Professional Documents
Culture Documents
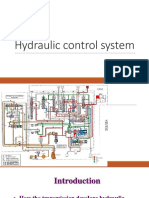
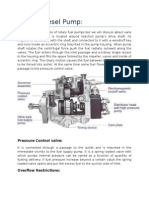
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT), Function
Uploaded by
Moaed Kanbar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesOriginal Title
ME7.0-CVVTfunction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesContinuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT), Function
Uploaded by
Moaed KanbarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
"VCC-106196 US 2002-07-11"
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT), function
In the unemployed position the Continuous
Variable Valve Timing valve is in the rear most
position (A) because of the valve spring. In this
position the piston connects the piston
housing center and rear grooves with each
other. At the same time the piston has
exposed the front piston housing groove so
that it is connected to the valve return
terminal. Then the oil pressure is guided from
the Continuous Variable Valve Timing valve
center terminal to the valves rear terminal.
From there the pressure is led through the
camshaft bearing into the camshaft rear
oilway, via the camshaft center channel to the
Continuous Variable Valve Timing unit hub.
The hub is connected to the Continuous
Variable Valve Timing unit front chamber. The
pressure in the Continuous Variable Valve
Timing unit hub thereby presses onto the
Continuous Variable Valve Timing unit piston
and presses it backwards.
The piston is rotationally borne, via angle cut
splines between the unit hub and cover. The
camshaft toothed pulley wheel is installed on
the cover and the camshaft is located in the
hub. When the piston presses backwards the
splines in the unit cover and hub rotate in
"VCC-106196 US 2002-07-11"
relation to each other. The arrangement gives
a gear ratio giving the piston the possibility of
affecting the camshaft a lot with a small
movement.
The oil at the rear of the piston is pressed out
through the outer hub channels into the
camshaft and out through the camshaft upper
front oilway The oil is led further through the
camshaft bearing, via the front Continuous
Variable Valve Timing valve piston housing
machining and back to the valve return
terminal.
When the Continuous Variable Valve Timing
valve receives the signal to move to the other
outer position (B) the pressure is led from the
piston housing center terminal to the front
terminal. The return oil is then sent through
the rear piston housing machining to the
center of the piston, via the piston rear
machining and the piston center channel to
the Continuous Variable Valve Timing valve
return terminal.
When the desired setting in the chamber is
achieved the Continuous Variable Valve
Timing valve moves to a central position
where none of the terminals are connected
with each other. When another camshaft
setting in the required the Continuous Variable
Valve Timing valve makes a short move in the
necessary direction. In this way the
Continuous Variable Valve Timing unit can
continuously adjust the camshaft.
You might also like
- Power Steering Pump For UD TRUCKS GWE 370Document9 pagesPower Steering Pump For UD TRUCKS GWE 370Bui Xuan DucNo ratings yet
- MAN B&W Fuel System 12K90MCDocument4 pagesMAN B&W Fuel System 12K90MCRaunaq Arora100% (3)
- 80-900 TransmissionDocument40 pages80-900 TransmissionjeevaNo ratings yet
- Bomba HidrostaticaDocument19 pagesBomba HidrostaticaJose Mendoza MirandaNo ratings yet
- 3512 Marine Engine Governor Operation and ComponentsDocument6 pages3512 Marine Engine Governor Operation and ComponentsChung ChungNo ratings yet
- Fuel Injection Systems ExplainedDocument9 pagesFuel Injection Systems ExplainedRaman RajputNo ratings yet
- NAVEDTRA 14050A Construction Mechanic Advanced Part 3 PDFDocument160 pagesNAVEDTRA 14050A Construction Mechanic Advanced Part 3 PDFMynor Witt100% (2)
- Fuel Injection PumpDocument8 pagesFuel Injection PumpSai Indrakaran Reddy Cherabuddi100% (1)
- NAVEDTRA 14050A Construction Mechanic Advanced Part 3 PDFDocument160 pagesNAVEDTRA 14050A Construction Mechanic Advanced Part 3 PDFSon Do100% (1)
