Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Techniques: Titration: Equipment Using A Pipette Filling The Burette
Uploaded by
Mark Cliffton BadlonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Techniques: Titration: Equipment Using A Pipette Filling The Burette
Uploaded by
Mark Cliffton BadlonCopyright:
Available Formats
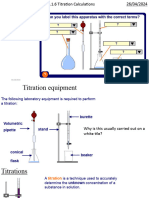
CHEMISTRY TECHNIQUES: TITRATION
Used to determine the concentration of a particular solution, by measuring how much of a solution of known concentration reacts with a known volume of it.
EQUIPMENT
USING A PIPETTE
FILLING THE BURETTE
BURETTE
PIPETTE
CONICAL FLASK
PIPETTE FILLER
INDICATOR
25ml
The pipette comes in a
range of fixed volumes, or in
graduated form, depending
on the volume you need to
measure. Burettes usually
hold 50 cm3 of solution.
USING INDICATORS
0
NONE
pH
NONE
10
25ml
WASH OUT WITH DISTILLED
WATER THEN THE SOLUTION
TO BE USED
Fill USING PIPETTE FILLER,
UNTIL BOTTOM OF MENISCUS
IS LEVEL WITH LINE
SLOWLY DRAIN LIQUID INTO
FLASK; TOUCH TIP TO WALL
TO REMOVE HANGING DROPS
FILL THE BURETTE ABOVE THE ZERO MARK,
THEN DRAIN UNTIL THE BOTTOM OF THE
MENISCUS IS LEVEL WITH THE ZERO MARK
Pipettes should never be filled direct from stock bottles
of solution as this could contaminate them. Instead, fill
them from some of the solution poured into a beaker.
They're calibrated to allow for a small amount of solution
remaining in the tip after the correct volume has been
delivered, so this remainder shouldn't be forced out.
As with the pipette, the burette should be rinsed with
distilled water then the solution it is to be filled with
before filling. It is necessary that the area under the tap
also contains solution as the burette's scale includes this
volume. Without doing this, the volume recorded for
titrations would be higher than the actual value.
CARRYING OUT THE TITRATION
12
CARRYING OUT CALCULATIONS
n = cv
14
PINK
TITRATE UNTIL
END POINT
ROUGH
TITRE 1
TITRE 2
TITRE 3
20.30 cm3
20.15 cm3
20.00 cm3
20.10 cm3
PHENOLPHTHALEIN
NO. OF MOLES
CONCENTRATION
VOLUME
in moles
in moles per decimetre cubed
(mol/dm3 or mol dm -3)
in decimetres cubed (dm3)
(value in cm3 1000)
= concordant titre values, used to calculate average
Average titre = (20.15 cm3 + 20.10cm3) 2 = 20.13 cm3
RED
YELLOW
YELLOW
METHYL ORANGE
In acid-base titrations, a range of indicators can be used. These
are solutions which change colour at a specific pH, and can be
used to precisely identify when the neutralisation reaction is
complete (the end point). Different indicators are suitable for
different acid-base combinations.
ALLOW SOME OF THE SOLUTION THROUGH
THE BURETTE'S TAP SO THAT THE AREA
UNDER THE TAP ALSO CONTAINS SOLUTION
To carry out the titration, the tap of the burette is opened to allow
the solution inside to flow into a known volume of the solution in
the conical flask. The amount of solution from the burette required
to reach the end point is recorded. A rough titration is usually
followed by more accurate runs. Multiple titrations are carried out
until concordant titres are obtained (within 0.10 cm3 of each other).
Assuming that the concentration of the solution in the burette is known...
Calculate number of moles of solution added from the burette.
Determine the number of moles of solution in the conical flask
using the equation for the reaction and reacting ratios.
Calculate the concentration of the solution in the conical flask
by rearranging the equation (c = n v).
COMPOUND INTEREST 2016 - WWW.COMPOUNDCHEM.COM | Twitter: @compoundchem | Facebook: www.facebook.com/compoundchem
This graphic is shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives International 4.0 licence.
