138 Express
A.
B.
2(5 h)
h3
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
h
h2
h 2 h 10
C.
h2
h 2 2h 10
h2
D.
h 2 h 13
h2
h 2 2h 13
h2
[2008, No.20]
139 Express
A.
B.
p3
p
p2 3
p
p2 6
2p2
p2
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
2p
C.
D.
p2 2p 3
p2
p2 4p 6
2p2
[J 2008, No.19]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(M)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
33
Algebraic Formulae 1 mark
140 Given that
5 p 1
p
=
, then n =
n
3
A.
3 (5 p 1) 2
p
C.
B.
3 (5 p 2 1) 2
p
D.
5 p 1
5 p 1
[2003, No.22]
2t
141 Given that
n 1
= 3, then n =
2
A.
36t2 + 1
C.
2t
B.
(6t 1)2
D.
2t
1
2
[2004, No.21]
142 Given that y
w
, express w in terms of y.
1 w
A.
y
1 y
C.
1 y
y
B.
y
1 y
D.
1 y
y
[2005, No.21]
143 Given that
8m 2 n
mn n , express m in term of n.
3
A.
n
8 3n
C.
5n
3n 8
B.
n
3n 8
D.
5n
8 3n
[2006, No.21]
144 Given that T =
1
3
A. m = 9kT2
B.
m = 3kT2
m
,
k
express m in terms of T and k.
C.
T2
9k
D.
T2
3k
[2007, No.20]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
145 Given that T = 10
A.
B.
10
T
100
T
1
H M
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
34
express H in terms of T and M.
C.
D.
100
T
10
T
T2M
T2M
[2008, No.21]
146 Given that k (m + 2) = 3m,
express m in terms of k.
A.
m=
k 2
2
C.
m=
k 2
4
B.
m=
k2
2
D.
m=
k2
4
[J 2008, No.20]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(N)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
35
Linea Equations 1 mark
147 Given that
1
p + 1 = 4, then p =
3
A.
C.
11
B.
D.
15
[2003, No.20]
148 Given that 3k 4 = 5 (2 k), then k =
A.
C.
7
2
B.
D.
7
4
[2004, No.22]
149 Given that 10 3 ( 2 w) = 9w + 2, calculate the value of w.
A.
1
6
C.
1
3
B.
1
4
D.
2
5
[2005, No.22]
150 Given that
5
4k 2 (3 k ) , then k =
2
A.
17
12
C.
17
6
B.
17
10
D.
17
4
[2006, No.22]
151 Given that
x 1
= 2x 1, find the value of x.
5
A.
2
9
C.
5
9
B.
4
11
D.
2
3
[2007, No.22]
152 Given that p + 2 =
3(1 2 p )
, calculate the value of p.
4
A.
1
2
C.
1
10
B.
1
5
D.
1
6
[2008, No.22]
153 Given that
1
( 3n + 2 ) = n 2, calculate the value of n.
5
A.
C.
B.
D.
6
[J 2008, No.21]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(O)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
36
Indices 1 2 marks
154 Simplify 4m 1 n 2
m2 p3
p9
A.
B.
16n
p
4mn
C.
p3
p3
16mn 2
D.
p6
[2003, No.23]
155 Find the value of
8 3
6
1
3
3 4 .
A.
1
4
C.
4
9
B.
1
9
D.
9
4
[2003, No.24]
156
3
4
, can also write as
A.
r3
C.
r 4
B.
r4
D.
r 3
[2004, No.23]
1
157 Simplify
m 6 (9e 2 ) 2
1
3 6 3
(m e )
A.
9m 2
e
C.
B.
9m 3
e
D.
3m 5
e
3m 5
e4
[2004, No.24]
158 (m2)4 m5 =
A.
C.
m11
B.
m3
D.
m13
[2005, No.23]
159 Given that 3x =
9
32x
, find the value of x.
A.
C.
2
3
B.
D.
1
2
[2005, No.24]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
14 2
A.
2 7
C.
212 75
B.
26 72
D.
216 71
37
82 7 3
160 Simplify
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
[2006, No.23]
161
7
3x 5
can be written as
A.
7 5
x
3
C.
21 x5
B.
7 5
x
3
D.
21 x5
[2007, No.23]
162 Simplify
1
3
e2 f 3.
A.
e7 f
C.
ef
B.
e7 f 3
D.
e f 3
[2007, No.24]
163 Given that
mn
= 32, find the value of m and of n.
A.
m = 2, n = 3
C.
m = 3, n = 2
B.
m = 2, n = 3
D.
m = 3, n = 2
[2008, No.23]
164 Simplify
( m 2 n 4 ) 1
m 4 n 3
A.
m2 n7
C.
m6 n1
B.
m2 n 7
D.
m6 n
[2008, No.24]
165 Simplify :
pn 3
n2 ( pn1 )
A.
n3
C.
p5 n3
B.
n5
D.
p5 n5
[J 2008, No.22]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(P)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
38
Linear Inequalities 1 2 marks
166 List all the integers x which satisfy both the inequalities 2x + 1 19 and
A.
