Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sickle Cell Test (Hook's Method)
Uploaded by
Ravindra SinghOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sickle Cell Test (Hook's Method)
Uploaded by
Ravindra SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Ravindra Singh
DMT 3107 Haematology
Sickle Cell Test (Hooks Method)
Title: Determination of the presence of Sickle Cell
Aim: To determine whether Sickle Cell is present in a given blood sample
Principle:
One drop of blood is placed on a slide. The slide is then sealed with Vaseline and a cover glass
preventing exposure to oxygen. This is left in a Petri dish with a piece of moist gauze/filter paper
for 24 hours which is then viewed under the microscope.
Procedure: As per lab handout
Method/Equipment: As per lab handout
Discussion:
Clinical Significance:
A sickle cell test is a simple blood test used to determine whether or not you have sickle cell
disease or sickle cell trait. Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell
disorders. People who have this disease have red blood cells that are shaped abnormally. Instead
of looking like doughnuts, which normal red blood cells do, they are shaped like a crescent
moon, or a C-shaped farm tool known as a sickle.
Sickle cell anemia and sickle cell trait are caused by hemoglobin S, which is an abnormal
hemoglobin. In the presence of hemoglobin S, the red cells take on a sickle-like shape when
oxygen supply is decreased. This is because the molecules of this abnormal hemoglobin combine
together and precipitates changing the erythrocyte shape.
The cells often become hard and sticky, which can increase the risk of blood clots. They also
tend to die off early, and this causes a constant shortage of red blood cells.
People with sickle cell trait are genetic "carriers" of sickle cell disease. They have no symptoms
of sickle cell disease and cannot develop the disease, but they may be able to pass it on to their
children. Those with the trait may have a higher risk of some other complications, including
unexpected exercise-related death.
This test is part of the routine screenings performed after a baby is born, but it may also be used
on older children and adults when needed.
Ravindra Singh
DMT 3107 Haematology
Sickle Cell Test (Hooks Method)
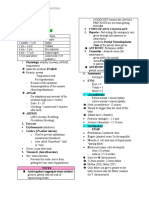
Sources of Error:
1
2
3
4
5
Formation of air bubbles. Cover slit wasnt placed gently onto sample.
Avoid contamination of high-dry objective (x 40) with petroleum jelly this may
obscure reading and invalidate the result.
Do not use contaminated sodium metabisulfite- test would be invalid. (Reagent is
usually stable for 8 hours after preparation).
Use equal drops of whole blood and reagent result can either be false positive or false
negative depending on the proportion of blood to reagent used or vice versa.
Cover slips should be scrupulously clean or result would be invalidated.
Results:
The red cells remained round hence, the results were negative
Conclusion:
The Sickle cell test was carried out using Hooks method and it can be concluded from the given
sample that the results were negative, hence Sickle cell was not present.
Ravindra Singh
DMT 3107 Haematology
Sickle Cell Test (Hooks Method)
References:
1. Labtestsonline.org. Sickle Cell Tests: The Test. 2015. Available at:
https://labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/sickle/tab/test/. Accessed
November 22, 2015.
2. Mayoclinic.org. Sickle cell anemia Tests and diagnosis - Mayo Clinic. 2015.
Available at: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sickle-cellanemia/basics/tests-diagnosis/con-20019348. Accessed November 22, 2015.
