Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry Concepts
Uploaded by
Hammad AmjadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry Concepts
Uploaded by
Hammad AmjadCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter
4 Triangles and Congruence
4.1
Answer Key
Triangle Sum Theorem
Answers
1.
m1 = 41
2.
m1 = 86
3.
m1 = 61
4.
m1 = 51
5.
m1 = 13
6.
m1 = 60
7.
m1 = 70
8.
84
9.
57
10.
21
11.
x = 14
12.
x = 9
13.
x = 22
14.
x = 17
15.
x = 12
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.2
Answer Key
Exterior Angles Theorem
Answers
1.
m1 = 118
2.
m1 = 68
3.
m1 = 116
4.
m1 = 161
5.
m1 = 141
6.
m1 = 135
7.
180
8.
360
9.
360
10.
x = 30
11.
x = 25
12.
x = 7
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.3
Answer Key
Congruent Triangles
Answers
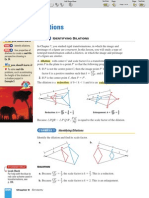
1.
Yes
2.
Yes
3.
Yes
4.
No
5.
No
6.
Yes
7.
No
8.
Yes
9.
No
10.
Yes
11.
No
12.
Yes
13.
Yes
14.
No
15.
No
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.4
Answer Key
Congruence Statements
Answers
1.
FGH KLM
2.
No, we do not know if , so we cannot say that the triangles are congruent.
3.
ABE DCE
4.
No, we only know that one pair of sides and one pair of angles are congruent. This is
not enough information to determine if the triangles are congruent.
5.
Line up the congruent sides: BCD ZYX
6.
Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent or CPCTC.
7.
T F, B A, S M, TB FA, BS AM,TS FM
8.
P S, A T, M E, PA ST , AM TE, PM SE
9.
I W, N E, T B, IN WE, NT EB,IT WB
10.
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.5
Answer Key
Third Angle Theorem
Answers
1.
88
2.
42
3.
50
4.
42
5.
47
6.
43
7.
47
8.
37
9.
Lines are not marked parallel, we cannot assume that mHIJ = 108.
10.
35
11.
Lines are not marked parallel, we cannot assume that mIHJ = 37.
12.
55
13.
63
14.
62
15.
63
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Answer Key
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.6
SSS Triangle Congruence
Answers
1.
Yes, DEF HJI, SSS
2.
No, one triangle is SSS and the other is SAS.
3.
Yes, ABC FED, SSS
4.
Yes, ATD ETD, SSS
5.
AB HI
6.
AB JL
7.
Statement
8.
Reason
1. B is the midpoint of DC , AD AC
Given
2. DB BC
Definition of a Midpoint
3. AB AB
Reflexive PoC
4. ABD ABC
SSS
Triangle #1: (-8, 0), (0, 3), and (-5, 9), Side #1 = 73, Side #2 = 90, Side #3 = 61
Triangle #2: (2, 5), (10, 2), and (5, -4), Side #1 = 90, Side #2 = 73, Side #3 = 61
The triangles are congruent by SSS.
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
9.
Answer Key
Triangle #1: (-7, 2), (1, 6), and (4, 5), Side #1 = 80, Side #2 = 130, Side #3 = 10
Triangle #2: (-1, -10), (-5, -2), and (-8, -1), Side #1 = 80, Side #2 = 130, Side #3
= 10
The triangles are congruent by SSS.
10.
ABC: AB = 18, AC= 58, BC = 52, DEF: DF = 17, DE = 58, EF = 137
The triangles are not congruent because not all the corresponding sides are congruent.
11.
ABC: AB = 37, AC = 45, BC = 34, DEF: DE = 37 ,DF = 45, EF = 34
The triangles are congruent by SSS.
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Answer Key
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.7
SAS Triangle Congruence
Answers
1.
No, these are both SSA, which is not a congruence postulate.
2.
Yes, ABC YXZ, SAS
3.
No, these are both SSA, which is not a congruent postulate
4.
C G
5.
C K
6.
AB ON
7.
Statement
Reason
1. B is a midpoint of DC , AB DC
Given
2. DB BC
Definition of a midpoint
3. ABD and ABC are right angles
lines create 4 right angles
4. ABD ABC
All right angles are
5. AB AB
Reflexive PoC
6. ABD ABC
SAS
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Answer Key
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
8.
