Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pema
Uploaded by
Shang Divina EbradaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pema
Uploaded by
Shang Divina EbradaCopyright:
Available Formats
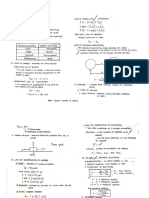
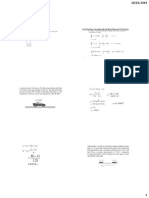
#13 EBRADA, SHARELE D.
MACHINCE AUTOMATION1
10:30-1:30/SATURDAY
BS-EE
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute is a private non-profit organization that oversees the
development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and
personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with
international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits
standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government
agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the
characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions
and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that
carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in
international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, DC. ANSI's
operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operating budget is funded by
the sale of publications, membership dues and fees, accreditation services, fee-based
programs, and international standards programs.
IEC The International Electrotechnical Commission
Logotype of the IEC.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: Commission lectrotechnique
internationale (CEI)) is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that
prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related
technologies collectively known as "electrotechnology". IEC standards cover a vast range of
technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and
office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology and
marine energy as well as many others. The IEC also manages three global conformity
assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its
International Standards. The IEC charter embraces all electrotechnologies including energy
production and distribution, electronics, magnetics and electromagnetics, electroacoustics,
multimedia, telecommunication and medical technology, as well as associated general
disciplines such as terminology and symbols, electromagnetic compatibility (by its Advisory
Committee on Electromagnetic Compatibility, ACEC), measurement and performance,
dependability, design and development, safety and the environment.
Deutsches Institut fr Normung
Logo of the German Institute for Standardization.
Deutsches Institut fr Normung e.V. (DIN; in English, the German Institute for Standardization)
is the German national organization for standardization and is the German ISO member body.
DIN is a Registered German Association (e.V.) headquartered in Berlin. There are currently
around thirty thousand DIN Standards, covering nearly every field of technology.
Founded in 1917 as the Normenausschu der deutschen Industrie (NADI, "Standardisation
Committee of German Industry"), the NADI was renamed Deutscher Normenausschu (DNA,
"German Standardisation Committee") in 1926 to reflect that the organization now dealt with
standardization issues in many fields; viz., not just for industrial products. In 1975 it was
renamed again to Deutsches Institut fr Normung, or 'DIN' and is recognized by the German
government as the official national-standards body, representing German interests at the
international and European levels.
The acronym, 'DIN' is often incorrectly expanded as Deutsche Industrienorm ("German Industry
Standard"). This is largely due to the historic origin of the DIN as "NADI". The NADI indeed
published their standards as DI-Norm (Deutsche Industrienorm). For example, the first
published standard was 'DI-Norm 1' (about tapered pins) in 1918. Many people still mistakenly
associate DIN with the old DI-Norm naming convention.
One of the earliest, and probably the best known, is DIN 476 the standard that introduced
the A-series paper sizes in 1922 adopted in 1975 as International Standard ISO 216.
Common examples in modern technology include DIN and mini-DINconnectors for electronics.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- DC Machines Solved Problems CharulathaDocument59 pagesDC Machines Solved Problems CharulathaShang Divina Ebrada88% (80)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ELECTRONICS Formulas and ConceptsDocument22 pagesELECTRONICS Formulas and ConceptsHarold Antonio100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BS en 01052-4-2000Document17 pagesBS en 01052-4-2000Habib Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 014-Din en 1503 2001 001 Steels Specified in European StandardsDocument9 pages014-Din en 1503 2001 001 Steels Specified in European StandardsQuality MSIPLNo ratings yet
- Electrical High Voltage BushingsDocument49 pagesElectrical High Voltage BushingsShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument46 pagesElectrical EngineeringRaja AbbasNo ratings yet
- How To Solve Worded Problems: G.M.R, Rce, Me1, RMPDocument35 pagesHow To Solve Worded Problems: G.M.R, Rce, Me1, RMPShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- 226 Electrical Machine-IIDocument99 pages226 Electrical Machine-IINuri BerishaNo ratings yet
- Common Mistakes Electrical Grounding and Bonding - JAIME V MENDOZA PDFDocument103 pagesCommon Mistakes Electrical Grounding and Bonding - JAIME V MENDOZA PDFShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- The Art & Science of Protective Relaying - C. Russell Mason - GEDocument357 pagesThe Art & Science of Protective Relaying - C. Russell Mason - GEAasim MallickNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Chemistry PDFDocument50 pagesChap 1 Chemistry PDFErwin Roquid Isaga0% (1)
- Practice Problems For The Mathematics Placement Test 051110Document12 pagesPractice Problems For The Mathematics Placement Test 051110Jessa LapayNo ratings yet
- Mathletics - Multiplications and Divisions - Series E StudentDocument73 pagesMathletics - Multiplications and Divisions - Series E StudentShang Divina Ebrada100% (1)
- Em IIIDocument64 pagesEm IIIGopinath B L NaiduNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument6 pagesPhysics NotesShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- EET306 Tutorial 3 2018 SolutionDocument11 pagesEET306 Tutorial 3 2018 SolutionShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Rupture 140919 PDFDocument57 pagesRupture 140919 PDFlalaNo ratings yet
- Managing Across Borders: Chapter 3: Global ManagementDocument13 pagesManaging Across Borders: Chapter 3: Global ManagementShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- R.A. 7920Document21 pagesR.A. 7920Jezreel P. ImportanteNo ratings yet
- Entrance PhysicsDocument399 pagesEntrance PhysicsBikram Shah77% (22)
- Analytic GeometryDocument110 pagesAnalytic Geometryeric salesNo ratings yet
- DRB Urm PDFDocument1 pageDRB Urm PDFShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Arc Flash Safety PDFDocument76 pagesArc Flash Safety PDFEdwin53No ratings yet
- AC Circuits PDFDocument15 pagesAC Circuits PDFRa SantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dynamics Part 1Document10 pagesIntroduction To Dynamics Part 1Shang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics Vector Mechanics For Engineers: DynamicsDocument3 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics Vector Mechanics For Engineers: DynamicsShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management & Inventory ModelsDocument27 pagesInventory Management & Inventory ModelsShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument2 pagesFluidsShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- EngmanDocument6 pagesEngmanShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- DRB Urm PDFDocument1 pageDRB Urm PDFShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Fluids DsDocument5 pagesFluids DsShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- 24 It Is Use To Disconnect B) : PracticeDocument1 page24 It Is Use To Disconnect B) : PracticeShang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet
- Lan SwitchingDocument49 pagesLan SwitchingrenjithkalaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document16 pagesLab 4CS:GO cFGNo ratings yet
- En 14587-1 (2018) (E) PDFDocument8 pagesEn 14587-1 (2018) (E) PDFhesti1405No ratings yet
- BS - en - 22768-2-1993Document16 pagesBS - en - 22768-2-1993Nyamcz CristianNo ratings yet
- Iec62056 21enDocument9 pagesIec62056 21enAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- TR ISO TS 22003-2017 - PreviewDocument10 pagesTR ISO TS 22003-2017 - Previewalbert DominguezNo ratings yet
- Unit 13Document16 pagesUnit 13Hadeel Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Iec TR 61491-2010Document22 pagesIec TR 61491-2010hertorNo ratings yet
- Description Description: Nvidia CorporationDocument32 pagesDescription Description: Nvidia CorporationluybNo ratings yet
- AE ElectricalDocument14 pagesAE ElectricalAbhay KumarNo ratings yet
- Isa 71.03 1995 PDFDocument18 pagesIsa 71.03 1995 PDFQuang Duan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram 43''Document12 pagesCircuit Diagram 43''Jorge Humberto DuqueNo ratings yet
- BS en 1964-1Document52 pagesBS en 1964-1Muhammad Nasir Siddique0% (1)
- BSI Standards Publication BS EN ISO 15494 - 2015Document10 pagesBSI Standards Publication BS EN ISO 15494 - 2015Kevin AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 SiemensDocument5 pagesIso 9001 Siemensluis_ordoNo ratings yet
- Condensed Metric Practice Guide For CorrosionDocument2 pagesCondensed Metric Practice Guide For CorrosionAli KhalilNo ratings yet
- FSSC 22000 Quality Q - A 20180115Document2 pagesFSSC 22000 Quality Q - A 20180115andik prasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Math0300 Metric Units of LengthDocument2 pagesMath0300 Metric Units of LengthPhoebe BironNo ratings yet
- DD Cen Iso TS 22476-11-2005 (2006)Document20 pagesDD Cen Iso TS 22476-11-2005 (2006)Jorge SalasënNo ratings yet
- NPT Packet System SpecificationsDocument166 pagesNPT Packet System Specificationsmexybaby80% (5)
- The Osi Reference Model Assignment 1 Submitted TO MR: Umair BabarDocument18 pagesThe Osi Reference Model Assignment 1 Submitted TO MR: Umair BabarAhmad Hassan100% (2)
- Kyland Opal10S Datasheet enDocument5 pagesKyland Opal10S Datasheet enSGQNo ratings yet
- De6bc3d6 7a90 48a0 Af4a Bc9f9b631e22.Bsi Training November 2022Document1 pageDe6bc3d6 7a90 48a0 Af4a Bc9f9b631e22.Bsi Training November 2022denoiNo ratings yet
- Material TranslationDocument10 pagesMaterial Translationmichel92748No ratings yet
- Nokia Academy RA4120-60A: Lte Rpess LTE - EPS OverviewDocument69 pagesNokia Academy RA4120-60A: Lte Rpess LTE - EPS Overviewmuhammad fadlun (RAMA)No ratings yet
- IMS Postgraduate Admission 2013 - 14Document2 pagesIMS Postgraduate Admission 2013 - 14Rashid BumarwaNo ratings yet
- Inauguration Style GuideDocument1 pageInauguration Style GuideMark Russell EncarguezNo ratings yet
- Materi 9 - Proses Pembangunan Panggilan GSMDocument69 pagesMateri 9 - Proses Pembangunan Panggilan GSMDhea Ayu AnggrainiNo ratings yet