Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Assessment Paper: Instructions
Uploaded by
RAZEN PARASOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Assessment Paper: Instructions
Uploaded by
RAZEN PARASCopyright:
Available Formats
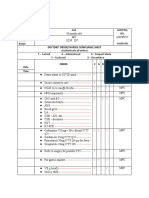
Drug Assessment Paper
Name:
Results
Band:
Calculations
Area Applied For:
Drug Problem
Solving
Instructions
This test has been designed to assess your drug knowledge and ability to calculate simple
drug calculations.
You are allocated 40 minutes to complete the entire paper. You may not leave the room if you
complete the paper before this time. Calculators are allowed however you are not permitted
to use your mobile phone.
This paper is in 2 sections the first section is some drug calculations and the second section
assesses your ability to problem solve.
Please clearly identify your answer in the box provided and show your workings out in the
space provided.
Read the questions carefully, think about your answer, would you do this on the
ward?
Formulae
Converting Metric Units
1
1
1
1
kilogram (kg)
gram (g)
milligram (mg)
litre (L)
=
=
=
=
1000
1000
1000
1000
Dosage of Oral Medicines
grams (g)
milligrams (mgs)
micrograms (mcg)
millilitres (mls)
Volume required = strength required x
volume of stock solution
Stock solution
OR
What you want x what its
in
Calculating drip rates
Drop rate/minute = Volume to be infused x
drops per ml
Hours of infusion time x
60 (minutes in hour)
The giving set delivers 20 drops per ml.
Administer 1000 ml 5% Dextrose over 8 hours
whilst blood sugar < (less than) 10 mmol
What youve got
Sliding Scale
50 units Actrapid in 50 ml 0.9% Sodium
Chloride (1 unit of Actrapid per ml)
Blood Sugar (mmol)
Infusion rate
Less than 3.0
3.1 4.9
5.0 6.9
7.0 8.9
9.0 10.9
11.0 13.9
14.0 17.9
18.0 and above
Stop and call Dr.
1 ml per hr
2 ml per hr
3 ml per hr
4 ml per hr
6 ml per hr
8 ml per hr
8ml per hour and call
Dr.
Administer 1000 ml 0.9% Sodium Chloride
over 8 hours
whilst blood sugar > (greater than) 10 mmol
Drug Calculations
Question
1.
Convert 1.75 mgs into micrograms
2.
Convert 480mls into litres
3.
Patient B is prescribed 9 mgs of
Diazepam. Diazepam comes as 2mg,
5mg and 10mg tablets. Identify the
correct combination using the least
amount of tablets to ensure the
correct dose is given.
4.
Patient C has been prescribed 1L of 0.9%
sodium chloride IV to be administered
over 12 hours. However, 2 hours after
the infusion was commenced, the patient
pulls out the cannula. How much fluid
has been infused?
5.
Patient A is on 100mgs of Flucloxacillin
oral suspension QDS. The medication is
available as 125 mgs/5mls suspension
only. How many mls will a patient take in
a 24 hour period?
6.
What are the drops per minute for a
prescription of 1L of 5% Dextrose if the
infusion is to be run over 10 hours?
7.
A patient has been prescribed 100mgs of
methylprednisolone IV. The vial contains
125mgs/ml, how much
methylprednisiolone will you give?
8.
A dose of Frusemide 250mgs IV has been
prescribed. The maximum rate is not
more than 4mgs/minute, how long will it
take to give?
9.
Please
carefully
examine
the
prescriptions and sliding scale on the
formula page and answer the following
questions :What rate would the infusion need to be
set at if the patients blood sugar was
12.5 mmols?
Which IV Fluid would need to be running?
9a
.
9b
.
10
.
Answer
Mark
Stock Heparin has strength of 5000 units
per ml. What volume must be drawn up
to give 8400 units?
Drug Problem Solving
1.
