Professional Documents
Culture Documents
High Tensile Steel 4340
Uploaded by
CarmenJuliaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
High Tensile Steel 4340
Uploaded by
CarmenJuliaCopyright:
Available Formats
HIGH TENSILE STEEL AISI 4340
AISI 4340 Nickel Chrome - Moly High
Tensile Steel, generally supplied
hardened and tempered to condition
U in sections up to 100mm, with a
tensile strength of 930 1080 MPa
and aiming for this strength range in
larger sections. It offers a very good
balance of strength, toughness and
wear-resistance.
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS:
Heavy-duty axles, shafts, heavy-duty gears,
spindles, pins, studs, collets, bolts, couplings,
sprockets, pinions, torsion bars, connecting rods,
crow bars, conveyor parts etc.
TYPICAL CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
Carbon
0.40%
Silicon
0.25%
Manganese
0.70%
Nickel
1.85%
Chromium
0.80%
Molybdenum
0.25%
RELATED SPECIFICATIONS:
AS 1444-1996
4340
BS EN10083-1-1991
817M40
BS 970-1955
EN 24
JIS G 4103
SNCM 439
SAE & UNS
4340 & G43400
Werkstoff - 1.6565
40NiCrMo6
SURFACE TREATMENT:
Will Nitride with a typical surface hardness up to HRC 60.
Will Flame or Induction harden with a typical surface hardness up to HRC 58.
MECHANICAL PROPERTY REQUIREMENTS IN CONDITION U to AS 1444-1996
Section
mm
0.2% Proof
Stress
MPa
Tensile Strength
MPa
Elongation
on 5.65So
%
*up to 63
755 min
930 - 1080
9 min
up to 100
740 min
930 - 1080
12 min
Impact
Izod Charpy
J
J
-
47min 42min
Hardness
HB
269 - 331
269 - 331
*Applies only to bars bright drawn after hardening and tempering
TYPICAL MECHANICAL PROPERTIES Hardened and tempered in section size listed
Section
mm
Yield Strength
MPa
Tensile Strength
MPa
Elongation
%
Impact Izod
J
Hardness
HB
50
880
1000
17
85
295
100
850
980
17
80
290
200
730
930
Typical Mechanical Properties for guidance only
17
75
275
HIGH TENSILE STEEL AISI 4340 - continued
WELDING:
Readily welded in the annealed condition but
avoid when possible if hardened and tempered
due to the effect on the mechanical properties.
Welding in the nitrided, flame or induction
hardened condition is not recommended.
Welding procedure:
Low hydrogen electrodes are recommended.
Pre-heat at 200C 300C and maintain during
welding. Cool slowly in ashes or sand etc and
stress relieve if this is possible.
Welding details for guidance only
HEAT TREATMENT:
Forging:
Flame and Induction Hardening:
Heat to 1150C
Hold till uniform
Minimum forging temperature 850C
Cool slowly in ashes or sand etc
Heat quickly to the required case depth at
850C 870C and quench immediately in water
or oil.
Annealing:
Tempering at 150C 200C will reduce stresses
in the case with minimal effect on its hardness.
Heat to 830C 850C
Cool in furnace
All de-carburised surface material must first be
removed to ensure best results
Stress Relieving:
Annealed: Heat to 600C 650C
Hardened: Heat to 500C 550C
Cool in still air
Nitriding:
Hardening:
Heat to 830C 880C
Cool in Oil or Polymer
Parts should be pre-hardened and tempered as
required and also pre-machined leaving a small
grinding allowance only.
