Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eczema and Dermatitis
Uploaded by
Dian BaldonadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eczema and Dermatitis
Uploaded by
Dian BaldonadoCopyright:
Available Formats
[ECZEMA/DERMATITIS] August 24, 2015
INTRODUCTION
Eczema
and
dermatitisused
interchangeably
Polymorphic inflammatory reaction
pattern of the epidermis and dermis
Various etiologies and wide range of
clinical findings
Acute eczema/dermatitis vs chronic
eczema/dermatitis
CONTACT DERMATITIS
Generic term for acute or chronic
inflammatory reactions to substances
that come in contact with the skin
Irritant contact dermatitis (ICD)caused by chemical irritants
Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD)caused by antigen that elicits a type
IV hypersensitivity reaction
IRRITANT CONTACT DERMATITIS
Caused by exposure of the skin to
chemical/physical agents capable of
irritating the skin, acute or chronic
Severe irritants cause toxic reactions
even after a short exposure
Mostly caused by chronic cumulative
exposure to one or more irritants
Hands- most commonly affected
EPIDEOMOLOGY
o Most
common
form
of
occupational
skin
disease
(80%)
o ICD need not be occupational
and not occur in anyone being
exposed to a substance irritant
or toxic to the skin
o OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE
Housekeeping
Medical
Veterinary services
Floral arranging
Horticulture
Food preparation and
catering
Painting
Mechanical engineering
Car maintenance
TWERK IT LIKE PABEBE
Construction; fishing
Hairdressing
Dental
Cleaning
Agriculture
Forestry
Printing
Metal work
ETIOLOGIC AGENTS: most common
irritants/Toxic agents
o Soaps, detergents, waterless
hand cleaners
o Acid and alkalis: hydrochloric
acid, cement, phosphorous,
ethylene oxide, phenol, metal
salts
o Industrial solvents: coal tar
solvents,
petroleum,
chlorinated
hydrocarbon,
alcohol
solvents,
ethylene
glycol ether, turpentine, ethyl
ether, acetone, carbon dioxide,
DMSO, dioxane, styrene
o Plants:
Euphorbiaceae
(spurges, crotons, poinsettias,
machneel tree). Racunculaceae
(buttercup), Cruciferae (black
mustard), Urticaceae (nettles),
Solanaceae (pepper,capsaicin),
Opuntia (priddy pear)
o Others: fiberglass, wool, rough
synthetic
clothing,
fireretardant fabrics, NCR paper
o LEAD TO CHEMICAL BURNS
AND
NECROSIS,
IF
CONCENTRATED
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
o Atopies with history of atopic
dermatitishighest
risk:
majority
of
workers
with
significant occupational ICD
are atopics
o Others
White skin
Climate (low humidity)
Mechanical irritation
Temperature (low)
Occlusion
PATHOGENESIS
Page 1
[ECZEMA/DERMATITIS] August 24, 2015
o
o
o
o
Chemical and physical irritants
cause cell damage if applied
for sufficient time and in
adequate concentration
Defense or repair capacity of
the skin is unable to maintain
normal skin integrity and
function
Penetration of chemical (s)
induces
an
inflammatory
response
Lesser irritants cause reaction
after prolonged exposure
Mechanisms in acute phase
of ICD
Direct cytotoxic damage
to keratinocytes
Mechanism of chronic phase
of ICD
Slow damage to cell
membranes, disrupting
the skin barrier leading
to protein denaturation
and cellular toxicity
ACUTE ICD
SYMPTOMS
o Subjective symptoms (burning,
stinging)
o Painful
sensations
within
seconds
after
exposure
(immediate-type stinging)
o Delayed-type stinging within 12 min, peaking at 5-10 min,
fading by 30 min
PHYSICAL EXAM
o SKIN FINDINGS
ACUTE
ICDsharply
demarcated
erythema
and superficial edema,
corresponding
to
application site of toxic
substance. Lesions dont
spread beyond the site
SEVERE
REACTIONvesicles
and
blisters
arise
within
erythematous
lesions
erosions & or necrosis
CONFIGURATIONSbizarre or linear
TWERK IT LIKE PABEBE
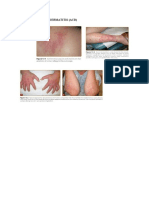
ICD of back, acute: croton oil: erythema and
edema on the back at sites in contact with
the irritant in 30 year old male. Croton oil
was mistakenly used as a remedy for back
pain and rubbed into the skin. Note spared
areas where contact with the irritants and
had not occurred.
