Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2016 12 Lyp Physics Board Set 02 All India Ques
Uploaded by
Chandan PatraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2016 12 Lyp Physics Board Set 02 All India Ques
Uploaded by
Chandan PatraCopyright:
Available Formats
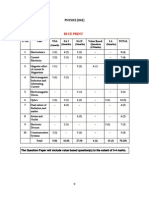
Physics
Code No. 1/2
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Set: 2
Maximum Marks: 100
General Instructions
(i) There are 26 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and
Section E.
(iii) Section A contains five questions of one mark each, Section B contains five questions of
two marks each, Section C contains twelve questions of three marks each, Section D
contains one value based question of four marks and Section E contains three questions
of five marks each.
(iv) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question
of two marks, one question of three marks and all the three questions of five marks
weightage. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
Q.1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Section A
In what way is the behaviour of a diamagnetic material different from that of a
paramagnetic, when kept in an external magnetic field?
The plot of the variation of potential difference across a combination of three identical
cells in series, versus current is shown below. What is the emf and internal resistance
of each cell?
Why does sun appear red at sunrise and sunset?
A charge 'q' is moved from a point A above a dipole of dipole moment 'p' to a point B
below the dipole in equatorial plane without acceleration. Find the work done in the
process.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Q5
Name the essential components of a communication system.
Section B
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
Q10
Calculate the de-Broglie wavelength of the electron orbitting in the n = 2 state of
hydrogen atom.
A battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 is connected to a 4 resistor as
shown in the figure.
(a) Show that a voltmeter when placed across the cell and across the resistor, in turn,
gives the same reading.
(b) To record the voltage and the current in the circuit, why is voltmeter placed in
parallel and ammeter in series in the circuit?
Define ionization energy. How would the ionization energy change when electron in
hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle of mass 200 times that of electron but having
the same charge?
OR
Calculate the shortest wavelength of the spectral lines emitted in Balmer series.
[Given Rydberg constant, R = 10 7 m 1 ]
Define modulation index. Why is it kept low? What is the role of a bandpass filter?
A ray PQ incident normally on the refracting face BA is refracted in the prism BAC
made of material of refractive index 1.5. Complete the path of ray through the prism.
From which face will the ray emerge? Justify your Answer.
Section C
Q11
(i) Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Q12
(ii) How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase in
temperature? Explain.
(a) Write the basic nuclear process involved in the emission of + in a symbolic form,
by a radioactive nucleus.
(b) In the reactions given below:
( i ) 116C zy B + x + v
( ii )
Q13
12
6
20
c
C + 12
6 C a Ne + b He
Find the values of x, y, and z and a, b and c.
Sketch the graphs showing variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident
radiations for two photosensitive materials A and B having threshold frequencies
v A > vB .
(i) In which case is the stopping potential more and why?
(ii) Does the slope of the graph depend on the nature of the material used? Explain.
Q14
(i) State law of Malus.
(ii) Draw a graph showing the variation of intensity (I) of polarised light transmitted
by an analyser with angle () between polariser and analyser.
(iii) What is the value of refractive index of a medium of polarising angle 60?
Q15
Define an equipotential surface. Draw equipotential surfaces:
(i) in the case of a single point charge and
(ii) in a constant electric field in Z-direction.
Why the equipotential surfaces about a single charge are not equidistant?
(iii) Can electric field exist tangential to an equipotential surface? Give reason.
Use Biot-Savart law to derive the expression for the magnetic field on the axis of a
current carrying circular loop of radius R.
Draw the magnetic field lines due to a circular wire carrying current I.
Define the term wave front. State Huygen's principle.
Consider a plane wave front incident on a thin convex lens. Draw a proper diagram to
show how the incident wave front traverses through the lens and after refraction
focusses on the focal point of the lens, giving the shape of the emergent wave front.
OR
Explain the following, giving reasons:
(i) When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the
reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident
frequency.
(ii) When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this
decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
(iii) In the wave picture of light, intensity of light is determined by the square of the
amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of
light?
Q16
Q17
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Q18
Q19
Q20
Q21
Q22
Q23
Q24
For a CE-transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector resistance of
2 k is 2 V. Suppose the current amplification factor of the transistor is 100, find the
input signal voltage and base current, if the base resistance is 1 k.
(i) Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
(a) suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation.
(b) produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons.
(ii) Why does a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of charging or
discharging a capacitor? Write the necessary expression to explain this
observation.
(i) Which mode of propagation is used by shortwave broadcast services having
frequency range from a few MHz upto 30 MHz? Explain diagrammatically how long
distance communication can be achieved by this mode.
(ii) Why is there an upper limit to frequency of waves used in this mode?
(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier
potential in a pn junction.
(ii) Draw the circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier and explain its working.
(i) When an AC source is connected to an ideal inductor show that the average power
supplied by the source over a complete cycle is zero.
(ii) A lamp is connected in series with an inductor and an AC source. What happens to
the brightness of the lamp when the key is plugged in and an iron rod is inserted
inside the inductor? Explain.
Section -D
Ram is a student of class X in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a
dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could
light the bulb and see the objects on the road. He, however, did not know how this
device works. he asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an
opportunity to explain the working to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(a) State the principle and working of a dynamo.
(b) Write two values each displayed by Ram and his school teacher.
Section -E
(i) Derive the mathematical relation between refractive indices n1 and n2 of two radii
and radius of curvature R for refraction at a convex spherical surface. Consider the
object to be a point since lying on the principle axis in rarer medium of refractive index
n1 and a real image formed in the denser medium of refractive index n2. Hence, derive
lens maker's formula.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Q25
Q26
(ii) Light from a point source in air falls on a convex spherical glass surface of
refractive index 1.5 and radius of curvature 20 cm. The distance of light source
from the glass surface is 100 cm. At what position is the image formed?
OR
(a) Draw a labelled ray diagram to obtain the real image formed by an astronomical
telescope in normal adjustment position. Define its magnifying power.
(b) You are given three lenses of power 0.5 D, 4 D and 10 D to design a telescope.
(i) Which lenses should be used as objective and eyepiece? Justify your Answer.
(ii) Why is the aperture of the objective preferred to be large?
(i) Use Gauss's law to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane
sheet. What is the direction of field for positive and negative charge densities?
(ii) Find the ratio of the potential differences that must be applied across the parallel
and series combination of two capacitors C1 and C2 with their capacitances in the
ratio 1 : 2 so that the energy stored in the two cases becomes the same.
OR
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having surface charge densities + and
are separated by a distance d in air, find the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer side of the plates. Specify
the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of Radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have same
surface charge density . If they are connected to each other with a conducting
wire, inn which direction will the charge flow and why?
(i) Draw a labelled diagram of a step-down transformer. State the principle of its
working.
(ii) Express the turn ratio in terms of voltages.
(iii) Find the ratio of primary and secondary currents in terms of turn ratio in an ideal
transformer.
(iv) How much current is drawn by the primary of a transformer connected to 220 V
supply when it delivers power to a 110 V 550 W refrigerator?
OR
(a) Explain the meaning of the term mutual inductance. Consider two concentric
circular coils, one of radius r1 and the other of radius r2 (r1< r2) placed coaxially
with centres coinciding with each other. Obtain the expression for the mutual
inductance of the arrangement.
(b) A rectangular coil of area A, having number of turns N is rotated at 'f' revolutions
per second in a uniform magnetic field B, the field being perpendicular to the coil.