BY
NC
ND
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Edexcel International Chemistry A-Level: Practical 3Document3 pagesEdexcel International Chemistry A-Level: Practical 3Sabrin OmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Acid Base TitrationsDocument6 pagesChapter 13 Acid Base Titrationsmukeshsriwastva14No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Titration (Updated Feb 2020)Document13 pagesA Guide To Titration (Updated Feb 2020)Prachi PriyaNo ratings yet
- 6-Volumetric AnalysisDocument48 pages6-Volumetric AnalysisOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry A-Level: Practical 3Document3 pagesEdexcel Chemistry A-Level: Practical 3Hady JawadNo ratings yet
- Titration of Vinegar Lab ExperimentDocument11 pagesTitration of Vinegar Lab ExperimentAchinthya PereraNo ratings yet
- Standardization of HCL Using Sodium CarbonateDocument2 pagesStandardization of HCL Using Sodium CarbonateJapol Arban100% (1)
- 1 - Volumetric Analysis v2Document14 pages1 - Volumetric Analysis v2skyeandoNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chem Lab #3Document4 pagesAnalytical Chem Lab #3kent galangNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Preparation of A Standard Solution & TitrationDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 - Preparation of A Standard Solution & TitrationAtn YoungNo ratings yet
- Acid Base TitrationDocument13 pagesAcid Base TitrationTsabit AlbananiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 Titration v2Document14 pagesExperiment 10 Titration v2Renu ReenuNo ratings yet
- YashDocument17 pagesYashayys1821No ratings yet
- Titration: Parth Hemant Patil Class: XIDocument19 pagesTitration: Parth Hemant Patil Class: XIHEMANT RAMJINo ratings yet
- Exp 4.3 PDFDocument1 pageExp 4.3 PDFEunnie ChongNo ratings yet
- AntacidDocument40 pagesAntacidmadmelzarNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Titration: Acids & BasesDocument4 pagesAcid-Base Titration: Acids & BasesIzzatNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Volumetric AnalysisDocument9 pagesCH 11 Volumetric Analysisapi-3774259No ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument5 pagesVolumetric AnalysisRiyhad YussufNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry A-Level: Practicals For Papers 3 and 5Document4 pagesCIE Chemistry A-Level: Practicals For Papers 3 and 5MaryamNo ratings yet
- Appendix 3: General ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesAppendix 3: General ConsiderationsNona NonicaaNo ratings yet
- Titration of HCL With NaohDocument9 pagesTitration of HCL With Naohapi-295783672No ratings yet
- Measuring The Amount of Acetic Acid in VinegarDocument4 pagesMeasuring The Amount of Acetic Acid in Vinegar10p11ed0067No ratings yet
- Sample of Chemistry ProjectDocument16 pagesSample of Chemistry ProjectSHIKHA BANSALNo ratings yet
- Neutralization Titration IDocument7 pagesNeutralization Titration IJarren BautistaNo ratings yet
- CHM256 Chapter 6Document89 pagesCHM256 Chapter 62022627178No ratings yet
- Lab Experiences DescriptionDocument8 pagesLab Experiences DescriptionCristiano PassarelliNo ratings yet
- TitrationDocument7 pagesTitrationJoseline SorianoNo ratings yet
- Titration CalculationsDocument52 pagesTitration Calculationswilliam.ongeri.tutoringNo ratings yet
- Acid/Alkali TitrationDocument2 pagesAcid/Alkali TitrationumisherruNo ratings yet
- Titration Techniques For Volumetric Analysis TutorialDocument13 pagesTitration Techniques For Volumetric Analysis TutorialLydia LamNo ratings yet
- The Art of Measuring VolumeDocument2 pagesThe Art of Measuring Volumehaiyan LINo ratings yet
- Titration Lab ReportDocument10 pagesTitration Lab Reportbotato. exeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project To Measure The Amount of Acetic Acid in VinegarDocument5 pagesChemistry Project To Measure The Amount of Acetic Acid in VinegarChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Titration CalculationsDocument52 pagesTitration Calculationswilliam.ongeri.tutoringNo ratings yet
- Types of TitrationDocument16 pagesTypes of TitrationShaher Bano Mirza73% (11)
- Volumetric Analysis: The Equipment The Terms The Process CalculationsDocument27 pagesVolumetric Analysis: The Equipment The Terms The Process Calculationskyle swayNo ratings yet
- Talplacido, Kristine Dianne M. BSMT 2D: Volumetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesTalplacido, Kristine Dianne M. BSMT 2D: Volumetric AnalysisAljo MojicaNo ratings yet
- Hse Plustwo Chemistry Svolumetric Analysis Anil HssliveDocument4 pagesHse Plustwo Chemistry Svolumetric Analysis Anil HssliveAryan ThakurNo ratings yet
- A2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20842 PDFDocument8 pagesA2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20842 PDFDanesha MccallumNo ratings yet
- VOLUMETRIC AnalysisDocument49 pagesVOLUMETRIC AnalysisLisa Dea SaryNo ratings yet