Statement
Reason
1. AB is an angle bisector of DAC, AD AC
Given
2. DAB BAC
Definition of an Angle Bisector
3. AB AB
Reflexive PoC
4. ABD ABC
SAS
9.
Statement
Reason
1. B is the midpoint of DE and AC ,
ABE is a right angle
Given
2. DB BE, AB BC
Definition of a Midpoint
3. mABE = 90
Definition of a Right Angle
4. mABE = mDBC
Vertical Angle Theorem
5. ABE CBD
SAS
10.
Statement
Reason
1. DB is the angle bisector of ADC, AD DC
Given
2. ADB BDC
Definition of an Angle Bisector
3. DB DB
Reflexive PoC
4. ABD CBD
SAS
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
Answer Key
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.8
ASA and AAS Triangle Congruence
Answers
1.
Yes, AAS, ABC FDE
2.
Yes, ASA, ABC IHG
3.
No, the triangles have congruent parts that would be SSA. This is not a congruence
theorem.
4.
DBC DBA because they are both right angles and created by perpendicular lines.
5.
CDB ADB
6.
from the Reflexive Property. We have enough to say that the triangles are
congruent
by ASA.
7.
Statement
1. DB AC ,
Reason
Given
DB is the angle bisector of CDA
2. DBC and ADB are right angles
Definition of perpendicular
3. DBC ADB
All right angles are
4. CDB ADB
Definition of an angle bisector
5. DB DB
Reflexive PoC
6. CDB ADB
ASA
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
10
Answer Key
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
8.
C A by CPCTC (corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent)
9.
L O and P N by the Alternate Interior Angles Theorem.
10.
LMP NMO by the Vertical Angles Theorem.
11.
There is more than one correct proof, this is one possible answer.
Statement
Reason
1. LP || NO , LP NO
Given
2. L O, P N
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
3. LMP OMN
ASA
12.
CPCTC
13.
Start with the proof from #11 and continue.
Statement
Reason
1. LP || NO , LP NO
Given
2. L O, P N
Alternate Interior Angles
3. LMP OMN
ASA
4. LM MO
CPCTC
5. M is the midpoint of PN .
Definition of a midpoint
14.
A N
15.
C M
16.
PM MN
17.
or
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
11
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.9
Answer Key
HL Triangle Congruence
Answers
1.
NM ZX
2.
FG RS or FE RQ
3.
VW DC and WX CB or VX DB
4.
Given/Definition of Perpendicular Lines
5.
AC CD
6.
ED AB
7.
HL Congruence
8.
No
9.
Yes, by SAS
10.
No
11.
Yes, by HL
12.
No
13.
No
14.
Yes, by SSS
15.
No
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
12
Answer Key
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.10
Isosceles Triangles
Answers
1.
x = 13
2.
y = 16
3.
x=1
4.
y=3
5.
x = 4, y = 11
6.
True
7.
False, only in an isosceles right triangle.
8.
False, only in the case of an equilateral triangle.
9.
True
10.
Statement
1. Isosceles CIS, with base angles C and
Reason
Given
S IO is the angle bisector of CIS
2. C S
Base Angles Theorem
3. CIO SIO
Definition of an Angle Bisector
4. IO IO
Reflexive PoC
5. CIO SIO
ASA
6. CO OS
CPCTC
7. IOC IOS
CPCTC
8. IOC and IOS are supplementary
Linear Pair Postulate
9. mIOC = mIOS = 90
Congruent Supplements Theorem
10. IO is the perpendicular bisector of CS
Definition of a bisector (Steps 6 and 9)
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
13
Answer Key
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
11.
Statement
1. Isosceles ICS with C and S, IO is the
Reason
Given
perpendicular bisector of CS
12.
2. C S
Base Angle Theorem
3. CO OS
Definition of a bisector
4. mIOC = mIOS = 90
Definition of a bisector
5. CIO SIO
ASA
6. CIO SIO
CPCTC
7. IO is the angle bisector of CIS
Definition of an Angle Bisector
Side #1 = 18, Side #2 = 18, Side #3 = 6
This is an isosceles triangle because Side #1 and Side #2 are equal.
13.
Side #1 = 17, Side #2 = 40, Side #3 = 9
No sides are equal, so this is a scalene triangle.
14.
Side #1 = 72, Side #2 = 234, Side #3 = 162
No sides are equal, so this is a scalene triangle.
15.
Side #1 = 104, Side #2 = 208, Side #3 = 104
This is an isosceles triangle because Side #1 and Side #3 are equal.
16.
Side #1 = 8, Side #2 = 65, Side #3 = 65
This is an isosceles triangle because Side #2 and Side #3 are equal.
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
14
Chapter 4 Triangles and Congruence
4.11
Answer Key
Equilateral Triangles
Answers
1.
x = 60
2.
y = 68
3.
x = 1.5
4.
y = 17
5.
z = 17
6.
n = 25
7.
x = 4 2
8.
x = 3, y = 2
9.
x = 2, y = 5
10.
z=4
11.
a = 1, 6
12.
m = 4, 15
13.
x = 4, 1
14.
x = 2 14
15.
x = 25, y = 19
CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts
15
You might also like
- Angle Relationships in CirclesDocument7 pagesAngle Relationships in CirclesPristine CharlesNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 PDFDocument715 pagesAlgebra 1 PDFEfraín Antonio Jovél100% (2)
- MS Answer Key - CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts (Revised)Document158 pagesMS Answer Key - CK-12 Basic Geometry Concepts (Revised)adar100% (1)
- Esolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroDocument30 pagesEsolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroNikunja PadhanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review Packet For BenchmarkDocument14 pagesFinal Exam Review Packet For BenchmarksdrrfsfesfNo ratings yet
- Course 3 Grade 8 Math Curriculum Map - Docx 1Document10 pagesCourse 3 Grade 8 Math Curriculum Map - Docx 1Junessa Sonio SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Polygon Interior/Exterior Angles: Geometry 5.1Document23 pagesPolygon Interior/Exterior Angles: Geometry 5.1Baskaran SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- Review Assignment - GeometryDocument7 pagesReview Assignment - Geometrycaspian43333No ratings yet
- Fraction FactsDocument2 pagesFraction FactsAshu Sri100% (1)
- Choice ADocument1 pageChoice Aapi-295097927No ratings yet
- Module 2 TrigonometryDocument23 pagesModule 2 TrigonometryScottie YanesNo ratings yet
- Intro To GeometryDocument73 pagesIntro To GeometryMr. Rhumer LanojanNo ratings yet
- Problem-Solving Strategy: Make A Model or A Drawing: ExampleDocument1 pageProblem-Solving Strategy: Make A Model or A Drawing: ExampleIan KrebsNo ratings yet
- Krishna's Question Bank Analytical GeometryDocument291 pagesKrishna's Question Bank Analytical Geometryijoky63% (8)
- Menu Math ProjectDocument2 pagesMenu Math Projectapi-3394620590% (1)
- 8$20 AreaDocument26 pages8$20 AreaBaskaran SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- Exercise: 1. in The Figure Below AD 4, AB 3 andDocument34 pagesExercise: 1. in The Figure Below AD 4, AB 3 andDina El GarhyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Power PointDocument70 pagesGeometry Power PointDavid Hernandez100% (1)
- PDE TextbookDocument310 pagesPDE Textbookrashid khanNo ratings yet
- 5 4Document17 pages5 4Seeta Anne0% (1)
- Revision Notes of Congruence 0f TrianglesDocument9 pagesRevision Notes of Congruence 0f Trianglesmeherr nandwani100% (1)
- Solid MensurationDocument32 pagesSolid MensurationEdgar Kenneth100% (1)
- Linear Equation 1Document25 pagesLinear Equation 1yaw197100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Document18 pagesChapter 1 Key Points: y F (X) + C y F (X) - C y F (X + C) y F (X - C)Angel Angel100% (1)
- Precal Exam Q1Document6 pagesPrecal Exam Q1CRISLY MAY JAICTIN100% (1)
- Botanical AffinityDocument10 pagesBotanical AffinityDanella RachmatikaNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Curriculum AlignmentDocument43 pagesAlgebra 2 Curriculum Alignmentapi-254765842No ratings yet
- Gases and Atmospheric ChemistryDocument10 pagesGases and Atmospheric ChemistryKatheeja MusatheekNo ratings yet