9, 10
C.
9, 10, 11
B.
10, 11
D.
10, 11, 12
3x
9.
4
[2003, No.25]
167 The diagram represents two simultaneous linear inequalities on a number line.
The inequality which represents the common value of both the inequalities is
A.
1 x 2
C.
1 < x 2
B.
1 x < 2
D.
1 < x < 2
[2003, No.26]
168 Given that x is an integer, find all the values of x that satisfy both of the inequalities x < 4 and
11 3x 5.
A.
2, 3
C.
2, 3, 4
B.
3, 4
D.
3, 4, 5
[2004, No.25]
169 The solution for
m
1 2m 4 is
2
A.
m 2
C.
m 2
B.
m2
D.
m 2
[2004, No.26]
170 List all the integers x that satisfy the inequalities 3x 8 < x 5 + 4x.
A.
0, 1, 2, 3
C.
1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
B.
1, 0, 1, 2, 3
D.
2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
[2005, No.25]
171 List all the integers x which satisfy both iequalities
x
1
1 x and
( x 4) x .
3
2
A.
1, 0, 1, 2, 3
C.
1, 0, 1
B.
0, 1, 2, 3
D.
0, 1
[2006, No.24]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
172 The solution for
4x + 5 < 1
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
39
2x
is
3
A.
7
3
C.
1
3
B.
6
7
D.
2
7
[2007, No.25]
173 Which number line represents the solution of the simultaneous linear inequalities 2x 3 5 and 4 x > 6 ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
[2008, No.25]
174 List all the integers x which satisfy the inequalities 2 < x + 1 < 6.
A.
3, 4
C.
2, 3, 4, 5
B.
2, 3, 4
D.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
[J 2008, No.23]
175 Which of the following inequalities satisfy the simultaneous line inequalities 4p 3 p and p + 2
A.
4 p 1
C.
p 1 and p 1
B.
1 p 4
D.
p 1 and p 4
1
p.
2
[J 2008, No.24]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(Q)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
40
Statistics ( 2 3 marks )
176 The diagram is a pictograph showing the sale of magazines in a particular week. The number of sports
magazines sold is not shown.
Fashion
Entertainment
# # # # # # # #
# # # # #
Sports
# represents 12 copies of magazines
Entertainment magazines make up 25% of the total sales that week. Calculate the number of sports magazines
sold.
A.
29
C.
84
B.
39
D.
94
[2003, No.39]
177 .The diagram is a pie chart showing the amount spent on five types of groceries in a shop on a particular day.
The total spend on these groceries is RM400. The amount spent on margerine is RM80.
Find the ratio of the amount spent on margarine to the amount spent on sugar.
A.
1:5
C.
3 : 10
B.
3:4
D.
4 : 15
[2003, No.40]
178 The diagram is a bar chart which shows the scores of a group of pupils in a test.
State the modal score..
A.
C.
B.
D.
2
[2004, No.27]
179 The diagram is a pie chart which shows the combined results of a test taken by two group of students. The table
shows the results of the groups, but is incomplete.
Calculate the number of students in the Bestari Group.
A.
300
C.
340
B.
310
D.
380
[2004, No.28]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
41
180 The table is a frequency table which shows the mass of fish caught by 20 fisherman.
Mass of fish caught (kg)
Frequency
11 13
14 16
17 19
20 22
23 25
Calculate the mean mass, in kg, of fish caught by a fisherman.
A.
16.1
C.
18.1
B.
17.1
D.
20.0
[2005, No.26]
181 The diagram is a pictograph which shows the number of fruit trees in an orchard.
Durian
Rambutan
Mangosteen
represents 25 trees
The ratio of rambutan trees to mangosteen trees is 3 : 2. Find the number of durian trees and mangosteen trees
altogether.
A.
225
C.
300
B.
275
D.
400
[2005, No.27]
182 The table shows the distribution of the scores of a group of pupils in a quiz.
Score
Frequency
The median score of the distribution is
A.
C.
B.
1.5
D.
2.5
[2006, No.25]
183 The diagram is a pictograph showing the number of eggs sold in January and February. The number of eggs
sold in March and April are not shown.
January
February
March
April
represents 200 eggs
A total of 5000 eggs were sold in those four months. The number of eggs sold in March was three times the
number of eggs sold in April. The number of eggs sold in March was
A.
1500
C.
2250
B.
2000
D.
3000
[2006, No.26]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
42
184 The diagram shows a set of six pieces of data where x represents an integer.
3, 3, 6, x, x, 3
The mode for the data is 3 and the median is 4. Two new pieces of data, 4 and 7, where put into the set.
Calculate the mean for those eight pieces of data.
A.
4.00
C.
4.25
B.
4.13
D.
4.50
[2006, No.27]
185 The diagram is a bar chart which shows the sales of handphones. The sales in August are not shown.
The sales in August is 40% of the total sales during the four months,
handphones were sold in August ?
A.
60
C.
120
B.
72
D.
140
from May to August. How many
[2007, No.26]
186 The bar chart showing the number of students from three schools, P, Q and R, who participate in the
Program Latihan Khidmat Negara. The pie chart showing the number of these students, according to
gender.
