Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Only 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered Version
Uploaded by
Syawal RahinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Only 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered Version
Uploaded by
Syawal RahinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Only 2 Pages are Converted
in the Unregistered Version
FUNCTION 3 - PART 03: INSTRUCTOR MANUAL
Many paints contain poisonous substances and release toxic fumes as solvents evaporate. The
vapours of most paint solvents will produce flammable or explosive mixtures with air in poorly
ventilated spaces.
The risks are greatest when using. spray equipment in enclosed spaces. Personnel must -wear
breathing apparatus, sources of ignition must be excluded and ventilation must be provided while
work is in progress. Precautions for entering enclosed spaces should be taken after painting has
been completed until the paint has thoroughly dried and no risk of release of vapour remains.
Manufacturers' instructions regarding protective clothing and safety precautions should be
followed.
(2
hours)
This section deals with the surveys and inspections required by classification societies. The
requirements for survey under international conventions are dealt with in subject module 3.2,
Maritime Law. The annual inspection required by the International Convention on Load Lines,
1966, is usually carried out by a classification society surveyor, acting on behalf of the flag State
Administration. The inspection is similar to that required for the classification society's annual
survey.
Surveys and dry-docking
The hardeners that are used in two-pack (or bi-pack) polyurethane and epoxy paints are toxic
and may also cause allergic 'reactions following contact with skin. Protective clothing and
disposable gloves should alw~ys b,e worn when working with these paints.
(S3
hours)
Calculations on box-shaped vessels have been introduced at a number of places in this syllabus.
They are included to illustrate basic principles and to aid trainees' understanding of actual ships'
data. The appendix to this instructor manual contains stability data and capacity tables for use
iX'l the preparation of exercises. Instructors should make a collection of data for other ships as
the opportunity arises. The application of the principles of stability to determining the final
draught, trim and initial GM for a given complete distribution of cargo is included in the function,
Cargo Handling and Stowage.
Stability
Approximate calculation of areas and volumes
This section covers the use of the trapezoidal rule and Simpson's rules for the calculation of
areas. The derivation of Simpson's rules and their use for finding moments or second moments
of area has not been included. The calculation of volume where the given ordinates are areas is
covered.
The use of Simpson's rules is required for finding areas under a GZ curve, for checking
compliance with recommendations on lntact stability. Trainees should also be able to apply
them for calculating areas of decks and volumes of compartments aboard ship.
.
Effects of density
In tidal estuaries the density of the water may vary considerably according to the state of the
tide. When checking draughts or freeboard near completion of loadinq it is essential to
289
You might also like
- Technical Aspects Related to the Design and Construction of Engineered Containment Barriers for Environmental RemediationFrom EverandTechnical Aspects Related to the Design and Construction of Engineered Containment Barriers for Environmental RemediationNo ratings yet
- Marine and Offshore Pumping and Piping SystemsFrom EverandMarine and Offshore Pumping and Piping SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Survey SorularDocument4 pagesSurvey SorularMuhammed Yusuf KaplanNo ratings yet
- Leaflet SOLAS 2009 - Damage Stability - V12Document10 pagesLeaflet SOLAS 2009 - Damage Stability - V12Mohamed ChelfatNo ratings yet
