Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Artificial Neural Network
Uploaded by
Tejaswini SkumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Artificial Neural Network
Uploaded by
Tejaswini SkumarCopyright:
Available Formats
1454629
ASSIGNMENT-1
07/16/2016
Artificial Neural Network
An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is an information processing paradigm that is inspired
by the way biological nervous systems, such as the brain, process information. The key
element of this paradigm is the novel structure of the information processing system. It is
composed of a large number of highly interconnected processing elements (neurons) working
in unison to solve problems.
Advantages:
Adaptive learning: An ability to learn how to do tasks based on the data given for
training or initial experience.
Self-Organisation: An ANN can create its own organisation or representation of the
information it receives during learning time.
Real Time Operation: ANN computations may be carried out in parallel, and special
hardware devices are being designed and manufactured which take advantage of this
capability.
Fault Tolerance via Redundant Information Coding: Partial destruction of a network
leads to the corresponding degradation of performance. However, some network
capabilities may be retained even with major network damage.
Working of an artificial neural network:
The other parts of the art of using neural networks revolve around the myriad of ways
these individual neurons can be clustered together. This clustering occurs in the human mind
in such a way that information can be processed in a dynamic, interactive, and self-organizing
way. Integrated circuits, using current technology, are two dimensional devices with a
limited number of layers for interconnection. This physical reality restrains the types, and
scope, of artificial neural networks that can be implemented in silicon.
Training an artificial neural network:
This basically consists of
Supervised training: In supervised training, both the inputs and the outputs are
provided. The network then processes the inputs and compares its resulting outputs
against the desired outputs
Unsupervised or adaptive training: In unsupervised training, the network is provided
with inputs but not with desired outputs.
Application:
Function approximation, or regression analysis, including time series prediction and
modelling.
Call control- answer an incoming call (speaker-ON) with a wave of the hand while
driving.
Classification, including pattern and sequence recognition, novelty detection and
sequential decision making.
1454629
ASSIGNMENT-1
07/16/2016
Skip tracks or control volume on your media player using simple hand motions- lean
back, and with no need to shift to the device- control what you watch/ listen to.
Data processing, including filtering, clustering, blind signal separation and
compression.
Conclusion:
Since an ANN can capture many kinds of relationships it allows the user to quickly and
relatively easily model phenomena which otherwise may have been very difficult or
impossible to explain otherwise. Today, neural networks discussions are occurring
everywhere. Their promise seems very bright as nature itself is the proof that this kind of
thing works. Yet, its future, indeed the very key to the whole technology, lies in hardware
development. Currently most neural network development is simply proving that the
principal works.
References:
[1] Bradshaw, J.A., Carden, K.J., Riordan, D., 1991. Ecological Applications Using a
Novel Expert System Shell. Comp. Appl. Biosci. 7, 7983.
[2] Lippmann, R.P., 1987. An introduction to computing with neural nets. IEEE Accost.
Speech Signal Process. Mag., April: 4-22.
[3] N. Murata, S. Yoshizawa, and S. Amari, Learning curves, model selection and
complexity of neural networks, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 5, S.
Jose Hanson, J. D. Cowan, and C. Lee Giles, ed. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1993,
pp. 607-614
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Userfiles Financial 14fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 14fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure DP 203 Cert Notes 1712494873Document151 pagesMicrosoft Azure DP 203 Cert Notes 1712494873Tejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- ACME Employee Schedule AssignmentDocument3 pagesACME Employee Schedule AssignmentTejaswini Skumar0% (2)
- Example Coding QuestionsDocument5 pagesExample Coding QuestionsTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document2 pagesQuestion 1Tejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- DW Assignment1Document11 pagesDW Assignment1Tejaswini Skumar100% (4)
- Userfiles Financial 7fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 7fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 11fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 11fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 13fDocument2 pagesUserfiles Financial 13fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 9fDocument2 pagesUserfiles Financial 9fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 3fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 3fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument10 pagesNetworkingTejaswini Skumar100% (1)
- Userfiles Financial 12fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 12fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 5fDocument2 pagesUserfiles Financial 5fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control of Engine Speeds of Hydraulic Excavator (Repaired)Document4 pagesAutomatic Control of Engine Speeds of Hydraulic Excavator (Repaired)Tejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 5fDocument2 pagesUserfiles Financial 5fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 6fDocument2 pagesUserfiles Financial 6fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 1fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 1fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 2fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 2fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 3fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 3fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
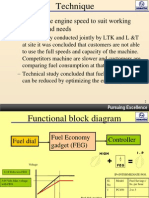
- Optimised The Engine Speed To Suit Working Conditions and NeedsDocument3 pagesOptimised The Engine Speed To Suit Working Conditions and NeedsTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Screen Capture BaisicsDocument27 pagesScreen Capture BaisicsTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- #Include : (For Both Circuits)Document1 page#Include : (For Both Circuits)Tejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- Userfiles Financial 4fDocument3 pagesUserfiles Financial 4fTejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- A Brief Mysql Tutorial: Cse 134A: Web Service Design and Programming Fall 2001 9/28/2001Document18 pagesA Brief Mysql Tutorial: Cse 134A: Web Service Design and Programming Fall 2001 9/28/2001Refat NafiuNo ratings yet
- GRE Vocabulary Flash Cards01Document2 pagesGRE Vocabulary Flash Cards01telecom_numl8233No ratings yet
- 0 000 0 0embedded System 8th Sem E& C Notes Written by Arunkumar G, Lecturer, STJIT, RanebennurDocument1 page0 000 0 0embedded System 8th Sem E& C Notes Written by Arunkumar G, Lecturer, STJIT, RanebennurTejaswini Skumar100% (1)
- Secondary Burst Cache Design Using The Idt71024 (As Cache-Data Srams and The Cache-Tag Sram)Document2 pagesSecondary Burst Cache Design Using The Idt71024 (As Cache-Data Srams and The Cache-Tag Sram)Tejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- 634124997373765000Document18 pages634124997373765000Tejaswini SkumarNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Secure Coding - PHP v.1.1Document137 pagesSecure Coding - PHP v.1.1Bond JamesNo ratings yet
- Ds Series Engine Combustion Analysis SystemDocument4 pagesDs Series Engine Combustion Analysis SystemF. Z.No ratings yet
- Advance ExcelDocument40 pagesAdvance ExcelSaurabh SainiNo ratings yet
- Manual Microprogel TC 323: KontaktinformationDocument10 pagesManual Microprogel TC 323: Kontaktinformationsyed maroof aliNo ratings yet
- Es Unit 2 MCQDocument7 pagesEs Unit 2 MCQPradnya NavaleNo ratings yet
- Integrated CircuitsDocument24 pagesIntegrated CircuitsmuktikantaNo ratings yet
- Mpi Lab1Document6 pagesMpi Lab1abdul shaggyNo ratings yet
- Exam (2000) AnswersDocument2 pagesExam (2000) AnswersassnadNo ratings yet
- Project 1Document12 pagesProject 1John SmithNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Registeration No: 20-Se-07, 20-Se-15 Section: Alpha Subject: Fmse Departement: Software EngineeringDocument9 pagesSubmitted By: Registeration No: 20-Se-07, 20-Se-15 Section: Alpha Subject: Fmse Departement: Software EngineeringRida ArshadNo ratings yet
- Light Meter: Operation ManualDocument26 pagesLight Meter: Operation ManualMarcos Calixto LopezNo ratings yet
- Mca 303 PDFDocument396 pagesMca 303 PDFRadha IshuNo ratings yet
- Azure CLIDocument134 pagesAzure CLIjotosi3304No ratings yet
- Discovering SubdomainsDocument4 pagesDiscovering SubdomainsRadhi ShatobNo ratings yet
- IT General Control Audit ProgramDocument20 pagesIT General Control Audit ProgramMohamad JbrNo ratings yet
- Tafl KCS 402 Cia-I 2019-20Document2 pagesTafl KCS 402 Cia-I 2019-20vikNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-07-03 at 17.23.05Document1 pageScreenshot 2023-07-03 at 17.23.05Invincible DestroyerNo ratings yet
- Samsung Galaxy A50 - SM-A505F - Administration GuideDocument20 pagesSamsung Galaxy A50 - SM-A505F - Administration GuideandresenriquelunamobileNo ratings yet
- Python Dictionary and TupleDocument4 pagesPython Dictionary and TupleStory TellingNo ratings yet
- Basic iOS Cheat Sheet For Android Developers v4 Jakub ChmielDocument4 pagesBasic iOS Cheat Sheet For Android Developers v4 Jakub ChmielSivam SelvanNo ratings yet
- Pencil Code (Coffeescript/javascript) : Class 7Document49 pagesPencil Code (Coffeescript/javascript) : Class 7Yashoda SNo ratings yet
- Corporate PPT Template 2Document5 pagesCorporate PPT Template 2Suyog BhujbalNo ratings yet
- HW User Manual (CZNEWTON)Document14 pagesHW User Manual (CZNEWTON)PETER YINGNo ratings yet
- Mansi Gupta Resume 2016Document1 pageMansi Gupta Resume 2016mansiNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Unit2 - 2.1Document23 pagesMicrocontroller Unit2 - 2.1Priyanka S LNo ratings yet
- Ecg Holter Recorder Via Mobile PhoneDocument5 pagesEcg Holter Recorder Via Mobile PhoneDulanjalee KatulandaNo ratings yet
- XPED JobisDocument3 pagesXPED JobisAnonymous hsRemjfwq5No ratings yet
- Data Pipeline Essentials: See Ya LaterDocument6 pagesData Pipeline Essentials: See Ya LaterDevNo ratings yet
- Mobile VirusesDocument2 pagesMobile Virusesk gowtham kumarNo ratings yet
- j1339 PIC Library MicrochipDocument36 pagesj1339 PIC Library Microchipcarlos pratoNo ratings yet