- 04 Hydraulic System OperationDocument24 pages04 Hydraulic System OperationJUAN MANUEL RUIZ BERMEJONo ratings yet
- 1927 Bosch Diesel Fuel Injection Pump DesignDocument16 pages1927 Bosch Diesel Fuel Injection Pump Designdivyanshpancholi100% (2)
- Caterpillar Sleeve Metering Fuel System ExplainedDocument6 pagesCaterpillar Sleeve Metering Fuel System ExplainedJosephNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Information On AutomotiveDocument6 pagesMiscellaneous Information On AutomotiveShashank ChheniyaNo ratings yet
- DieselDocument9 pagesDieselvandanaharikumar100% (1)
- VVT (Variable Valve Timing)Document26 pagesVVT (Variable Valve Timing)PramodPradhan100% (1)
- Puncture ValveDocument2 pagesPuncture ValveSanjeev SainiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Control SystemDocument22 pagesHydraulic Control SystemRahul DandugulaNo ratings yet
- Inline Injection PumpDocument93 pagesInline Injection PumpElias Girma100% (2)
- HYZ Oil Pressure Tank PDFDocument12 pagesHYZ Oil Pressure Tank PDFNguyễn Văn QuýNo ratings yet
- Fuel PumpDocument19 pagesFuel Pumpsevero97100% (1)
- VOLVO SD116F SINGLE-DRUM ROLLER Service Repair Manual PDFDocument20 pagesVOLVO SD116F SINGLE-DRUM ROLLER Service Repair Manual PDFfjjsjekdmmeNo ratings yet
- Manual Del Estudiante D8T - 12Document14 pagesManual Del Estudiante D8T - 12David CeronNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Fluid Power SymbolsDocument23 pagesUnit - 3 Fluid Power Symbolsyuvaraja sNo ratings yet
- Fuel Pump1Document5 pagesFuel Pump1Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- 8 - Valve Body Circuits PDFDocument49 pages8 - Valve Body Circuits PDFhenok80% (5)
- Lesson Control BlockDocument10 pagesLesson Control Blockmister pogiNo ratings yet
- Operational Information The MAN B&W MC Engine VIT Fuel PumpDocument16 pagesOperational Information The MAN B&W MC Engine VIT Fuel PumpAbhishek Singh Chauhan100% (1)
- Ci Fuel System Notes PDFDocument19 pagesCi Fuel System Notes PDFNduati JohnNo ratings yet
- Axial Piston PumpDocument4 pagesAxial Piston PumpAmanda HooverNo ratings yet
- EHTCDocument2 pagesEHTCewfsd100% (1)
- PSG Princible of OperationDocument4 pagesPSG Princible of Operationmehdi kamaliNo ratings yet
- Hyundai HD78 Steering SystemDocument54 pagesHyundai HD78 Steering SystemBigfair HD78100% (1)
- VIT Fuel PumpDocument16 pagesVIT Fuel PumpAbhishek Singh Chauhan50% (2)
- What Is Capacity Control?: The Simplest Forms of Controlling The Room Temperature AreDocument7 pagesWhat Is Capacity Control?: The Simplest Forms of Controlling The Room Temperature ArearunNo ratings yet
- Presentation On:Governing of Pelton Wheelturbine: Government Engineering College DahodDocument16 pagesPresentation On:Governing of Pelton Wheelturbine: Government Engineering College Dahodl8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Hydraulic CircuitsDocument25 pagesHydraulic CircuitspriyanthabandaraNo ratings yet
- CPP PDFDocument69 pagesCPP PDFiqha iqhoNo ratings yet
- Partial Delivery Lecture - Hydraulic CircuitsDocument39 pagesPartial Delivery Lecture - Hydraulic CircuitsAbdelkader EldjouNo ratings yet
- Rotary Diesel Pump:: Pressure Control ValveDocument4 pagesRotary Diesel Pump:: Pressure Control Valvemsaqibraza93No ratings yet
- Swash-Plate Pump (Portfolio)Document2 pagesSwash-Plate Pump (Portfolio)Jannen V. ColisNo ratings yet
- Basic HydraulicsDocument17 pagesBasic HydraulicsDennis Roldan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Zexel Fuel SystemDocument6 pagesZexel Fuel SystemascoattascoNo ratings yet
- Floating Cup PrincipleDocument27 pagesFloating Cup Principlemanilrajkrr6302No ratings yet
- Fuel Pumps, Systems & Timing-1Document51 pagesFuel Pumps, Systems & Timing-1Nikhil SonarbagkerNo ratings yet
- Unit 17 - 02 - Starting & ManoeuvringDocument16 pagesUnit 17 - 02 - Starting & ManoeuvringAisha ZaheerNo ratings yet
- MAN B&W Fuel PumpDocument8 pagesMAN B&W Fuel PumpNick Konor100% (2)
- Sistema HidráulicoDocument36 pagesSistema HidráulicoValdir AlexandreNo ratings yet
- Control valve functions guideDocument39 pagesControl valve functions guideAstrit StratiNo ratings yet