Calculate the value of x.
A.
120
C.
200
B.
150
D.
210
[2007, No.27]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
43
187 The diagram is a bar chart showing the number of medals obtained by a school in a sports championship in the
year 2007.
If a pie chart is drawn to represent the given information, calculate the difference of the angle sector which
represent the bronze and silver medals.
A.
10
C.
40
B.
30
D.
60
[2008, No.26]
188 The table shows the sales of four types of gifts.
Gifts
Flowers
Toys
Books
Pens
Frequency
18
10
Given that the mode of the gifts is flowers, find the maximum value x.
A.
16
C.
18
B.
17
D.
19
[2008, No.27]
189 The diagram is a pie chart which shows the types of drink commonly ordered by the customers in a caf.
Determine the mode of the types of drink.
A.
Fruit juice
C.
Syrup
B.
Coffee
D.
Tea
[J 2008, No.25]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
44
190 The diagram is a bar chart showing the total sales of washing machines for a company in June. The company
has a total of 400 washing machines of brands, K, L and M in stock at the beginning of June.
Calculate the number of remaining washing machines that the company has in stock at the end of June.
A.
120
C.
260
B.
220
D.
340
[J 2008, No.26]
191 Scores obtained by a group of students in a game are as follows :
4, 5, 2, 3, 2, 1, 5, 2, 4, 8
Find the score median of the distribution.
A.
1.5
C.
B.
D.
3
3.5
[J 2008, No.27]
192 The table shows the distribution of the score of 30 students in a quiz.
Score
Number of students
09
10 19
20 29
11
30 39
40 49
Find the mean score.
A.
21.67
C.
26.17
B.
25.67
D.
26.67
[J 2008, No.28]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(R)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
45
Graph of Functions 1 mark
193 Which one of the following graphs represents y = x2 3 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2003, No.30]
194 Which of the following graphs represents y =
2
?
x
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2004, No.29]
195 Which of the following graphs represents y = x2 4 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2005, No.28]
196 Which of the following graphs represents y = 10 2x ?
3
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2006, No.28]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
46
197 Which of the following graph represents y = x2 + 5 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2007, No.28]
198 Which graph represents y = x2 x + 2 ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2008, No.28]
199 Which graph represents y =
1
x3 ?
2
A.
C.
B.
D.
[J 2008, No.29]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(S)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
47
Sets 3 marks
200 Given that the universal set = J K L, J K and K L = , the Venn diagram that represent these
relationships is
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2003, No.32]
201 The diagram shows a Venn diagram with the universal set = E F G.
Considering the four regions, A, B, C and D, which of these represents the set E F G ?
[2003, No.33]
202 The diagram shows a Venn diagram with the universal set = {Year Five pupils}, set M = {Pupils who read a
Malay language newspaper} and set R = {Pupils who read an English language newspaper}.
Given that n (M) = 80, n (R) = 104, n (M R) = 12 and the number of pupils who do not read either
newspaper is 4, find the total number of Year Five pupils.
A.
172
C.
196
B.
176
D.
200
[
2003, No.34]
203 The diagram is a Venn diagram which shows the elements of set P, Q and R.
If the universal set = P Q R, then set Q is
A.
{1, 2}
C.
{1, 2, 5}
B.
{3, 6}
D.
{3, 4, 6}
[2004, No.30]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
48
204 The diagram is a Venn diagram which shows the universal sel , set P, and set Q.
The shaded region in the Venn diagram represents the set
A.
P Q
C.
P Q
B.
P Q
D.
PQ
[2004, No.31]
205 It is given that the universal set = { x : 1 x 12, x is an integer}, set P = {2, 3, 7, 9 }, set Q = { x : x is a
prime number}, and set R = { x : x is a multiple of 4 }. The elements of the set (PR) Q are
A.
5, 11
B.
1, 5, 11
C.
2, 3, 11
D.
2, 3, 9
[2004, No.32]
206 Which of the following Venn diagrams represent set R S such that the universal set = R S ?
A.
C.
B.
D.
[2005, No.29]
207 Diagram is a Venn diagram with the universal set = P Q R.
Which of the region, A, B, C, and D, represents the set P Q R ?
[2005, No.30]
208 Diagram is a Venn diagram that shows the elements of set R, set S, and set T.
It is given that the universal set = R S T and n (S) = n (S T). Find the value of x.
A.
C.
10
B.
D.
11
[2005, No.31]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
49
209 It is given that the universal set, = { x : 19 x < 31, x is an integer } and set R = { x : x is a number such
that the sum of its two digits is an even number }. Find set R.
A.
{ 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 }
C.
{ 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29 }
B.
{ 21, 23, 25, 27, 29 }
D.
{ 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 30 }
[2006, No.29]
210 The diagram is a Venn diagram showing the universal set , set P and set Q.
The region (P Q) is equivalent to the region
A.
P Q
C.
P Q
B.
P Q
D.