Tempering:
Heat treatment details for guidance only
Heat to 450C 660C cool in still air
NB. Tempering within the range 250C 450C
will result in temper brittleness and should be
avoided
Heat to 500C 530C and hold for sufficient
time to develop the depth of case required
You might also like
- High Temperature Stainless Steel EN 1.4835 - UNS S 30815 - 253 MA®Document2 pagesHigh Temperature Stainless Steel EN 1.4835 - UNS S 30815 - 253 MA®ivanoliveira3261No ratings yet
- AISI 4140 Alloy Steel (UNS G41400) : Topics CoveredDocument3 pagesAISI 4140 Alloy Steel (UNS G41400) : Topics Covereda.mohamedlathifNo ratings yet
- SWRCH18A Steel DatasheetDocument2 pagesSWRCH18A Steel DatasheetHari SuthanNo ratings yet
- Jis S45CDocument2 pagesJis S45CyendikesumaNo ratings yet
- Saph 440Document1 pageSaph 440rinkumax2003No ratings yet
- Aisi 4140 En8 En19Document1 pageAisi 4140 En8 En19Jose KurianNo ratings yet
- En9 070M55Document1 pageEn9 070M55Tridib DeyNo ratings yet
- EN42JDocument1 pageEN42Jpavan_joshi_5No ratings yet
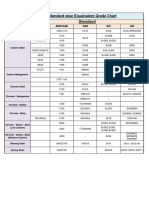
- Equivalent Grade ChartDocument1 pageEquivalent Grade ChartDipesh Patel100% (1)
- Aisi 4140 Alloy Steel (Uns g41400)Document3 pagesAisi 4140 Alloy Steel (Uns g41400)diogolabegNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For Steel Grades Structure Steel Q235Document2 pagesDatasheet For Steel Grades Structure Steel Q235Percy TorresNo ratings yet
- Effect of Various Heat Treatments On Microstructure of Aisi 4130 SteelDocument6 pagesEffect of Various Heat Treatments On Microstructure of Aisi 4130 SteelДмитрий РыбаковNo ratings yet
- SPCCDocument10 pagesSPCCDeepak JainNo ratings yet
- High-Silicon Molybdenum Ferritic Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForDocument7 pagesHigh-Silicon Molybdenum Ferritic Iron Castings: Standard Specification Formohammed karasnehNo ratings yet
- DIN 1681 Chemical CompositionDocument12 pagesDIN 1681 Chemical CompositionAshish Kesharwani100% (1)
- Aisi 1010 Carbon Steel (Uns g10100)Document5 pagesAisi 1010 Carbon Steel (Uns g10100)spiderblackNo ratings yet
- Is 3930Document19 pagesIs 3930IPSITNo ratings yet
- 1 7335Document5 pages1 7335stamatsNo ratings yet
- Jis G4052-1979Document39 pagesJis G4052-1979RanjithkumarNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Material & Mettalurgy II - 2008 PDFDocument30 pagesFerrous Material & Mettalurgy II - 2008 PDFBui Chi TamNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Mechanical PropertiesDocument5 pagesChemical and Mechanical PropertiesAristotle MedinaNo ratings yet
- 1570 (Part II Sec I) Revised - Wrought Steeks For PlatesDocument20 pages1570 (Part II Sec I) Revised - Wrought Steeks For PlatesKaushik Sengupta67% (3)
- Surface Vehicle Standard: Chemical Compositions of SAE Alloy SteelsDocument6 pagesSurface Vehicle Standard: Chemical Compositions of SAE Alloy SteelsDhandapani MetallionNo ratings yet
- C43Document1 pageC43rudramansingh123No ratings yet
- Data Table For Grades Tool Die Steels SKD-11Document3 pagesData Table For Grades Tool Die Steels SKD-11Adhi candra irawanNo ratings yet
- Alloy Steel Composition and Heat Treatment GuideDocument2 pagesAlloy Steel Composition and Heat Treatment GuideweldmindNo ratings yet
- Datesheet 039R - MW450Document2 pagesDatesheet 039R - MW450jhhvgNo ratings yet
- Q235BDocument2 pagesQ235BGoh Boon TiongNo ratings yet
- Hot Dip GalvanizingDocument3 pagesHot Dip Galvanizingapply19842371No ratings yet
- AISI 1045 Medium Carbon Steel - AZoMDocument4 pagesAISI 1045 Medium Carbon Steel - AZoMLuis NunesNo ratings yet
- Asme Section Ii A-2 Sa-675 Sa-675mDocument6 pagesAsme Section Ii A-2 Sa-675 Sa-675mdavid perezNo ratings yet
- Stainless steel electrode AWS specifications guideDocument11 pagesStainless steel electrode AWS specifications guideTito FernandezNo ratings yet
- Aisi 4340 Alloy Steel (Uns g43400)Document4 pagesAisi 4340 Alloy Steel (Uns g43400)Muhamad Ikbal TrismanaNo ratings yet