- SM - VOLVO L180F WHEEL LOADER Service Repair ManualDocument8 pagesSM - VOLVO L180F WHEEL LOADER Service Repair ManualEng-AhmedRashad0% (3)
- Installation and OperationDocument9 pagesInstallation and Operationabdullatif_asNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Travel Device: 1. ConstructionDocument9 pagesGroup 4 Travel Device: 1. ConstructionthierrylindoNo ratings yet
- Transmission 5800 - 16800 8-Speed ManualDocument65 pagesTransmission 5800 - 16800 8-Speed ManualMauro Perez100% (1)
- MAN B&W MC Engine VIT Fuel Pump OperationDocument16 pagesMAN B&W MC Engine VIT Fuel Pump OperationAayush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Robert Bosch Type VE Diesel Injection PumpDocument5 pagesRobert Bosch Type VE Diesel Injection PumpShahrizan abdul rahman0% (1)
- Fuel injection pump operationDocument21 pagesFuel injection pump operationHERMAWAN97% (31)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesFrom EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- الأزمنة في الإنكليزيDocument23 pagesالأزمنة في الإنكليزيMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- اسئلة تمهيدي انكليزي من 2014 -2020Document114 pagesاسئلة تمهيدي انكليزي من 2014 -2020Moaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Denoxtronic PDFDocument29 pagesDenoxtronic PDFanshel100% (2)
- PB AT A4CF1 EngDocument19 pagesPB AT A4CF1 EngMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- PB Engine Kappa EngDocument15 pagesPB Engine Kappa EngMoaed Kanbar50% (2)
- PB AT A4CF1 EngDocument19 pagesPB AT A4CF1 EngMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Manual Transmission: (M5/6Cfx-1)Document10 pagesManual Transmission: (M5/6Cfx-1)Moaed Kanbar100% (2)
- PB MDPS EngDocument9 pagesPB MDPS EngMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- PB Air Conditioning EngDocument18 pagesPB Air Conditioning EngMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- PB SRS EngDocument18 pagesPB SRS EngMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- PB Engine Gamma EngDocument14 pagesPB Engine Gamma EngMoaed Kanbar100% (3)
- PB Engine U-II EngDocument12 pagesPB Engine U-II EngMoaed Kanbar100% (1)
- Mitsubishi Galant 4g63 Engine Repair ManualDocument29 pagesMitsubishi Galant 4g63 Engine Repair ManualMoaed Kanbar100% (1)
- صمام التمددDocument5 pagesصمام التمددnazar750No ratings yet
- In-Vehicle Repair: Timing Drive Components - Hydraulic Chain Tensioner, RHDocument1 pageIn-Vehicle Repair: Timing Drive Components - Hydraulic Chain Tensioner, RHMoaed Kanbar100% (1)
- Clean and Cool PDFDocument4 pagesClean and Cool PDFMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Manual 6488 OTCDocument6 pagesManual 6488 OTCjr100100100% (1)
- 28-01008 2254-2262 PDFDocument9 pages28-01008 2254-2262 PDFMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- 28-01008 2254-2262 PDFDocument9 pages28-01008 2254-2262 PDFMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Piston Ring Assembly Tips 4strk - Ringinstall2!24!05Document2 pagesPiston Ring Assembly Tips 4strk - Ringinstall2!24!05michaelmangaaNo ratings yet
- VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-Intelligent) System: GeneralDocument5 pagesVVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-Intelligent) System: GeneralsadiksnmNo ratings yet
- Acl Pistonproducts Pp99Document275 pagesAcl Pistonproducts Pp99Moaed Kanbar100% (1)
- 05Document7 pages05Moaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Fuel InjectionDocument37 pagesFuel InjectionBence M ZoltanNo ratings yet
- Cross Section F8M F8Q Engine Repair (Motor Diesel F8M F8Q Dacia Papuc Solenza 1307)Document107 pagesCross Section F8M F8Q Engine Repair (Motor Diesel F8M F8Q Dacia Papuc Solenza 1307)bogdanxp2000100% (4)
- Variable Valve TimingDocument3 pagesVariable Valve TimingAjay AgarwalNo ratings yet
- SSP 275 Phaeton Air Suspension 3 PDFDocument21 pagesSSP 275 Phaeton Air Suspension 3 PDFMoaed Kanbar0% (1)
- Eng 2013031916240410Document6 pagesEng 2013031916240410Moaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- Variable Valve TimingDocument19 pagesVariable Valve TimingShrigopal PrajapatNo ratings yet