ICD of hand, acute: kerosene. This airport
worker hand repeatedly spilled kerosene
over his hands and developed acute bullous
and extremely painful ICD 24h later
Acute ICD following the application of a
cream containing and nicotinic acid.
___________ ii has been prescribed for lower
back pain. The steaky pattern indicates an
outside ich, the eruption is characterized
by massive erythematous vesiculation and
blister formation and is confined to the site
exposed to the toxic agents.
Acute ICD on the hand due to an industrial
solvents. There is massive blistering on the
palm.
Acute ICD in resolution. This is a florist who
had contact with croton, poinsettias, and
buttercup so that it could not be determined
which of these was the eliciting plant. Note
the steaky pattern of the eruption on the
lefty hand.
ICD on the dorsum of the hand due to
soluble oils.
ICD due to oxalic acid in a Dressmaker.
LESIONS AND SYMPTOMS
o DISTRIBUTION
Isolated, localized to one
region or generalized,
depending on contact
with toxic agent
o DURATION
Days, weeks depending
on tissue damage
o CONSTITUTIONAL SYMPTOMS
Usually none
Widespread acute ICD
Page 2
[ECZEMA/DERMATITIS] August 24, 2015
Acute
illness
syndrome
including fever.
CHRONIC ICD
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
o SKIN FINDINGS
Dryness,
chapping,
erythema,
hyperkeratosis
and
scaling, fissures, and
crusting
Sharp
margination
ill-defined
borders,
lichenification
Irritant reaction ICD: also
vesicles, pustules, and
erosions
ICD of hand: subacute/chronic: Erythema,
edema, scaling, fissuring, crusting of the
palmar aspect of the hand and wrist: the
other hand had similar involvement. The
patient, a housewife, is atopic and has
ignored instructions to wear gloves during
work in the kitchen and to use lubricating
creams.
Subacute/chronic irritant contact dermatitis.
Erythema, edema, scaling, vesiculation in a
housewife with atopic dermatitis who had
ignored instructions to wear protective
gloves during work.
Chronic irritant contact dermatitis in a
housewife.
There
is
a
erythema,
hyperkeratosis,
scaling,
and
fissures
particularly on the fingertips in a patients
With an atopic background.
Early chronic irritant contact dermatitis in a
housewife. This has resulted from repeated
exposure to soaps and detergents. Note
glistening fingertips (pulpitis)
Chronic irritant contact dermatitis in a 50
year old housewife and farmer. Note edema,
thickening of the skin, lichenification, and
slight scaling.
TWERK IT LIKE PABEBE
Chronic irritants dermatitis with acute
exacerbation in a housewife. The patient
had used turpentine to clean her hands
after a paint job. Erythema, fissuring, and
scaling. Differential diagnosis is allergic
contact dermatitis and palmar psoriasis.
Patch tests to turpentine were negative.
Chronic irritant contact dermatitis in a
construction worker. There is massive
hyperkeratosis and fissuring
Chronic irritant contact dermatitis in a
mechanic who came into repeated contact
with chlorinated hydrocarbons
DISTRIBUTION
o Usually on hands, starts at
finger web spaces, spreads to
sides and dorsal hands and
palms
o Rare in other locations e.g., in
violinists on mandible or neck,
or on exposed sites as in
airborne ICD
DURATION
o Chronic: months to years
Chronic irritants contact dermatitis in a
brick layer probably due to the corrosive
effects of cement. Patch testing for
chromatase
was
negative.
Note
hyperkeratosis and fissuring. Differential
diagnosis is palmar psoriasis.