Question
In the UK it is illegal for a registered nurse to administer drugs
which have not been prescribed. What would you do if a Doctor
asked you to do this
Answer
Mark
a) Give the drug to the patient it.
b) inform the Doctor that he must first write the prescription
before you administer it
c) give the drug after making the Doctor promise he will not
forget to come to the ward and documenting everything in the
patients notes
2.
You are on a night shift. The other Registered Nurse working with
you is off the ward on her break. A patient requires Morphine for
her extreme pain. Do you:a) give the Morphine and leave the chart and Controlled Drugs
(CD) book out as a reminder for the other nurse to sign when
she returns
b) Prepare the drug yourself but get a Health Care Support
Worker to go with you whilst you administer it
c) Tell the patient they will have to wait for your colleagues to
return
d) Bleep the Site Manager / Practitioner and request they come
to the ward to prepare and administer a CD with you
3.
A patient has been prescribed Trimethroprim 200mg QDS for an
uncomplicated urine infection. You suspect the frequency of
administration may be incorrect. However the nurse in charge
tells you that she thinks the prescription is correct and you
should give it anyway to prevent any deterioration in the
patients condition. Do you :a) With hold the drug and bleep the pharmacist
b) With hold the drug, look it up in the British National Formulary
(BNF) and contact the prescriber.
c) do as the nurse in charge says ensuring you have
documented your concerns clearly in the patients notes and
asked the prescriber to check it next time he is on the ward
4.
You are doing the 6pm drug round and you have given Mrs Smith
100mgs of Tramadol, you get to the next lady Mrs Brown and
discover that you have given Mrs Smith Mrs Browns Tramadol.
What are you going to do?
a) Carry on with the rest of the drug round but keep a closer eye
on Mrs Smith for the rest of the shift.
b) Tell the nurse in charge who tells you to document in the
medical notes but not to worry.
c) Escalate to the General Manager on call for the evening and
the patients consultant.
d) Check the patient, inform the doctors on call and nurse in
charge, complete an adverse incident form and inform patient
and next of kin.
5.
Question
Mr Jones has been admitted to the ward and when you go
through his medical notes to complete his admission you identify
he is allergic to Codeine. You note on his drug chart that he was
given 15mgs of Dihydrocodeine at 08.00, he is now due another
15 mgs at 12.00. What are you going to do?
Answer
Mark
a) Give the drug as he displayed no sign of allergy earlier and
see what happens.
b) Omit the drug, document reasons for not giving and contact
the prescriber.
c) Give him an alternative analgesic now and discuss your
actions with the doctor later.
6.
Identify the 6 rights or important checks of Drug administration?
7.
In the UK controlled drugs have to be counted daily, while
counting these drugs it has been discovered the count is
incorrect what actions will you take?
a) Lock the drugs away and leave a note for sister on her return
tomorrow.
b) Immediately alert the on call pharmacist, ring the police and
complete an incident form.
c) Check the cupboard thoroughly and all packets inside the
cupboard, double check the CD record book to ensure the
entries are correct, check the ordering and delivery book and
if the count remains incorrect alert the Night Practitioner,
complete incident form and await further instruction.
8.
A patient is due to have Frusemide 80mgs and Metoprolol
25mgs.The most recent observations indicate the BP was
80/60mm/Hg. What will you do?
a) Give the medication and recheck the BP in one hour.
b) Omit tablets, document reasons and inform doctors.
c) Give the tablets and put the patient on a 30 tilt and push oral
fluids.
9.
A patient has been prescribed Fentanyl patch 12mcgs every
72hrs. In the CD cupboard you find Fentanyl patch 25mcgs. The
next dose is now due, what action will you take?
a) Cut the patch in approximately half and place on the patient
b) Order it in the pharmacy book and tell the patient they will
have to wait for it to come from pharmacy in a few hours.
c) Order it in the CD book, call the ward pharmacist and go to
pharmacy to collect as soon as possible.
