Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hooke Law
Uploaded by
LiuJiewChuan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views3 pagesThis document contains 10 problems about Hooke's law and springs. It addresses concepts like spring constant, potential energy stored in springs, work done compressing springs, and force-compression graphs. It asks questions about determining spring constants from graphs, calculating potential energy and work, relating force and compression for individual springs, and identifying the spring with the lowest spring constant from a force-compression graph.
Original Description:
Original Title
hooke law.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 10 problems about Hooke's law and springs. It addresses concepts like spring constant, potential energy stored in springs, work done compressing springs, and force-compression graphs. It asks questions about determining spring constants from graphs, calculating potential energy and work, relating force and compression for individual springs, and identifying the spring with the lowest spring constant from a force-compression graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views3 pagesHooke Law
Uploaded by
LiuJiewChuanThis document contains 10 problems about Hooke's law and springs. It addresses concepts like spring constant, potential energy stored in springs, work done compressing springs, and force-compression graphs. It asks questions about determining spring constants from graphs, calculating potential energy and work, relating force and compression for individual springs, and identifying the spring with the lowest spring constant from a force-compression graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Hookes Law Exercise
1. What determines the spring
constant (k) of a spring?
2. A coiled spring is stretched 0.05 m
by a weight of 0.50 N hung from
one end.
a. How far will the spring stretch if
a 1.0 N weight replaces the 0.50
N weight?
[0.1 m]
b. What weight will stretch the
spring a distance of 0.03 m? [0.3
N]
3. When the spring force is plotted
versus the elongation of the spring:
a. How do you determine the
spring constant (k) from the
graph?
b. How do you determine the
potential energy (EP) stored in a
spring from the graph?
4. An ideal spring, whose spring
constant is 14.0 N/m, is stretched
0.40 m when a mass of 0.560 kg is
hung from it, how much potential
energy (EP) is stored in this spring?
[1.12 J]
5. The work done to compress a
spring from 0 to 0.15 m is 8.0 J.
How much work is required to
compress this spring from 0 to 0.30
m? [32 J]
7. A spring is compressed 0.10 m
when a force of 2.0 N is exerted
upon it. What force must be used
to compress this spring 0.40
meters? [8.0 N]
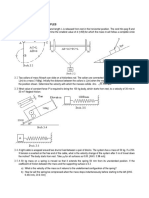
8. A mass of 10 kg, having a velocity
of 5 m/s, slides into a spring as
illustrated in the diagram on the
right. Assuming the system is
frictionless, which of the following
statements is correct?
At maximum compression, the
EK of the mass is zero.
[
]
At maximum compression, the
EP of the spring equals the EK
of the mass. [
]
After the interaction, the mass
moves with a velocity of 5 m/s.
[
]
9. A block of unknown mass moves at
2 m/s towards a horizontal spring
whose spring constant is 1000 N/m.
If the spring is compressed a
maximum distance of 0.4 m, what
is the mass of the block? [100 kg]
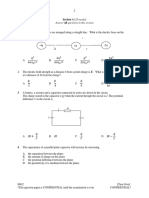
6. The graph on the right represents
the force-compression graph of an
ideal spring.
a. Determine the spring constant.
[100 N/m]
b. Calculate the loss in kinetic
energy of an object that collides
with this spring and compresses it
a distance of 0.60 m. [18 J]
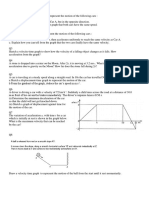
10.The graph on the left displays the
force-compression curve of four
springs labeled Spring-A, Spring-B,
Spring-C and Spring D. Which
spring is the springiest?
(Springiest means lowest spring
constant)
Hookes Law Exercise
1. What determines the spring
constant (k) of a spring?
2. A coiled spring is stretched 0.05 m
by a weight of 0.50 N hung from
one end.
a. How far will the spring stretch if
a 1.0 N weight replaces the 0.50
N weight?
[0.1 m]
b. What weight will stretch the
spring a distance of 0.03 m? [0.3
N]
3. When the spring force is plotted
versus the elongation of the spring:
a. How do you determine the
spring constant (k) from the
graph?
b. How do you determine the
potential energy (EP) stored in a
spring from the graph?
4. An ideal spring, whose spring
constant is 14.0 N/m, is stretched
0.40 m when a mass of 0.560 kg is
hung from it, how much potential
energy (EP) is stored in this spring?
[1.12 J]
5. The work done to compress a
spring from 0 to 0.15 m is 8.0 J.
How much work is required to
compress this spring from 0 to 0.30
m? [32 J]
6. The graph on the right represents
the force-compression graph of an
ideal spring.
a. Determine the spring constant.
[100 N/m]
b. Calculate the loss in kinetic
energy of an object that collides
with this spring and compresses it
a distance of 0.60 m. [18 J]
7. A spring is compressed 0.10 m
when a force of 2.0 N is exerted
upon it. What force must be used
to compress this spring 0.40
meters? [8.0 N]
8. A mass of 10 kg, having a velocity
of 5 m/s, slides into a spring as
illustrated in the diagram on the
right. Assuming the system is
frictionless, which of the following
statements is correct?
At maximum compression, the
EK of the mass is zero.
[
]
At maximum compression, the
EP of the spring equals the EK
of the mass. [
]
After the interaction, the mass
moves with a velocity of 5 m/s.
[
]
9. A block of unknown mass moves at
2 m/s towards a horizontal spring
whose spring constant is 1000 N/m.
If the spring is compressed a
maximum distance of 0.4 m, what
is the mass of the block? [40 kg]
10.The graph on the left displays the
force-compression curve of four
springs labeled Spring-A, Spring-B,
Spring-C and Spring D. Which
spring is the springiest?
(Springiest means lowest spring
constant)
You might also like
- Thermo 1 & 2Document4 pagesThermo 1 & 2Oloj YuNo ratings yet
- PDF 38 1 PDFDocument190 pagesPDF 38 1 PDFCharan GorentlaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Friction: Experiment #13Document8 pagesKinetic Friction: Experiment #13kate anne del castroNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law ExperimentDocument3 pagesHookes Law ExperimentKhairul Razmin AbdurakmanNo ratings yet
- Units: Basic MathematicsDocument38 pagesUnits: Basic MathematicsGraham MooreNo ratings yet
- PHY10L - Resolution of ForcesDocument14 pagesPHY10L - Resolution of Forcesdenzel94No ratings yet
- Free-Samples Amie Chapters Bernoulli S Equation and Their ApplicatiDocument31 pagesFree-Samples Amie Chapters Bernoulli S Equation and Their ApplicatiFei LeeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - ch2, 100Document2 pagesGrade 10 - ch2, 100NayLinNo ratings yet
- Chap2 StrainDocument36 pagesChap2 Strainasif kiyaniNo ratings yet
- Edited Module1 ThermoDocument18 pagesEdited Module1 ThermoAnnaliza Alcazar ApostolNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motions JEE Question BankDocument15 pagesRotational Motions JEE Question BankVinayak GuptaNo ratings yet
- F4 Phy Pre-Necta I (2023)Document6 pagesF4 Phy Pre-Necta I (2023)Abdallah Kunamba100% (1)
- 081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - Notes PDFDocument78 pages081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - Notes PDFKrish NarayananNo ratings yet
- HMT Unit 1Document9 pagesHMT Unit 1rp0212No ratings yet
- 6 PDFDocument4 pages6 PDFLethal Illusion0% (1)
- Metacentre and Metacentric HeightDocument4 pagesMetacentre and Metacentric HeightleonNo ratings yet
- Constant Acceleration Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesConstant Acceleration Practice ProblemsDeema AljaririNo ratings yet
- 8 Stresses in BeamDocument6 pages8 Stresses in BeamAnkit SinghNo ratings yet
- NUmerical SolutionsDocument76 pagesNUmerical SolutionsLiaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument3 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesRalph Lauren RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Torque and Equilibrium 2Document1 pageWorksheet in Torque and Equilibrium 2Ronalyn Guiyadan PacnaNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument7 pagesSimple Harmonic MotionRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Application of Numerical Methods To Truss Bridge Using Finite Element AnalysisDocument12 pagesApplication of Numerical Methods To Truss Bridge Using Finite Element AnalysisBenmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document5 pagesExperiment 1Timmy TrinhNo ratings yet
- Interpolation Direct MethodDocument16 pagesInterpolation Direct MethodSri Peni WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Chap4 000Document5 pagesChap4 000pja752No ratings yet
- MENG - 331 - Spring 2019-2020 - TUTORIAL PROBLEMSDocument66 pagesMENG - 331 - Spring 2019-2020 - TUTORIAL PROBLEMSİREM Taşlı100% (1)
- Areas by IntegrationDocument9 pagesAreas by IntegrationRona ChanNo ratings yet
- PR Closed System 2Document2 pagesPR Closed System 2Mareta DanarNo ratings yet
- ENGN.2050 Assignment 07 SolutionDocument4 pagesENGN.2050 Assignment 07 SolutionAri Meliasta Ginting04No ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Non-Concurrent ForcesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium of Non-Concurrent ForcesTamilManiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Final Exam Problem & SolutionsDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Final Exam Problem & SolutionsRonard Pa–a0% (1)
- Experiment 6 and Experiment 7Document5 pagesExperiment 6 and Experiment 7Gebre TensayNo ratings yet
