Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENGG252 Fluids Lab Manual 2016 Exp-1 Hydrostatics
Uploaded by
JeromeClintonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGG252 Fluids Lab Manual 2016 Exp-1 Hydrostatics
Uploaded by
JeromeClintonCopyright:
Available Formats
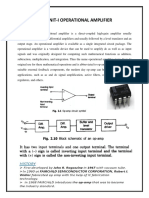
EXPERIMENTS 1A, 1B, 1C and 1D:
HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON A PLANE SURFACE
1.
Aim
To investigate the hydrostatic force acting on a submerged rectangular plane surface and
compare experimental results with those obtained by theoretical analysis.
2.
Theory
The hydrostatic force F acting on a flat surface of any shape and orientation, and submerged in a
liquid, is given by:
F g hc A
(1.1)
where is the mass density of the liquid, g is the gravitational acceleration, A is the total
submerged area of the plane surface, and hc the vertical depth of the centroid of the submerged
area below the free liquid surface. The line of action of F is located at a distance y p along the
inclined plane from the free surface, such that
y p yc
I xx,c
(1.2)
A yc
where y c is the distance of the centroid along the inclined plane below the free surface and Ixx,c is
the second moment of area of the plane surface A about its centroid.
Therefore, note that the Centre of Pressure will always lie at a distance
I xx ,c
below the centroid of
Ay c
the area. The hydrostatic force F acts at right angles to the surface as shown in Figure 1.1.
Free Liquid Surface
hc
yc
yp
F = g hc A
Side
View
Flat Surface of
arbitrary shape,
Area A
Figure 1.1
Plan
View
Centre of
Pressure CP
Centroid
C
Hydrostatic Force on Plane Submerged Surface
Fluids Lab. Manual 2016 A/Prof M Sivakumar
(Contributions made to the previous versions by A/Profs M J Boyd, W K Soh and Dr Ajit Godbole are acknowledged)
Page 1
EXPERIMENTS 1A, 1B, 1C and 1D:
HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON A PLANE SURFACE
3.
Experimental Apparatus (1A, 1B, 1C and 1D)
The apparatus shown in Figure 1.2 consists of a perspex quadrant mounted so as to rotate on a
knife-edge fulcrum, about which the moments are measured. The curved surfaces have their radii
centred on the fulcrum; consequently all hydrostatic forces on them, acting normal to the curved
surfaces, have zero moment about the fulcrum.
Fulcrum
Jockey
Weight
Slot for hanging
pan + masses
Perspex
Quadrant with
Depth Scale
Test surface
Stop-Cock
Spirit Level
Leveling
Screws
Fig. 1.2
Experimental apparatus 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D
Fulcrum
Jockey
Weight
hd
m
hc
hp
Water level h
C
CP
F = g hc A
Figure 1.3 Schematic diagram Experimental Apparatus 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D
Fluids Lab. Manual 2016 A/Prof M Sivakumar
(Contributions made to the previous versions by A/Profs M J Boyd, W K Soh and Dr Ajit Godbole are acknowledged)
Page 2
EXPERIMENTS 1A, 1B, 1C and 1D:
HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON A PLANE SURFACE
Only the hydrostatic force on the front rectangular face of the quadrant produces a moment about
the fulcrum. All other forces either cancel each other or go through the fulcrum. The force on the
rectangular face is measured by balancing the moment due to the hydrostatic force with the
moment due to weights placed on the beam or on the balance pan. Since the rectangular face is
vertical y=h.
For static equilibrium
Mfulcrum = 0
(1.3)
Measured moment due to weights
Mexp = m g X
(1.4)
Theoretical moment due to hydrostatic force Mtheory
(1.5)
= F ( h p + h d)
where hd is the height of fulcrum above the free water surface.
Table 1.1 Dimensions of Apparatus
Equipment
1A, 1B, 1C, 1D
X (mm)
Plane face dimensions (mm)
Breadth (b)
Depth (d)
75
100
275
Face
Fully
Submerged
( hc hd ) (mm)
Face
Partially
Submerged *
(2 hc hd )(mm)
150
200
* Take special note of this case.
4. Experimental Procedure
(i)
Level the tank using the adjustable feet and spirit level.
(ii)
Move the counter balance jockey weight until the balance arm is horizontal and lock it with
the help of the locknut.
(iii)
Close the drain cock and pour water until the level reaches the bottom edge of the quadrant.
(iv) Place the balance pan of 50 g mass on the specified slot of the arm. Add water slowly into
the tank until the balance arm is horizontal.
(v)
Record the water level (h) on the quadrant and the weight on the balance pan. Fine
adjustment of the water level can be achieved by overfilling and slowly draining, using the
stop-cock or using a pipette.