Prove that the maximum emf induced in the coil is 2 f NBA.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- Class 12 Pre Board Exam 2022-23Document4 pagesClass 12 Pre Board Exam 2022-23VishwasNo ratings yet
- 2013 PDFDocument7 pages2013 PDFnandagopanNo ratings yet
- 12 2005 Physics 1Document6 pages12 2005 Physics 1Shudhanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- PB 2 Physics XII 2020-21Document5 pagesPB 2 Physics XII 2020-21Atul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Sample Papers Class 12 PhysicsDocument53 pagesSample Papers Class 12 Physics0910ashuNo ratings yet
- Sri Kumaran Children’s Home - CBSE Class XII Physics Pre-Board Examination 2015 - 2016Document6 pagesSri Kumaran Children’s Home - CBSE Class XII Physics Pre-Board Examination 2015 - 2016tranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- CBSE 12th Physics 2013 Unsolved PaperDocument6 pagesCBSE 12th Physics 2013 Unsolved PaperSunita AnandNo ratings yet
- Phy Set-2 QPDocument5 pagesPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniNo ratings yet
- 2010Document30 pages2010zelNo ratings yet
- CBSE MODEL TEST PAPER 2009 – 2010Document1 pageCBSE MODEL TEST PAPER 2009 – 2010Maulik KarasaliyaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Physics PB I 2023-24Document6 pagesQuestion Paper Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2Document7 pagesClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2kamali.v777No ratings yet
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Document4 pagesFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Physics Set 9: Section - ADocument4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Physics Set 9: Section - AI dont have a NameNo ratings yet
- CBSE PHYSICS Exam Derivations and long answer questionsDocument23 pagesCBSE PHYSICS Exam Derivations and long answer questionsAham GtyNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE PAPER-09 (Unsolved)Document3 pagesSAMPLE PAPER-09 (Unsolved)ShantanuSinghNo ratings yet
- Modern Middle East Physics ExamDocument9 pagesModern Middle East Physics ExamNazneen AliNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Physics Set 3: All Questions Are Compulsory. There Are 27 Questions in AllDocument4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Physics Set 3: All Questions Are Compulsory. There Are 27 Questions in AllI dont have a NameNo ratings yet
- PB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Document4 pagesPB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Uday SinghNo ratings yet
- PM Shri Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPM Shri Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024maxers.xdNo ratings yet
- Test Paper 8Document8 pagesTest Paper 8rajeshsharma4121No ratings yet
- Physice 2010 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFDocument6 pagesPhysice 2010 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFSunita AnandNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Document7 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023shagun sinhaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Joshi Classes: A Premier Institute for Quality EducationDocument15 pagesJoshi Classes: A Premier Institute for Quality EducationPaavni SharmaNo ratings yet
- QP Xii Phy PB1 2023-24Document7 pagesQP Xii Phy PB1 2023-24Puskar SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics Spectrum - PsDocument46 pagesPhysics Spectrum - PsiitforumNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Document6 pagesClass 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- Physice 2011 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFDocument5 pagesPhysice 2011 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFSunita AnandNo ratings yet
- Q Bank MLL Cbse 2022-23Document5 pagesQ Bank MLL Cbse 2022-23Deepesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Class XII 2023 2024 Prelims IDocument10 pagesClass XII 2023 2024 Prelims ITanishkha RaajNo ratings yet
- CBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PaperDocument7 pagesCBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PapermisostudyNo ratings yet
- LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS SURE SHOTDocument50 pagesLONG ANSWER QUESTIONS SURE SHOTPiyush ManeNo ratings yet
- LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS SURE SHOTDocument50 pagesLONG ANSWER QUESTIONS SURE SHOTAnant GiriNo ratings yet
- Phy2 PDFDocument8 pagesPhy2 PDFkevin786786No ratings yet
- CbseDocument5 pagesCbserockstar104No ratings yet
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFDocument14 pagesSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- 7 SQPDocument7 pages7 SQPlanfury45No ratings yet
- CBSE Class XII Physics Sample PaperDocument7 pagesCBSE Class XII Physics Sample PaperAbhimanyu MalhotraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1PallavNo ratings yet