SYMPTOMS
o Stinging and itching, pain as
fissures develop OR none
except when infection occurs
o Chronic ICD (e.g., hand) can
become a severe occupational
and emotional problem
LABORATORY EXAMINATION
o HISTOPATHOLOGY
Acute ICD:
Epidermal
cell
necrosis,
neutrophils,
vrsiculation, and
necrosis
o Chronic ICD
Page 3
[ECZEMA/DERMATITIS] August 24, 2015
Acanthosis,
hyperkeratosis,
lymphocytotic
infiltrate
o PATCH TESTS
Negative in ICD unless
allergic
contact
dermatitis is also present
DIAGNOSIS
AND
DIFFERENTIAL
DIAGNOSIS
o DIAGNOSIS
History
and
clinical
examination
(lesions,
pattern, site)
DDX
ACD
Palmoplantar
psoriasis
(palms and soles)
Photoallergic
contact
dermatitis
(exposed
sites)
Difference Between Irritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis
IRRITANCT CD
ALLERGIC CD
SYMTOMS
Acute
Chronic
LESION
Acute
Chronic
MARGINATION AND Acute
SITE
EVOLUTION
Stinging, smarting Itching
or itching
pain
Itching pain
Itching/pain
Erythema
,
Papules, Vesicles,
Erosions,
Crust,
Scaling
Papules, plaques,
fissures,
Scaling,
Crust
Sharp,
strictly
confined to site of
exposure
Chronic
Ill-defined
Acute
Rapid (few hours
after exposure)
Chronic
Months to years of
repeated exposure
CAUSATIVE AGENT
TWERK IT LIKE PABEBE
Dependent
on
concentration
of
agent and state of
skin barrier, occurs
only
above
Erythema
,
Papules, Vesicles,
Erosions,
Crust,
Scaling
Papules, plaques,
Scaling, Crust
Sharp, confined to
site of exposure
but spreading in
the
periphery;usually
tiny papules; may
become
generalized
Ill-defines, spread
Not so rapid (1272h
after
exposure)
Months or longer;
exacerbation alter
every reexposure
Relatively
independent
of
amount
applied,
usually very low
concentrations
Page 4
[ECZEMA/DERMATITIS] August 24, 2015
threshold level
INCIDENCE
May
occur
practically
everyone
COURSE AND PROGNOSIS
o Healing within 2 wks of
removal
of
noxious
stimuli
o Chronic cases heals in 6 weeks
o Occupational ICD
1/3 of cases have
complete
remission
May
require
allocation
to
another job
o Atopics
With
worse
prognosis
o Chronic subcritical levels
or irritant
Some
workers
develop tolerance
or hardening
MANAGEMENT
o PREVENTION
Avoid irritant or
caustic chemicals
by
wearing
protective clothing
(i.e.
goggles,
shields, gloves)
If contact occurs,
wash with water
or
weak
neutralizing
solution
Barrier creams
In
occupation
al ICD that
persists in
spite of the
adherence
to
the
TWERK IT LIKE PABEBE
in
sufficient
but
depends
on
degree
of
sensitization
Occurs only in the
sentizied
above
measures,
change of
job may be
necessary.
TREATMENT
o ACUTE
Identify and remove
the etiologic agents
Wet dressing with
gauze
soaked
in
Burrows
solution
changed q 2-3h
Larger vesicles may
be drained but tops
shoud
not
be
removed
Topical
Class
I
glucocorticoids
preparations
In
severe
cases,
systemic
glucocorticoids
(Prednisone: 2 wk
course, 60 mg and
tampering by steps
of 10mg)
o SUBACUTE AND CHRONIC
Identify and remove
the etiologic agents
Potent
topical
glucocorticoid
preparation
and
adequate lubrication
As healing occurs,
continue lubricating
protective
cream
ointments
Chronic ICD of the
hands
Hardening
effect
by
Page 5
[ECZEMA/DERMATITIS] August 24, 2015
topical (soak
or
bath)PUVA therapy
Topical
antiinflammatory
agents
(pimecrolimus
and
tacrolimus)
still
being
evaluated
ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS
An eczematous dermatitis due to
re-exposure to a substance of
previously sensitized individuals
EPIDEMIOLOGY
o 7%
of
occupationally
related illness (US)
o Non-occupational ACD is
3X occupational ACD
o Age of onset
Uncommon in young
children and >70yrs
Occupation
One of the
most
important
causes
disability
industry
of
in
PATHOGENESIS
o SENSITIZATION
Strong sensitizer- in
a week or so
Weak
allergenmonths to years
o Ag taken up by Langerhans
cells
in
epidermis,
processed, migrates to the
draining LN
Ag with
MHC class II molecules
presented to T cells which
proliferate
sensitized T
cells enter circulation and
home to skin
o Langerhans cells with the
same
specific
Ag
sensitized T cells
(-)
cytokines, skin become
hypersensitive to contact
allergens,
will
react
wherever
the
specific
allergen is (+)
Top Ten Contact Allergens (North American Contact Dermatitis Group) and other
Common Contact Allergen
ALLERGENS
PRINCIPAL SOURCES OF CONTACT
Nickel sulfate
Metals, metals in clothing, jewelry,
catalyzing agents
Neomycin sulfate
Usually contained in creams, ointment
Balsam of Peru
Topical medication
Fragrance
Fragrance, cosmetics
Aerosol???
antiseptics
Sodium gold thiosulfate
Medication
Formaldehyde
Disinfectant, curing agents, plastics
Quarter????