- Surveying Lecture 100620Document2 pagesSurveying Lecture 100620John Dalton ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument6 pagesHooke's LawngwaNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsDocument32 pagesAcceleration Analysis of MechanismsThahir Shah100% (1)
- BB101 Chapter 2 Linear Motion - EditDocument9 pagesBB101 Chapter 2 Linear Motion - EditAidi AmarNo ratings yet
- Uclm Cesafi QuestionsDocument1 pageUclm Cesafi QuestionsBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PHM 601 Question Bank-2018Document4 pagesPHM 601 Question Bank-2018Abhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1 Analysis of Strain - Concepts and Definitions-2 - CE 205-CE22S2 - Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument12 pagesModule 2.1 Analysis of Strain - Concepts and Definitions-2 - CE 205-CE22S2 - Mechanics of Deformable BodiesRUSSELNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GeneralitiesDocument24 pagesChapter 1 GeneralitiesPuwa CalvinNo ratings yet
- Banking of Curves - PhysicsDocument2 pagesBanking of Curves - PhysicsRanjith EkanayakeNo ratings yet
- Applying The Work-Energy TheoremDocument2 pagesApplying The Work-Energy TheoremHaziel PavonNo ratings yet
- HW 9Document14 pagesHW 9Siva RamNo ratings yet
- EE2224 - Solid Mechanics - TorsionDocument19 pagesEE2224 - Solid Mechanics - TorsionPreedep BaradidathanNo ratings yet
- Dynamics (Work and Energy) TutorialDocument5 pagesDynamics (Work and Energy) TutorialYadana1No ratings yet
- Fluid Statics - Problems and Solutions - Solved Problems in Basic PhysicsDocument12 pagesFluid Statics - Problems and Solutions - Solved Problems in Basic PhysicsEsther oluwatosin AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits: Prepared byDocument12 pagesDC Circuits: Prepared byRuth DVNo ratings yet
- Problems On Fluid PropertiesDocument1 pageProblems On Fluid PropertiesTOOBA KHALILNo ratings yet
- Single Stage CompressorDocument5 pagesSingle Stage CompressorHaziq HanifahNo ratings yet
- 7 Physics Nos. 162-232Document69 pages7 Physics Nos. 162-232Cherry-Ann C. OlajayNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment 1 - ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesFinal Assignment 1 - Thermodynamicsjovan avery dalluay0% (2)
- Introduction To Heat Transfer PDFDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Heat Transfer PDFMohamed RadwanNo ratings yet
- CHPT 26 PacketDocument8 pagesCHPT 26 Packethongling240% (2)
- Physics Unit 1 AnsDocument230 pagesPhysics Unit 1 AnsChristopher Antonio Sarmales-Murga100% (1)
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsFrom EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter13 PDFDocument16 pagesTB Chapter13 PDFsuryapmohantyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 & 4Document13 pagesUnit 3 & 4Ram Chandra0% (1)
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocument19 pagesHapter: Conceptual Problemsadel0% (1)
- STPM 2019 Physics Practical Schedule: Experiment DateDocument2 pagesSTPM 2019 Physics Practical Schedule: Experiment DateLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exe 2 Trial STPMDocument9 pagesExe 2 Trial STPMLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Fail Induk Kelab Ping Pong SMK Green RoadDocument1 pageFail Induk Kelab Ping Pong SMK Green RoadLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Lessonplan State of MatterDocument5 pagesLessonplan State of MatterLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 24.4Document2 pagesExercise 24.4LiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- 24.5 NanoscienceDocument1 page24.5 NanoscienceLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Tan X Is Equal To Sin XDocument1 pageTan X Is Equal To Sin XLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument9 pagesGeometrical OpticsLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9.1 2020Document1 pageExercise 9.1 2020LiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8.3 2020 StudentDocument2 pagesExercise 8.3 2020 StudentLiuJiewChuan100% (1)
- Exercise 8.1 2020 StudentDocument2 pagesExercise 8.1 2020 StudentLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Designer'S Notebook: Effective Capacitance Vs FrequencyDocument1 pageCircuit Designer'S Notebook: Effective Capacitance Vs FrequencyLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12.1Document13 pagesExercise 12.1LiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 12.4Document5 pagesExercise 12.4LiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Period For 20 Oscillations, 20T: What Is The Relationship Between Inertia and Mass ?Document2 pagesPeriod For 20 Oscillations, 20T: What Is The Relationship Between Inertia and Mass ?LiuJiewChuan100% (1)
- Exercise 2 Term 1 STPMDocument10 pagesExercise 2 Term 1 STPMLiuJiewChuan100% (1)
- General Physics (PHYS101) : Golibjon BerdiyorovDocument26 pagesGeneral Physics (PHYS101) : Golibjon BerdiyorovLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 C - AnswerDocument2 pagesBab 6 C - AnswerLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.3 Term 2 STPMDocument7 pagesExercise 1.3 Term 2 STPMLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.4 Term 2 STPMDocument5 pagesExercise 1.4 Term 2 STPMLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Analisis STPM Semester 1 2019Document3 pagesLaporan Analisis STPM Semester 1 2019LiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- MSEG 667: 3: Guided Wave OpticsDocument26 pagesMSEG 667: 3: Guided Wave OpticsJuan Carlos GarayNo ratings yet
- Shallco Series 1610 Part No.: 16A10A1-B-1: GeneralDocument1 pageShallco Series 1610 Part No.: 16A10A1-B-1: GeneralRodNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On Energy and ThermochemistryDocument6 pagesPractice Problems On Energy and ThermochemistryMichael MangaoangNo ratings yet
- AVO International Battery TesterDocument2 pagesAVO International Battery TesterVikrant100% (1)
- Experiment 6 ProcedureDocument4 pagesExperiment 6 ProcedureNathaniel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Free Fall: Nattanon VeerakulDocument9 pagesFree Fall: Nattanon Veerakulapi-327824456No ratings yet
- 损伤力学教程 勒迈特Document293 pages损伤力学教程 勒迈特曹斯厚No ratings yet
- Appendix. A List of Studies ReviewedDocument8 pagesAppendix. A List of Studies ReviewedIlma HusnahNo ratings yet
- Basics of Vibrations - M Ghosh BHELDocument9 pagesBasics of Vibrations - M Ghosh BHELSuhas JoshiNo ratings yet
- 4 Point Method / Measurement of Low Resistances: (Item No.: P2410101)Document20 pages4 Point Method / Measurement of Low Resistances: (Item No.: P2410101)fatjonmusli2016No ratings yet
- Malla Reddy Engineering College: B. Tech. Iv Semester (Mr15) Regular End ExaminationsDocument2 pagesMalla Reddy Engineering College: B. Tech. Iv Semester (Mr15) Regular End ExaminationsNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Newton's 3rd Law of MotionDocument33 pagesNewton's 3rd Law of MotionRamona EstevesNo ratings yet
- SSC JE Electrical SyllabusDocument4 pagesSSC JE Electrical SyllabusHarpal SainiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 7 DynamicsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 7 DynamicsGift TanNo ratings yet
- Implement Field-Oriented Control (FOC) Induction Motor Drive Model - SimulinkDocument13 pagesImplement Field-Oriented Control (FOC) Induction Motor Drive Model - SimulinkRizkia PratamaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 2018Document3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 2018Faculty, Shahid Matangini Hazra Government College for WomenNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current & Mechanical Effct of Electric CurrentDocument41 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current & Mechanical Effct of Electric CurrentShweta Y KNo ratings yet
- Kelvin Bridge: 2 Principle of OperationDocument3 pagesKelvin Bridge: 2 Principle of OperationDen AdenNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: ProblemsDocument67 pagesForces and Newton'S Laws of Motion: ProblemsangelicaNo ratings yet
- The Book of KINDocument81 pagesThe Book of KINMiroslav Pavicevic100% (2)
- Rail Structure Interaction For Multiple Span Railway Viaducts With Direct FIXED TRACKDocument10 pagesRail Structure Interaction For Multiple Span Railway Viaducts With Direct FIXED TRACKsandeep tanavadekarNo ratings yet
- Suction Cups/grippers: BFF40P, BFF60P, BFF80P, BFF110PDocument2 pagesSuction Cups/grippers: BFF40P, BFF60P, BFF80P, BFF110PBe HappyNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Electrical Drives Dated: 01-12-2014 Course Code: EEE 3422 Course Structure: 3-1-0-4 Course ObjectivesDocument3 pagesCourse Title: Electrical Drives Dated: 01-12-2014 Course Code: EEE 3422 Course Structure: 3-1-0-4 Course ObjectivesAR-TNo ratings yet
- Pendulum Underdamped SystemDocument7 pagesPendulum Underdamped SystemJitender YadavNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC MotorsDocument7 pagesBrushless DC MotorsRonald LugwireNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Plumbing ArithmeticDocument10 pagesModule 2 - Plumbing ArithmeticPermanente Health Plan Corporation PHPNo ratings yet
- Locking Systems: 490 Vehicle Security Systems Central Locking Systems, Locking SystemsDocument20 pagesLocking Systems: 490 Vehicle Security Systems Central Locking Systems, Locking SystemsJulio MezaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of Universal GravitationDocument10 pagesNewtons Law of Universal Gravitationdheerajr97No ratings yet
- Electrical-Engineering FormulasDocument19 pagesElectrical-Engineering FormulasShara Lorraine EstiponaNo ratings yet
- Resonance Magazine, March 1996Document127 pagesResonance Magazine, March 1996Kiran Kumar KuppaNo ratings yet