(vi) Repeat the above for each increment of 50g mass til the total mass is 350g (a minimum of 7
water readings).
(vii) Add some more water to bring the arm in balance keeping total mass at 350g.
(viii) Now remove the water till the balance arm becomes level and take the water level reading
again.
(ix) Now start removing each decrement of mass noting mass and water levels until all the mass
has been removed.
Fluids Lab. Manual 2016 A/Prof M Sivakumar
(Contributions made to the previous versions by A/Profs M J Boyd, W K Soh and Dr Ajit Godbole are acknowledged)
Page 3
EXPERIMENTS 1A, 1B, 1C and 1D:
HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON A PLANE SURFACE
5. Experimental Measurements
Date:___________________________ Group Name:________________________
Student names: (Surname, First name)
______________________________________
______________________________________
______________________________________
______________________________________
Equipment used: (Specify 1A, 1B, 1C or 1D) Circle one.
Water Temperature: Start:__________oC
Finish:_____________oC
Table 1.2 Observations
Water level h (m)
Obs
Total
Mass
(kg)
Add
Remove
hd
hc
hp
(m)
(m)
(m)
Mean
Theoretical
Hydrostatic
Force F (N)
Eqn. 1.1
Moment about
Fulcrum (Nm)
M
exp
theory
Eqn.1.4
Eqn.1.5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
6.
Calculations to be undertaken during lab. class and should be shown to the tutor
(i)
Undertake hand calculations for one observation.
(ii)
Complete section 5 in the EXCEL spread sheet shown in the computer screen.
(iii)
Plot Mtheory versus Mexp.
(iv)
Plot of (a) F versus hc and (b) M versus hc.
(v)
Save the excel file in a USB drive for your records. (Must bring your own USB drive)
7.
Discussion and answer to questions
(i)
Discuss reasons for any discrepancies between experimental and theoretical results of
the Moment about the fulcrum.
(ii)
Comment on the variation of F and M with depth below the surface.
(iii)
Derivations of equations for each of the following:
Fully Submerged Flat Surface: (a) Hydrostatic Force F
(b) Theoretical Moment Mtheory
Partially Submerged Flat Surface: (a) Hydrostatic Force F
(b) Theoretical Moment Mtheory
Fluids Lab. Manual 2016 A/Prof M Sivakumar
(Contributions made to the previous versions by A/Profs M J Boyd, W K Soh and Dr Ajit Godbole are acknowledged)
Page 4
You might also like
- LV07 KDocument11 pagesLV07 KSalman Shah83% (6)
- Hydrostatic Force - Centre of Pressure Lab ReportDocument10 pagesHydrostatic Force - Centre of Pressure Lab ReportMartin83% (18)
- Stadium Planning and Construction.Document60 pagesStadium Planning and Construction.shrikant96% (68)
- Center of PressureDocument13 pagesCenter of Pressurehazheer188% (33)
- Flow-Induced Vibrations: An Engineering GuideFrom EverandFlow-Induced Vibrations: An Engineering GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Me313 3W08Document3 pagesMe313 3W08nidhalsaadaNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface-8Document2 pagesHydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface-8Fahad AreebNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Hydrostatic Force and Center of Pressure: Lecturer: T.ADocument17 pagesExperiment 1 Hydrostatic Force and Center of Pressure: Lecturer: T.AeidalinNo ratings yet
- Fmcpra2 Lab Report PDFDocument20 pagesFmcpra2 Lab Report PDFNzeza Carine100% (1)
- EXPERIMENT HydrostaticDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT HydrostaticRegine OlayaNo ratings yet
- بلا عنوانDocument13 pagesبلا عنوانdes33uqNo ratings yet
- 01.1 Experiment #1 Hydrostatic PressureDocument4 pages01.1 Experiment #1 Hydrostatic PressureحيدرNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Exp 4Document8 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Exp 4Muhammad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- ERT 205 Lab 1Document16 pagesERT 205 Lab 1Ang Kien HauNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure - Fluid-Mechanics-Lab-Manual-15-23Document9 pagesHydrostatic Pressure - Fluid-Mechanics-Lab-Manual-15-23Yasir A. Al-ShataifNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force and Center of PressureDocument7 pagesHydrostatic Force and Center of PressureIsraafil Ahmad0% (1)
