Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Weld Filler Metal Selection
Uploaded by
susanwebCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Weld Filler Metal Selection
Uploaded by
susanwebCopyright:
Available Formats
WELD FILLER METAL SELECTION
GUIDELINE FOR VARIOUS METAL
COMBINATIONS
DIVISION OF FACILITIES DEVELOPMENT
REVISION01/06/2014
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Weld Filler Metal Selection Chart for Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) For Various
Metal Combinations:.........................................................................................................................3
Welding Filler Metal Designators:...................................................................................................4
1. Carbon Steel Electrodes:.......................................................................................................4
2. Alloy Steel Electrodes:............................................................................................................5
3. Stainless Steel Filler Metal.....................................................................................................5
Table 1:
Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel Welding Consumables for SMAW Process............6
Table 2:
Austenitic, Super-Austenitic and Duplex Stainless Steel Alloys............................7
REVISION01/06/2014
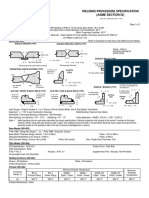
Weld Filler Metal Selection Chart for Shielded Metal Arc Welding
(SMAW) For Various Metal Combinations:
The attached Tables provide generally accepted electrode selections for the
base materials shown, along with process areas that need special consideration.
The special consideration cases have come about from past experiences in
industry. The attached tables are as follows:
Table 1: Carbon and Alloy Steels
Table 2: Austenitic, Super-austenitic and Duplex Stainless Steels
Note that these tables DO NOT attempt to include all possible choices.
Further, there are a number of proprietary base materials and castings for which
the filler metals used do not have an AWS Classification available at this time.
When you are faced with a particular material or combination of materials
not shown in these tables, please consult the manufacturer or the DFD
There is an explanation of the salient designations where appropriate (next two
pages). For a complete listing of electrode designations, usability Classifications,
weld metal chemical compositions and testing methods involved, refer to the
appropriate AWS Filler metal specifications mentioned in tables 1 and 2.
REVISION01/06/2014
Welding Filler Metal Designators:
1. Carbon Steel Electrodes:
Mandatory Classification Designators:
Designates an Electrode
Designates minimum tensile strength, in Ksi,
of the as-deposited weld metal
XX YY 1 HZ R
Designates the welding position, the type of
covering and the type of welding current for which
the electrodes are suitable (see table below)
Optional Supplemental Designators:
Designates that the electrode meets
the requirements of absorbed moisture
Designates that the electrode meets the requirements of the
diffusible hydrogen testwith an average value not
exceeding Z mL of H2 per 100gms of deposited metal
Designates that the electrode meet the
requirements for improved toughness and ductility
AWS
Classification
E 6010
E 6011
E 7018
E 7024
Electrode Classification
Type of Covering
Welding
Positiona
High cellulose, sodium
High Cellulose, Potassium
Low hydrogen, Potassium,
Iron Powder
Iron Powder, Titania
Type of
currentb
F, V, OH, H
F, V, OH, H
F, V, OH, H
dcep
ac or dcep
ac or dcep
H-Fillets, F
ac, dcep or dcen
Notes: a. The abbreviations indicate the welding positions
F=Flat; V= Vertical, OH= Overhead, H= Horizontal,
H-Fillets=Horizontal Fillets.
b. The term dcep refers to direct current electrode positive (dc, reverse polarity).
The term dcen is direct current electrode negative (dc, straight polarity)
Also note that the above electrode classifications are the most widely used and does not include
all of the available classifications. Refer to AWS A 5.1 for complete listing.
REVISION01/06/2014
2. Alloy Steel Electrodes:
Mandatory Classification Designators:
Designates an Electrode
Designates minimum tensile strength, in Ksi,
of the as-deposited weld metal
Designates the welding position, the type of
covering and the type of welding current for
which the electrodes are suitable
Designates the chemical composition of the undiluted weld
metal produced by the electrode using SMAW process
E (X) XX YY X HZ R
Optional Supplemental Designators:
Designates that the electrode meets
the requirements of absorbed moisture
Designates that the electrode meets the
requirements of the diffusible hydrogen testwith
an average value not exceeding ZmL of H2 per
100gms of deposited metal, where Z is 4, 8 or 16
Refer to AWS A 5.5 for complete listing of mechanical properties, chemical
composition of as-deposited weld metal and testing procedures for SMAW
process.