- Titration NotesDocument3 pagesTitration Notesshaheer ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument22 pagesChemistry Projectpradeeshsivakumar2006No ratings yet
- Shubh ProjectDocument19 pagesShubh ProjectShubh KhareNo ratings yet
- Fill The Burette With The Sodium Hydroxide Solution Using A Funnel. Place The BeakerDocument2 pagesFill The Burette With The Sodium Hydroxide Solution Using A Funnel. Place The BeakerMalik MuhammadNo ratings yet
- AntacidDocument42 pagesAntacidumesh123patilNo ratings yet
- Method or MadnessDocument2 pagesMethod or MadnessTristan Andrew GowNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Neutralisation ReactionsDocument14 pagesLesson 3 Neutralisation ReactionsSimaleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry ProjectSourabh NandwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Titration GuideDocument7 pagesChemistry Titration Guidedaniellelynch2007No ratings yet
- Measuring The Amount of Acetic Acid in Vinegar: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesMeasuring The Amount of Acetic Acid in Vinegar: Chemistry Investigatory ProjectShaurya TripathiNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Complete - 0Document8 pages4.2 Complete - 0Leo TaylorNo ratings yet
- AcidDocument43 pagesAcidIntan SaviraNo ratings yet
- Assay of Commercial BleachDocument7 pagesAssay of Commercial BleachMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Pipetting Post LabDocument29 pagesPipetting Post Labrrchard100% (3)
- Nat Sci July 2015Document15 pagesNat Sci July 2015Mark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Infrared SpectrosDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Infrared SpectrosMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Period (Year Started - Year Ended) Field University/ School Scholarship (If Applicable) RemarksDocument3 pagesPeriod (Year Started - Year Ended) Field University/ School Scholarship (If Applicable) RemarksMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Section 1-Verbal Ability: 30 Questions-30 MinutesDocument10 pagesSection 1-Verbal Ability: 30 Questions-30 MinutesApocalypto StatumNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectroscopic Methods: Instrumental AnalysisDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Spectroscopic Methods: Instrumental AnalysisMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Applications of Infrared SpectrometryDocument20 pagesIntroduction & Applications of Infrared SpectrometryMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UltravioletVisible Molecular Absorption SpectrometryDocument19 pagesIntroduction To UltravioletVisible Molecular Absorption SpectrometryMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UltravioletVisible Molecular Absorption SpectrometryDocument19 pagesIntroduction To UltravioletVisible Molecular Absorption SpectrometryMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- High Performance Liquid ChromatographyDocument22 pagesHigh Performance Liquid ChromatographyDeden Aldila ZulkhidaNo ratings yet
- How Equilibrium Calculations Can Be Applied To Complex SystemsNot MineDocument16 pagesHow Equilibrium Calculations Can Be Applied To Complex SystemsNot MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- How Equilibrium Calculations Can Be Applied To Complex Systems Not MineDocument11 pagesHow Equilibrium Calculations Can Be Applied To Complex Systems Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Infrared SpectrometryDocument18 pagesInfrared SpectrometryMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- High Performance Liquid ChromatographyDocument17 pagesHigh Performance Liquid ChromatographyOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- High Performance Liquid ChromatographyDocument17 pagesHigh Performance Liquid ChromatographyOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of A Specific Ion Electrode Not MineDocument7 pagesEvaluation of A Specific Ion Electrode Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Not MineDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Analytical Parameters in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography Not MineDocument14 pagesGas Chromatography Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- GC1 Not MineDocument18 pagesGC1 Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatography Not MineDocument28 pagesGas Chromatography Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- FTIR SOP Not MineDocument1 pageFTIR SOP Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical Chemistry (Nadya) Ver.2 Not MineDocument37 pagesElectroanalytical Chemistry (Nadya) Ver.2 Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Effects Activity or Concentration Not MineDocument12 pagesElectrolyte Effects Activity or Concentration Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Effects Activity or Concentration Not MineDocument14 pagesElectrolyte Effects Activity or Concentration Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical Chemistry (1) Not MineDocument23 pagesElectroanalytical Chemistry (1) Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, MicroprocessorsDocument21 pagesDigital Electronics, Microprocessorsjeetu1jeetu1No ratings yet