- AbstractDocument9 pagesAbstractEssam Ahmed Abd MeguidNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual MOIDocument44 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Manual MOIIsaac NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic ForceDocument6 pagesHydrostatic ForceAhmad MuzakkirNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Expt 2Document19 pagesHydraulics Expt 2Besufkad YirguNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: τ = μ (du/dy)Document7 pagesAbstract:: τ = μ (du/dy)Yahya IsiedNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Hydrostatic ForceDocument14 pagesMeasurement of Hydrostatic ForceIhsan Samoh เพี่อนดีดี100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Report.Document17 pagesFluid Mechanics Report.e'mir danielNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic PressureDocument6 pagesHydrostatic Pressurebkewill6No ratings yet
- 2 - Hydrostatic PressureDocument8 pages2 - Hydrostatic PressureDastm BgraNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Lab ManualsDocument53 pagesGroup 5 Lab ManualsMUHAMMAD ALMASNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Hydrostatic ForceDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Hydrostatic ForceVimal Mathivanan100% (2)
- Hydrostatic Pressure CenterDocument19 pagesHydrostatic Pressure CenterTinotendaNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic PressureDocument20 pagesHydrostatic PressureHaziq Itik King67% (3)
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Theodore James RomoNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure Experiment On Armfield F1-12 Apparatus: Name: Fares Girum Class: 11A R.NO: 20Document16 pagesHydrostatic Pressure Experiment On Armfield F1-12 Apparatus: Name: Fares Girum Class: 11A R.NO: 20fares girumNo ratings yet
- ملزمة Hydraulics Lab 2Document111 pagesملزمة Hydraulics Lab 2CHEL TAK100% (1)
- FM Fall 2019 E1 PDFDocument8 pagesFM Fall 2019 E1 PDFUZAIR MANSOORNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Fluid Mechanics LabDocument6 pagesExperiment 1 Fluid Mechanics LabjameeloNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 - Hydrostatic PressureDocument18 pagesPresentation 1 - Hydrostatic PressureMandisa ZibulaNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure (Document10 pagesHydrostatic Pressure (Ahmad Abdullah0% (1)
- 1 - Hydrostatic PressureDocument15 pages1 - Hydrostatic PressureromasokyNo ratings yet
- G2 - Hydrostatic Pressure & ForcesDocument18 pagesG2 - Hydrostatic Pressure & ForcesAnnisa ShabrinaNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Equipment Set UpDocument3 pagesPart 1: Equipment Set UpNur Syahirah Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Student Outcomes (Sos) Addressed by The Activity: Mechanics of Fluid Laboratory ManualDocument6 pagesStudent Outcomes (Sos) Addressed by The Activity: Mechanics of Fluid Laboratory ManualRainier RamosNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic ThrustDocument9 pagesHydrostatic ThrustAngelica Gicom100% (1)
- Thermo-Fluid Lab Prof. Taha AldossDocument5 pagesThermo-Fluid Lab Prof. Taha AldossAbo AusNo ratings yet
- CC501 - Lab - 1 HydraulicDocument11 pagesCC501 - Lab - 1 HydraulicMuhammad Azizul100% (1)
- Impact of JetDocument12 pagesImpact of JetShafizNo ratings yet
- "Hydrostatic Pressure On Submerged Surfaces": Civil Engneering Department Fluid Mechanicks (CIV412)Document5 pages"Hydrostatic Pressure On Submerged Surfaces": Civil Engneering Department Fluid Mechanicks (CIV412)amalayman2003246No ratings yet
- Hydrostatic G4 PDFDocument23 pagesHydrostatic G4 PDFMuhammad FarisNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1 - Hydrostatic Pressure - Applied Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument1 pageExperiment #1 - Hydrostatic Pressure - Applied Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualgebremichaelNo ratings yet
- DR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 4Document48 pagesDR Ahmed Soil Mechanics Notes Chapter 4Usman PervaizNo ratings yet
- CE 2020 - Fluid Mechanics LaboratoryDocument67 pagesCE 2020 - Fluid Mechanics LaboratoryMd.Tarequl IslamNo ratings yet
- Impact of Jet - Ec2203a1b - Group 3Document10 pagesImpact of Jet - Ec2203a1b - Group 3idrisNo ratings yet
- Khulna University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument9 pagesKhulna University of Engineering & Technology17044 AZMAIN IKTIDER AKASHNo ratings yet
- EN2711-Lab A-1 (WR) Centre of PressureDocument9 pagesEN2711-Lab A-1 (WR) Centre of PressureVanessa Boey Khai LingNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic PressureDocument20 pagesHydrostatic PressureShoby Kesavan PillaiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document6 pagesExperiment 1Nor Farah AlwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Effective StressDocument97 pagesChapter 3 Effective Stressanon_917763370No ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Hydrostatic Force and Center of PressureDocument10 pagesExperiment 1 Hydrostatic Force and Center of Pressureجلال البركانيNo ratings yet