3. Stainless Steel Filler Metal
Usability Classification
Type of Welding Current and Position of Welding
AWS Classification
Welding Current
Welding position
EXXX(X)-15
EXXX(X)-16
EXXX(X)-17
EXXX(X)-25
EXXX(X)-26
dcep
dcep or ac
dcep or ac
dcep
dcep or ac
All
All
All
H, F
H, F
For more details on the usability classifications, refer to AWS A 5.4
REVISION01/06/2014
Table 1: Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel Welding Consumables for
SMAW Process
Carbon steel
AB
1 and 1 1/4 Cr - 1/2 Mo Steel
2 1/4 Cr - 1 Mo Steel
5 Cr - 1/2 Mo Steel
9 Cr- 1 Mo Steel
AC
C
AD
CD
D
AE
CE
DE
E
5Cr- 1/2 Mo Steel
2 1/4 Cr-1Mo Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon-Molybdenum Steel
1and 1 1/4 Cr-1/2 Mo Steel
Carbon-Molybdenum Steel
AF
CF
DF
EF
F
9Cr-1Mo Steel
Base Material
AG
CH
DH
EH
FH
H
Legend:
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
AWS A 5.1 Classification E 70XX low hydrogen (E7018 preferred)
AWS A 5.1 Classification E6010
AWS A 5.5 Classification E70XX - A1, low hydrogen
AWS A 5.5 Classification E70XX-B2L or E80XX-B2, low hydrogen
AWS A 5.5 Classification E80XX-B3L or E90XX-B3, low hydrogen
AWS A 5.5 Classification E80XX-B6 or E80XX-B6L, low hydrogen
AWS A 5.5 Classification E80XX-B7 or E80XX-B7L, low hydrogen
AWS A 5.5 Classification E80XX-B8 or E80XX-B8L, low hydrogen
Notes:
1. Table 1 refers to coated electrodes (SMAW process) only. For bare wire welding (SAW,
GMAW, GTAW and FCAW), use equivalent electrode classifications (AWS A 5.14, A 5.17, A 5.18,
A 5.20, A 5.23, A 5.28)
2. Higher alloy electrode specified in the table should normally be used to meet the required tensile
and toughness after post weld heat treatment (PWHT). If no PWHT is required, the lower alloy
electrode specified may be required to meet the hardness requirements.
REVISION01/06/2014
Table 2:
Austenitic, Super-Austenitic and Duplex Stainless Steel Alloys
Carbon and Low Alloy Steel
Type 304L Stainless Steel
Type 304H Stainless Steel
Type 316L Stainless Steel
Type 317L Stainless Steel
Type 904L Stainless Steel
Type 6% Mo Stainless Steel
Eg: 254 SMO, AL 6XN
Type 7% Mo Stainless Steel
Eg: 654 SMO
Type Alloy 20Cb-3
Type 2304 Duplex SS
Type 2205 Duplex SS
ABC
D
ABC ABC ABC
DE
DF
DG
E
EF
EG
FG
FG
GC
ABC
C
*
FC
GC
C
CJK
2205 Duplex
SS
2304 Duplex
SS
Alloy 20Cb-3
7% Mo SS
6% Mo SS
ABC
DC
*
FC
GC
C
904L SS
317L SS
316L SS
304L SS
304H SS
Base Metal
ABC
C
*
FC
GC
C
CJK
ABC N
DCH NL
ECH *
FCH NL
GC
L
C
L
*
*
N
NL
*
NL
L
L
*
CJK
*
LM
*
LM
LM
Notes:
1. Table 2 refers to coated electrodes only. For wire
welding (GMAW & GTAW) use equivalent electrode
classification (AWS A 5.14)
Legend
A - AWS A 5.4 Classification E309L-XX
B - AWS A 5.11 Classification ENiCrFe-2 or -3
(-2 is Alloy 718 and -3 is Inconel 182)
C - AWS A 5.11 Classification ENiCrMo-3 (Inconel 625)
D - AWS A 5.4 Classification E308L-XX
E - AWS A 5.4 Classification E308H-XX
F - AWS A 5.4 Classification E316L-XX
2. There are many proprietary alloys available in the
market and material combinations you might encounter.