Disinfectant
Cobalt chloride
Cement, galvanization, industrial oils,
cooling agents, eyeshades
Bacitracin
Ointment, powder
Methyldihydroxy?????
Preservative and cosmetics
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
o SIN LESIONS
ACUTE
TWERK IT LIKE PABEBE
Page 6
[ECZEMA/DERMATITIS] August 24, 2015
Well demarcated erythema and edema on top of which are
closely spaced, non-umbilicated vesicles and /or papules
In severe reactions, bullae, confluent erosions exuding serum
and crusts
SUBACUTE
Erythematous plaques with small, dry, scale, sometimes
associated with small, red, pointed or rounded, firm papules
CHRONIC
Lichenified plaques, scaling with small satellite papules,
excoriations, erythema and pigmentation
LABORATORY EXAMINATIONS
o DERMATOPATHOLOGY
ACUTE
Inflammation
with
intraepidermal
intercellular
edema
(spongiosis), lymphocytes and eosinophils in E. monocytes and
histiocyte infiltration in D
CHRONIC
Spongiosis, acanthosis, elongation of rete ridges, elongation
and broadening of papillae, hyperkeratosis and lymphocytic
infiltrate
o PATCH TEST
(-) IN ACD
Should be delayed until the dermatitis has subsuded for at least 2
weeks and should be performed on a previously involved site.
TWERK IT LIKE PABEBE
Page 7
You might also like
- Irritant Contact DermatitisDocument5 pagesIrritant Contact DermatitisJohn P M SinagaNo ratings yet
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis 2Document39 pagesIrritant Contact Dermatitis 2Imam SalehudinNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis & Eczema 2007Document83 pagesDermatitis & Eczema 2007La Ode Rinaldi100% (2)
- DermatitisDocument46 pagesDermatitisHadi AbdulhadiNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis DR Citra 260907Document56 pagesDermatitis DR Citra 260907Adam AriwibawaNo ratings yet
- DermatitisDocument46 pagesDermatitisAaditya IndoliaNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis: Key PointsDocument8 pagesContact Dermatitis: Key Pointssaimon reyNo ratings yet
- Case Report Dermatitis ContactDocument10 pagesCase Report Dermatitis ContactMuhammad Aktora Tarigan100% (1)
- Contact DermatitisDocument31 pagesContact DermatitisBrendaNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis - Eczema: Eko Krisnarto RSU Kota SemarangDocument136 pagesDermatitis - Eczema: Eko Krisnarto RSU Kota SemarangfachruNo ratings yet
- DermatitisDocument44 pagesDermatitisAyuMardewi50% (2)
- Allergic and Irritant Contact DermatitisDocument8 pagesAllergic and Irritant Contact DermatitisFenni OktoberryNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Dermatitis: Dr. Kristo A. Nababan, SPKKDocument47 pagesPenyakit Dermatitis: Dr. Kristo A. Nababan, SPKKDaniel Suarez ParapatNo ratings yet
- Kostner 2017Document12 pagesKostner 2017Daisy HamdaliNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis and Eczema: Ailing Zou (邹爱玲) 2021.10.18Document31 pagesDermatitis and Eczema: Ailing Zou (邹爱玲) 2021.10.18AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis: Allergic and IrritantDocument9 pagesContact Dermatitis: Allergic and IrritantatikaNo ratings yet
- ECZEMADocument88 pagesECZEMASajin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Occupational Dermatoses2Document3 pagesOccupational Dermatoses2Alaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Eczema and DermatitisDocument47 pagesEczema and DermatitisDeborah ChemutaiNo ratings yet
- Contact Dermatitis Contact Dermatitis Is A Term For A Skin Reaction (Dermatitis) Resulting From Exposure To AllergensDocument4 pagesContact Dermatitis Contact Dermatitis Is A Term For A Skin Reaction (Dermatitis) Resulting From Exposure To AllergensAlbert Simon GalizaNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis and EczemaDocument67 pagesDermatitis and EczemaIts AnythingNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis & Urticaria: Department of Dermato Venereology Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityDocument34 pagesDermatitis & Urticaria: Department of Dermato Venereology Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityadystiNo ratings yet