- Experiment (1) : Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface: ObjectivesDocument25 pagesExperiment (1) : Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface: ObjectivesBatool Al-kharabshehNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Expirements: Submitted By: Alipaspas, Jill Anne Sumitted To: Eng. Clark Jason AmoresDocument16 pagesLaboratory Expirements: Submitted By: Alipaspas, Jill Anne Sumitted To: Eng. Clark Jason AmoresJudd CortezNo ratings yet
- Bsen 3310 Hydrostatic Pressure Lab 3Document9 pagesBsen 3310 Hydrostatic Pressure Lab 3api-505242963100% (1)
- Exp 6 Hydrostatic PressureDocument15 pagesExp 6 Hydrostatic PressureGriezmann HaziqNo ratings yet
- Piping and Plumbing Symbols ListDocument1 pagePiping and Plumbing Symbols Listsiddarth amaravathiNo ratings yet
- Ic NotesDocument67 pagesIc NotesVijaya Kumar VadladiNo ratings yet
- 193-Cable Tray QtyDocument4 pages193-Cable Tray QtyprkshshrNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mek I-9 OktDocument2 pagesTugas Mek I-9 OktAlifani SofiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Flow Induced by Air-Bubble SystemsDocument16 pagesAnalysis of The Flow Induced by Air-Bubble SystemsStephany CamacaroNo ratings yet
- Letter B Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLetter B Lesson Planapi-300212612100% (1)
- INF 370 Lab ManualDocument15 pagesINF 370 Lab ManualDr.nagwa yaseenNo ratings yet
- SPPU Report FormatDocument50 pagesSPPU Report FormatAmit Devidas AherNo ratings yet
- TAPCON® 240: Voltage Regulator For Regulating TransformersDocument6 pagesTAPCON® 240: Voltage Regulator For Regulating TransformerscastrojpNo ratings yet
- Project Profile AdamaDocument4 pagesProject Profile AdamaYohannes AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Hannah Van GeeresteinNo ratings yet
- How To "Revert-Back" To "Previous-Version"???: Build 1 Testing DeploymentDocument19 pagesHow To "Revert-Back" To "Previous-Version"???: Build 1 Testing DeploymentClaudiu Stefan HaiduNo ratings yet
- Non-Parametric TestsDocument1 pageNon-Parametric TestssdvdsvNo ratings yet
- Parrot: by Alan BrownjohnDocument2 pagesParrot: by Alan BrownjohnPADUMI SASIKALA50% (2)
- Updated Eva ResumeDocument1 pageUpdated Eva Resumeapi-534826411No ratings yet
- Karatina University: University Examinations 2017/2018 ACADEMIC YEARDocument4 pagesKaratina University: University Examinations 2017/2018 ACADEMIC YEARKimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Pijat BayiDocument5 pagesJurnal Internasional Pijat BayiAna SafitriNo ratings yet
- BARAKA Modelling ProposalDocument9 pagesBARAKA Modelling Proposalmurali.5482No ratings yet
- Ludo (Sorry) - Game StrategyDocument8 pagesLudo (Sorry) - Game Strategysuperyoopy100% (1)
- MODEL: SC330 Industrial Range Powered by Cummins: Diesel Generating Set 400/230 V - 50 HZ - 3phaseDocument4 pagesMODEL: SC330 Industrial Range Powered by Cummins: Diesel Generating Set 400/230 V - 50 HZ - 3phaseDefly GustiNo ratings yet
- Roundel 1961-06 Vol 13 No 5Document36 pagesRoundel 1961-06 Vol 13 No 5TateNo ratings yet
- Survey of Mechanical Working: A. IntroductionDocument4 pagesSurvey of Mechanical Working: A. IntroductionAsif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Business Research Methods 9th Edition Zikmund Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Business Research Methods 9th Edition Zikmund Solutions Manual PDFerichuel33a100% (14)
- The Influence of Social Media On Crowd Behavior and The Operational EnvironmentDocument78 pagesThe Influence of Social Media On Crowd Behavior and The Operational EnvironmentangryTXNo ratings yet
- Cover Modul 4 TMJ 2012Document7 pagesCover Modul 4 TMJ 2012Haura Nadya AmaliaNo ratings yet
- THMT 3312: Research Methods For Tourism & Hospitality ManagementDocument13 pagesTHMT 3312: Research Methods For Tourism & Hospitality Managementmilrosebatilo2012No ratings yet
- ATS Monitoring Device InstructionsDocument25 pagesATS Monitoring Device InstructionsVinhNo ratings yet
- 2014 04 14 Veterinary Instrumentation Presented The Simon Award 2014 For Outstanding Contribution in The Field of Veterinary Surgery To Michael Guilliard MA, VetMB, CertSAO, FRCVSDocument2 pages2014 04 14 Veterinary Instrumentation Presented The Simon Award 2014 For Outstanding Contribution in The Field of Veterinary Surgery To Michael Guilliard MA, VetMB, CertSAO, FRCVSHenry ScheinNo ratings yet