Consult the manufacturer or the DFD for proper filler
metal selection
G - AWS A 5.4 Classification E317L-XX
H - AWS A 5.4 Classification E320LR-XX
J - AWS A 5.11 Classification ENiCrMo-4
(Hastelloy C-276)
K - AWS A 5.11 Classification ENiCrMo-11
(Hastelloy G-30)
L - AWS A 5.4 Classification E2209-XX
M - AWS A 5.4 Classification E2553-XX
N - AWS A 5.4 Classification E309MoL-XX
REVISION01/06/2014
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Visual InspectionDocument49 pagesFundamentals of Visual InspectionsusanwebNo ratings yet
- The Alternative To PWHT Temper Bead Welding by Walter J SperkoDocument64 pagesThe Alternative To PWHT Temper Bead Welding by Walter J Sperkosusanweb100% (3)
- 01 - WELDING DEFECTS (Surface) - May 2021Document28 pages01 - WELDING DEFECTS (Surface) - May 2021Gerry Dan ChanliongcoNo ratings yet
- Filler Metal SelectionDocument7 pagesFiller Metal SelectionMidhun K ChandraboseNo ratings yet
- WC-478 - Effects of Welding Variables PDFDocument1 pageWC-478 - Effects of Welding Variables PDFNathanLaertePiaiNo ratings yet
- Material With Electrode SelectionDocument2 pagesMaterial With Electrode SelectionJithuJohn100% (3)
- WPS List For Piping: (Asme Section Ix)Document2 pagesWPS List For Piping: (Asme Section Ix)Ali MoosaviNo ratings yet
- TWI Cswip 3.1wis 5 Welding Inspection Welding Symbols BSEN ISO 22553 /AWS A2Document68 pagesTWI Cswip 3.1wis 5 Welding Inspection Welding Symbols BSEN ISO 22553 /AWS A2Ali ClubistNo ratings yet
- Select Arc Catalogue Part 1Document10 pagesSelect Arc Catalogue Part 1lionheartedNo ratings yet
- Filler Metal Selection-SignedDocument14 pagesFiller Metal Selection-Signedamine bouizarNo ratings yet
- Properties of Aluminum Alloys: Tensile, Creep, and Fatigue Data at High and Low TemperaturesDocument7 pagesProperties of Aluminum Alloys: Tensile, Creep, and Fatigue Data at High and Low TemperaturesBalakrishnan RagothamanNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant Inspection ProcedureDocument13 pagesDye Penetrant Inspection ProcedureHafidzManaf100% (1)
- RT Level Iii TestDocument4 pagesRT Level Iii Testsusanweb0% (1)
- Electrodes ConsumablesDocument2 pagesElectrodes Consumablesranjith_007100% (2)
- Brazing BPS 107-1 PDocument5 pagesBrazing BPS 107-1 Pmbe josephNo ratings yet
- SS - Filler Wire SelectionDocument26 pagesSS - Filler Wire SelectionBaraa AzebNo ratings yet
- Scor Model in Supply ChainDocument25 pagesScor Model in Supply ChainGopikrishna S Nair100% (1)
- Welding Electrode Selection GuideDocument2 pagesWelding Electrode Selection GuideShanmuga Navaneethan100% (1)
- Unitor Maintenance and Repair Welding: The Solutions GuideDocument1 pageUnitor Maintenance and Repair Welding: The Solutions GuideNuzhat Ali100% (1)
- Welcome To Preheat Calculation Program: C.brak@it - Fnt.hvu - NLDocument16 pagesWelcome To Preheat Calculation Program: C.brak@it - Fnt.hvu - NLKelvin Labarez100% (1)
- PDF Engineering) Esab Welding Handbook - 5 EditionDocument143 pagesPDF Engineering) Esab Welding Handbook - 5 Editionmarshall, of course100% (3)
- WPS BhelDocument2 pagesWPS BhelpradhankruhsnaNo ratings yet
- Welding of Nickel AlloysDocument12 pagesWelding of Nickel Alloysaj87_goswamiNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects Poster 600x900 Lores enDocument1 pageWelding Defects Poster 600x900 Lores enMostafa ZedNo ratings yet
- Electrodes EnglishDocument139 pagesElectrodes Englishcostelino72No ratings yet
- PMI ProcedureDocument7 pagesPMI Procedureosito1214100% (1)