- Camarillo, John Mark B. Bsed Math 3 EDUC 108 Second Summative Test in Math 7 Third Quarter Name: - Date: - ScoreDocument5 pagesCamarillo, John Mark B. Bsed Math 3 EDUC 108 Second Summative Test in Math 7 Third Quarter Name: - Date: - ScorekhrizzaNo ratings yet
- Map Scales and Bearing PPT - 15.27.08Document20 pagesMap Scales and Bearing PPT - 15.27.08Kelvin Lau100% (1)
- Geometry CurriculumDocument5 pagesGeometry CurriculumWendy Millheiser MenardNo ratings yet
- CK 12 TrigonometryDocument552 pagesCK 12 TrigonometryjesusNo ratings yet
- q1w1 NewDocument60 pagesq1w1 NewMarie renden FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document22 pagesChapter 19Divya SrijuNo ratings yet
- ML Geometry 8-7 DilationsDocument8 pagesML Geometry 8-7 Dilationsashish663No ratings yet
- Joliet Junior College Geometry Compass Test Review Packet: Marilyn Berrill M.Ed. 1Document6 pagesJoliet Junior College Geometry Compass Test Review Packet: Marilyn Berrill M.Ed. 1Nandang Arif SaefulohNo ratings yet
- SPII - Grade 8 Mathematics - Curriculum REVISEDDocument50 pagesSPII - Grade 8 Mathematics - Curriculum REVISEDJay B Gayle0% (1)
- 2nd PRE BOARD FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING LICENSURE EXAMINATIONDocument7 pages2nd PRE BOARD FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING LICENSURE EXAMINATIONEngineer0% (1)
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsDocument15 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsLymenson BoongalingNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDFDocument16 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 01 Basic Geometry Concepts PDFValery Liz0% (1)
- Day 38 Right Triangle TrigDocument32 pagesDay 38 Right Triangle TrigArchessNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Thinking Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Thinking Lesson Planapi-284504897No ratings yet
- Unit Lessons On TransformationsDocument29 pagesUnit Lessons On TransformationsmagdammNo ratings yet
- Geometry Rules PDFDocument21 pagesGeometry Rules PDFVadlamudiMohanKumarNo ratings yet
- Radian Measure Arcs Sectors and SegmentsDocument5 pagesRadian Measure Arcs Sectors and SegmentsTitser LaarniNo ratings yet
- Q1 - W1-2 - Distance and Midpoint FormulaDocument5 pagesQ1 - W1-2 - Distance and Midpoint FormulaF-CABAGUING, HANNAH M.No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument13 pagesQuadratic EquationsRenDenverL.DequiñaIINo ratings yet
- Ratios Choice BoardDocument1 pageRatios Choice BoardKaitlyn AprilNo ratings yet
- Lines and Angles 2Document21 pagesLines and Angles 2Pratik LahotiNo ratings yet
- Batdangthuc DDTHDocument40 pagesBatdangthuc DDTHTuyếnĐặng100% (1)
- School of Mathematical Sciences MAT 3044 Discrete MathematicsDocument20 pagesSchool of Mathematical Sciences MAT 3044 Discrete MathematicsThalika RuchaiaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Graphs Practice: (Example 1)Document2 pagesQualitative Graphs Practice: (Example 1)MALAK SHEHADEHNo ratings yet
- 1.3: Determining The Equation of A Line: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pages1.3: Determining The Equation of A Line: Learning ObjectivesZenic TzyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 TRANSFORMATIONS FINAL PLANDocument27 pagesUnit 6 TRANSFORMATIONS FINAL PLANerdawati nurdinNo ratings yet
- High School Geometry Days 102-112Document49 pagesHigh School Geometry Days 102-112eclecticOTANo ratings yet
- Bearing and Scale DrawingDocument10 pagesBearing and Scale DrawingChar LesNo ratings yet
- The (Ultimate) Geometry Review SheetDocument16 pagesThe (Ultimate) Geometry Review SheetsenjicsNo ratings yet
- Systems of Equations - Substitution and EliminationDocument3 pagesSystems of Equations - Substitution and EliminationNick HershmanNo ratings yet
- 7th and 8th Grade Math Integer RulesDocument3 pages7th and 8th Grade Math Integer RulesjanetNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calc CH 4 Review Quiz 4.1-4.3Document5 pagesPre-Calc CH 4 Review Quiz 4.1-4.3aggieNo ratings yet
- Discovering Congruent Triangles ActivityDocument7 pagesDiscovering Congruent Triangles ActivityMd YusofNo ratings yet
- ME Math 10 Q2 0902 SGDocument20 pagesME Math 10 Q2 0902 SGIcia VillegasNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsDocument15 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 04 Basic Geometry ConceptsLymenson BoongalingNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Geometry ConceptsDocument20 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Geometry ConceptsPrimoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Geometry Concepts PDFDocument20 pagesAnswer Key - CK-12 Chapter 09 Geometry Concepts PDFJoseph LopezNo ratings yet
- 11 Mathematics Conic Section Test 02 Answer 7s22Document3 pages11 Mathematics Conic Section Test 02 Answer 7s22Ankit TiwariNo ratings yet
- 6432 D 621 A 4417Document3 pages6432 D 621 A 4417Retal I'mNo ratings yet
- CBSE Maths Guess Paper Based On CBSE Pattern Guess Paper For 2018 Class X by CBSEGuess Expert Mr. Agyat Gupta PDFDocument10 pagesCBSE Maths Guess Paper Based On CBSE Pattern Guess Paper For 2018 Class X by CBSEGuess Expert Mr. Agyat Gupta PDFprem guptaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Jan2021 Solution Class 11 Chapter 11 Conic Ex 4Document8 pagesNcert Jan2021 Solution Class 11 Chapter 11 Conic Ex 4Parimala deviNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing and Graphics - Basant Agrawal & C M Agrawal - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesEngineering Drawing and Graphics - Basant Agrawal & C M Agrawal - Multiple Choice QuestionsSnehashish MukerjiNo ratings yet
- Aquino Lab03Document12 pagesAquino Lab03Ai RahNo ratings yet
- IGO 2017problems and SolutionsDocument27 pagesIGO 2017problems and SolutionsAnonymous j6r5KRtrH2100% (1)
- Questions On ProjectionsDocument14 pagesQuestions On ProjectionsSeema SharmaNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Isometric Projection PDFDocument49 pagesSession 5 Isometric Projection PDFAshin VsNo ratings yet
- Triangles, Quadrilaterals and Polygons: Properties of AnglesDocument2 pagesTriangles, Quadrilaterals and Polygons: Properties of AnglesCleopatra sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Math IV Conic Sections2Document30 pagesMath IV Conic Sections2GabrielGitaNo ratings yet
- ArMath 1 - Presentation1Document24 pagesArMath 1 - Presentation1Jayson RamirezNo ratings yet
- Spatial VocabularyDocument1 pageSpatial VocabularySarah FawcettNo ratings yet
- TessellationsDocument10 pagesTessellationsJanet WangNo ratings yet
- International Competitions CentroAmerican 2019 30Document2 pagesInternational Competitions CentroAmerican 2019 30Wei FerrousNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lesson 5 Medians Altitudes and Midsegements in Triangles NotesDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Lesson 5 Medians Altitudes and Midsegements in Triangles Notesapi-264764674No ratings yet
- Revision Sheet - XII - 2Document2 pagesRevision Sheet - XII - 2Anubhab Dutta GuptaNo ratings yet
- Polygons Form 1Document38 pagesPolygons Form 1graciezaynNo ratings yet
- Ellipse AnswerDocument2 pagesEllipse AnswerXhyllieght VœuxNo ratings yet
- ShapesDocument11 pagesShapesanissafeniNo ratings yet
- DPP-2 (Determinant)Document4 pagesDPP-2 (Determinant)Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- Radius of Circular Base of Cylindrical Bowl CM: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 23Document23 pagesRadius of Circular Base of Cylindrical Bowl CM: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 23Shiv Ram YadavNo ratings yet
- Math III SolutionSet PDFDocument4 pagesMath III SolutionSet PDFqwertyNo ratings yet
- Math Is Fun Form 2 Chapter 6Document4 pagesMath Is Fun Form 2 Chapter 6Francis YongNo ratings yet