- Guide For Vessels Intended To Carry Compressed Natural Gases in Bulk 2020Document235 pagesGuide For Vessels Intended To Carry Compressed Natural Gases in Bulk 2020EIRINI KONDYLINo ratings yet
- 85 Inf 4Document3 pages85 Inf 4Erwin Paulian SihombingNo ratings yet
- MGN - 423 Entry Into Enclosed SpaceDocument4 pagesMGN - 423 Entry Into Enclosed SpaceThomas JoseNo ratings yet
- Bio FoulllingDocument14 pagesBio FoulllingAlbert StratingNo ratings yet
- Ssep - July - 2023Document2 pagesSsep - July - 2023Mano ShankarNo ratings yet
- Eebd Singapore PDFDocument3 pagesEebd Singapore PDFmehedi2636No ratings yet
- BCGA Code of PracticeDocument18 pagesBCGA Code of PracticeSivakumar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Survey ProgrammeDocument3 pagesEnhanced Survey Programmevirendra302No ratings yet
- MSC.1-Circ.1620 - Guidelines For Inspection and Maintenance of Mooring Equipment Including Lines (Secretariat)Document7 pagesMSC.1-Circ.1620 - Guidelines For Inspection and Maintenance of Mooring Equipment Including Lines (Secretariat)Muhammed SabeehNo ratings yet
- Hatch Cover Maintenance PlanDocument5 pagesHatch Cover Maintenance Planvinay3972No ratings yet
- Emergency Escape Breathing Device (Eebd) Requirements and Recommendations For Singapore-Flag Ships (Chapter II-2 of SOLAS 1974, As Amended)Document3 pagesEmergency Escape Breathing Device (Eebd) Requirements and Recommendations For Singapore-Flag Ships (Chapter II-2 of SOLAS 1974, As Amended)boujniteNo ratings yet
- Oralquestionandanswer GoodDocument464 pagesOralquestionandanswer GoodMariyath Muraleedharan KiranNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Survey ProgrammeDocument14 pagesEnhanced Survey ProgrammeleopradeepNo ratings yet
- REC 15 pdf178Document6 pagesREC 15 pdf178Ruly Abdillah GintingNo ratings yet
- Marine Vapour ControlDocument3 pagesMarine Vapour Controlgatzbu81100% (1)
- ESP Guidance For All Ships V13.7Document53 pagesESP Guidance For All Ships V13.7Jayasankar GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- TMS Airbags Vs PNE WhitepaperDocument28 pagesTMS Airbags Vs PNE WhitepaperJeff TrinidadNo ratings yet
- IMO Guide To Cargo Tank CoatingDocument19 pagesIMO Guide To Cargo Tank CoatingnnuekNo ratings yet
- Rom31 99 PART IDocument30 pagesRom31 99 PART Ieparquio100% (1)
- Workboat Guidelines IAGC 5Document20 pagesWorkboat Guidelines IAGC 5Paul H TampubolonNo ratings yet
- 2TSCF Intertanko ManualDocument10 pages2TSCF Intertanko Manualnapoleonpt20% (1)
- MMC 144 SEGUMAR Apr2023 Rev MRDocument6 pagesMMC 144 SEGUMAR Apr2023 Rev MRRICHCON INTERNATIONAL CO., LTD.No ratings yet
- Cargo Compressor GuidanceDocument8 pagesCargo Compressor GuidanceRam B. ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ESP Guidance For All Ships V13.6 Jan 2019Document53 pagesESP Guidance For All Ships V13.6 Jan 2019Sreenivasan VaralilNo ratings yet
- Pumproom SafetyDocument7 pagesPumproom Safetysergiytitov100% (2)
- Module 1Document32 pagesModule 1Jovan saldivoNo ratings yet
- ISOTANK Protocol Prevention FallsDocument10 pagesISOTANK Protocol Prevention FallsAnonymous 1XHScfCINo ratings yet
- DR 68Document27 pagesDR 68JOSE PRASOBH..JNo ratings yet
- 229-77111 Esp Guidance Booklet For All Ships.2 PDFDocument43 pages229-77111 Esp Guidance Booklet For All Ships.2 PDFarunNo ratings yet
- Shipright Procedures Overview Sep 2007Document6 pagesShipright Procedures Overview Sep 2007Ravikumar mahadevNo ratings yet
- International Convention On Load LinesDocument60 pagesInternational Convention On Load LinesSharad Kishore0% (1)
- Ed Well IntegrityDocument46 pagesEd Well IntegrityBabacar DieyeNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Ph1 March 2022 Safety Internals' With YouDocument6 pagesI Am Sharing 'Ph1 March 2022 Safety Internals' With YouGANESAN velNo ratings yet
- Ibp2184 12Document7 pagesIbp2184 12Marcelo Varejão CasarinNo ratings yet
- Coating Performance Standard (CPS) : Guide For The Class NotationDocument11 pagesCoating Performance Standard (CPS) : Guide For The Class NotationGilberto Zamudio100% (1)
- Reasons & Basic Layout of An LNG VesselDocument7 pagesReasons & Basic Layout of An LNG VesselRhiannon BallardNo ratings yet
- ICAO Aerodrome Best PracticeDocument16 pagesICAO Aerodrome Best Practicenimsv1980100% (2)
- VOCDocument27 pagesVOCAnthony Roger ViegasNo ratings yet
- Entry Into Enclosed Spaces New Regulations MGN 659 M+F MCA 2022Document12 pagesEntry Into Enclosed Spaces New Regulations MGN 659 M+F MCA 2022ARE YOU TECH CRAZYNo ratings yet
- Ssep - March - 2023Document3 pagesSsep - March - 2023Mano ShankarNo ratings yet
- DNV Template Biofouling Management Plan Rev1 Tcm4-524330Document14 pagesDNV Template Biofouling Management Plan Rev1 Tcm4-524330Mary Smith100% (1)
- RGEREREEDocument3 pagesRGEREREEGulzarNo ratings yet
- FN 3Document75 pagesFN 3tiyiti1926No ratings yet
- Huatai Insurance Agency Consultant Service LTD Circular PNI2001Document15 pagesHuatai Insurance Agency Consultant Service LTD Circular PNI2001cong binh trang100% (1)
- LGC Storage Guide E-Nov16Document8 pagesLGC Storage Guide E-Nov16이훈No ratings yet
- The Imo Performance Standard For ProtectDocument34 pagesThe Imo Performance Standard For ProtectBranko Brezec100% (1)
- Model Ship To Ship Transfer Operations Plan - tcm155-200644Document43 pagesModel Ship To Ship Transfer Operations Plan - tcm155-200644Gabriel Montero100% (4)
- Guidelines On Safety Management Systems For Hot Work and Entry Into Enclosed SpacesDocument9 pagesGuidelines On Safety Management Systems For Hot Work and Entry Into Enclosed SpacessotprymNo ratings yet
- Bulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersFrom EverandBulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Guide to the Collision Avoidance RulesFrom EverandA Guide to the Collision Avoidance RulesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Marine Rudders, Hydrofoils and Control Surfaces: Principles, Data, Design and ApplicationsFrom EverandMarine Rudders, Hydrofoils and Control Surfaces: Principles, Data, Design and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Radar and ARPA Manual: Radar, AIS and Target Tracking for Marine Radar UsersFrom EverandRadar and ARPA Manual: Radar, AIS and Target Tracking for Marine Radar UsersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Piloting, Seamanship and Small Boat Handling - Vol. VFrom EverandPiloting, Seamanship and Small Boat Handling - Vol. VRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Handbook of Adhesive Bonded Structural RepairFrom EverandHandbook of Adhesive Bonded Structural RepairRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
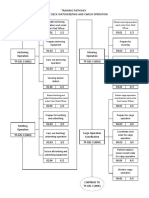
- Training Pathway l3 1Document1 pageTraining Pathway l3 1Syawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Training Pathway l3 1Document1 pageTraining Pathway l3 1Syawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Only 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionDocument2 pagesOnly 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionSyawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Only 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionDocument2 pagesOnly 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionSyawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Notices To Mariners: Monthly Edition 2 of 2015 28 FEBRUARY 2015Document9 pagesMalaysian Notices To Mariners: Monthly Edition 2 of 2015 28 FEBRUARY 2015Syawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Only 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionDocument2 pagesOnly 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionSyawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Only 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionDocument3 pagesOnly 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionSyawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Only 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionDocument2 pagesOnly 2 Pages Are Converted in The Unregistered VersionSyawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- Saturday, June 11, 2016 6:09 AM: Unfiled Notes Page 1Document3 pagesSaturday, June 11, 2016 6:09 AM: Unfiled Notes Page 1Syawal RahinaNo ratings yet
- SOP SOP0003 Nail GunDocument2 pagesSOP SOP0003 Nail Gunjeevan georgeNo ratings yet
- On-Farm Biosecurity, Dr. DoDocument32 pagesOn-Farm Biosecurity, Dr. DodawnNo ratings yet
- Safety Audit ChecklistDocument8 pagesSafety Audit ChecklistSURJIT SINGH100% (1)
- TR Health Care Services NC IIDocument67 pagesTR Health Care Services NC IIMELODY AMOR NISNEANo ratings yet
- Aral Getriebeoel Atf J Germany English-Gb SDB 465826Document12 pagesAral Getriebeoel Atf J Germany English-Gb SDB 465826Техник СвязиNo ratings yet
- Heavy Equipment OperationDocument2 pagesHeavy Equipment OperationKarhysNo ratings yet
- RA For Installation & Insulation of CHW Pipe SystemDocument4 pagesRA For Installation & Insulation of CHW Pipe SystemDong VanraNo ratings yet
- Guide To Hazardous Paint Management - ASNZS 4361.2.2017 - Part 2 - Lead Paint in Residential, Public and Commercial BuildingsDocument10 pagesGuide To Hazardous Paint Management - ASNZS 4361.2.2017 - Part 2 - Lead Paint in Residential, Public and Commercial Buildingshitman13630% (1)
- Facility Inspection ChecklistDocument9 pagesFacility Inspection ChecklistdesignselvaNo ratings yet
- Accident Investigation Report: Investigator's InformationDocument2 pagesAccident Investigation Report: Investigator's InformationJack PNo ratings yet
- Hse-Questions For ARAMCODocument22 pagesHse-Questions For ARAMCOChristian PetrovicNo ratings yet
- 25-Risk Assessment For Fabrication & NDT During Night ShiftDocument2 pages25-Risk Assessment For Fabrication & NDT During Night Shiftgulryz84100% (9)
- PaintDocument22 pagesPaintZubair Ahmed KhaskheliNo ratings yet
- Rope Replacement Risk AssessmentDocument53 pagesRope Replacement Risk AssessmentFrancois Johannes BrinkNo ratings yet
- SG 257 Cyclopentane - tcm410 39649Document6 pagesSG 257 Cyclopentane - tcm410 39649binalNo ratings yet
- BSC Unit 2 AssignmentDocument17 pagesBSC Unit 2 AssignmentJamshar Kt89% (9)
- Abc Sealant SDSDocument5 pagesAbc Sealant SDSKissa DolautaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5, 6 & 7: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in The Construction IndustryDocument35 pagesChapter 5, 6 & 7: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in The Construction IndustrySuraj PantNo ratings yet
- Airside Safety & Security Training Reference Book - Aruba Airport AuthorityDocument63 pagesAirside Safety & Security Training Reference Book - Aruba Airport AuthorityRichard R M Thodé75% (4)
- Activity Hazard Analysis: Well DiggingDocument1 pageActivity Hazard Analysis: Well DiggingarjunkoiralaNo ratings yet
- Hand and Power Tools PDFDocument4 pagesHand and Power Tools PDFBrionna RogersNo ratings yet
- MSDS, Hydrochloric-Methanol Nital Etch SolutionDocument4 pagesMSDS, Hydrochloric-Methanol Nital Etch SolutionFitri Mega NugrahaNo ratings yet
- SW 830Document2 pagesSW 830Yến BùiNo ratings yet
- All About Spray FoamDocument40 pagesAll About Spray FoamRafael ShalashNo ratings yet
- Igc 1 Element - 4Document12 pagesIgc 1 Element - 4Dump FacilityNo ratings yet
- Memo and Health Declaration Form FinalDocument5 pagesMemo and Health Declaration Form FinalALDINNo ratings yet
- List of PpeDocument4 pagesList of PpeRohit AttriNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Manual - Conventional Catering (Nov 17) PDFDocument74 pagesFood Safety Manual - Conventional Catering (Nov 17) PDFAshish GaurNo ratings yet
- 2 CV215-229-01 - OM - S226 051-02 en PDFDocument130 pages2 CV215-229-01 - OM - S226 051-02 en PDFАлександр100% (1)
- MSDS MpiDocument4 pagesMSDS MpiBachrul UlumNo ratings yet