You might also like
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Case Scenerio Nephrotic SyndromeDocument4 pagesCase Scenerio Nephrotic SyndromeEllen AngelNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument14 pagesAddison's Diseasedivya4nirmalaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsDocument4 pagesSurgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsAprille Claire MoralesNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document4 pagesCase Study 2api-2451636590% (1)
- Hypertension in PregnancyDocument31 pagesHypertension in PregnancyradhabobbyNo ratings yet
- Addison Disease, Penyakit AddisonDocument11 pagesAddison Disease, Penyakit AddisonKertiasihwayanNo ratings yet
- Pathological Changes of DM - 2023Document53 pagesPathological Changes of DM - 2023Visura PrabodNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Fetal DeathDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Fetal DeathVinisia TakaraiNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY (Gastro)Document3 pagesCASE STUDY (Gastro)Jake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Pat 2 Medsurg1Document20 pagesPat 2 Medsurg1api-300849832No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument21 pagesCase StudyLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Type B (Hib) Vaccine: Haemophilus InfluenzaeDocument2 pagesType B (Hib) Vaccine: Haemophilus InfluenzaeEnce MalatambanNo ratings yet
- HYDROCELEDocument3 pagesHYDROCELESean Patrick Acoba100% (2)
- Final Patient Scenario Chapter 44 Nursing Care of Family When A Child Has A Hematologic DisorderDocument53 pagesFinal Patient Scenario Chapter 44 Nursing Care of Family When A Child Has A Hematologic DisorderDay Meds100% (1)
- GASTROSCHISISDocument4 pagesGASTROSCHISISVin Custodio100% (1)
- Importance of Honesty in MedicineDocument3 pagesImportance of Honesty in MedicineSuiweng WongNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument5 pagesPyloric Stenosisensoooooooooo100% (1)
- Kaposi's SarcomaDocument6 pagesKaposi's SarcomaveremkovichNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis Ppt. DR Dilip S. RajpalDocument42 pagesAcute Cholecystitis Ppt. DR Dilip S. Rajpaldiliprajpal73100% (1)
- Case Report - Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument12 pagesCase Report - Deep Vein ThrombosisAndi Meidin AnugerahNo ratings yet
- Case Stude NNJDocument6 pagesCase Stude NNJmuzamirNo ratings yet
- Missed AbortionDocument5 pagesMissed AbortionDesta MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Patient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument93 pagesPatient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDay MedsNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Atun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableDocument2 pagesAtun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Case Study CKD Pinakafinal Na TalagaDocument80 pagesCase Study CKD Pinakafinal Na TalagaLance SilvaNo ratings yet
- Live Preterm Baby Delivered NSDDocument13 pagesLive Preterm Baby Delivered NSDKristine Anne SorianoNo ratings yet
- RBC AliquotsDocument1 pageRBC AliquotsARIF AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument12 pagesNeonatal JaundiceJustine NyangaresiNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument3 pagesNursing AssessmentJanine PelayoNo ratings yet
- Preventing Neonatal InfectionsDocument27 pagesPreventing Neonatal Infectionsmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- NCP GeDocument14 pagesNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hypersensitivity Type IIDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Hypersensitivity Type IItwin_smartyNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument35 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyWilliam Soneja CalapiniNo ratings yet
- Case Study of HypospadiaDocument19 pagesCase Study of Hypospadialicservernoida100% (2)
- Cretenism Case StudyDocument8 pagesCretenism Case StudyMonica Marie MoralesNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyDocument12 pagesThyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyAgustina100% (1)
- Alport SyndromeDocument7 pagesAlport SyndromeNTA UGC-NET100% (1)
- Jaundice NeonatalDocument26 pagesJaundice Neonatalhunk2662No ratings yet
- NCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisScarlet ScarletNo ratings yet
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument5 pagesChronic PyelonephritisIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms Case StudyDocument13 pagesMechanisms Case Studyshane_tin143No ratings yet
- Anemia 130809044630 Phpapp01Document21 pagesAnemia 130809044630 Phpapp01Siddharth Das100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Addison'sDocument4 pagesAddison'sKoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia in NewbornDocument25 pagesPolycythemia in NewbornTheva Thy100% (2)
- Child's HerniaDocument13 pagesChild's HerniaKreshnik HAJDARINo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung Disease Case Study: Maecy P. Tarinay BSN 4-1Document5 pagesHirschsprung Disease Case Study: Maecy P. Tarinay BSN 4-1Maecy OdegaardNo ratings yet
- Case Study OligoDocument7 pagesCase Study OligomutiaNo ratings yet
- Phototherapy For Neonatal JaundiceDocument5 pagesPhototherapy For Neonatal JaundiceMichael RameresNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis SeminarDocument42 pagesAcute Cholecystitis SeminarNatnaelNo ratings yet
- I Patient Assessment Data BaseDocument12 pagesI Patient Assessment Data BaseJanice_Fernand_1603No ratings yet
- AADocument20 pagesAAAiyaz AliNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan School Age: Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Normal Road, Zamboanga CityDocument12 pagesHealth Teaching Plan School Age: Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Normal Road, Zamboanga CityJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii Is A RodDocument9 pagesBacillus Clausii Is A RodGrax DeeNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacilli (Corynebacterium)Document7 pagesMICROBIOLOGY Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacilli (Corynebacterium)Ravindra SinghNo ratings yet
- DMT 3107 - Haematology 1: University of Guyana Turkeyen CampusDocument3 pagesDMT 3107 - Haematology 1: University of Guyana Turkeyen CampusRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- Fixation IV PDFDocument7 pagesFixation IV PDFRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- FixationDocument12 pagesFixationRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- Common ICD-10 DiagnosesDocument2 pagesCommon ICD-10 DiagnosesnernstNo ratings yet
- Vanessa LeprosyDocument18 pagesVanessa LeprosyMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease Concept MapDocument1 pageParkinson's Disease Concept MapKyle Santos100% (1)
- Chapter 019Document28 pagesChapter 019Esteban Tabares GonzalezNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument13 pagesPresentationLohcchana MoganNo ratings yet
- ANSDocument8 pagesANSTracy Megan Rusillon0% (1)
- Maya Semrau - Service User and Caregiver Involvement in Mental Health System Strengthening in Low - and Middle-Income Countries Systematic ReviewDocument18 pagesMaya Semrau - Service User and Caregiver Involvement in Mental Health System Strengthening in Low - and Middle-Income Countries Systematic ReviewsukmarahastriNo ratings yet
- Uterin InversionDocument8 pagesUterin InversionZahra AlSaif100% (1)
- SummariesDocument140 pagesSummariesmalik003No ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument3 pagesAtelectasisabdo mo . M7.No ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument56 pagesNephrotic Syndromeapi-19916399No ratings yet
- 7 Implant Post Op InstructionsDocument2 pages7 Implant Post Op InstructionsmrcalvintineNo ratings yet
- DR Sonam's High Yield Notes For ST 2 & 5 2nd EditionDocument251 pagesDR Sonam's High Yield Notes For ST 2 & 5 2nd EditionMuhammad Fahad100% (1)
- Common Diseases Review - Community MedicineDocument15 pagesCommon Diseases Review - Community Medicinelas85% (13)
- Lecture CasesDocument12 pagesLecture CasesGLEE ANN UYCOCONo ratings yet
- Betadine Douche - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageBetadine Douche - Google Search PDFIgn Haryo SusenoNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument48 pagesPediatricsNeha OberoiNo ratings yet
- Cassidy Spatz 1100 Exploratory EssayDocument8 pagesCassidy Spatz 1100 Exploratory Essayapi-430754451No ratings yet
- Vaccinations: Slam Shraf AhmyDocument11 pagesVaccinations: Slam Shraf AhmyFahad Alkenani100% (1)
- Sindroma Nefrotik Vs NefritikDocument23 pagesSindroma Nefrotik Vs NefritikBobby Fildian Siswanto100% (3)
- Kelainan Kongenital GenetikDocument39 pagesKelainan Kongenital GenetikvictorNo ratings yet
- TABLE 56-4 - Neurological Side Effects of Antipsychotic DrugsDocument1 pageTABLE 56-4 - Neurological Side Effects of Antipsychotic DrugsDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Guideline For The Diagnosis, Treatment and Long-Term Management of Cutaneous Lupus ErythematosusDocument16 pagesGuideline For The Diagnosis, Treatment and Long-Term Management of Cutaneous Lupus ErythematosusMariana de la VegaNo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbations of Pulmonary DiseasesDocument258 pagesAcute Exacerbations of Pulmonary DiseasesOxana TurcuNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument50 pagesEndocrinologyCut TirayaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerAntonio G. Cordillon100% (1)
- Assessment of Subclinical Symptoms PDFDocument6 pagesAssessment of Subclinical Symptoms PDFPatriciaNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 11th Edition PDFDocument47 pagesEbook PDF Wongs Nursing Care of Infants and Children 11th Edition PDFalan.greer58697% (32)
- Pedia TranscriptDocument18 pagesPedia TranscriptUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Plain Language Summary: Hoarseness (Dysphonia)Document5 pagesPlain Language Summary: Hoarseness (Dysphonia)opi akbarNo ratings yet