- Is 1570 1Document17 pagesIs 1570 1Raj K Sharma100% (1)
- Xuper 680 CGSDocument1 pageXuper 680 CGSArbind RajrishiNo ratings yet
- MS Iso 683-17 - 2010 - Prev PDFDocument6 pagesMS Iso 683-17 - 2010 - Prev PDFtiffanyyy00No ratings yet
- ASM 4E - Chapter Cu and Alloys1Document14 pagesASM 4E - Chapter Cu and Alloys1Rudrash Biradar50% (2)
- S.G.Iron GuidelinesDocument28 pagesS.G.Iron GuidelinesTarun Chakraborty100% (3)
- Bluefracturemnm 2018Document8 pagesBluefracturemnm 2018Gomathi RNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard Designation of SteelsDocument1 pageIndian Standard Designation of Steelssushil.vgi75% (4)
- Jis B0203Document11 pagesJis B0203Muhammad Ridwan50% (2)
- Tabel AISI ASTM (Selected)Document5 pagesTabel AISI ASTM (Selected)Dini Adilah PrabowoNo ratings yet
- SAE 8620H Chemical Composition, SAE 8620H Mechanical Properties, SAE 8620H Heat TreatmentDocument2 pagesSAE 8620H Chemical Composition, SAE 8620H Mechanical Properties, SAE 8620H Heat TreatmentAnush Swaminathan100% (1)
- Nisshin Cold-Rolled Special Steel GuideDocument28 pagesNisshin Cold-Rolled Special Steel GuideekopujiantoeNo ratings yet
- Geared Motor: Product ManualDocument178 pagesGeared Motor: Product Manualsanjibkrjana100% (1)
- Type 347-347H Stainless SteelDocument2 pagesType 347-347H Stainless SteelPravin PawarNo ratings yet
- Material Datea 2.4602Document3 pagesMaterial Datea 2.4602Charwin XiaoNo ratings yet
- 50 Casting DefectsDocument49 pages50 Casting DefectsmohammadNo ratings yet
- SAE J434 1986 Automotive Ductile Iron Castings Nodular Iron CastingsDocument10 pagesSAE J434 1986 Automotive Ductile Iron Castings Nodular Iron Castingsvinicius_bacellarNo ratings yet
- High Tensile Steel 4340Document2 pagesHigh Tensile Steel 4340Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- HighTens AISI4340Document2 pagesHighTens AISI4340wellengineerNo ratings yet
- High Tensile Steel - Aisi 4140Document2 pagesHigh Tensile Steel - Aisi 4140tetirichieNo ratings yet
- HighTens AISI4140Document2 pagesHighTens AISI4140shifaNo ratings yet
- High Tensile Steel 4140Document2 pagesHigh Tensile Steel 4140Sadullah TaşkınNo ratings yet
- Medium Tensile Steel A Is I 1045Document2 pagesMedium Tensile Steel A Is I 1045Madhav RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- HighTens EN25Document2 pagesHighTens EN25Annamali Thiayagarajan0% (1)
- High Tensile Steel 4140Document2 pagesHigh Tensile Steel 4140Lazzarus Az GunawanNo ratings yet
- AISI 8620 Case HardeningDocument2 pagesAISI 8620 Case HardeningjarnebergNo ratings yet
- MeduimTens AISI1045Document2 pagesMeduimTens AISI1045Rajesh R RajeshNo ratings yet
- CG460-4100/CG575-4100 Crankshaft & Cylindrical GrindingDocument5 pagesCG460-4100/CG575-4100 Crankshaft & Cylindrical GrindingCarmenJuliaNo ratings yet
- Harris Products MIG Welding Parameters for Mild SteelDocument1 pageHarris Products MIG Welding Parameters for Mild SteeljesycubanNo ratings yet
- 4140HW Alloy Steel Technical Data PDFDocument8 pages4140HW Alloy Steel Technical Data PDFCarmenJuliaNo ratings yet
- Practical Data For Metallurgists, TIMKENDocument129 pagesPractical Data For Metallurgists, TIMKENspocajtNo ratings yet
- 4140 Chrome-Moly Electrode: Alloy Description and ApplicationDocument1 page4140 Chrome-Moly Electrode: Alloy Description and ApplicationCarmenJuliaNo ratings yet
- Small Modular ReactorDocument7 pagesSmall Modular ReactorCarmenJuliaNo ratings yet
- Rodamientos SKFDocument1,380 pagesRodamientos SKFSebastian Lobos OpitzNo ratings yet
- Tipos de Tratamientos PDFDocument1 pageTipos de Tratamientos PDFJose PerezNo ratings yet
- Fe-C Phase DiagramDocument34 pagesFe-C Phase DiagramYoung-long Choi100% (1)
- A Duplex Stainless Steel With PREN 24 SPDocument2 pagesA Duplex Stainless Steel With PREN 24 SPFarhad MalikNo ratings yet
- Presentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningDocument37 pagesPresentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningRizwanNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Microalloying With Boron On Properties of Austenite Stainless Steel X8crnis18-9Document6 pagesThe Influence of Microalloying With Boron On Properties of Austenite Stainless Steel X8crnis18-9IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- MSM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-5 23112020052908AMDocument14 pagesMSM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-5 23112020052908AMVijayNo ratings yet
- Cracking Furnace Tube Metallurgy Part 1 ADocument21 pagesCracking Furnace Tube Metallurgy Part 1 AKaren Romero100% (1)
- Localized CorrosionDocument11 pagesLocalized CorrosionJack AndreasNo ratings yet
- Crack Characterisation For In-Service Inspection Planning: Jan Wåle, SAQ Kontroll AB - Peter Ekström, ABB Atom ABDocument112 pagesCrack Characterisation For In-Service Inspection Planning: Jan Wåle, SAQ Kontroll AB - Peter Ekström, ABB Atom ABPhoenix RomeoNo ratings yet
- TMT Boron CoatingDocument6 pagesTMT Boron Coatingcvolkan1100% (2)
- R.D. DOHERTY Et Al. - Current Issues in Recrystallization A ReviewDocument56 pagesR.D. DOHERTY Et Al. - Current Issues in Recrystallization A ReviewBruno FreitasNo ratings yet
- Review On Jominy Test and Determination of Effect of Alloying On Hardenability of Steel Using Jominy End Quench Test Copyright Ijaet1Document8 pagesReview On Jominy Test and Determination of Effect of Alloying On Hardenability of Steel Using Jominy End Quench Test Copyright Ijaet1enrico susantoNo ratings yet
- Silicon Carbide Porcelain Housed Arrester Identification GuideDocument9 pagesSilicon Carbide Porcelain Housed Arrester Identification GuideHarold NaiborhuNo ratings yet
- Yaln 1999Document12 pagesYaln 1999Fabio MoralesNo ratings yet
- Parts list and assembly drawingDocument1 pageParts list and assembly drawingChoirull HidayatNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Iron and Steel Industry in NigeriaDocument17 pagesOverview of The Iron and Steel Industry in NigeriaPushkar SharmaNo ratings yet
- VUT Electrical Engineering: Process InstrumentationDocument16 pagesVUT Electrical Engineering: Process InstrumentationWilfried BarrosNo ratings yet
- MIL-H-6875H Heat Treatment of SteelDocument29 pagesMIL-H-6875H Heat Treatment of Steelgoathead61No ratings yet
- GALVASTEELDocument15 pagesGALVASTEELRodimar Eduagin100% (1)
- Upgrading Magnetite OrebodiesDocument12 pagesUpgrading Magnetite OrebodiesKtishna100% (1)
- Grade 10.9 Bolt Failures: Causes and SolutionsDocument3 pagesGrade 10.9 Bolt Failures: Causes and Solutionshiren_mistry55No ratings yet
- Chemical Composition Limit (Cast Analysis, %) Tempering Temperature Property Class Material and Heat TreatmentDocument1 pageChemical Composition Limit (Cast Analysis, %) Tempering Temperature Property Class Material and Heat TreatmentAhmed Saber NassarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 EM MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 4 EM MCQPratik Wakchoure100% (1)
- Stainless Steel StandardDocument2 pagesStainless Steel StandardVarma DantuluriNo ratings yet
- 1-Forms of CorrosionDocument59 pages1-Forms of Corrosion이선엽100% (1)
- Ferrous and Nonferrous Alloys Technical UpdateDocument8 pagesFerrous and Nonferrous Alloys Technical Updateatfrost4638No ratings yet
- Aji ProjectDocument105 pagesAji ProjectRoopa Ranjith100% (1)
- National Institute of Technology WarangalDocument18 pagesNational Institute of Technology WarangalGopi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 17B2 - 1.5502 - SteelNumber - Chemical Composition, Equivalent, PropertiesDocument2 pages17B2 - 1.5502 - SteelNumber - Chemical Composition, Equivalent, PropertiesSergiNo ratings yet
- Cu-Removal Form The Skorpion Circuit Using Emew TechnologyDocument18 pagesCu-Removal Form The Skorpion Circuit Using Emew Technologysebastian_javier_bNo ratings yet