P Q
[2006, No30]
211 The table shows data obtained from a survey of 100 television viewers, and the diagram is a Venn diagram that
represents part of the information in the table.
Find the number of viewer who watched sports or news and also entertainment programmes
A.
26
C.
47
B.
39
D.
51
[2006, No31]
212 List all the subsets of set X = { m , n }.
A.
{ m }, { n }
B.
{ m }, { n }, {
C.
{ m }, { n }, { m , n }
D.
{ m }, { n }, { m , n } , {
}
[2007, No29]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
50
213 The diagram is a Venn diagram showing the universal set, = { Form Five students }, set L = { Students who
play badminton } and set M = { Students who play tennis }.
Given n ( ) = 60, n (L) = 25, n (M) = 12 and n (L M) = 8, find the number of students who do not play
the two games.
A.
15
C.
31
B.
23
D.
52
[2007, No30]
214 Given the universal set = P Q, set P = { 0, 1, 2 } and set Q = { 2, 3, 4, 5 }, find the value of n { }
A.
C.
B.
D.
4
[2007, No31]
215 The diagram is a Venn diagram showing the elements of the universal set, , set T and set U
List all the elements of set U.
A.
{q}
C.
{ l, p, q}
B.
{ l, q }
D.
{ l, p, q, n}
[2008, No29]
216 The diagram shows a Venn diagram with the unisersal set, = R S.
Given that n (R) = 95, n (S) = 78 and n (R S) = 25, find n ( ).
A.
123
C.
173
B.
148
D.
198
[2008, No.30]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
51
217 The diagram is a Venn diagram showing the number of students in set G, M and S. It is given that set
G = { Geography Society Members}, set M = {Mathematics Society Members}, set S = {Science Society
Members} and universal set, = G M S.
If the number of students who join both the Science and the Mathematics Society is 8, find the number of
students who join only two societies.
A.
13
C.
16
B.
15
D.
18
[2008, No31]
218 The diagram shows a Venn diagram with the universal set, ,, set T and set S
List all the elements of set S.
A.
{ 1, 4 }
C.
{ 1, 4, 5 }
B.
{ 3, 7 }
D.
{ 1, 3, 4, 7 }
[J 2008, No.30]
219 The diagram shows a Venn diagram with the unisersal set, = { Form Five Students }, set P = { Members of
Science Society }, set Q = { Members of Mathematics Society } and set R = { Members of Geography Society }
It is given that n (P) = 82, n (Q) = 90, n (R) = 40 and n (P Q) = 24. The number of Form Five students
who are not a member of any of the three societies is 35. Find the total number of Form Five stedents.
A.
271
C.
223
B.
236
D.
188
[J 2008, No.31]
220 The diagram is a Venn diagram showing the number of elements in sets P, Q and R
It is given that the universal set, = P Q R. Find n ( P (Q R ) ).
A.
C.
10
B.
D.
17
[J 2008, No.32]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(T)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
52
The Straight Line 1 2 marks
221 The gradient of the straight line 2x 7y = 14 is
A.
2
7
B.
C.
7
2
D.
7
[2003, No.31]
222 The diagram shows a straight line LM on a Cartesian plane.
The gradient of LM is
A.
B.
1
2
C.
1
2
D.
1
[2004, No.33]
223 The diagram shows two straight lines, PQ and QR, on a Cartesian plane.
The gradient of QR is 4 and the distance of PQ is 15 units. Find the x-intercept of PQ.
A.
C.
9
4
B.
12
D.
15
4
[2004, No.34]
224 Find the y-intercept of the straight line 3x 4y = 24.
A.
B.
3
4
4
3
C.
D.
8
[2005, No.32]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
53
225 In the diagram, PQ is a straight line.
What is the gradient of PQ ?
A.
B.
C.
1
2
D.
1
2
2
[2005, No.33]
226 The coordinates of point P are (1, 1) and the gradient of the straight line PQ is 2. The coordinates of point
Q could be
A.
(3, 3)
C.
(3, 1)
B.
(3, 9)
D.
(3. 7)
[2006, No.32]
227 In the diagram, EF is a straight line with gradient
1
.
4
Find the x-intercept of the straight line EF.
A.
1
12
C.
B.
3
4
D.
12
[2006, No.33]
228 The gradient of the straight line 3x + 2y = 5 is
A.
C.
3
2
B.
D.
2
3
[2007, No.32]
229 Determine the y-intercept of the straight line 4x + 2y + 5 = 0.
A.
5
2
B.
C.
5
2
5
4
D.
5
4
[2007, No.33]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
54
230 The diagram shows a straight line PQ on a Cartesian plane
Find the gradient of PQ.
A.
C.
1
2
B.
D.
1
3
[2008, No.32]
231 State the x-intercept of the straight line 3x 4y + 24 = 0.
A.
C.
B.
D.
8
[2008, No.33]
232 The diagram shows a straight line, KL on a Cartesian plane
The gradient of KL is
3
. Find the value of h.
2
A.
11
3
C.
B.
13
3
D.
11
[J 2008, No.33]
233 Find the y-intercept of the straight line 5y = 3x 6.
A.
B.