- Positive Material Identification (Pmi)Document2 pagesPositive Material Identification (Pmi)MurugadossRajendranNo ratings yet
- Talent ManagementDocument40 pagesTalent ManagementPratibha Goswami100% (1)
- Electrode Selection Excel SheetDocument1 pageElectrode Selection Excel Sheetchandrakit047No ratings yet
- Ferrous MetalDocument39 pagesFerrous MetalAshwani DograNo ratings yet
- British Standards For WeldingDocument8 pagesBritish Standards For Weldingsusanweb100% (2)
- Jan 2015 - Licensee Factory ListDocument8 pagesJan 2015 - Licensee Factory ListTr1ValNo ratings yet
- 484 Welding Guidelines For Design EngineersDocument4 pages484 Welding Guidelines For Design EngineersPham Song Hong100% (1)
- Garcia Welding: Filler Metal Selection GuideDocument8 pagesGarcia Welding: Filler Metal Selection GuideGustavo MorilloNo ratings yet
- Usability Designators FCAWDocument5 pagesUsability Designators FCAWAnonymous dh6DITNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Inspection ProcedureDocument9 pagesMagnetic Particle Inspection Procedurentah84100% (1)
- Casting, Forming & WeldingDocument90 pagesCasting, Forming & WeldingmahdiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Chart: AWS Advani Esab D & H GEE NucorweldDocument4 pagesComparative Chart: AWS Advani Esab D & H GEE NucorweldAnik Desai100% (2)
- Covered Welding ElectrodesDocument11 pagesCovered Welding ElectrodesAqsa BanoNo ratings yet
- API Welding ProcedureDocument2 pagesAPI Welding ProcedureSamarakoon BandaNo ratings yet
- Welding Electrode SelectionDocument1 pageWelding Electrode SelectionNadeemNo ratings yet
- Welding Checklist For Field WeldingDocument1 pageWelding Checklist For Field Weldingnapster386No ratings yet
- Paint Slip Coefficient PDFDocument28 pagesPaint Slip Coefficient PDFRk Sabarinathan100% (1)
- Tungsten ElectrodesDocument2 pagesTungsten ElectrodesSyed Furqan Rehmani0% (2)
- Quality Oriented and ISO Approved Stainless Steel 904L Buttweld Pipe Fittings Manufacturer in IndiaDocument5 pagesQuality Oriented and ISO Approved Stainless Steel 904L Buttweld Pipe Fittings Manufacturer in IndiaPetromat Oil and Gas Equipment Pvt. Ltd.No ratings yet
- Electrode Selection Excel ChartDocument2 pagesElectrode Selection Excel ChartMahesh Kumar100% (2)
- Petroleum Refining NotesDocument4 pagesPetroleum Refining Notesapi-304149645No ratings yet
- WPS 316 L PDFDocument4 pagesWPS 316 L PDFIrinaNo ratings yet
- Economics Sba GuidelineDocument30 pagesEconomics Sba GuidelineSHABBA MADDA POT33% (3)
- Brazing Procedure Specification (BPS) : (Automatic, Manual, Machine, or Semi-Automatic)Document3 pagesBrazing Procedure Specification (BPS) : (Automatic, Manual, Machine, or Semi-Automatic)Joyce GordonioNo ratings yet
- Electrode SelectionDocument1 pageElectrode SelectionVijayabaraniNo ratings yet
- Bohler Welding Guide PDFDocument515 pagesBohler Welding Guide PDFParveen (Atam Valves)100% (1)
- Weld Filler Metal SelectionDocument7 pagesWeld Filler Metal SelectionRajesh AutorajeshNo ratings yet
- TGN-PE-02 Temper Bead WeldingDocument9 pagesTGN-PE-02 Temper Bead WeldingNatrajiNo ratings yet
- Welding BisplateDocument12 pagesWelding BisplateLim Senglin100% (1)
- Metrode Dissimilar Consumable SelectorDocument7 pagesMetrode Dissimilar Consumable SelectorClaudia MmsNo ratings yet
- CON-03!03!22 Temper Bead Welding ProcedureDocument6 pagesCON-03!03!22 Temper Bead Welding ProceduresusanwebNo ratings yet
- NSSW Welding Handbook Web PDFDocument334 pagesNSSW Welding Handbook Web PDFTran Chi Binh DDC100% (1)