You might also like
- VTE Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesVTE Risk AssessmentpriyopanjiNo ratings yet
- Sedation and Analgesia in The Intubated Patient (Adult Critical Care)Document12 pagesSedation and Analgesia in The Intubated Patient (Adult Critical Care)Beatriz Maria Espinosa HernandezNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Calculating Tablet Dosages: Dosage CalculationsDocument4 pagesCalculating Tablet Dosages: Dosage CalculationsNu'man 'Zeus' AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 34, Engaging Accountable Care Organizations in Urgent Care CentersFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 34, Engaging Accountable Care Organizations in Urgent Care CentersNo ratings yet
- Error Reduction Strategies For Look Alike Sound Alike Medications PDFDocument1 pageError Reduction Strategies For Look Alike Sound Alike Medications PDFFeby Kusuma DewiNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Environmental Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandHealthcare Environmental Services A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- MdsMgtModule Calculations FinalDocument35 pagesMdsMgtModule Calculations FinalChrissieNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration PolicyDocument188 pagesMedication Administration Policyليراث ليNo ratings yet
- Methods of CalculationDocument14 pagesMethods of CalculationMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Fundamental's FinalDocument21 pagesFundamental's FinalShaunn Diesto Caberto100% (1)
- Drug Calculation ReviewDocument124 pagesDrug Calculation Reviewhgfree41392100% (1)
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS I: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Fresenius 2008T Dialysis System - User's Troubleshooting ManualDocument20 pagesFresenius 2008T Dialysis System - User's Troubleshooting ManualCesar AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Scenario 12 - Ethics Committee Serves As GuardianDocument5 pagesScenario 12 - Ethics Committee Serves As GuardianVictoria100% (1)
- ISMP AssessmentDocument56 pagesISMP AssessmentKamalakar KaramchetiNo ratings yet
- AO 43 Series of 1999 PDFDocument92 pagesAO 43 Series of 1999 PDFJoslin Roz GalileaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Contraindicated in PregnancyDocument2 pagesDrugs Contraindicated in PregnancyErum IftikharNo ratings yet
- Medicaid Claims Examiner: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandMedicaid Claims Examiner: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Navigating Long-Term Care - A Practical Approach for NursesFrom EverandNavigating Long-Term Care - A Practical Approach for NursesNo ratings yet
- Narcotic Controlled and Semi-Controlled Medications ManagementDocument11 pagesNarcotic Controlled and Semi-Controlled Medications Managementshajahanputhusseri100% (1)
- 2008T Hemodialysis Machine Operator's ManualDocument285 pages2008T Hemodialysis Machine Operator's ManualKarim AmerNo ratings yet
- Revised FMLA Forms Feb. 2013Document24 pagesRevised FMLA Forms Feb. 2013Molly DiBiancaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingFrom EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionDocument13 pagesChapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionadenNo ratings yet
- Intravenous MonitorDocument39 pagesIntravenous MonitorGeogrina WatsonNo ratings yet
- TransitionDocument13 pagesTransitionDonna NituraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills ChecklistDocument6 pagesNursing Skills Checklistapi-456149894No ratings yet
- Draft: Jurisprudence Learning Module & ExaminationDocument45 pagesDraft: Jurisprudence Learning Module & ExaminationDeepanshi RajputNo ratings yet