6
5
C.
D.
3
5
3
[J 2008, No.34]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(U)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
55
Probability I 2 3 marks
234 In a group of 90 students, 70 are girls. A further 10 boys then joined the group. If a student chosen at random
from the group, state the probability that the student chosen is a boy.
A.
2
9
C.
1
10
B.
7
9
D.
3
10
[2003, No.37]
235 A jar contains 240 sweets of orange, lychee, and coffee flavour. There are 90 orange flavoured sweets. If a
1
sweet is picked at random from the jar, the probability of picking a lychee flavoured sweet is
. How
3
many coffee flavoured sweets are there ?
A.
10
C.
70
B.
50
D.
80
[2003, No.38]
236 The diagram shows some number cards
A card is picked at random. State the probability that a prime number is picked.
A.
2
3
C.
1
2
B.
1
3
D.
1
6
[2004, No.35]
237 Irma has a collection of stamps from Kelantan, Perak, and Sarawak. She picks one stamp at random. The
4
1
probability of picking a Perak stamp is
and the probability of picking a Sarawak stamp is
. Imran
9
3
has 10 Kelantan stamps. Calculate the total number of stamps in her collection.
A.
20
C.
45
B.
25
D.
90
[2004, No.36]
238 20 coupons with serial number 21 to 40 are put in a box. One coupon is drawn at random. The probability of
drawing a coupon with a number which is not a multiple of 5 is
A.
1
5
C.
3
5
B.
2
5
D.
4
5
[2004, No.37]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
56
239 The table shows the distribution of a group of 90 pupils playing a game.
Girls
Boys
Form Four
33
18
Form Five
15
24
A pupil is chosen at random from the group to start the game. What is the probability that a girl from Form
Four will be chosen ?
A.
11
30
B.
7
15
C.
D.
8
15
11
17
[2005, No.34]
240 A container holds 28 yellow marbles and a number of green marbles. A marble is picked at random from the
7
container. The probability of picking a yellow marble is
. How many green marbles are there in the container
8
?
A.
C.
21
B.
D.
24
[2005, No.35]
241 It is given that set G is { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 13, 14, 15 }. A number is chosen at random from the
elements of set G. Find the probability that the number chosen is a prime number.
A.
4
11
B.
5
11
C.
6
11
D.
7
11
[2006, No.34]
242 A box contains 4 red marbles, 2 white marbles and a number of blue marbles. A marble is chosen at random
1
from a box. The probability of choosing a white marble is
. Find the probability of choosing a blue
8
marble.
A.
1
4
C.
5
8
B.
3
8
D.
3
4
[2006, No.35]
243 A box contains 5 red marbles and 21 green marbles. Lim put another 4 red marbles and 1 green marble inside
the box. A marble is chosen at random from the box. What is the probability that a red marble is chosen ?
A.
5
31
C.
5
26
B.
9
31
D.
9
26
[2007, No.34]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
57
244 In a training session, Ann has many trials to score a goal. The probability that Ann scores a goal in a trail is
9
. In 60 trials chosen randomly, how many times does Ann fail to score a goal ?
20
A.
11
C.
33
B.
27
D.
49
[2007, No.35]
245 A box contains 48 cups. There are blue cups and white cups. A cup is chosen at random from the box. The
1
probability that a blue cup is chosen is
. How many blue cups need to be added to the box so that the
6
probability that a blue cup is chosen is
1
?
2
A.
C.
24
B.
16
D.
32
[2008, No.34]
246 The diagram shows 16 identical cubes, labelled X, Y and Z.
A cube is chosen at random. State the probability that the cube chosen is not labeled Y
A.
3
16
B.
5
16
C.
7
16
D.
9
16
[2008, No.35]
247 Form Five Bestari had 40 students. When a student was chosen at random from this class, the probability of
3
. A group of 4 girls is transferred to another class and replaced by 7 boys. A student
4
is then chosen at random from this class. Calculate the probability of choosing a boy from this class.
choosing a girl was
A.
17
47
C.
17
43
B.
10
47
D.
10
43
[ J2008, No.35]
248 The table shows the number of students in the Science stream and the Arts stream in a school.
Stream
Science
Arts
Number of students
55
65
A group of k students is transferred from the Arts stream to the Science stream. A student is chosen at random
3
from the group. The probability of choosing a student from the Science stream is
. Calculate the value of
5
k.
A.
17
C.
33
B.
26
D.
72
[J 2008, No.36]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(V)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
58
Variations 2 3 marks
249 Given that p is directly proportional to n2 and p = 36 when n = 3, express p in terms of n.
A.
p = n2
C.
p = 9n2
B.
p = 4n2
D.
p = 12n2
[2003, No.35]
250 The table shows some values of the variables w, x and y, which satisfy the relation w
w
18
x
y
Calculate the value of n.
A.
C.
12
B.
D.
36
[2003, No.36]
251 P varies directly as the square root of Q. The relation between P and Q is
A.
PQ
B.
P Q2
1
2
C.
D.