- XII-Physics Original PDFDocument13 pagesXII-Physics Original PDFDeepNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics First Term Paper 22-23 PDFDocument8 pagesClass 12 Physics First Term Paper 22-23 PDFlets physicsNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2010: Time Allowed: 3 HoursDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2010: Time Allowed: 3 HoursTanmoy MitraNo ratings yet
- 12 Lyp Physics s1Document7 pages12 Lyp Physics s1jashwanth kumar58No ratings yet
- Cbse 12th Question Bank PhysicsDocument6 pagesCbse 12th Question Bank Physicsramayodi223No ratings yet
- Xii-Cbse-Physicspreboardexam (03032024) 240303 143620Document8 pagesXii-Cbse-Physicspreboardexam (03032024) 240303 143620sramalingam.ecbNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument4 pagesPHYSICSxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice ExamDocument4 pagesPhysics Practice ExamDETECTIVE UNKNOWNNo ratings yet
- Phy 2015Document5 pagesPhy 2015ANASNo ratings yet
- PB - I Physics Xii 2023-24Document7 pagesPB - I Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091No ratings yet
- CLASS 12 PRE BOARD PAPER PhysicsDocument13 pagesCLASS 12 PRE BOARD PAPER Physicsaditya singhNo ratings yet
- Physice 2010 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFDocument6 pagesPhysice 2010 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFSunita AnandNo ratings yet
- QP - Physics - Xii - SPDocument7 pagesQP - Physics - Xii - SPriteshsamrath440No ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFDocument9 pagesCbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFIshika SinghNo ratings yet
- SBR Pu Ii Model PapersDocument39 pagesSBR Pu Ii Model Paperstechwithtarun477No ratings yet
- CBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006Document5 pagesCBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006venkithebossNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INo ratings yet
- SE Lab File - NotesHub2017-11-27 12 - 44 - 37Document50 pagesSE Lab File - NotesHub2017-11-27 12 - 44 - 37aryaNo ratings yet
- Software OdtDocument1 pageSoftware OdtChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Examination & Syllabus OF: Kashmere Gate DELHI 110006Document16 pagesScheme of Examination & Syllabus OF: Kashmere Gate DELHI 110006Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Text1 (Lines With Upper)Document1 pageText1 (Lines With Upper)Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Project File: Chandan PatraDocument34 pagesComputer Science Project File: Chandan PatraChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Stacks 1Document3 pagesStacks 1Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Circle ArrayDocument3 pagesCircle ArrayChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument1 pageSoftwareChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Text3 (Copy Except Upper Vow)Document1 pageText3 (Copy Except Upper Vow)Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Write A CDocument29 pagesWrite A CChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- C++ Queue ProgramDocument3 pagesC++ Queue ProgramAnonymous MLUUN9SeNo ratings yet
- Text2 (Convert To Upper)Document1 pageText2 (Convert To Upper)Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- 2 NDDocument1 page2 NDChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Stacks 2Document3 pagesStacks 2Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- CircularDocument4 pagesCircularChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Vii. Observ@Tions: Standardization of HCL SolutionDocument2 pagesVii. Observ@Tions: Standardization of HCL SolutionChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Objective of VisualDocument2 pagesObjective of VisualChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Binary (10pt)Document12 pagesBinary (10pt)Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument18 pagesComputerChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document38 pagesBinder 1Chandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Document10 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Aaditya Divyam100% (1)
- ProjectDocument30 pagesProjectChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Jee Advance 2016 Paper 2 SolutionDocument63 pagesJee Advance 2016 Paper 2 SolutionChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Document10 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation-1Aaditya Divyam100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12thDocument1 pageChemistry Investigatory Project Class 12thChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2015 Paper2Document120 pagesJEE Advanced 2015 Paper2debasij100% (2)
- Ai TS Test PlanDocument5 pagesAi TS Test PlanChandan PatraNo ratings yet
- 55-1 Physics (Theory) SSO-CDocument12 pages55-1 Physics (Theory) SSO-CAbhishek100% (1)
- ZZ - Electricity & MagnetismDocument137 pagesZZ - Electricity & Magnetismvenkyrocker777750% (4)
- Electrolysis of Potassium Iodide ProjectDocument10 pagesElectrolysis of Potassium Iodide ProjectChandan Patra50% (2)