Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
LinaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
LinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan
School
: SMP
Subject
: Mathematics
Class/ Semester
: VIII/ II
Time Allocation
: 2 x 45 minutes
A. Standard Competence
Understading the characteristics of cubes, rectangular prisms, prisms,
pyramids, and their parts, also determine their measure
B. Basic Competence
To identify the characteristics of cubes, rectangular prisms, prisms, pyramids,
and their parts
C. Indicator
Student can determine the characteristic of cubes
Students can determine the characteristics of rectangular prisms
Students can determine the characteristics of prisms
Students can determine the characteristics of pyramids
D. Learning Achievement
Students can determine the characteristics of cubes, rectangular prisms,
prisms, pyramids, and their parts
E. Main Material
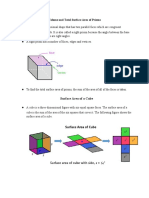
- A polyhedron is a solid that is bounded by polygons called faces, that
-
enclose a single region of space.
An edge of a polyhedron is a line segment formed by intersection of two
faces.
A vertex of a polyhedron is a point where three or more edges meet.
The plural of polyhedron is polyhedra or polyhedrons.
Mathematics for Junior High School Grade
VIII
A prism is a special type of polyhedron, with two faces called bases, that
are congruent, parallel polygons. The other faces of the polyhedron, called
lateral faces, are parallelogram that connect the corresponding sides of the
bases.
Cubes and rectangular prisms have 6 sides, 12 edges, and 8 vertexs
A cube has 6 sides that formed by congruent squares
A rectangular prism has 6 pairs of sides that formed by a rectangle that
each pairs are congruent
A pyramid is another special type of polyhedron. Pyramids have only one
base. As in a prism, the other faces are called the lateral faces, and they
meet to form the lateral edges. The common vertex of the lateral faces is
the vertex of the pyramid.
The names of prisms and pyramids based on their base
The relationship of vertices (V), edges (E), and faces (F) of each
polyhedron can be written as below:
F+V=E+2
F. Learning Methods
Inquiry method
G. Teaching and Learning Activities
1. Introduction
- Teacher opens the learning process
Apperception:
Students will give a problem to collect some object that have same
classification
2. Main activities
- Teacher give problems in worksheet
- Students read the rule to finish the task in worksheets
- Students use their Cabri 3D to find the answer of the task
- Students manipulate the objects
- By those, students finish the questions in students worksheets
- Students make a conclusion base on their investigating
- Teacher and students make a conclusion together
- Finally, to check student understanding, teacher give some problem
related with their investigating
3. Closing
Teacher reviews, and guides the students to make summary
Mathematics for Junior High School Grade
VIII
a. The students give argument to draw conclusion and then discuss it
together to make a right conclusion.
b. Teacher reminds the student to read the material that will be studied
next meeting.
H. Learning Sources
Nuharini Dewi, dkk. 2008. Matematika SMP: Matematika, Konsep, dan
Aplikasinya . Jakarta:BSE.
Urban, et all. 2004. Mathematics for the international student mathematics
HL
(Core) e-book. Australia: Haese and Harris Publications
Holliday,et all. 2008. Algebra 1 (e-book). New York: Glencoe Mc Graw Hill
Murdock, Gerald et all. 2007. Discovering Geometry: An Investigate
Approach (e book). United States of America: Key Curriculum Press
I. Teaching Aids
Students worksheets helping by Cabri 3D
J. Evaluation
1. Can a polyhedron have for its faces
(i)
3 triangles?
(ii)
A square and four triangles?
(iii) 4 triangles?
(iv) Two triangles and 3 squares?
2. From question number 1, is it possible a polyhedron with any given
number of faces? (Hint: Think a pyramid).
3. Which are prisms among the following?
A nail
A table weight
Unsharpened pencil
Mathematics for Junior High School Grade
VIII
A box
Mathematics for Junior High School Grade
VIII
4. What are the differences between rectangular prism and rectangular
pyramid?
5. Can a polyhedron has 10 faces, 20 edges, and 15 vertices? Explain your
answer!
K. Assessment
Students understanding
Process to find the result
General conclusion
Presentation
15%
50%
25%
10%
L. Worksheet
Attached
Approved
____________
NIP.
Yogyakarta, 24 April 2012
Author
Lina Wulandari
NIM 09313244002
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Crystallography With Paper ModelDocument11 pagesCrystallography With Paper ModelDzakiyahNo ratings yet
- lp2 Report PDFDocument4 pageslp2 Report PDFSri WinayuNo ratings yet
- 1-3 Points Lines and PlanesDocument4 pages1-3 Points Lines and PlanesDanilo de MesaNo ratings yet
- Problem SolutionsDocument170 pagesProblem SolutionsSaeed Mahmud UllahNo ratings yet
- Platonic SolidDocument6 pagesPlatonic SolidThelma EdisonNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 StructureDocument5 pagesHomework 2 StructureDouglas FelixNo ratings yet
- MSM Re-2Document1 pageMSM Re-2Vijay GajeraNo ratings yet
- Multi-Sized Sphere Packing: Shuji Yamada Jinko Kanno Miki MiyauchiDocument45 pagesMulti-Sized Sphere Packing: Shuji Yamada Jinko Kanno Miki Miyauchimadden08No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document7 pagesUnit 1PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Atomic and Ionic Arrangements: 3-1 SolutionDocument52 pagesChapter 3: Atomic and Ionic Arrangements: 3-1 SolutionMarcos Jose100% (1)
- Problems in Solid Geometry 2017 PDFDocument4 pagesProblems in Solid Geometry 2017 PDFWendyWendyUNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument8 pagesSurface Area and VolumeAngelo CabralNo ratings yet
- Ed Tut 5Document2 pagesEd Tut 5Aman_Juneja_1455No ratings yet
- Summative Test No. 1Document6 pagesSummative Test No. 1Shaine Dzyll KuizonNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument2 pagesSolid StateKamal KishoreNo ratings yet
- Applying X-Ray Diffraction in Material AnalysDocument40 pagesApplying X-Ray Diffraction in Material Analysehagar60100% (1)
- Eulers Formula ActivityDocument2 pagesEulers Formula Activityapi-355107616No ratings yet
- On Crystal StructureDocument32 pagesOn Crystal StructureDeathEaterReturnNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structures (Chapter 3) 3.1. Unit Cell: (A, B, C), and Angles (Document13 pagesCrystal Structures (Chapter 3) 3.1. Unit Cell: (A, B, C), and Angles (PULLNo ratings yet
- Math - Week2 - Plane and Solid FiguresDocument26 pagesMath - Week2 - Plane and Solid FiguresMarlene Tagavilla-Felipe DiculenNo ratings yet
- Crystals - NotesDocument20 pagesCrystals - NotesJade Dhalle EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Dhruv KuchhalNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics: Bravais LatticeDocument13 pagesSolid State Physics: Bravais LatticeSumman IshfaqNo ratings yet
- MCQ Materials ScienceDocument4 pagesMCQ Materials SciencePrashantNo ratings yet
- G6 Q3 Notes5Document3 pagesG6 Q3 Notes5Kate100% (1)
- 1st Summative Test in MatheDocument2 pages1st Summative Test in MatheGrace RañolaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 2Document11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 2MARY JOY BASCO CANOYNo ratings yet
- TSA Andvolume of SolidsDocument14 pagesTSA Andvolume of SolidsJairNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics NotesDocument4 pagesSolid State Physics NotesTariq MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Methods, Problems and Solutions - and TutorialsDocument13 pagesMethods, Problems and Solutions - and TutorialsAienzCamuzt ChieTinkerbellNo ratings yet