1
1
Q2
1
Q2
[2004, No.38]
252 The table shows the relation between three variables, p, m and r.
Given that p
m
r
, calculate the value of w.
A.
16
C.
36
B.
24
D.
81
[2004, No.39]
253 The table shows some values of the variables x and y such that y varies inversely as the square root of x.
x
16
Find the relation between y and x.
A.
y=3
B.
y=
12
x
C.
y=
D.
y=
3 2
x
8
96
x2
[2005, No.36]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
59
254 It is given that y varies directly as the square root of x and y = 15 when x = 9. Calculate the value of x when
y = 30
A.
C.
25
B.
18
D.
36
[2005, No.37]
255 The table shows some values of the variables w, x and y such that w varies directly as the square of x and
inversely as y.
w
40
Calculate the value of m.
A.
90
C.
30
B.
45
D.
15
[2005, No.38]
256 It is given that w varies directly with the cube of p and w = 8 when p = 4. Calculate the value of p when
w = 27.
A.
3
8
C.
B.
3
2
D.
24
[2006, No.36]
257 It is given that y
1
x
and y = 3 when x = 36 . Calculate the value of y when x = 4.
A.
C.
18
B.
D.
48
[2006, No.37]
258 The table shows two sets of values of p, q and r, which satisfy r pq.
p
10
12
Calculate the value of w.
A.
0.2
C.
2.4
B.
1.2
D.
7.2
[2006, No.38]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
60
259 The table shows some values of the variables x and y.
x
32
It is given that y varies directly as the cube of x. Calculate the value of n.
A.
C.
16
B.
D.
30
[2007, No.36]
260 P varies inversely as the square root of M. Given that the constant is k, find the relation between P and M
A.
P = kM
B.
P=
1
2
C.
P = kM2
D.
P=
k
M
1
2
k
M2
[2007, No.37]
261 The relation between the variables x, y and z is x
Calculate the value of z when x =
y
5
. It is given that x =
when y = 2 and z = 8.
z
4
5
and y = 6.
3
A.
C.
32
B.
18
D.
72
[2007, No.38]
262 The table shows some values of the variables R and T.
It is given that R varies directly as
54
72
36
A.
24
C.
48
B.
27
D.
64
T. Find the value of y.
[2008, No.36]
263 Given y varies inversely as x3, and that y = 4 when x =
A.
1
8
C.
B.
1
2
D.
1
1
. Calculate the value of x when y =
.
16
2
[2008, No.37]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
61
264 It is given that P varies directly as the square root of Q and inversely as the square of R. Find the relation
between P, Q and R.
A.
B.
Q2
R
Q
R
C.
D.
R2
Q
R
R2
[2008, No.38]
265 It is given that p varies directly as the square root of w and that p = 5 when w = 4. Express p in
terms of w.
A.
p=
B.
p=
5 2
w
16
80
w
C.
p=
D.
p=
5
2
10
w
[J 2008, No.37]
266 The table shows some values of the variables m and n, such that m varies inversely as the cube of n.
Calculate the value of x.
A.
4
27
B.
4
9
1
2
3
C.
D.
9
16
27
16
[J 2008, No.38]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
(W)
Matrices 1 3 marks
267
A.
15
C.
B.
12
D.
1
2
3 +
62
13
15
13
[2003, No.27]
x
1
268 Given that
= ( 18 ), find the value of x.
A.
C.
B.
D.
6
[2003, No.28]
5
269
3
=
4
A.
10
C.
10
16
B.
12
28
D.
10
12
16
[2003, No.29]
270 Given that the matrix equation 2 4
h k 1
2 13
A.
C.
10
B.
D.
11
8 , find the value of h + k.
[2004, No.40]
3
271 2
4
1
1
6
1
A.
10
B.
4
3
C.
D.
8
[2005, No.39]
272 Given
3
5
k
0
= 24
1
5 , calculate the value of k.
A.
12
C.
B.
D.
8
[2005, No.40]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
5
273
7
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
2
3
1
2
0
3
3
2
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
63
A.
14
15
13
C.
15
13
B.
13
16
D.
10
0
[2006, No.39]
4p
274 If
= ( 7 ), then p =
A.
C.
1
2
B.
D.
7
9
[2006, No.40]
3
275
1
5
=
2
C.
15
35
D.
15
A.
B.
20
4
8
4
[2007, No.39]
276 Find the value of m in the following matric equation :
0
2
7
3
2
m
2
A.
C.
B.
D.
6
[2007, No.40]
3
1
=
0
4
277 3
4
A.
10
3
0
B.
3
0
C.
2
3
4
12
0
4
12
D.
1
[2008, No.39]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
278
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ SPM MATEMATIK 1449/1, 2003 - 2008 ]
2 1
A.
15
C.
B.
D.
15
7 + 3 1
64
2 =
[2008, No.40]
5
279
8
1
2
A.
14
B.
10
5
2
1
10
2
3
=
1
C.
10
12
D.
12
5
[ J 2008, No.39]
1
280 Given that
2
3
5
=
, find the value of x.
2
0
A.
C.
B.
D.