- Mild Steel Welding ElectrodeDocument12 pagesMild Steel Welding ElectrodeVĩnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Welding Rod SelectionDocument1 pageWelding Rod Selectionbikas_sahaNo ratings yet
- Nickel Alloy Based Filler MetalDocument1 pageNickel Alloy Based Filler MetaljoehodohNo ratings yet
- FCAW Electrode DesignationDocument3 pagesFCAW Electrode DesignationthedreampowerNo ratings yet
- Welding ElotrodeDocument3 pagesWelding ElotrodeNiranjan khatuaNo ratings yet
- Astm hk40 Chemical Composition Astm hk40 Mechanica 2 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm hk40 Chemical Composition Astm hk40 Mechanica 2 PDFprashant mishraNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Electrode Comparison ChartDocument7 pagesStainless Steel Electrode Comparison Chartmiker100No ratings yet
- WPS & PQR (E Co Cr-E)Document3 pagesWPS & PQR (E Co Cr-E)HossamSAshourNo ratings yet
- Piping Inspection 22.01.2020Document72 pagesPiping Inspection 22.01.2020KarthikNo ratings yet
- Selection of Welding ConsumablesDocument13 pagesSelection of Welding ConsumablesbassemaeNo ratings yet
- Wps GT 9b Cvn90 Rev 1 PDFDocument6 pagesWps GT 9b Cvn90 Rev 1 PDFM. Zaki RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Factors in Selection of Filler Metals in WeldingDocument2 pagesFactors in Selection of Filler Metals in WeldingBalakumarNo ratings yet
- Lincoln Welding MachineDocument4 pagesLincoln Welding MachinemevansmetreelNo ratings yet
- Welding AISI 4130 PDFDocument5 pagesWelding AISI 4130 PDFDarioNo ratings yet
- Welding Rod For c5 & f5 - Er 80s-b6Document1 pageWelding Rod For c5 & f5 - Er 80s-b6SatyamEngNo ratings yet
- KMT Stellite Alloys Brochure FINALDocument15 pagesKMT Stellite Alloys Brochure FINALIkhsan LyNo ratings yet
- Selection of Filler Metal For WeldingDocument21 pagesSelection of Filler Metal For WeldingRegu vlogsNo ratings yet
- Rail WeldingDocument4 pagesRail WeldingOlga Sandoval RomeroNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Referencia de Materiales: Material Reference ChartDocument2 pagesTabla de Referencia de Materiales: Material Reference Chartsateesh chandNo ratings yet
- Asme Ix - WPS - Gtaw Fcaw Gmaw PDFDocument1 pageAsme Ix - WPS - Gtaw Fcaw Gmaw PDFThe Welding Inspections CommunityNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding Filler Metal Selection ChartDocument7 pagesArc Welding Filler Metal Selection Chartepriyono0% (1)
- Filler Metals For Welding: Part One: AbstractDocument4 pagesFiller Metals For Welding: Part One: AbstractsierthinNo ratings yet
- wj1106 54Document5 pageswj1106 54koner_debasishNo ratings yet
- WTIA-TN07 Health and Safety in Welding PDFDocument148 pagesWTIA-TN07 Health and Safety in Welding PDFMphilipTNo ratings yet
- A78857-2 2.21 Hydrostaticting Testing Standard - A5E3L0Document32 pagesA78857-2 2.21 Hydrostaticting Testing Standard - A5E3L0susanwebNo ratings yet
- Us DM4 DLDocument38 pagesUs DM4 DLBalan DanutNo ratings yet
- What Is A Steel Casting Casting Process ASMDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Steel Casting Casting Process ASMsusanwebNo ratings yet
- Southern Pmi Verification Procedure 203204Document3 pagesSouthern Pmi Verification Procedure 203204susanwebNo ratings yet
- WeldingFumesGases 1990 PDFDocument38 pagesWeldingFumesGases 1990 PDFsusanwebNo ratings yet
- PmiDocument6 pagesPmiSai FujiwaraNo ratings yet
- Schaeffler DiagramDocument1 pageSchaeffler Diagrambmdbmdbmd100% (1)