- RN Job Description PDFDocument1 pageRN Job Description PDFvhon100% (1)
- Caremark Drug ListDocument10 pagesCaremark Drug ListRahul DocNo ratings yet
- Calculations For NursingDocument9 pagesCalculations For NursingChris MitrevskiNo ratings yet
- Admistration of Controlled Narcotic and Controlled Non-Narcotic MedicationsDocument37 pagesAdmistration of Controlled Narcotic and Controlled Non-Narcotic MedicationsKrezielDulosEscobarNo ratings yet
- Iv Drug Preperation: Gina S. Cuenca, RN, MNDocument49 pagesIv Drug Preperation: Gina S. Cuenca, RN, MNJainah Rose Ferrer GubacNo ratings yet
- Formula of IVF Calculation and Drug CalculationDocument1 pageFormula of IVF Calculation and Drug Calculationjessa hortelanoNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument36 pagesAntidotesMohamed Haggag100% (1)
- LWW Nursing Catalogue 2009Document80 pagesLWW Nursing Catalogue 2009Lippincott Williams and Wilkins- Europe0% (1)
- Lincoln Memorial University: Caylor School of NursingDocument37 pagesLincoln Memorial University: Caylor School of NursingMbi1965100% (2)
- NURSING THE CHILDBEARING FAMILY: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING THE CHILDBEARING FAMILY: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs and Early Warning ScoresDocument47 pagesVital Signs and Early Warning Scoresdr_nadheem100% (1)
- 18 WB - CC - Practice - Adminstration - and - Development - Pharmacoeconomics - and - Safe - Medication - UseDocument36 pages18 WB - CC - Practice - Adminstration - and - Development - Pharmacoeconomics - and - Safe - Medication - UsekushishaNo ratings yet
- High Alert MedicationsDocument1 pageHigh Alert MedicationspucukjayaNo ratings yet
- TXTDocument356 pagesTXTJec AmracNo ratings yet
- Homework Adam LabDocument6 pagesHomework Adam LabaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Chapter 1Document2 pagesMed Surg Chapter 1Judy072100% (1)
- Avant US-RN Recruitment Program: Apply NowDocument11 pagesAvant US-RN Recruitment Program: Apply Nowrajat mehrotraNo ratings yet
- Poct John Hopkins NovaDocument34 pagesPoct John Hopkins NovaRossy MeilaniNo ratings yet
- Thinking Like A NurseDocument3 pagesThinking Like A Nurseapi-519359726No ratings yet
- Arthroplasty CareDocument3 pagesArthroplasty CareEmjhay Swakida100% (1)
- Hospitalist Program Toolkit: A Comprehensive Guide to Implementation of Successful Hospitalist ProgramsFrom EverandHospitalist Program Toolkit: A Comprehensive Guide to Implementation of Successful Hospitalist ProgramsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Syllabus Bio 408 Sum 2017Document6 pagesPharmacology Syllabus Bio 408 Sum 2017Grafika DiahNo ratings yet
- Pharma 1Document42 pagesPharma 1Carl Josef C. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dosage CalculationsDocument46 pagesDosage CalculationsjisooNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Orientation ResourcesDocument111 pagesPerioperative Orientation ResourcesRAZEN PARAS100% (3)
- IELTS For Academic Purposes - Teacher Book PDFDocument98 pagesIELTS For Academic Purposes - Teacher Book PDFCin Drizzle0% (1)
- Start Here: Study Plan For The IELTS Speaking ModuleDocument2 pagesStart Here: Study Plan For The IELTS Speaking ModuleRAZEN PARASNo ratings yet
- Drug CalculationDocument1 pageDrug CalculationRAZEN PARASNo ratings yet
- Training Plan For NursesDocument7 pagesTraining Plan For NursesRAZEN PARAS100% (1)
- Pharmacy Internship Manual - New-1Document14 pagesPharmacy Internship Manual - New-1Rajeswari enterpriseNo ratings yet
- Rini Hamsidi, Adryan Fristiohady, Nasyrah Musabar: Majalah Farmasi, Sains, Dan Kesehatan ISSN 2442-9791Document4 pagesRini Hamsidi, Adryan Fristiohady, Nasyrah Musabar: Majalah Farmasi, Sains, Dan Kesehatan ISSN 2442-9791Puskesmas SambongNo ratings yet
- ULAT KAMBAL (Pishach Karpas) - Abroma Augusta: A Study On Its Pharmacological Actions From An Ayurvedic PerspectiveDocument7 pagesULAT KAMBAL (Pishach Karpas) - Abroma Augusta: A Study On Its Pharmacological Actions From An Ayurvedic PerspectiveIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Jbptitbche GDL Publ 2003 Yasuhikohi 1 AAA221282 4Document11 pagesJbptitbche GDL Publ 2003 Yasuhikohi 1 AAA221282 4Anonymous cgKtuWzNo ratings yet
- World Pharma Today Magazine - April 2017 IssueDocument56 pagesWorld Pharma Today Magazine - April 2017 IssueWorld Pharma Today100% (1)
- Retriksi Obat KronisDocument57 pagesRetriksi Obat Kronisalfa dholiNo ratings yet
- Pelletization PDFDocument6 pagesPelletization PDFASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- Dosage Lec - Unit 2 Drug DiscoveryDocument8 pagesDosage Lec - Unit 2 Drug DiscoveryJohn Lorenz BordadorNo ratings yet
- Appl Sartobind Virus Purification Removal SL-4038-e06012Document4 pagesAppl Sartobind Virus Purification Removal SL-4038-e06012Yaser WazirNo ratings yet
- Controlled Substances - Alphabetical OrderDocument14 pagesControlled Substances - Alphabetical Orderjacinc2No ratings yet
- Regulation of SterlizationDocument43 pagesRegulation of SterlizationKapil SharmaNo ratings yet
- No Natural Home: Placing The Promise of BiopharmingDocument333 pagesNo Natural Home: Placing The Promise of BiopharmingrjmilneNo ratings yet
- Daftar Lasa Ham Obat Resiko JatuhDocument4 pagesDaftar Lasa Ham Obat Resiko JatuhAbu Hisyam Al KhendaryNo ratings yet
- AmpicillinsulbactamupdateDocument14 pagesAmpicillinsulbactamupdateOrlando EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Price V UnilabDocument2 pagesPrice V UnilabMarioneMaeThiamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Law Name - 2 Year Pharmacy TechnicianDocument9 pagesPharmacy Law Name - 2 Year Pharmacy TechnicianridaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Monitoring HandbookDocument38 pagesEnvironmental Monitoring HandbookKraken Ur100% (3)
- Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesJob DescriptionswethashakiNo ratings yet
- Dosage - Chapter 14Document57 pagesDosage - Chapter 14Kim Manlangit100% (1)
- 150 Years of PharmacovigilanceDocument2 pages150 Years of PharmacovigilanceCarlos José Lacava Fernández100% (1)
- LECTURE 2 - Organon 2 The Highest Ideal of A Cure - LECTURES ON HOMOEOPATH1Document7 pagesLECTURE 2 - Organon 2 The Highest Ideal of A Cure - LECTURES ON HOMOEOPATH1madhukarNo ratings yet
- M.pharm. Pharmaceutics SyllabusDocument8 pagesM.pharm. Pharmaceutics SyllabusMohan VarmaNo ratings yet
- The Wolbam Destiny 6Document12 pagesThe Wolbam Destiny 6Michael WolfsonNo ratings yet
- Gentral Rate Contract: For Supply of Drugs DressingsDocument73 pagesGentral Rate Contract: For Supply of Drugs Dressingschetan_nirmaNo ratings yet
- Herbal Mixtures in The Traditional Medicine of Eastern Cuba - Hernandez and Volpato 2004-LibreDocument24 pagesHerbal Mixtures in The Traditional Medicine of Eastern Cuba - Hernandez and Volpato 2004-LibreJimmy Horn100% (1)
- Sustained ReleaseDocument9 pagesSustained ReleaseFenny rahmadhanyNo ratings yet
- WHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter No 3 2023 1693146010Document18 pagesWHO Pharmaceuticals Newsletter No 3 2023 1693146010vivek rakhaNo ratings yet
- Apply Crush Drop Gargle Insert Place Rub Shake Swallow Take UseDocument2 pagesApply Crush Drop Gargle Insert Place Rub Shake Swallow Take UseReka KutasiNo ratings yet
- Managing Otitis ExternaDocument34 pagesManaging Otitis ExternaramaNo ratings yet
- Doctor's Order Day 1: Doctors' Order/ Nurses Compliance SheetDocument2 pagesDoctor's Order Day 1: Doctors' Order/ Nurses Compliance SheetMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet