Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Video Worksheet Electrostatics and Electricity
Uploaded by
api-322906128Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Video Worksheet Electrostatics and Electricity
Uploaded by
api-322906128Copyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Electricity:
Introduction to Electricity:
During the Program
1.
What was the first example of electricity seen by the earliest humans?
2.
What is amber?
a.
What did Thales discover he could pick up with rubbed amber?
b.
What does the word electricity and electron mean?
3.
What two materials were rubbed together in the demonstration to show static electricity?
4.
What are all substances around us made up of?
a.
The positively charged particles in the atoms are called?
b.
The negatively charged particles in the atom are called?
5.
When the number of protons and electrons are NOT equal, the object becomes?
6.
Circle the correct answer. Opposite charges attract repel
a.
Give two examples of where you can become charged.
b.
Circle the correct answer. Opposite charges attract, but the same charges attract repel
Introduction to Electricity:
c.
When strands of hair stand on end, do the strands have the same or opposite charges?
7.
What is current electricity?
8.
What type of material are electrical wires made of?
9.
The particles that move in a wire when an electric current is flowing are called?
10. What do we call the completed pathway through which electricity flows?
11. What provides the energy needed to push the electrons along a wire?
12. An electric circuit in which two globes are in the same path is called a ___________ circuit.
13. A circuit in which two globes are in their own path is called a ___________circuit.
14. The word used to describe how well a material can conduct electricity is?
15. In each case below, circle the wire that has the greatest resistance.
a.
A long piece of wire or a shorter piece of the same wire?
b.
A thin piece of wire or a thicker piece of the same wire?
16. a.
What do we call material that is not good at carrying electricity?
17. Give two examples of insulating materials.
Introduction to Electricity:
18. Which situations below are safe in a lightning storm? Write safe or not safe for each.
a.
Inside an aeroplane.
b.
Inside a stationary car.
c.
In a sailing boat.
d.
Under a tree.
e.
Inside a metal shed with timber posts.
19. The unit of electricity, measuring the rate at which electrons move around the wire, is called?
20. What do we call the force, provided by batteries, with which the electrons are pushed around the wire?
21. What are the two sources of electricity mentioned?
22. What is a fossil fuel commonly used to generate electricity?
23. List three renewable sources of energy mentioned.
24. How many more times efficient is a compact fluorescent globe compared to a traditional incandescent one?
You might also like
- Put A Spark In ElectricityDocument8 pagesPut A Spark In ElectricityKristel TelmoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Unit Test Review AnswersDocument12 pagesElectricity Unit Test Review AnswersRon ChongNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Electricity and Magnetism Answer KeyDocument4 pagesLong Quiz Electricity and Magnetism Answer KeyLyka AldayaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument30 pagesReportapi-462604325No ratings yet
- Class 6 Science QuestionsDocument7 pagesClass 6 Science Questionsfratnawati05No ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis I Notes MooreDocument68 pagesCircuit Analysis I Notes MooreEngineer Zeeshan RasheedNo ratings yet
- Science Test - ElectricityDocument6 pagesScience Test - ElectricitySarah Lou OrrockNo ratings yet
- Science Test ReviewDocument7 pagesScience Test ReviewDariana MercadoNo ratings yet
- Important Questions With Answers Part IDocument5 pagesImportant Questions With Answers Part Iashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Buku Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesTugas Buku Bahasa InggrisFandi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Quarter 3Document34 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Quarter 3Ashanty CruzNo ratings yet
- 9.01 Static ElectricityDocument38 pages9.01 Static ElectricitychristinaNo ratings yet
- BSME 2B Electric Circuit and Static Electricity QuestionsDocument1 pageBSME 2B Electric Circuit and Static Electricity QuestionsCheru BibzNo ratings yet
- 7 Electrical Technolgy - Electron TheoryDocument4 pages7 Electrical Technolgy - Electron TheoryGuyan GordonNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Electricity and Circuit Exercise Question and Answer Plus Inner(Extra) Question and AnswerDocument7 pagesClass 6 Electricity and Circuit Exercise Question and Answer Plus Inner(Extra) Question and Answerdebasishnath9593913213No ratings yet
- Int Reader Study GuideDocument8 pagesInt Reader Study GuideAzalia Delgado VeraNo ratings yet
- ETM 10 Basic Electricity: Engr. Romano A. Pimentel InstructorDocument17 pagesETM 10 Basic Electricity: Engr. Romano A. Pimentel InstructorWynne LiNo ratings yet
- Quiz About Electricity and emDocument41 pagesQuiz About Electricity and emJomalyn DaduyoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Current ExplainedDocument4 pagesElectric Charge and Current ExplainedfluffNo ratings yet
- Работа №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentDocument5 pagesРабота №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentлюдмилаNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Electricty (Test)Document5 pagesForm 2 Science Electricty (Test)chaiseng yongNo ratings yet
- Discussion of Theory: Ohm's LawDocument7 pagesDiscussion of Theory: Ohm's LawJulia Bianca ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Electricity For Grade 9: Department of Technology Teacher EducationDocument10 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Electricity For Grade 9: Department of Technology Teacher Educationlania100% (1)
- Chemical Effects Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesChemical Effects Revision WorksheetAbhyuday SwamiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis I: DC Circuits FundamentalsDocument68 pagesCircuit Analysis I: DC Circuits FundamentalsTeddyNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Experiencing ElectricityDocument23 pagesModule 6 Experiencing ElectricityMelvin Cabonegro0% (1)
- Week 6Document4 pagesWeek 6JUAN CAMILO BRIEZ MONTEALEGRENo ratings yet
- Askiitians: Class: Vi Subject: Physics Topic: Electricity and Circuits No. of Questions: 21Document4 pagesAskiitians: Class: Vi Subject: Physics Topic: Electricity and Circuits No. of Questions: 21Parijat Roy ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- A Reconstructed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesA Reconstructed Lesson PlanPrecious BalgunaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis forCIDocument171 pagesCircuit Analysis forCIsbuesoNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"From EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"No ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument34 pagesElectricity and MagnetismDanea Shianne Sadiua100% (1)
- electricityDocument21 pageselectricityshalinee.daydayNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Basic ElectricityDocument18 pagesModule 3: Basic ElectricityApriljoy DannugNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument5 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsDwij RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument4 pagesElectric ChargeDis DoodNo ratings yet
- Science QNADocument17 pagesScience QNAShourjya SarkarNo ratings yet
- Electricity and CircuitDocument6 pagesElectricity and CircuitVarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Tema 2 FizikaDocument6 pagesTema 2 Fizika4p4xvyqtfqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectricityDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Electricityhazreen othman100% (4)
- Electric ChargeDocument6 pagesElectric ChargeDiana Joy Ancheta CldheiNo ratings yet
- Tubon, Royally Y. Electricity Module 1Document7 pagesTubon, Royally Y. Electricity Module 1Jonel BarrugaNo ratings yet
- Strengthened Technical-Vocational Education Program (STVEP) Quarter 4 Week 1-2Document8 pagesStrengthened Technical-Vocational Education Program (STVEP) Quarter 4 Week 1-2JERIEL BONGANCISONo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory 2 PDF FreeDocument24 pagesPhysics Investigatory 2 PDF FreekirtanNo ratings yet
- 7th Physics, Lesson-7, Electricity and MagnetismDocument5 pages7th Physics, Lesson-7, Electricity and MagnetismmilliNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 1 Safety Electron TheoryDocument20 pagesModule 1 Lecture 1 Safety Electron TheoryChona ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 AssessmentDocument3 pagesChapter 20 AssessmentAlex Willis50% (2)
- Group 1 Compilation of Quizes and ReviewerDocument40 pagesGroup 1 Compilation of Quizes and ReviewerCatherine PalarcaNo ratings yet
- Krish Physics Practical MLZ ElctrcicityDocument18 pagesKrish Physics Practical MLZ Elctrcicityajitkgupta145No ratings yet
- Preguntas TecnologíaDocument4 pagesPreguntas TecnologíaMARINA DEL AMO BERNALNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Electric Circuits GuideDocument27 pagesModule 7 Electric Circuits GuideMelvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Current Voltage - Resistance El1-002 Unit 2Document58 pagesCurrent Voltage - Resistance El1-002 Unit 2NichoNo ratings yet
- 7 Practice Oei ExperimentDocument2 pages7 Practice Oei Experimentapi-322906128No ratings yet
- ForcesDocument5 pagesForcesapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Paper Helicopter Air Resistence Gravity Experiment 2012Document1 pagePaper Helicopter Air Resistence Gravity Experiment 2012api-322906128No ratings yet
- 07 Fast FeathersDocument2 pages07 Fast Feathersapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Forces Balncd UnblactDocument2 pagesForces Balncd Unblactapi-322906128No ratings yet
- AtomsfamDocument4 pagesAtomsfamapi-322906128No ratings yet
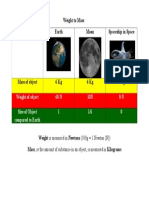
- Weight To Mass DiagramDocument1 pageWeight To Mass Diagramapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Forces Cont NonconactDocument2 pagesForces Cont Nonconactapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Parachute ActivityDocument2 pagesParachute Activityapi-322906128No ratings yet
- The Pull of Gravity: Mass and Weight Are Not The SameDocument4 pagesThe Pull of Gravity: Mass and Weight Are Not The Sameapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Like Unlike Charges ExptDocument2 pagesLike Unlike Charges Exptapi-322906128No ratings yet
- ElectroscopeDocument1 pageElectroscopeapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Yr 7 Electrostatics ExperimentDocument1 pageYr 7 Electrostatics Experimentapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Explaining Static ElectricityDocument1 pageExplaining Static Electricityapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Magnetism WorkstationsDocument7 pagesMagnetism Workstationsapi-322906128No ratings yet
- 7 Forces TestDocument3 pages7 Forces Testapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Yr 7 Electro Magnet ExperimentDocument1 pageYr 7 Electro Magnet Experimentapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Forces and Motion - Revision Carousel Teaching Notes: Teachit TimerDocument23 pagesForces and Motion - Revision Carousel Teaching Notes: Teachit Timerapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Magnets WorksheetDocument1 pageMagnets Worksheetapi-322906128No ratings yet
- MagnetismwshtDocument2 pagesMagnetismwshtapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Electromagnet-Demonstration Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageElectromagnet-Demonstration Risk Assessmentapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldDocument1 pageMagnetic Fieldapi-322906128No ratings yet
- 7 Forces BookletDocument20 pages7 Forces Bookletapi-322906128No ratings yet
- Electromagnets WorksheetDocument1 pageElectromagnets Worksheetapi-322906128No ratings yet
- The Effect of Geographical Setting in Detecting Stray Muon Particle Using Cloud ChamberDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Geographical Setting in Detecting Stray Muon Particle Using Cloud ChamberKathNo ratings yet
- Is800 2007Document2 pagesIs800 2007S S HARISHNo ratings yet
- Clock, Variation, Progression and Miscellaneous ProblemsDocument10 pagesClock, Variation, Progression and Miscellaneous ProblemsDebbie Abaoag CariñoNo ratings yet
- Improve Power Integrity With Decoupling Solutions - EDI CON 201020Document32 pagesImprove Power Integrity With Decoupling Solutions - EDI CON 201020tiendungNo ratings yet
- Science G9: Quarter 2Document44 pagesScience G9: Quarter 2Ericha Solomon100% (7)
- Chapter 1 - Design of Special BeamsDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Design of Special BeamsSine EntertaimentNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chapter 2 VectorDocument64 pages2 - Chapter 2 VectorRavi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Model SK 6150 6155Document14 pagesModel SK 6150 6155Abdalhakeem AlturkyNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Enhanced Math For Parents 26-102023Document1 page6th Grade Enhanced Math For Parents 26-102023api-644148799No ratings yet
- Sat Practice Test 9 PDFDocument26 pagesSat Practice Test 9 PDFHaryo PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Math formula cheat sheetDocument16 pagesMath formula cheat sheetNathan HurwitzNo ratings yet
- University Physics With Modern Physics 2nd Edition Bauer Test BankDocument24 pagesUniversity Physics With Modern Physics 2nd Edition Bauer Test BankJustinTaylorepga100% (42)
- Poisson Equation: by Li ChenDocument18 pagesPoisson Equation: by Li ChenCristofer TejedaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Properties of Oil and Natural Gas - 2007 - Petroleum Production EngineeringDocument9 pages2 - Properties of Oil and Natural Gas - 2007 - Petroleum Production EngineeringHaziq YussofNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P1 June 2008 CambridgeDocument16 pagesMathematics P1 June 2008 CambridgeTafadzwa NyazorweNo ratings yet
- Matrices Rosniza's Module 4Document14 pagesMatrices Rosniza's Module 4Rosniza Ab GhaniNo ratings yet
- Addisu LemmaDocument84 pagesAddisu LemmaSELAMNo ratings yet
- #385421375 Personal Statement - EditedDocument4 pages#385421375 Personal Statement - EditedjoeNo ratings yet
- FORMAT UAS GANJIL 21-22 Bahasa Inggris (Dr. H. Masrupi, M.Pd.2021Document15 pagesFORMAT UAS GANJIL 21-22 Bahasa Inggris (Dr. H. Masrupi, M.Pd.2021IfdaNo ratings yet
- AFF2 Stellar AdventuresDocument130 pagesAFF2 Stellar AdventuresRhys1100% (1)
- Practice Test 1 Listening ComprehensionDocument26 pagesPractice Test 1 Listening ComprehensionSanjaya PutraNo ratings yet
- The AME2016 Atomic Mass Evaluation (I) - Evaluation of Input Data and Adjustment ProceduresDocument345 pagesThe AME2016 Atomic Mass Evaluation (I) - Evaluation of Input Data and Adjustment ProceduresInês AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Physics of InformationDocument739 pagesIntroduction to the Physics of Informationkevinchu021195No ratings yet
- Ley LinesDocument8 pagesLey Lineslilian_armstrong8401No ratings yet
- Dropsa YoensaDocument73 pagesDropsa YoensaCAGERIGONo ratings yet
- Scales: Engineering GraphicsDocument12 pagesScales: Engineering GraphicsNaman Dave100% (2)
- Lp-Research DesignDocument10 pagesLp-Research DesignCharmalou Pampilo OgarteNo ratings yet
- ACP0LED Series: American Compact LED FloodlightDocument4 pagesACP0LED Series: American Compact LED FloodlightWilliam MartinezNo ratings yet
- Optimization of CNC MachiningDocument3 pagesOptimization of CNC MachiningVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- Portafolio 2-B1Document2 pagesPortafolio 2-B1Natalia PantojaNo ratings yet