Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Minimization of Power Loss in Distribution Networks by Different Techniques
Uploaded by
raghvendraprasadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Minimization of Power Loss in Distribution Networks by Different Techniques
Uploaded by
raghvendraprasadCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012
ISSN 2229-5518
Minimization of Power Loss in Distribution
Networks by Different Techniques
Mr.Rudresh.B.Magadum, Mr.Tejaswi.M.Timsani
Abstract This paper proposes accurate loss minimization is the critical component for efficient electrical distribution power flow. The contribution of
this work presents loss minimization in power distribution system through network reconfiguration, DTC relocation, voltage regulator placement, express
feeders and building new substation.
Index Terms Distribution system, Network Reconfiguration, Express Feeder, Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) placement,
1. INTRODUCTION
energy theft are included in the total, losses go as high as 65%
in some states and average about 35- 40%. The financial loss
has been estimate at 1.5% of the national GDP.
he distribution system is the most visible part of the
supply chain, and as such the most exposed to the
critical observation of its users. It is, in many cases, the
largest investment, maintenance and operation expense, and
the object of interest to government, financial agencies, and
associations of concerned citizens. About 30 to 40 % of total
investments in the electrical sector go to distribution systems
[3], but nevertheless, they have not received the technological
impact in the same manner as the generation and
transmission systems.
TABLE.1 COMPARISON OF LOSSES IN DIFFERENT
STATES OF INDIA [2]
Less than
20%
Ideally, losses in an electric system should be around 3 to 6%.
In developed countries, it is not greater than 10%.However, in
developing countries, the percentage of active power losses is
around 20%; therefore, utilities in the electric sector are
currently interested in reducing it in order to be more
competitive, since the electricity prices in deregulated
markets are related to the system losses. In India, collective of
all states, in 2008 the technical and non technical losses are
accounted as 23% of the total input energy [2]. To manage a
loss reduction program in a distribution system it is necessary
to use effective and efficient computational tools that allow
quantifying the loss in each different network element for
system losses reduction. Various authors have discussed loss
minimization in different aspects.
Indias transmission and distribution losses are among the
highest in the world. When non-technical losses such as
Goa
Between
20-30%
Andra
Pradesh
karnataka
Delhi
Tamilnadu
Gujarat
kerala
Uttar Pradesh
West
Bengal
Assam
Bihar
Himachal
Pradesh
Between
30-40%
Haryana
Above 40%
Jharkhand
Maharastra
Rajstan
Madhya
Pradesh
Tripuar
Meghalaya
Arunachal
Pradesh
Punjab
Mizam
Manipal
Uttaranchal
Chattisgarh
Nagaland
2. LOSS REDUCTION AND VOLTAGE
IMPROVEMENT TECHNIQUES.
Technical losses can be reduced by up-gradation of the
existing network using.
IJSER 2012
http://www.ijser.org
Network reconfiguration
DTC relocation (Change of feed)
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012
ISSN 2229-5518
Network re-conduct ring
Voltage regulator placement
Use of express feeder
Adoption of High voltage distribution system (HVDS)
Building new substation
2.1 Network Reconfiguration
Optimal
distribution
planning
involves
network
reconfiguration for distribution loss minimization, load
balancing under normal operating conditions and fast service
restoration minimizing the zones without power under
failure conditions. Network Reconfiguration is the process of
operating switches to change the circuit topology so that
operating costs are reduced while satisfying the specified
constraints.
2. Investment required is less
Demerits
1. The extent of voltage improvement is limited
2. For further improvement of voltage profile we have
to adopt for other methodologies which involves
extra investment.
2.3 Network Re-conductoring
Replacement of the existing conductor on the feeder with an
optimal conductor size for optimal length of the feeder since,
size of the conductor is the parameter that decides current
density and resistance. This scheme is applied when Network
reconfiguration is not possible
The existing conductor is no more optimal due to rapid load
growth Re-conductoring depends on Load expected to serve
and capacity required in future.
Merits
1. Increases the capability to handle load growth
Demerits
1. Additional investment is required
2.4 Voltage Regulator Placement
The capability of a voltage regulator to maintain smooth
voltages is an attractive solution. The optimal location of the
placement can be determined by conducting feasibility study.
Merits
1. Smooth variation of voltage is possible.
Demerits
1. The extent of voltage improvement is limited
2. Extensive use will further deteriorate the network.
Fig.1 Simple example for network reconfiguration
2.2 Distribution Transformer (DTC) Relocation
DTC relocation involves the change of feed point. This
scheme is adopted as an immediate solution. The new point
of connection can be determined by feasibility study.
Merits
1. Supports further reconfiguration
2.5 Use of Express Feeder
Express feeder is the feeder running from the source to any
load point with no tapping intermediately. The use of express
feeder is recommended when Reconfiguration or Reconductoring is not possible. The point of connection depends
upon the quotient of voltage difference.
Merits
1. More effective in improving the voltage profile
2. Supports more load growth compared to
reconfiguration and re-conductoring schemes
3. Further reconfiguration is made possible
Demerits
1. Additional investment is required
2.6 Adoption of High voltage distribution
IJSER 2012
http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012
ISSN 2229-5518
System (HVDS)
Conversion of existing LVDS to HVDS reduces the technical
losses effectively
Example: For a 100 KVA load the current for 11kV system
is 5.2 A whereas for 415 V it is 140 A.
Merits
1. Reduced losses and improved voltage profile
Demerits
1. Additional investment is required
2. Regular maintenance is required
2.7. Building new substation
This involves addition of new substation in addition to the
existing. Location of the installation is determined by
feasibility study. This scheme has to be adopted as the last
option.
Merits
1. More reliable
2. Reduction in losses and improved voltage profile
Demerits
1. Additional investment for building new
substation
3. ORDER OF PRECEDENCE FOR ADOPTION
OF METHODOLOGIES
Network reconfiguration
DTC relocation (Change of feed)
Line re-conductoring
Voltage regulator placement
Use of express feeder
Adoption of HVDS
Building new substation
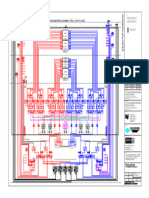
Fig.2 Single line diagram of 415 volt distribution centre drawn in
MiPower software package
4. SIMULATION RESULTS OBTAINED FROM
MIPOWER SOFTWARE PACKAGE.
MiPower is a highly interactive, user-friendly windows
based Power System Analysis package. It includes a set of
modules for performing a wide range of power system design
and analysis study. MiPower features include Windows GUI
with centralized database. Steady state, transient and electromagnetic transient analysis can be performed with more
accuracy and tolerance.
TABLE.2 SIMULATION RESULTS
IJSER 2012
http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012
ISSN 2229-5518
Topology
Loss(in kw)
Original
58.9786
Network reconfigration
34.3152
DTC Relocation
30.3047
Network reconductoring
21.0285
Expree feeder
19.5944
HVDS
15.8442
Topology
Applying cost benefit analysis considering MiPower software
package the network reconfiguration no additional
investments are required hence it is considered feasible. The
building of new substation is carried out only in unavoidable
situations where no further augmentation is possible. So, four
topologies DTC relocation, network re-conductoring, Express
feeder and HVDS are considered. A cost benefit is analysis is
performed for the fore-mentioned topologies and the results
are furnished the necessary inputs required are listed and are
taken as specified.
Benefit to
Investment
ratio
Payback period
(in years)
DTC
relocation
20.0389
Less than
one year
Network reconductoring
13.185
Less than
one year
Express
feeder
5.34224
Between
1-2
HVDS
2.82409
Between
3-4
5. RESULTS OBTAINED FROM COST BENEFIT
ANALYSIS
The Benefit to Investment ratio and payback periods of the
projects considered are as tabulated below.
Table.5 cost benefit analysis results
TABLE.3 OTHER INVESTMENTS PARAMETER CONSIDERED.
Input
Value considered
Interest
12 %
O & M charges
3%
Project life
20 years
Unit charges
Rs. 2.5/-
Load factor
0.6
Constant
A
computing LLF)
(for
Topology
Investment (in Rs)
DTC relocation
1,00,000
Network re-conductoring
2,00,000
Express feeder
5,00,000
HVDS
10,00,000
0.3
TABLE.4 OTHER INPUTS TAKEN FOR COST BENEFIT ANALYSIS
IJSER 2012
http://www.ijser.org
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012
ISSN 2229-5518
6. CONCLUSION
In this paper, the cost benefit calculation is done using
MiPower software results. From cost benefit calculation it is
clear that DTC relocation having benefit to investment ratio
20.038, it clears that the DTC relocation having less payback
period hence which helps in distribution loss reduction in
very easy way.
7. REFERENCES
[1].
P. V. V. Rama Rao and S. Sivanagaraju, Radial Distribution
Network Reconfiguration for Loss Reduction and Load Balancing using
Plant Growth Simulation Algorithm International Journal on Electrical
Engineering and Informatics - Volume 2, Number 4, 2010
[2].
L.Ramesh, S.P.Chowdhury, S.Chowdhury, A .A. Natarajan,
C.T.Gaunt,Minimization of Power Loss In Distribution Networks by
Different methods, International Journal of Electrical and Electronics
Engineering 3:9 2009.
[3].
S. A. Qureshi and F. Mahmood ,
Evaluation by
Implementation of Distribution System Planning for Energy Loss
Reduction Pak. J. Engg. & Appl. Sci. Vol. 4, Jan 2009 (p. 43-55)
[4].
F. V. Gomes, S. Carneiro, J. L. R. Pereira, M. P. Vinagre, P. A. N.
Garcia, and L. R.Araujo, A new distribution system reconfiguration
approach using optimum power flow.And sensitivity analysis for loss
reduction, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., vol. 21, no. 4, pp.16161623, Nov.
2006.
[5].
S. Sivanagaraju, et.al, An Efficient Genetic Algorithm for Loss
Minimum DistributionSystem Reconfiguration, International Journal of
Electrical Power Components and Systems, Vol.34, No.3, March 2006,
pp.249-258.
[6].
Prabha kundur, Power system stability and control McGraw
Hill,Inc
BIOGRAPHY
Rudresh.B.Magadum
was
born
in
Karnataka, India on 09 July 1987. He
obtained B.E (Electrical and Electronics)
from
Vishveswaraya
Technological
University, Belgaum, and Karnataka, India.
He is currently pursuing M.Tech Degree in
Power and Energy Systems in Electrical and
Electronics
Engineering,
Basaveshwar
Engineering College, Bagalkot, India.
Tejaswi.M.Timsani was born in Karnataka,
India on 14 April 1986. He obtained B.E
(Electrical
and
Electronics)
from
Vishveswaraya Technological University,
Belgaum, and Karnataka, India. He is
IJSER 2012
http://www.ijser.org
currently pursuing M.Tech Degree in Power
and Energy Systems in Electrical and
Electronics
Engineering,
Basaveshwar
Engineering College, Bagalkot, India. His
areas of interest are Distribution Generation,
Renewable energy, FACTS.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Wright 2020Document5 pagesWright 2020raghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledraghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Resume 4may2022Document7 pagesResume 4may2022raghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Resume R DeshpandeDocument7 pagesResume R DeshpanderaghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Classification of Power Quality Variations in Wind Power Systems-A Simulation ApproachDocument10 pagesClassification of Power Quality Variations in Wind Power Systems-A Simulation ApproachraghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Resume R DeshpandeDocument7 pagesResume R DeshpanderaghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Analysis of Electrical Distribution Systems With Asynchronous GeneratorsDocument8 pagesPower Quality Analysis of Electrical Distribution Systems With Asynchronous GeneratorsraghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Analysis of Electrical Distribution Systems With Renewable Energy SourcesDocument5 pagesPower Quality Analysis of Electrical Distribution Systems With Renewable Energy SourcesraghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Atv Eldb3Document116 pagesAtv Eldb3raghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Power Quality Variations in Distributed Generation SystemsDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Power Quality Variations in Distributed Generation SystemsraghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- International Conference NitteDocument677 pagesInternational Conference NitteraghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Transformers and Induction Machines: - Unit Iii - Transformers - Continued .Document33 pagesTransformers and Induction Machines: - Unit Iii - Transformers - Continued .raghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- EE103/EE203: Basic Electrical Engineering LTPC: (3-1-2) 5Document3 pagesEE103/EE203: Basic Electrical Engineering LTPC: (3-1-2) 5raghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- Diesel Plants IndiaDocument2 pagesDiesel Plants IndiaraghvendraprasadNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- S11 Axera 5 Electric SystemDocument22 pagesS11 Axera 5 Electric SystemAnonymous iu95trpxNNo ratings yet
- Megapack Battery Fire InvestigationDocument3 pagesMegapack Battery Fire InvestigationSimon AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Section B: Property, Plant and Equipment Assets.: MHC Plantation SDN BHDDocument3 pagesSection B: Property, Plant and Equipment Assets.: MHC Plantation SDN BHDYong JinNo ratings yet
- Rotating Machines in BoilersDocument23 pagesRotating Machines in Boilerssudhirkumar99No ratings yet
- ABB Leaflet Comem BR-En 2018-06-07Document2 pagesABB Leaflet Comem BR-En 2018-06-07Dave ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Steady State Solution of Electric Power Systems With Accent On Fault ModellingDocument151 pagesSteady State Solution of Electric Power Systems With Accent On Fault Modellingwvargas926No ratings yet
- 695 NEC Rules For Fire PumpsDocument5 pages695 NEC Rules For Fire PumpsJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Kinetic Theory of Gases and Statistical Physics: Alexander A. SchekochihinDocument157 pagesLectures On Kinetic Theory of Gases and Statistical Physics: Alexander A. SchekochihinRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Biomass Plants - Detailed GuideDocument123 pagesBiomass Plants - Detailed GuideBrkaBrkatiNo ratings yet
- SJVN Question Paper With Answer-2013 For EeeDocument19 pagesSJVN Question Paper With Answer-2013 For EeeSatnam Singh100% (1)
- Grade 4 Science - FrictionDocument5 pagesGrade 4 Science - FrictionMis Gloria67% (3)
- Hydropower As A Renewable Energy Source Seminar PPT by Caleb PradhanDocument18 pagesHydropower As A Renewable Energy Source Seminar PPT by Caleb PradhanCaleb Quizzomatic PradhanNo ratings yet
- Final Updated Contractor List As On Sep 19Document25 pagesFinal Updated Contractor List As On Sep 19Vishal JiyaniNo ratings yet
- Power Station OverviewDocument11 pagesPower Station OverviewjamilNo ratings yet
- Manual-EnglishDocument29 pagesManual-EnglishMycastNo ratings yet
- 1265e-201 Elec Main Schematic - T2Document1 page1265e-201 Elec Main Schematic - T2Rangga SetaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration NotesDocument56 pagesMechanical Vibration NotesYadanaNo ratings yet
- Combined Over-Voltage & Under-Voltage Protection System Submitted byDocument9 pagesCombined Over-Voltage & Under-Voltage Protection System Submitted byAdarsh ChavdaNo ratings yet
- PV5Document2 pagesPV5Bogdan ChindrisNo ratings yet
- Dual B Series Inverter 1500vdcDocument4 pagesDual B Series Inverter 1500vdcrockydarkNo ratings yet
- Portable Inverter Generator: 2000 Max Watts / 1700 Rated WattsDocument30 pagesPortable Inverter Generator: 2000 Max Watts / 1700 Rated WattsWilmer SuarezNo ratings yet
- Turbine Protection NewDocument7 pagesTurbine Protection Newbk kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.energy ResoursesDocument41 pagesChapter 2.energy ResoursesPrathamesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines Lab ManualDocument8 pagesHydraulic Machines Lab ManualMuneeb MalikNo ratings yet
- 2011 Physics 5058 O-Level AnswersDocument7 pages2011 Physics 5058 O-Level Answersheyitsvan100% (1)
- Global Electric Service Provider: TBEA Shandong Luneng Taishan Cable Co., LTDDocument32 pagesGlobal Electric Service Provider: TBEA Shandong Luneng Taishan Cable Co., LTDmd saikotNo ratings yet
- Online Ups With Iso Ld1000 2000t-070917Document2 pagesOnline Ups With Iso Ld1000 2000t-070917NaviNo ratings yet
- Manpower Supply For Gas TurbineDocument3 pagesManpower Supply For Gas TurbinePrashanta NaikNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning in Primary and Secondary Mathematics: Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument11 pagesTeaching and Learning in Primary and Secondary Mathematics: Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaushaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Distribution Automation System (DAS)Document18 pagesPresentation On Distribution Automation System (DAS)A I Md. Sajed Arefin83% (6)