- Identifying The Cause of Contact DermatitisDocument6 pagesIdentifying The Cause of Contact DermatitiswadejackNo ratings yet
- Eczema, Psoriasis, Cutaneous Infections, Acne, and Other Common Skin DisordersDocument6 pagesEczema, Psoriasis, Cutaneous Infections, Acne, and Other Common Skin DisordersElrey InocianNo ratings yet
- Dematitis and EczemaDocument22 pagesDematitis and Eczematassiatavares.workNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR. Dr. Benny E. Wiryadi, SP - KK (K)Document30 pagesProf. DR. Dr. Benny E. Wiryadi, SP - KK (K)Margaretta WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Eczematous EruptionsDocument27 pagesEczematous EruptionsSmartcool SoNo ratings yet
- EczemaDocument87 pagesEczemaHrishikesh NachinolkarNo ratings yet
- Bercak MerahDocument16 pagesBercak MerahFary SatriadiNo ratings yet
- DddsDocument50 pagesDddsOsama AlhaseNo ratings yet
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Practice EssentialsDocument4 pagesIrritant Contact Dermatitis: Practice EssentialsHiedajatNo ratings yet
- Calixtro, LJ Contact Dermatitis NarrativeDocument2 pagesCalixtro, LJ Contact Dermatitis NarrativeKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Dermatitisslide 200715172028Document45 pagesDermatitisslide 200715172028enam professorNo ratings yet
- Eczema & Psoriasis: Dr. MburuDocument69 pagesEczema & Psoriasis: Dr. MburuKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- Ns. M. Nurman, M. KepDocument30 pagesNs. M. Nurman, M. KepSabaniaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Burns - 1Document32 pagesPathophysiology of Burns - 1Y. Beatrice Abigail50% (2)
- Allergic Skin Conditions - Causes, Clinical Features and TreatmentDocument4 pagesAllergic Skin Conditions - Causes, Clinical Features and TreatmentAnshuman PadheeNo ratings yet
- Allergic Contact DermatitisDocument6 pagesAllergic Contact DermatitisCrysnaNo ratings yet
- Referensi 7Document9 pagesReferensi 7iffaNo ratings yet
- ECZEMADocument47 pagesECZEMASalsabila Al-Basheer100% (1)
- Patho-Physiology Pharm Lecture 11Document15 pagesPatho-Physiology Pharm Lecture 11Manar AlzobiNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis: K. Puviyarasi Dept of MSN MNCDocument26 pagesDermatitis: K. Puviyarasi Dept of MSN MNCPuviyarasi100% (2)
- Contact Dermatitis. The Major Occupational Allergic Skin DiseasesDocument66 pagesContact Dermatitis. The Major Occupational Allergic Skin DiseasesJulius HabibiNo ratings yet
- The 3rd Year Derma Missing TableDocument6 pagesThe 3rd Year Derma Missing TableEmil GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Topical Corticosteroid AbuseDocument34 pagesTopical Corticosteroid AbuseDr Daulat Ram DhakedNo ratings yet
- Contact DermatitisDocument2 pagesContact DermatitisMIR SARTAJNo ratings yet
- Erythroderma: 3. Erythema Chronicum Migrans (ECM)Document4 pagesErythroderma: 3. Erythema Chronicum Migrans (ECM)iisisiisNo ratings yet
- Allergic Contact DermatitisDocument11 pagesAllergic Contact DermatitisSf AkhadiyatiNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Eczema: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument19 pagesDermatology Eczema: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAiman Tymer100% (1)
- Gaspari Dermatitis EczemaDocument32 pagesGaspari Dermatitis EczemaAzizNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 Skin DisorderDocument37 pagesWEEK 6 Skin DisorderRaghad NaifNo ratings yet
- 002 - Additional MaterialDocument30 pages002 - Additional MaterialLucas Victor AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Dermatitides, Eczema, NeurodermatoseDocument20 pagesDermatitides, Eczema, NeurodermatoseElephant ksmileNo ratings yet
- Lection 3 EczemaDocument37 pagesLection 3 EczemaAtawna AtefNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading: Preceptor: Dr. Vitalis, SP - KK Created By: Devina - 07120110064Document14 pagesJournal Reading: Preceptor: Dr. Vitalis, SP - KK Created By: Devina - 07120110064Devina TandiasNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis: Maria Soleil Bernadette M. MalonzoDocument29 pagesDermatitis: Maria Soleil Bernadette M. MalonzoMacey MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Section 1. Disorders of Sebaceous and Apocrine Glands: EpidemiologyDocument7 pagesSection 1. Disorders of Sebaceous and Apocrine Glands: EpidemiologyPutri Fitriana SariNo ratings yet
- Acute Inflammatory DermatosesDocument29 pagesAcute Inflammatory DermatosesHaniya KhanNo ratings yet
- Complete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisFrom EverandComplete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Themodynamic Functions From EMF MeasurementsDocument5 pagesExperiment 3 - Themodynamic Functions From EMF MeasurementsjojoNo ratings yet
- DSU D InstallDocument2 pagesDSU D InstallstarykNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid PDFDocument23 pagesDrilling Fluid PDFcristinelbNo ratings yet
- APECCalculations QADocument275 pagesAPECCalculations QAshasha111 shasha1110% (1)
- Welding SymbolsDocument53 pagesWelding SymbolsLâm Thanh100% (9)
- Chapter 0211 With AnswersDocument17 pagesChapter 0211 With Answersjosephjoy123050% (1)
- 13 Ionic Equilibria Notes PDFDocument37 pages13 Ionic Equilibria Notes PDFUchiha YogesNo ratings yet
- Kestopour PL 15Document1 pageKestopour PL 15Mantas ButrimaviciusNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced CFRCDocument22 pagesCarbon Fiber Reinforced CFRCVince Carlo C GarciaNo ratings yet
- Jan 23 WCH12 SolvedDocument28 pagesJan 23 WCH12 Solvedthe dsNo ratings yet
- Home Made Soap: Using Glitz Caustic SodaDocument1 pageHome Made Soap: Using Glitz Caustic Sodaabeiasa_biomedNo ratings yet
- ML For Dummies TotalDocument167 pagesML For Dummies TotalNataša ZekaNo ratings yet
- Alccofine 1108SRDocument2 pagesAlccofine 1108SRLaxmana PrasadNo ratings yet
- Dowtherm sr-1Document16 pagesDowtherm sr-1Rafael LealNo ratings yet
- Beets Take Home AssignmentDocument5 pagesBeets Take Home Assignmentapi-487667605No ratings yet
- (Martin Moeller, Krzysztof Matyjaszewski) PolymerDocument1,052 pages(Martin Moeller, Krzysztof Matyjaszewski) PolymerGrayNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi KarnitinDocument61 pagesFisiologi Karnitinmusta QiblatNo ratings yet
- Pre-Sanded Cemwash: PRE-SANDED CEMWASH Is An Economical Attractive Decorative Portland Cement-Based Paint Manufactured byDocument1 pagePre-Sanded Cemwash: PRE-SANDED CEMWASH Is An Economical Attractive Decorative Portland Cement-Based Paint Manufactured byTonderai RusereNo ratings yet
- Linnhoff Presentation Cold & Hot Recycling - 2009Document27 pagesLinnhoff Presentation Cold & Hot Recycling - 2009willypraviantoNo ratings yet
- Building Repairs and MaintenanceDocument167 pagesBuilding Repairs and MaintenanceAnshul Soni100% (1)
- 5070 s03 QP 4Document16 pages5070 s03 QP 4karan79No ratings yet
- Carregadeira LiebherrDocument17 pagesCarregadeira Liebherrsanches pita100% (5)
- Trends and Evolution of Thread Lifting - PDO Vs PLLA Vs PCL (Type)Document6 pagesTrends and Evolution of Thread Lifting - PDO Vs PLLA Vs PCL (Type)Anonymous LnWIBo1G100% (1)
- Rheology and Hydraulics: Rheology Is The Science of Deformation and Flow of MatterDocument36 pagesRheology and Hydraulics: Rheology Is The Science of Deformation and Flow of Matterhassan haddadiNo ratings yet
- CorrosionDocument9 pagesCorrosionhesampirNo ratings yet
- Bioinspiration and BiomimeticsDocument7 pagesBioinspiration and BiomimeticsAyush 100niNo ratings yet
- Workbook - AcidsDocument132 pagesWorkbook - AcidsAgustina Itin100% (1)
- Lesson Plan ME-220 Engineering MaterialsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan ME-220 Engineering MaterialsHajiasifAliNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology HandoutDocument21 pagesConcrete Technology HandoutsainathNo ratings yet
- The Human Genome ProjectDocument19 pagesThe Human Genome ProjectSuraj Bhattarai100% (3)