- Exploring Temper BeadDocument11 pagesExploring Temper BeadvaseaNo ratings yet
- Welding SymbolsDocument78 pagesWelding Symbolsuttamtm100% (1)
- Measurement and Numerical Prediction of Residual Stresses in Steel Welds Subject To Heat TreatmentDocument29 pagesMeasurement and Numerical Prediction of Residual Stresses in Steel Welds Subject To Heat TreatmentsusanwebNo ratings yet
- p91 WeldingDocument5 pagesp91 Weldingsaji_t1984100% (1)
- NDTDocument9 pagesNDTDenzil D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive EvaluationDocument25 pagesNon Destructive EvaluationsusanwebNo ratings yet
- NDTDocument9 pagesNDTDenzil D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Non Destructive InspectionDocument41 pagesNon Destructive InspectionsusanwebNo ratings yet
- ASTM E 2500 Standard For Pharma and Biopharma ManufacturingDocument30 pagesASTM E 2500 Standard For Pharma and Biopharma ManufacturingMohsinShaikh100% (2)
- Mds SM13CRM 110 enDocument5 pagesMds SM13CRM 110 enColinNo ratings yet
- Form Ability Od A8011 Aluminium Alloy SheetDocument6 pagesForm Ability Od A8011 Aluminium Alloy SheetwojciechsciezorNo ratings yet
- Taig Lathe ManualDocument12 pagesTaig Lathe Manualpeter smithNo ratings yet
- A 1Document4 pagesA 1Izreen FaraNo ratings yet
- Steel June 2017Document54 pagesSteel June 2017Bipin Bansal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual MEC224 Mechanical Engineering WorkshopDocument30 pagesLaboratory Manual MEC224 Mechanical Engineering WorkshopSunil SharmaNo ratings yet
- GeneralDocument111 pagesGeneraloliveiralauroNo ratings yet
- CV Tauarai CVDocument5 pagesCV Tauarai CVgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Lean and Agile ManufacturingDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Lean and Agile ManufacturingjvanandhNo ratings yet
- Management Information System in Asset-Intensive Industries: Perspective in Choosing The Right SolutionDocument20 pagesManagement Information System in Asset-Intensive Industries: Perspective in Choosing The Right SolutionHasni HalimNo ratings yet
- Endurance LimitDocument13 pagesEndurance LimitOmkar Kumar Jha0% (1)
- 00 Lean ManufacturingDocument12 pages00 Lean ManufacturingErnesto Rascon Basaldua0% (1)
- M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology Department of CIVIL ENGINEERINGDocument10 pagesM S Ramaiah Institute of Technology Department of CIVIL ENGINEERINGPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Wear Behavior of Magnesium Alloy AZ91 Hybrid Composite MaterialsDocument10 pagesWear Behavior of Magnesium Alloy AZ91 Hybrid Composite MaterialstarasasankaNo ratings yet
- Rolling ProcessDocument17 pagesRolling ProcessRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- LogitechDocument1 pageLogitechAkshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Pilot Plant Simulation As A Tool For More Efficient Mineral ProcessingDocument6 pagesPilot Plant Simulation As A Tool For More Efficient Mineral ProcessingEngineering Office ShahrakNo ratings yet
- Daimlerfinalpresentationpdf 111122092224 Phpapp02Document39 pagesDaimlerfinalpresentationpdf 111122092224 Phpapp02Marius CiuculanNo ratings yet
- Mr. Munyao-Mulwa: Department of Management Science Uon, School of BusinessDocument61 pagesMr. Munyao-Mulwa: Department of Management Science Uon, School of BusinessstudentNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes - FullDocument5 pagesMetal Forming Processes - FullArjun NbNo ratings yet
- Ador - Welding RodDocument4 pagesAdor - Welding RodManoj DoshiNo ratings yet