3
[ J 2008, No.40]
You might also like
- Chapter 1-Standard FormDocument4 pagesChapter 1-Standard FormQihui NgNo ratings yet
- Circumference and Area of CirclesDocument6 pagesCircumference and Area of CirclesSashineka SumbulingamNo ratings yet
- 08 SBP Trial Mat k1Document26 pages08 SBP Trial Mat k1Yap FrancescoNo ratings yet
- SMK DATO' JAAFAR MATH TEST 1 REVIEWDocument5 pagesSMK DATO' JAAFAR MATH TEST 1 REVIEWNurun Nadia MasromNo ratings yet
- Nama Sekolah / School Name Test 1 Paper 1Document7 pagesNama Sekolah / School Name Test 1 Paper 1Norlida ZulNo ratings yet
- 4 ExercisesDocument55 pages4 ExercisesSashineka SumbulingamNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education MathematicsDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education MathematicsnshoulyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Review Booklet: Instructions To Students and Parents: This Booklet Is Intended To Help YouDocument24 pagesGeometry Review Booklet: Instructions To Students and Parents: This Booklet Is Intended To Help YouKathleen MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- SMK Keat Hwa March 2015 Monthly Test ReviewDocument8 pagesSMK Keat Hwa March 2015 Monthly Test ReviewHengLowNo ratings yet
- Standard FormDocument4 pagesStandard FormShaliza AzaharNo ratings yet
- Microsoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures NewDocument10 pagesMicrosoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures Newuzai88No ratings yet
- SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK Mathematics Formulas & ConceptsDocument50 pagesSM. ST. PETER TELIPOK Mathematics Formulas & ConceptsQihui NgNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument20 pagesCirclesabummathewNo ratings yet
- 4024 w08 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w08 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- CircleDocument20 pagesCirclejuriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Transformations Graph PaperDocument20 pagesTransformations Graph PaperjayeshpNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1Document8 pagesAdditional Mathematics 2003 November Paper 1lornarifaNo ratings yet
- Circles II: Properties of Circles and Angles in CirclesDocument11 pagesCircles II: Properties of Circles and Angles in Circlessims363No ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF PAST YEAR QUESTIONS FORM 4 MATHEMATICSDocument8 pagesANALYSIS OF PAST YEAR QUESTIONS FORM 4 MATHEMATICSJarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelKhalid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- PPTG Eva MM f3Document3 pagesPPTG Eva MM f3kirstenlingNo ratings yet
- Circ MeasureDocument15 pagesCirc MeasureKaren OngNo ratings yet
- Selangor 2011 P2Document4 pagesSelangor 2011 P2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Gerak Gempur 4Document23 pagesGerak Gempur 4Ru FangNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Form 4Document7 pagesMid Year Form 4Sathis KumarNo ratings yet
- 4024 s09 QP 2Document12 pages4024 s09 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- 0580 w08 QP 04Document12 pages0580 w08 QP 04MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Rumus-Rumus Berikut Boleh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunakanDocument31 pagesRumus-Rumus Berikut Boleh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunakanNordiana IdrisNo ratings yet
- Maths Form 2 Exam P3Document5 pagesMaths Form 2 Exam P3JKNo ratings yet
- FE6Document109 pagesFE6Jyoti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- MATHS2008F2PAPER1Document15 pagesMATHS2008F2PAPER1Jeff EunusNo ratings yet
- Part A.: Objective Questions. Answer All QuestionsDocument8 pagesPart A.: Objective Questions. Answer All QuestionsShafira AzmiNo ratings yet
- SPM 2011 Paper 2Document4 pagesSPM 2011 Paper 2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- 0580 w10 QP 41Document16 pages0580 w10 QP 41MohammedKamelNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSEDocument12 pagesCambridge IGCSEHannah LohNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan SPM Add MathsDocument17 pagesKoleksi Soalan SPM Add MathsCheegu EmmaNo ratings yet
- MRSM 2011paper 2Document4 pagesMRSM 2011paper 2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Maths Paper 2 (Ver 2)Document12 pagesMid Year Maths Paper 2 (Ver 2)Eng KengNo ratings yet
- Men Su Rations ClassifiedDocument58 pagesMen Su Rations ClassifiedMohammed BasitNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Form 4 (Tangents)Document21 pagesEngineering Drawing Form 4 (Tangents)farah sakinah100% (3)
- Soalan Matematik Kertas 2 LabuanDocument9 pagesSoalan Matematik Kertas 2 LabuanZeZe ZeZeNo ratings yet
- TCW2204200808 Engineering Survey IIDocument5 pagesTCW2204200808 Engineering Survey IILindelwe MoyoNo ratings yet
- SPM Maths exam questionsDocument6 pagesSPM Maths exam questionsNur NadiahNo ratings yet
- Mathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsFrom EverandMathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsRoderick MelnikNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualFrom EverandPressure Vessel and Stacks Field Repair ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- A Neolithic Ceremonial Complex in Galloway: Excavations at Dunragit and Droughduil, 1999–2002From EverandA Neolithic Ceremonial Complex in Galloway: Excavations at Dunragit and Droughduil, 1999–2002No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Model Answers in Ordinary National Certificate Mathematics for EngineersFrom EverandModel Answers in Ordinary National Certificate Mathematics for EngineersNo ratings yet
- M.A.M College of Engineering: Department of Electrical and Electronics EnggDocument16 pagesM.A.M College of Engineering: Department of Electrical and Electronics EnggKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- DC30-010 - ODYSSEY Operator Manual - Rev PDocument92 pagesDC30-010 - ODYSSEY Operator Manual - Rev PYolanda Peña100% (1)
- 100 Years Werner HeisenbergDocument308 pages100 Years Werner Heisenbergmvmbapple100% (3)
- Researchtaro RopeDocument23 pagesResearchtaro RopeAlyssa Gian CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Huygens' Principle, Maxwell's Displacement CurrentDocument7 pagesHuygens' Principle, Maxwell's Displacement CurrentGalleta Galleta MetralletaNo ratings yet
- Moc3011 PDFDocument7 pagesMoc3011 PDFAlvaro Mompi RuizNo ratings yet
- Conduits ASSIGNMENTDocument12 pagesConduits ASSIGNMENTishaq kazeemNo ratings yet
- Volumes by Cylindrical ShellsDocument7 pagesVolumes by Cylindrical Shellseomer1968No ratings yet
- Engineering Calculation Sheet Consulting EngineersDocument17 pagesEngineering Calculation Sheet Consulting EngineersParthiban ArivazhaganNo ratings yet
- DEVELOPMENT AND TEST OF THE BO 105 RIGID ROTOR HELICOPTERDocument16 pagesDEVELOPMENT AND TEST OF THE BO 105 RIGID ROTOR HELICOPTERГригорий ОмельченкоNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Seismic Analysis of Multi Storyed Building Using Shear Wall in Seismic Zones III and IVDocument8 pagesComparison of Seismic Analysis of Multi Storyed Building Using Shear Wall in Seismic Zones III and IVEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Panel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Fixed Electrical DowntiltDocument2 pagesPanel Dual Polarization Half-Power Beam Width Fixed Electrical DowntiltEmmersonLisboaNo ratings yet
- BS en 10297 2Document36 pagesBS en 10297 2Sharma ShailenNo ratings yet
- Equipment Design - BOILERSDocument24 pagesEquipment Design - BOILERSEmyu ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6-4 Homework Examples 17, 21, 27Document2 pagesLesson 6-4 Homework Examples 17, 21, 27Jay-anne CruzNo ratings yet
- Grade F: Tabulation Allowable Within TheDocument1 pageGrade F: Tabulation Allowable Within ThelechepinitoNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan Optimasi Formula Sediaan Sirup Mukolitik in (Hibiscus Rosa-Sinensis L.)Document30 pagesRingkasan Optimasi Formula Sediaan Sirup Mukolitik in (Hibiscus Rosa-Sinensis L.)rahmi73No ratings yet
- Introduction to PCA and FA: Dimension Reduction ToolsDocument29 pagesIntroduction to PCA and FA: Dimension Reduction ToolsPushpaRasnayakeNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument16 pagesEngineering MaterialsYosef Ganang Jati NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Part Number 26-84: Illustrated Parts BreakdownDocument90 pagesPart Number 26-84: Illustrated Parts BreakdownJesus OliverosNo ratings yet
- Ut Procedure 1Document8 pagesUt Procedure 1abhinavsmash66666No ratings yet
- The Consumption of Compressed Air: Applications and ComponentsDocument24 pagesThe Consumption of Compressed Air: Applications and Componentsibong tiriritNo ratings yet
- KNX Fan Coil Actuator REG-K, Light Grey: CharacteristicsDocument1 pageKNX Fan Coil Actuator REG-K, Light Grey: CharacteristicsRazvan RazNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Multi Life Cycle Center: R. Knoth, M. Brandstötter, B. Kopacek, P. KopacekDocument5 pagesCase Study: Multi Life Cycle Center: R. Knoth, M. Brandstötter, B. Kopacek, P. KopacekgroventoNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesMagnetism and Electromagnetism - Electrical Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersNagesh GillNo ratings yet
- Qa TableDocument9 pagesQa Tableapi-299403846No ratings yet
- M/M/1 Queues With Working Vacations (M/M/1/WV) : L.D. Servi, S.G. FinnDocument12 pagesM/M/1 Queues With Working Vacations (M/M/1/WV) : L.D. Servi, S.G. FinnSadek AlaouiNo ratings yet
- Operation and Supply ChainDocument34 pagesOperation and Supply ChainAqib LatifNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Random MatricesDocument508 pagesIntroduction To Random Matricesjorelex100% (1)
- Calculation of Vapor-Liquid-Liquid Equilibria For The Fischer-Tropsch Reactor Effluents Using Modified Peng-Robinson Equation of StateDocument31 pagesCalculation of Vapor-Liquid-Liquid Equilibria For The Fischer-Tropsch Reactor Effluents Using Modified Peng-Robinson Equation of StatekenymorenoNo ratings yet