- Electroanalytical Chemistry Not MineDocument37 pagesElectroanalytical Chemistry Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components and Circuits Not MineDocument21 pagesElectrical Components and Circuits Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components and Circuits Not MineDocument22 pagesElectrical Components and Circuits Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Microprocessors and Computers Not MineDocument11 pagesDigital Electronics Microprocessors and Computers Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic Table Chem 111 Not MineDocument7 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic Table Chem 111 Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- R05422105 Hypersonic AerodynamicsDocument4 pagesR05422105 Hypersonic AerodynamicsPratap VeerNo ratings yet
- rr222303 Enzyme Engineering and TechnologyDocument4 pagesrr222303 Enzyme Engineering and TechnologySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 5.17 - A10706002 - Lely Ayu NingsihDocument8 pages5.17 - A10706002 - Lely Ayu NingsihLely Ayu NingsihNo ratings yet
- Deep Set Enclosed Lineshaft Component PartsDocument1 pageDeep Set Enclosed Lineshaft Component PartsFayez Al-ahmadiNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub - Rocket Propulsion 1108422276 9781108422277Document587 pagesDokumen - Pub - Rocket Propulsion 1108422276 9781108422277Kyle OvertonNo ratings yet
- 3 MassSpectrometry - PPSXDocument13 pages3 MassSpectrometry - PPSXZebBrahviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 3 DynamicsIzzat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Module Electricity and MagnetismDocument21 pagesModule Electricity and MagnetismNoorain PurhanudinNo ratings yet
- (UPDATED) Time HistoryDocument10 pages(UPDATED) Time HistoryShaina Mariz PanaliganNo ratings yet
- 0131 0136 PDFDocument6 pages0131 0136 PDFWahid KarolNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Prediction of The Solubility of CO2 and H2S inDocument6 pagesCorrelation and Prediction of The Solubility of CO2 and H2S inYogesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Defensive Weather Control - Tornado FINAL - 6Document18 pagesDefensive Weather Control - Tornado FINAL - 6Morgan Boardman100% (1)
- MSDS UreaDocument4 pagesMSDS UreaSharjeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- B.SC Electronics - Semiconductor Devices (.PDF) - Course Syllabus & Material - All Units (Bharathiar University)Document102 pagesB.SC Electronics - Semiconductor Devices (.PDF) - Course Syllabus & Material - All Units (Bharathiar University)KUMARNo ratings yet
- C5RA01911GDocument55 pagesC5RA01911GAndrew LondonNo ratings yet
- Solid State Practice MidtermDocument18 pagesSolid State Practice MidtermAppleJuiceNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter Three Fossile FuelDocument70 pages3 Chapter Three Fossile FuelyonasNo ratings yet
- SBM Schiedam Compressor Piping DesignDocument45 pagesSBM Schiedam Compressor Piping DesignSeudonim SatoshiNo ratings yet
- Design Guide For Aircraft HydraulicsDocument71 pagesDesign Guide For Aircraft HydraulicsLysterNo ratings yet
- Dimethoate Eval Specs WHO June 2012Document33 pagesDimethoate Eval Specs WHO June 2012MartuaHaojahanSaragihSidabutarNo ratings yet
- Base ShearDocument3 pagesBase ShearLaxman ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Compare and ContrastDocument5 pagesCompare and Contrastchrist sonNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project: Topic-Unit CellsDocument4 pagesInvestigatory Project: Topic-Unit CellsShifa SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Liquid ExtractionDocument68 pagesChapter 12 Liquid ExtractionNurul AinNo ratings yet
- UV-J221 - Operating Manual - Jun18Document3 pagesUV-J221 - Operating Manual - Jun18Michael LloydNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringDocument881 pagesSoil Mechanics and Foundation EngineeringGilberto Rendón Carrasco100% (4)
- Scrubber and Demister Sizing - Form 2Document2 pagesScrubber and Demister Sizing - Form 2eka resmana100% (2)
- 신소재과학 시험문제모음Document9 pages신소재과학 시험문제모음Hanjin SeoNo ratings yet
- Micro Alloyed Steels Voestalpine EN 30102020Document4 pagesMicro Alloyed Steels Voestalpine EN 30102020pierocarnelociNo ratings yet
- Ex. 7. Winogradsky ColumnDocument6 pagesEx. 7. Winogradsky ColumnPrecious Mae Cuerquis BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionFrom EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3From EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- High School Chemistry: Comprehensive Content for High School ChemistryFrom EverandHigh School Chemistry: Comprehensive Content for High School ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet