Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide (V100R010C10 05) (PDF) - en
Uploaded by
Md AtaullaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide (V100R010C10 05) (PDF) - en
Uploaded by
Md AtaullaCopyright:
Available Formats
3900 Series Base Station
V100R010C10
LMT User Guide
Issue
05
Date
2015-12-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2015. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address:
Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website:
http://www.huawei.com
Email:
support@huawei.com
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
About This Document
About This Document
Purpose
This document describes how to log in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT) for 3900
series base stations and how to use the LMT to operate and maintain 3900 series base stations.
NOTE
Unless otherwise stated, a base station in the following part of this document refers to a 3900 series base
station.
Product Version
The following table lists the product versions related to this document.
Product Name
Solution Version
Product Version
BTS3900
l
l
l
l
V100R010C10
BTS3900A
BTS3900L
SRAN10.1
GBSS17.1
RAN17.1
eRAN8.1
BTS3900AL
l SRAN10.1
DBS3900
l GBSS17.1
l RAN17.1
l eRAN8.1
l eRAN TDD 8.1
DBS3900 LampSite
l SRAN10.1
l RAN17.1
l eRAN8.1
l eRAN TDD 8.1
BTS3900C
l SRAN10.1
l RAN17.1
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
About This Document
Intended Audience
This document is intended for:
l
System engineers
Field engineers
Network shift engineers
Network operators
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Contents
Contents
About This Document.....................................................................................................................ii
1 Changes in 3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide..........................................................1
2 Introduction to the LMT...............................................................................................................5
2.1 Definitions of LMT........................................................................................................................................................ 7
2.2 Types of LMT................................................................................................................................................................. 7
2.3 Functions of the LMT.....................................................................................................................................................9
2.4 System Requirements for LMT Installation................................................................................................................. 10
2.5 Installing and Verifying the LMT Application Software..............................................................................................13
2.5.1 Installing the LMT Application Software................................................................................................................. 13
2.5.2 Verifying the LMT Application Software................................................................................................................. 16
2.6 Components of the LMT Main Window...................................................................................................................... 17
2.7 LMT Offline Tools........................................................................................................................................................20
2.7.1 Installing the LMT Offline Tool................................................................................................................................ 21
2.7.2 Operations Related to LMT Offline MML................................................................................................................22
2.7.3 Traffic Recording Review Tool................................................................................................................................. 26
2.7.4 FTP Client..................................................................................................................................................................27
2.8 Configuring an Emergency OM Channel..................................................................................................................... 28
2.9 Obtain Documentation List.......................................................................................................................................... 30
3 Getting Started with the LMT...................................................................................................32
3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the LMT............................................................................................................................. 33
3.2 Managing Rights...........................................................................................................................................................40
3.2.1 Concepts Related to Rights Management..................................................................................................................40
3.2.2 Managing User Accounts.......................................................................................................................................... 44
3.2.3 Managing Login Passwords.......................................................................................................................................45
3.2.4 Managing Command Groups.....................................................................................................................................47
3.3 Setting Office Information on the LMT....................................................................................................................... 47
4 Running MML Commands........................................................................................................52
4.1 Basic Concepts Related to MML Commands.............................................................................................................. 53
4.1.1 Introduction to MML Commands..............................................................................................................................53
4.1.2 Components of the MML Command Window.......................................................................................................... 54
4.2 Running a Single MML Command.............................................................................................................................. 55
4.3 Running MML Commands in Batches......................................................................................................................... 57
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Contents
4.4 Checking the Syntax..................................................................................................................................................... 59
4.5 Setting Parameters........................................................................................................................................................ 59
5 Managing Alarms and Events................................................................................................... 61
5.1 Basic Concepts Related to Alarms or Events............................................................................................................... 62
5.1.1 Alarm or Event Categories........................................................................................................................................ 62
5.1.2 Alarm Severity...........................................................................................................................................................62
5.1.3 NM Alarm Type.........................................................................................................................................................63
5.1.4 Alarm Flags............................................................................................................................................................... 64
5.2 Handling Alarms and Events........................................................................................................................................ 65
5.2.1 Setting Alarm or Event Query Properties..................................................................................................................65
5.2.2 Browsing Active Alarms or Events........................................................................................................................... 65
5.2.3 Querying Alarm or Event Logs................................................................................................................................. 66
5.2.4 Querying Alarm or Event Configurations................................................................................................................. 68
5.2.5 Querying Alarm or Event Handling Suggestions...................................................................................................... 69
5.2.6 Manually Refreshing Alarms or Events.................................................................................................................... 69
5.2.7 Manually Clearing Alarms or Events........................................................................................................................ 70
5.2.8 Deleting Cleared Alarms or Events........................................................................................................................... 70
5.2.9 Saving the Information About Alarms or Events...................................................................................................... 71
6 Managing Message Tracing.......................................................................................................72
6.1 Overview of Message Tracing......................................................................................................................................73
6.2 General Operations Related to Message Tracing......................................................................................................... 75
6.2.1 Browsing Traced Messages Online........................................................................................................................... 75
6.2.2 Viewing Message Details.......................................................................................................................................... 76
6.2.3 Saving Traced Messages............................................................................................................................................77
6.2.4 Browsing Traced Messages Offline...........................................................................................................................78
6.3 Common Tracing Tasks................................................................................................................................................ 81
6.3.1 PTP Trace.................................................................................................................................................................. 81
6.3.2 MAC Trace................................................................................................................................................................ 83
6.3.3 LACP Trace............................................................................................................................................................... 86
6.3.4 PPP Trace...................................................................................................................................................................88
6.3.5 MP Trace....................................................................................................................................................................89
6.3.6 IP Layer Protocol Trace.............................................................................................................................................91
6.3.7 SCTP Trace................................................................................................................................................................95
6.3.8 CMPV2 Trace............................................................................................................................................................ 96
6.3.9 IKE Trace...................................................................................................................................................................97
6.3.10 PNP Trace................................................................................................................................................................ 99
6.3.11 Proxy PNP Trace....................................................................................................................................................100
6.3.12 ICP Trace............................................................................................................................................................... 101
6.3.13 SAAL Trace...........................................................................................................................................................103
6.3.14 HDLC Trace.......................................................................................................................................................... 104
6.3.15 IUANT Trace.........................................................................................................................................................106
6.3.16 485 Trace............................................................................................................................................................... 107
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Contents
6.3.17 IPMI Trace.............................................................................................................................................................109
6.3.18 RF Link Trace........................................................................................................................................................ 110
6.3.19 Process Message Trace.......................................................................................................................................... 112
6.3.20 RF Message Trace..................................................................................................................................................114
6.4 GSM-specific Tracing Tasks.......................................................................................................................................115
6.4.1 Abis Interface CS Trace (RSL)................................................................................................................................115
6.4.2 Abis Interface CS Trace (CSL)................................................................................................................................117
6.4.3 TRX RF Sampling................................................................................................................................................... 118
6.5 UMTS-specific Tracing Tasks.................................................................................................................................... 118
6.5.1 DSP Trace................................................................................................................................................................ 119
6.5.2 Cell Trace.................................................................................................................................................................120
6.5.3 User Trace................................................................................................................................................................122
6.5.4 Iub Trace.................................................................................................................................................................. 125
6.6 LTE-specific Tracing Tasks........................................................................................................................................ 126
6.6.1 S1 Interface Trace....................................................................................................................................................126
6.6.2 X2 Interface Trace................................................................................................................................................... 128
6.6.3 Uu Interface Trace................................................................................................................................................... 130
6.6.4 IFTS Trace............................................................................................................................................................... 131
6.6.5 M2 Interface Trace...................................................................................................................................................135
6.6.6 Se Interface Trace.................................................................................................................................................... 136
6.6.7 EPCInside NAS Interface Trace.............................................................................................................................. 138
6.6.8 EX2 Interface Trace.................................................................................................................................................140
6.6.9 SO Interface Trace................................................................................................................................................... 141
7 Managing Performance Monitoring...................................................................................... 143
7.1 Overview of Real-time Performance Monitoring.......................................................................................................144
7.2 General Operations Related to Real-time Performance Monitoring.......................................................................... 145
7.2.1 Browsing Performance Monitoring Results Online................................................................................................ 146
7.2.2 Setting the Chart Display Mode.............................................................................................................................. 146
7.2.3 Saving Performance Monitoring Results.................................................................................................................147
7.2.4 Browsing Performance Monitoring Results Offline................................................................................................147
7.3 Common Monitoring Tasks........................................................................................................................................ 148
7.3.1 Transport Port Traffic Monitoring........................................................................................................................... 148
7.3.2 Transport Link Traffic Monitoring.......................................................................................................................... 151
7.3.3 IP Performance Monitoring..................................................................................................................................... 154
7.3.4 IPsec Performance Monitoring................................................................................................................................ 155
7.3.5 Local Pass-By Traffic Monitoring........................................................................................................................... 156
7.3.6 IP Clock Data Collection Monitoring......................................................................................................................157
7.3.7 Clock Quality Test Monitoring................................................................................................................................157
7.3.8 CPU/DSP Usage Monitoring...................................................................................................................................159
7.3.9 Board Temperature Monitoring............................................................................................................................... 160
7.3.10 RRU/RFU Output Power Monitoring....................................................................................................................161
7.3.11 Rx Frequency Scanning......................................................................................................................................... 162
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vi
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Contents
7.3.12 DTF Test................................................................................................................................................................ 164
7.3.13 FFT Frequency Scan..............................................................................................................................................165
7.3.14 Board RTWP..........................................................................................................................................................168
7.3.15 Antenna Radiation Pattern.....................................................................................................................................169
7.3.16 Transport OAM Monitoring.................................................................................................................................. 170
7.3.17 Transport Auto Setup User Plane Monitoring....................................................................................................... 171
7.3.18 DTP Test................................................................................................................................................................ 172
7.4 GSM-Specific Monitoring Tasks................................................................................................................................174
7.4.1 Offline Spectrum Scan Monitoring......................................................................................................................... 174
7.4.2 Online Spectrum Scan Monitoring.......................................................................................................................... 175
7.4.3 Codec Mode Test..................................................................................................................................................... 177
7.5 UMTS-specific Monitoring Tasks.............................................................................................................................. 177
7.5.1 HSPA Monitoring.................................................................................................................................................... 178
7.5.2 Sector Equipment Group RTWP............................................................................................................................. 179
7.5.3 Cell Throughput Statistic.........................................................................................................................................180
7.5.4 Cell Service Resource Query...................................................................................................................................181
7.5.5 Cell RTWP...............................................................................................................................................................182
7.5.6 Frequency Scan Monitoring.................................................................................................................................... 182
7.5.7 Repeater Interfere Frequency Scan Monitoring...................................................................................................... 184
7.6 LTE-specific Monitoring Tasks.................................................................................................................................. 186
7.6.1 Sector Performance Monitoring.............................................................................................................................. 186
7.6.2 Cell Performance Monitoring.................................................................................................................................. 188
8 Maintaining the Base Station.................................................................................................. 192
8.1 Device Panel Operations............................................................................................................................................ 193
8.1.1 Introduction to the Device Panel............................................................................................................................. 193
8.1.2 Starting the Device Panel........................................................................................................................................ 194
8.1.3 Querying the Board Version Information................................................................................................................ 194
8.1.4 Listing Active Alarms............................................................................................................................................. 195
8.1.5 Resetting a Board.....................................................................................................................................................195
8.1.6 Querying the Current Version Information of the Base Station.............................................................................. 196
8.1.7 Blocking a Board..................................................................................................................................................... 197
8.1.8 Unblocking a Board.................................................................................................................................................197
8.1.9 Querying the Clock Status....................................................................................................................................... 198
8.1.10 Querying the Board Status.....................................................................................................................................199
8.1.11 Querying the Software Version of the Base Station.............................................................................................. 199
8.1.12 Querying the CPU/DSP Usage.............................................................................................................................. 200
8.1.13 Querying the Manufacturing Information of a Board............................................................................................200
8.1.14 Querying the E1/T1 Port Status.............................................................................................................................201
8.2 Common Maintenance Tasks......................................................................................................................................202
8.2.1 Concepts Related to Software and Files.................................................................................................................. 202
8.2.2 Configuring the FTP Server.................................................................................................................................... 203
8.2.3 Software Management............................................................................................................................................. 205
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vii
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Contents
8.2.4 Extra Configuration File Transfer............................................................................................................................209
8.2.5 Device Archive Transfer..........................................................................................................................................210
8.2.6 Data Configuration File Transfer.............................................................................................................................211
8.2.7 Other File Transfer...................................................................................................................................................213
8.2.8 Proxy GBTS Transmission Maintenance................................................................................................................ 216
8.2.9 Proxy File Transfer.................................................................................................................................................. 218
8.2.10 IP Transport Selftest.............................................................................................................................................. 222
8.3 Maintaining the GSM Base Station............................................................................................................................ 223
8.3.1 Querying Frequency Scan....................................................................................................................................... 223
8.3.2 Configuring Frequency Scan................................................................................................................................... 224
8.3.3 Monitoring Channel Status...................................................................................................................................... 225
8.3.4 Testing Channel Loopback...................................................................................................................................... 226
8.3.5 Testing TRX Loopback............................................................................................................................................227
8.3.6 Modifying the Cell Management Status.................................................................................................................. 228
8.3.7 Testing Idle Timeslot............................................................................................................................................... 229
8.4 Maintaining the LTE Base Station..............................................................................................................................230
8.4.1 Engineering Quality Check..................................................................................................................................... 230
8.5 BTS Self-test...............................................................................................................................................................231
9 FAQ.............................................................................................................................................. 233
9.1 How to Switch a Minimum LMT Package to a Complete LMT Package..................................................................238
9.2 Functions of the LMT Become Abnormal After an LMT Version Upgrade or Rollback.......................................... 241
9.3 How to Increase the LMT Response Speed During the Use of the Firefox Browser.................................................242
9.4 How to Handle Incorrect Display of Colors of the LMT Main Window................................................................... 243
9.5 How to Handle Failed Display of the Verify Code in the LMT Login Dialog Box................................................... 243
9.6 How to Handle No Responses to the Operations Performed on the Menu of the LMT Main Window.....................244
9.7 How to Clear Garbled Characters That Occurred in a CSV File................................................................................245
9.8 How to Set a Correct SSL Security Certificate.......................................................................................................... 245
9.9 How to Rectify Errors That Occurr While Saving a File........................................................................................... 247
9.10 How to Avoid the Failure to Log In to the LMT Due to a High Default Internet Explorer Security Level.............248
9.11 How to Handle the Slow Redirection After Logging in to the LMT........................................................................250
9.12 How to Handle the LMT Interface Disorder............................................................................................................ 250
9.13 How to Handle the Unknown Error Occurrs on LMT Interface or MML Command Execution Failure After a
Browser Upgrade.............................................................................................................................................................. 251
9.14 How to Handle Error Message Displayed on the LMT or No Responses to Operations Performed on the LMT
Login Window.................................................................................................................................................................. 251
9.15 How to Install OS Patches........................................................................................................................................ 252
9.16 What Do I Do if Tracing, Monitoring or Other Functions Cannot Be Used?.......................................................... 253
9.17 What Do I Do If There Is No Response or Any Error Message After a Tracing, Monitoring or Other Task Is
Created..............................................................................................................................................................................255
9.18 How to Handle the Problem That Only the Error Code Is Displayed in an Error Message After a Tracing or
Monitoring Task Is Created.............................................................................................................................................. 256
9.19 Any Further Operation Performed When Some LMT Web Pages Fail to Update Causes the Web Pages to Turn
Blank.................................................................................................................................................................................256
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
viii
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Contents
9.20 How to Handle the LMT Exit After Clicking Trace, Monitor, or Device Maintenance Tab in Window 7.......... 257
9.21 How to Handle the Disconnection Between the LMT and Base Station After the Device Digital Certificate Is
Replaced........................................................................................................................................................................... 257
9.22 How to Handle Exceptions in the LMT Due to Insufficient PC Memory................................................................258
9.23 Error Message "This user session already exists" Upon Login to LMT.................................................................. 259
9.24 Interfaces for Performing Tracing or Monitoring Tasks Blinking............................................................................260
9.25 The web site's certificate cannot be verified.Do you want to continue? Is Displayed During Tracing or
Monitoring........................................................................................................................................................................ 260
9.26 Batch Execution of MML Commands Fails Because Some MML Commands Contain Invisible Carriage Returns
or Line Feeds.................................................................................................................................................................... 261
9.27 How to Handle Shortcut Key Invalidation............................................................................................................... 261
9.28 What Do I Do If A Message "Stop running this script?" Is Displayed?...................................................................262
9.29 The Internet Explorer Fails to Respond or the Login Window Is Displayed After the LMT Is Running for a While
or Multiple Functions Are Concurrently Enabled on the LMT........................................................................................262
9.30 A Message checking client environment... Is Displayed on the Login Window and the browser Does Not
Respond............................................................................................................................................................................ 263
9.31 LMT Login Window Being Stopped by the Browser...............................................................................................264
9.32 The Application Blocked by Security Settings Dialog Box Is Displayed When Batch Processing, Tracing,
Monitoring, or Device Maintenance Is Enabled...............................................................................................................264
9.33 Help for Installing and Using the Java Plug-in.........................................................................................................265
9.34 What Do I Do If the Message Your Java version is out of date Is Displayed?..................................................... 267
9.35 How to Configure Wireless NIC on a Computer......................................................................................................267
Index................................................................................................................................................269
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ix
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
1 Changes in 3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide
Changes in 3900 Series Base Station LMT
User Guide
This chapter describes the changes in 3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide.
05 (2015-10-30)
This is the fifth commercial release.
Compared with 04 (2015-08-30), this issue does not include any new topics.
Compared with 04 (2015-08-30), this issue includes the following changes:
Topic
Change Description
2.2 Types of LMT
Added the base station with the main
control board being LMPT in scenarios
where the built-in WebLMT is used.
3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the LMT
Added the description that a maximum of
total four local users and EMS users can log
in to the LMT at the same time when the
BBU3900 is configured with the LMPT.
6.1 Overview of Message Tracing
Added the description of the scenario that
the sequence of the messages corresponding
to the collection time is inconsistent with
the actual message sequence.
Compared with 04 (2015-08-30), this issue does not exclude any topics.
04 (2015-08-30)
This is the fourth commercial release.
Compared with 03 (2015-06-30), this issue does not include any new topics.
Compared with 03 (2015-06-30), this issue includes the following changes:
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
1 Changes in 3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide
Topic
Change Description
3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the LMT
Modified descriptions about the default
password in Step 4.
7.6.2 Cell Performance Monitoring
Modified descriptions about the Monitor
Period parameter.
Compared with 03 (2015-06-30), this issue does not exclude any topics.
03 (2015-06-30)
This is the third commercial release.
Compared with 02 (2015-05-08), this issue does not include any new topics.
Compared with 02 (2015-05-08), this issue includes the following changes:
Topic
Change Description
3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the LMT
Added the description of the change in the
local maintenance IP address after the
minimum configuration is enabled.
2.2 Types of LMT
Added the login method and icon of a
locally deployed WebLMT.
Compared with 02 (2015-05-08), this issue does not exclude any topics.
02 (2015-05-08)
This is the second commercial release.
Compared with 01 (2015-03-23), this issue does not include any new topics.
Compared with 01 (2015-03-23), this issue includes the following changes:
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Topic
Change Description
7.5.7 Repeater Interfere Frequency Scan
Monitoring
Added the descriptions about the Index of
RX Channel 1 parameter in the output
results.
7.3.12 DTF Test
Added the support for the DTF test function
on the RRU3269 and RRU3249.
7.3.13 FFT Frequency Scan
Added the description that offline FFT
frequency scan automatically deactivates
cells or carriers to the Context part.
7.2.1 Browsing Performance Monitoring
Results Online
Changed the maximum number of
monitored tasks to 60 in the Note part.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
1 Changes in 3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide
Topic
Change Description
8.2.2 Configuring the FTP Server
Added the setting notes for the Working
directory parameter.
2.4 System Requirements for LMT
Installation
Added the descriptions about the JRE
versions supported by the WebLMT and the
conditions under which the HttpOnly
attribute for cookies can be configured on
the WebLMT.
Compared with 01 (2015-03-23), this issue does not exclude any topics.
01 (2015-03-23)
This is the first commercial release.
Compared with Draft B (2015-02-10), this issue does not include any new topics.
Compared with Draft B (2015-02-10), this issue includes the following changes:
Topic
Change Description
7.2.1 Browsing Performance Monitoring
Results Online
Added the descriptions about the Switch
Display Mode operation.
About This Document
Added the eRAN TDD 8.1 solution version
that matches the DBS3900 LampSite.
Compared with Draft B (2015-02-10), this issue does not exclude any topics.
Draft B (2015-02-10)
This is the release of Draft B.
Compared with Draft A (2015-01-15), this issue does not include any new topics.
Compared with Draft A (2015-01-15), this issue does not include any changes.
Compared with Draft A (2015-01-15), the following information is deleted from this issue:
l
Frequency Scanning Intermodulation Interference Detection
Draft A (2015-01-15)
This is the release of Draft A.
Compared with issue 06 (2014-11-15) of V100R009C00, this issue includes the following
new topics:
l
7.5.7 Repeater Interfere Frequency Scan Monitoring
8.2.8 Proxy GBTS Transmission Maintenance
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
1 Changes in 3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide
Compared with issue 06 (2014-11-15) of V100R009C00, this issue includes the following
changes:
Topic
Change Description
3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the LMT
Added the descriptions about how to locally
log in to the base station in wireless mode.
2.5.1 Installing the LMT Application
Software
Changed the default installation path of the
local LMT software.
7.3.2 Transport Link Traffic Monitoring
Added the descriptions about the GPM link
type.
8.2.9 Proxy File Transfer
Added the descriptions that the GBTS
supports obtaining run logs.
2.2 Types of LMT
Added the base station with the main
control board being GTMUb in scenarios
where the external WebLMT is used.
6.4.1 Abis Interface CS Trace (RSL)
Added the descriptions that the base station
with the main control board being GTMUb
does not support this function.
6.3.2 MAC Trace
Added the descriptions that the GTMUb
board does not support the IP-layer
extended filtering function of MAC tracing.
6.6.1 S1 Interface Trace
Added the descriptions about the Local Cell
ID and CPU ID parameters in the output
results.
6.6.2 X2 Interface Trace
6.6.3 Uu Interface Trace
6.6.4 IFTS Trace
Added the descriptions about the CRNTI
parameter in the output results.
Compared with issue 06 (2014-11-15) of V100R009C00, this issue does not exclude any
topics.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Introduction to the LMT
About This Chapter
This chapter describes the functions, system requirements, and main window of the local
maintenance terminal (LMT).
2.1 Definitions of LMT
Before you use the local maintenance terminal (LMT), you need to know the following
concepts: LMT, LMT PC, and LMT software.
2.2 Types of LMT
The LMT consists of the built-in WebLMT and external WebLMT depending on different
application scenarios.
2.3 Functions of the LMT
The local maintenance terminal (LMT) is used to assist with base station deployment, and
locally locate and fix faults.
2.4 System Requirements for LMT Installation
This section describes the system requirements for the local maintenance terminal (LMT)
installation.
2.5 Installing and Verifying the LMT Application Software
This chapter describes how to install the local maintenance terminal (LMT) application
software and how to verify the installation.
2.6 Components of the LMT Main Window
This section describes the components of the local maintenance terminal (LMT) main window
and the functions of each component.
2.7 LMT Offline Tools
LMT offline tools include the traffic recording review tool, offline MML tool, FTP client, and
HedEx Lite.
2.8 Configuring an Emergency OM Channel
For a separate-MPT multimode base station, an emergency OM channel is used to maintain a
faulty base station through the OM channel of a normal base station. The maintenance
includes proxy PNP tracing, operations using MML commands, and proxy file transfer for the
faulty base station through the emergency OM channel of the normal base station.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
2.9 Obtain Documentation List
This section describes how to query and obtain documentation packages of the corresponding
product version.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
2.1 Definitions of LMT
Before you use the local maintenance terminal (LMT), you need to know the following
concepts: LMT, LMT PC, and LMT software.
LMT
The LMT is a logical concept. It refers to an operation and maintenance (OM) terminal
installed with the Huawei Local Maintenance Terminal software and connected to the OM
network for the base station. You can use the LMT to operate and maintain the base station.
LMT PC
The LMT PC is a hardware concept. It refers to a computer where the Huawei Local
Maintenance Terminal software is installed.
LMT Software
The LMT software refers to the Huawei Local Maintenance Terminal software developed by
Huawei and installed on the LMT PC.
2.2 Types of LMT
The LMT consists of the built-in WebLMT and external WebLMT depending on different
application scenarios.
Table 2-1 lists the application scenarios for the built-in WebLMT and external WebLMT.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Table 2-1 Application scenarios for the built-in WebLMT and external WebLMT
Type
Application Scenario
How to Start the WebLMT
Built-in
WebLMT
l The UMPT works as the
main control board and
UMTS or LTE base
stations are deployed, that
is, the base station works
in GU, GL, GUL, UO, or
LO mode.
Start the IE browser, enter the IP address
of the base station in the address box,
and click Enter to log in to the
WebLMT.
l Both the following
conditions are true: The
UMPT works as the main
control board and only
GSM base stations are
deployed. The GSM base
station has an OM
bandwidth greater than 64
kbit/s.
l For the base station that
uses the LMPT as the
main control board.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Type
Application Scenario
How to Start the WebLMT
External
WebLMT
l BTS3900-1U and
DBS3900-1U.
After the LMT application software is
successfully installed, log in to the LMT
using either of the following methods:
l For the base station that
uses the WMPT as the
main control board.
l For the base station that
uses the GTMUb as the
main control board.
l Both the following
conditions are true: The
UMPT works as the main
control board and only
GSM base stations are
deployed. The GSM base
station has an OM
bandwidth less than or
equal to 64 kbit/s.
l Choose Start > All Programs >
HUAWEI Local Maintenance
Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT) >
Web Local Maintenance
Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT),
The Local Maintenance Terminal
window is displayed.
l If the local WebLMT service manager
is started, enter http://127.0.0.1:822
in the address box of the browser and
click Enter.
NOTE
l After the local WebLMT service manager
will be displayed at
starts, an icon
the right of the taskbar. If the local
WebLMT service manager is not started,
start it by choosing Start > All Programs
> HUAWEI Local Maintenance
Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT) > Web
Local Maintenance
Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT).
l The service port number is 822 by
default. If the service port number of the
local WebLMT is changed, ensure that
the entered port number is consistent with
the changed service port.
For details about how to install the application Web Local Maintenance Terminal, see 2.5
Installing and Verifying the LMT Application Software.
The certificate-based peer party authentication mode is meaningless to external WebLMTs.
This because the server of an external WebLMT is installed on the PC connected to the base
station but the PC cannot obtain the certificate of the base station.
2.3 Functions of the LMT
The local maintenance terminal (LMT) is used to assist with base station deployment, and
locally locate and fix faults.
Use the LMT to operate and maintain a base station in the following scenarios:
l
When the operation and maintenance (OM) channel between the base station and U2000
is unavailable, use the LMT to deploy the base station locally.
When communication between the base station and the U2000 is interrupted, use the
LMT to locate and fix the faults.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
When alarms are generated on the base station and related boards must be locally
replaced, use the LMT to locate and fix the faults.
NOTE
When the base station is appropriately communicating with the U2000, it is recommended that you
operate and maintain the base station on the U2000. When you must obtain real-time information about
a base station from the U2000 to locate faults, the U2000 may fail to provide adequate information
because it manages many network elements (NEs). In this situation, use the LMT to operate and
maintain the base station.
The LMT provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI), which helps users operate and maintain
the base station on the Web. The LMT implements the following local OM functions:
l
Executes man-machine language (MML) commands
Manages alarms and events
Runs MML commands in batches
Traces messages
Monitors base station performance
Maintains equipment
Enables the base station to perform self-tests
NOTE
The LMT records user operations, such as login, deregistration, user addition, and user removal, in the
operation log. You can run the ULD LOG command to export and view the operation log. For details
about to how to use this command, see the related MML command reference.
2.4 System Requirements for LMT Installation
This section describes the system requirements for the local maintenance terminal (LMT)
installation.
Hardware Configurations
Table 2-2 lists the hardware requirements for the LMT PC.
Table 2-2 Hardware configurations
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Item
Recommended
Configuration
Minimum Configuration
CPU
2.8 GHz or higher
866 MHz
RAM
1 GB
512 MB
Hard disk
80 GB
10 GB
Video card resolution
1024 x 768 or higher
1024 x 768
CD-ROM drive
Wireless network interface
card
802.11n
802.11g
Network interface card
10 Mbit/s or 100 Mbit/s
10 Mbit/s
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Item
Recommended
Configuration
Minimum Configuration
Others
A keyboard, a mouse, a
modem, an audio card, and a
sound box
A keyboard and a mouse
Software Configurations
Table 2-3 describes the software requirements for the PC where the LMT is to be installed.
Table 2-3 Software configurations
Item
Recommended Configuration
Operating system
l Microsoft Windows Server 2003 with patch KB938397
l Microsoft Windows Server 2008
l Microsoft Windows Vista
l Microsoft Windows 7
NOTE
Currently, the LMT supports only web browsers and 32-bit
operating systems.
Default language of the
operating system
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
English (United States)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Item
Recommended Configuration
Web browser
l Internet Explorer 8 (recommended)
l Internet Explorer 9 (recommended)
l Internet Explorer 10 (recommended)
l Internet Explorer 6 (not recommended)
l Internet Explorer 7 (not recommended)
l Internet Explorer 11 or later (not recommended)
l Firefox 10.X (X indicates a digit, not recommended)
l Firefox 17.X (X indicates a digit, not recommended)
l Firefox 24.X (X indicates a digit, not recommended)
l Firefox 31.0 (recommended)
NOTE
l You must set the security level of the web browser to medium or
low. Otherwise, the LMT menus cannot be viewed.
l If the LMT is terminated abnormally or does not respond when
you use the Internet Explorer of a version earlier than Internet
Explorer 8, you are advised to upgrade Internet Explorer 6 or 7
to Internet Explorer 8.
l Firefox of a version other than Firefox 10.X, Firefox 17.X,
Firefox 24.X , and Firefox 31.0 is not supported.
l If Firefox 10.X is used, the plug-ins of the Firefox application
center must be disabled.
l If a non-recommended web browser is used to log in to LMT,
the message You are advised to use Windows Internet
Explorer 8, 9, 10, or Firefox 31.0 to access WebLMT;
otherwise, other browsers may be incompatible with
WebLMT. will be displayed.
l On the Advanced tab page in the Internet Options dialog box,
select all check boxes under HTTP1.1 settings.
l If Internet Explorer and JRE 1.7 series versions supported by the
WebLMT are used, the HttpOnly attribute for cookies can be
configured on the WebLMT, reducing cross-site scripting
attacks. If other browsers or JRE versions are used, the HttpOnly
attribute cannot be configured.
l To improve system security, it is good practice to configure the
Internet Explorer browser as follows: choose Tools > Internet
Options > Advanced and select Use TLS 1.2.
Java plug-in called Java
Platform Standard Edition
Runtime Environment
(JRE)
JRE 1.7.0.65 are recommended. JRE 1.8.0.00 and versions
between JRE 1.7.0.0 and JRE 1.7.0.45 are not supported.
Note that JRE 1.7.0.0 is not supported and JRE 1.7.0.45 is
supported.
NOTE
l This plug-in can be downloaded from the Java official website
http://java.com/.
l After installing the JRE 1.7.0.65 version, modify default settings
of Java by referring to section 9.32 The Application Blocked
by Security Settings Dialog Box Is Displayed When Batch
Processing, Tracing, Monitoring, or Device Maintenance Is
Enabled.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Port Requirements
If a firewall exists between the base station and the LMT PC, ports 20, 21, and 80 must be
enabled on the firewall. If Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) needs to be used,
ports 20, 21, and 443 must be enabled on the firewall.
NOTE
Ports 20 and 21 are used for the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). They need to be enabled in the case
of file transfer using FTP.
Port 80 is used for the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) by default. The port is used for web
browsing by default.
Port 443 is used for the HTTPS protocol by default.
HTTP does not ensure secure access. That is, data transmitted between the LMT and NEs can be
easily intercepted and decrypted. Therefore, you are advised to use HTTPS to access the NEs.
Communication Capability
The LMT PC must support TCP/IP protocols.
The minimum effective bandwidth for the LMT is 512 kbit/s. The recommended bandwidth is
2 Mbit/s or larger.
NOTE
The network bandwidth limits the web page opening speed. If the recommended effective
bandwidth is provided, the LMT runs fast. If the minimum effective network bandwidth is
provided, all the functions can be performed but the LMT runs slowly.
The effective bandwidth is the bandwidth occupied by the LMT. If multiple applications compete
for the bandwidth, the LMT may run slowly even if a 2 Mbit/s bandwidth is provided.
2.5 Installing and Verifying the LMT Application
Software
This chapter describes how to install the local maintenance terminal (LMT) application
software and how to verify the installation.
2.5.1 Installing the LMT Application Software
This section describes how to install the local maintenance terminal (LMT) application
software on the LMT PC.
Prerequisites
l
You have obtained the installation CD-ROM and installation instructions from Huawei.
You have obtained the valid CD KEY for the LMT application software.
You have logged in to the LMT PC as an administrator.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Context
l
The PC user for installing the LMT application software must be configured with
administrator rights so that the user has the write rights on drive C. Otherwise, the PC
user will fail to log in to the LMT using the U2000 proxy function.
For details about local LMT software installation scenarios, see 2.2 Types of LMT.
NOTE
l The LMT application software must be installed when you use a browser to visit the base station that
uses the WMPT/GTMUb/GTMUc as the main control board.
l The LMT application software must be installed when you use a browser to visit BTS3900-1U or
DBS3900-1U.
l For the base station that uses the UMPT as the main control board, you are advised to log in to the
web LMT by entering the IP address of the base station in the browser for operation and
maintenance. Based on the actual requirements, LMT application software can be installed on the
the co-MPT GSM base station that uses the UMPT as the main control board.
Procedure
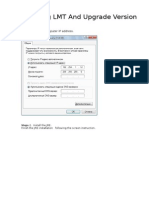
Step 1 Insert the installation CD-ROM of the LMT application software into the CD-ROM drive.
In a normal situation, the operating system automatically runs the CD-ROM drive. If the
operating system cannot automatically run the CD-ROM drive, open the folder in the
installation CD-ROM and double-click setup.exe.
NOTE
To install the LMT application software in a 32-bit Windows 7 operating system, perform the following
operations first:
l If the installation package is compressed, right-click the compressed installation package and choose
Properties. In the displayed Properties dialog box, click Compatibility and select Run this
program in compatibility mode for. Then, click OK.
l If the installation package is a folder or is decompressed, right-click setup.exe in the installation
package and choose Properties. In the displayed Properties dialog box, click Compatibility and
select Run this program in compatibility mode for. Then, click OK.
The compatibility message will not be displayed after the previous operations complete.
Step 2 In the displayed dialog box, select the language.
Step 3 Click OK.
A dialog box displays the introduction of the installation.
Step 4 Click Next.
A dialog box displays the copyright notice.
Step 5 Read the copyright notice. If you agree, choose I accept these terms.
NOTE
The Next button is available only after you choose I accept these terms.
Step 6 Click Next.
An Installation Directory dialog box is displayed.
Step 7 Use the default installation path or specify another installation path, and click Next.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
NOTE
l If the LMT application software is installed for the first time, the default installation path is D:
\WEBLMT_Enhanced.
l If the LMT application software of another version or for another NE has been installed, the default
path is the installation path of the installed LMT application software and cannot be changed.
If the installation path needs to be changed, uninstall the LMT application software of another
version or for another NE.
Step 8 In the window for selecting components, select the required components and click Next. (You
are advised to select all components.)
A CD KEY dialog box is displayed.
NOTE
If LMT software is running during installation, a Warning dialog box is displayed, prompting you
whether to continue the installation? Click Yes. The running LMT software stops, and the installation
continues.
Step 9 Enter the correct CD KEY, and click Next.
A Confirm installation dialog box is displayed.
NOTE
The CD KEY is saved in SN.TXT in the folder of the installation CD-ROM.
The Next button is available only after you enter the correct CD KEY.
Step 10 Confirm the installation information and click Next.
A progress indicator is displayed, showing the installation progress.
After all files are copied, an Initializing Components dialog box showing the component
initializing progress is displayed.
After all programs are installed, an Installation completed dialog box is displayed.
Step 11 Click Finish.
NOTE
To ensure that the installation file can be restored in case of file damage, you are advised to back up the
installation file in a path different from the installation path.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
After the installation is complete, you can use HUAWEI Local Maintenance Terminal to
start the following programs:
l
Web Local Maintenance Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT)
Uninstall Local Maintenance Terminal
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
NOTICE
l A maximum of 30 versions of the LMT application software can be installed on one PC. If
the limit is exceeded, you cannot log in to the LMT. Uninstall the versions no longer to be
used.
l During an upgrade of the LMT, if LmtView Common component under Select Software
Components is selected, the FTP tool started with the LMT will be updated, and the
password of the FTP tool is restored to the default password hwbs@com.
l If the running FTP tool is SingleRAN V100R007C00, NodeB V200R015C00, LTE
V100R005C01, or an earlier version before an upgrade of the LMT, stop the FTP tool and
then perform the upgrade. Ensure that the upgraded LMT can automatically start the FTP
tool of the latest version.
2.5.2 Verifying the LMT Application Software
You can verify the LMT application software installation by starting the LMT.
Context
Table 2-4 describes some folders in the directory structure for the LMT application software
installation.
Table 2-4 Some folders in the directory structure for the LMT application software
installation
Directory
Description
\adaptor\clientadaptor\MBTS
\version number of the LMT
application software
Saves the web page file for the LMT application
software and related resource files.
\adaptor\serveradaptor\MBTS
\version number of the LMT
application software
Saves executable programs for the local LMT server
and related resource files.
\uninstall
Saves the file of component uninstall information.
NOTE
The system automatically creates other folders when related tasks are created and data about the tasks
are saved.
Procedure
l
Start the LMT.
is displayed in the status area of the taskbar. If it is not displayed,
Check whether
choose Start > All Programs > HUAWEI Local Maintenance Terminal(WEBLMT
CLIENT) > Web Local Maintenance Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT) to start Web
Local Maintenance Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT). If a login window is displayed in
the browser, the LMT application software has been successfully installed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
NOTE
For details about how to log in to and log out of the LMT, see 3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the
LMT.
----End
2.6 Components of the LMT Main Window
This section describes the components of the local maintenance terminal (LMT) main window
and the functions of each component.
Main Window
Figure 2-1 shows the main window of an LMT for DBS3900 GUL.
Figure 2-1 LMT main window
Table 2-5 describes the components of the LMT main window.
Table 2-5 Components of the LMT main window
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
No.
Compo
nent
Parameter
Description
Status
bar
Displays the user type, user name, connection status,
and NE time.
Function
s
MML
Used to run man-machine language (MML) commands.
For details, see 4.1.2 Components of the MML
Command Window.
Alarm/Event
Used to query active alarms or events, alarm or event
logs, and alarm or event configurations.
Batch
Used to run MML commands in batches.
Trace
Used to trace base station messages.
Monitor
Used to monitor the base station performance in real
time.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
No.
2 Introduction to the LMT
Compo
nent
Menu
bar
Parameter
Description
Device
Maintenance
Used to manage equipment.
Self Test
Enables the base station to perform self-tests.
Configure
Emergency
OM Channel
Click Configure Emergency OM Channel on the
LMT. On the displayed Configure Emergency OM
Channel dialog box, select and configure the target
base station that requires emergency maintenance. For
details, see 2.8 Configuring an Emergency OM
Channel.
Obtain
Documentati
on List
Choose Obtain Documentation List on the LMT. The
documentation packages of the corresponding product
version are listed in the displayed dialog box. For
details, see 2.9 Obtain Documentation List.
FTP Tool
Used to download the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) tool.
1. Click FTP Tool. A File Download - Security
Warning dialog box is displayed.
2. Click Save to save the FTP server software
SFTPServer.exe to the computer where the LMT is
installed.
Command
Group
Settings
Some MML commands, GUI commands, and virtual
commands are added to comprise a command group,
command group is used to add commands to a specified
command group so that an admin user can add
operation authorities for authority-limited users.
1. Click Command Group Settings. The Command
Group Settings dialog box is displayed.
2. Select a customized command group (G_22 to
G_31) from Command group drop-down list.
3. Select the MML command or GUI command to be
. The added
added from the left pane, and click
MML command or GUI command is displayed in
the right pane. Then, click Apply.
4. Select the MML command or GUI command
options to be removed from the right pane, and click
. The removed MML command or GUI
command is displayed in the left pane. Then, click
Apply.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
No.
Compo
nent
Parameter
Description
Password
Used to change the password.
1. Click Password. A Password dialog box is
displayed.
2. Enter the old password in the Old Password text
box and the new password in the New Password
and Confirm Password text boxes.
3. Click OK. The password is changed.
About
Displays the version information.
Lockup
Locks the LMT window.
System
Settings
Used to set the automatic lockup time and specify the
path to save trace files.
1. Click System Settings. A System Settings dialog
box is displayed.
2. Enter the automatic lockup time and the path in the
Auto lock if no operation within (s) and Save path
text boxes, respectively.
3. Click Submit. The system setting is complete.
Others
Logout
Used to log out of the LMT.
Help
Used to open online help files.
Layout
Used to indicate the layout management function. Four
window layouts are available: cascade, tile horizontal,
tile vertical, and dock window.
NOTE
l If the LMT detects a change in the base station application, you will be prompted with a message. If this
happens, log in to the LMT again.
l If the IP address of the remote maintenance channel, local maintenance IP address in wired mode, or local
maintenance IP address in wireless mode changes after the SET OMCONNPOLICY command with
ONLYOMIP set to ENABLE is executed, the LMT will restart. In this case, log in to the LMT again.
l NE Time displayed in the status bar may deviate from the actual NE time, but the deviation does not
affect services.
l In addition to MML commands and GUI commands, a customized command group includes virtual
commands. The virtual commands are applicable to the communication between the eCoordinator and
eNodeB.
l The Firefox browser does not support window layouts.
Online Help
The LMT provides two types of online help:
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
LMT help
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
19
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
MML help
Table 2-6 describes the online help of the LMT.
Table 2-6 Online help of the LMT
Name
Description
Startup Operation
LMT
help
Provides the following
information:
If you are using Internet Explorer:
l LMT user guide
l Alarm details
l Press F1 or click Help in the LMT main
window to display LMT help topics.
l Click the mouse button in the displayed dialog
box, and press F1 to display the help
information about the dialog box.
l Event details
If you are using a Firefox browser, click Help in the
LMT main window to display the help information.
MML
help
Provides the following
information about an
MML command:
l Function
Enter an MML command in the Command text
box. Press Enter or click Assist, and then click the
Help tab. The help information about the command
is displayed on the tab page.
l Precaution
l Parameters
l Example
l Output Description
2.7 LMT Offline Tools
LMT offline tools include the traffic recording review tool, offline MML tool, FTP client, and
HedEx Lite.
Table 2-7 lists application scenarios for different offline tools.
Table 2-7 Application scenarios for different offline tools
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Tool
Application Scenario
Traffic recording review tool
Browses the tracing files in the .tmf format or monitoring
files in the .mmf format in offline mode.
Offline MML tool
Displays the MML command help for a version in offline
or makes offline MML scripts.
HedEx Lite
Browses the product documentation in the .hdx format.
FTP client
Obtains the logs and data configuration files.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
NOTE
If any of the preceding application scenarios is available, the four LMT offline tools will be
automatically installed.
2.7.1 Installing the LMT Offline Tool
This section describes how to install the local maintenance terminal (LMT) offline tool on the
LMT PC.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT as an administrator.
A valid LMT software serial number has been obtained.
The PC on which the LMT offline tool is to be installed meets the configuration
requirements.
Context
When the LMT offline tools of the current version have been installed:
l
If the LMT offline tools of a version later than the current version are required, install
them directly.
If the LMT offline tools of a version earlier than the current version are required,
uninstall the tools of the current version, install the tools of a version earlier than the
current version, and reinstall the tools of the current version.
NOTE
The preceding operations are not involved in patch versions of the same R version.
Procedure
Step 1 Insert the installation CD-ROM for the LMT offline tool in the CD-ROM drive of the LMT
PC.
l
If the operating system can automatically operate the CD-ROM drive, the installation
program automatically starts.
If the operating system cannot automatically operate the CD-ROM drive, open the folder
in the installation CD-ROM and double-click setup.bat or setup.vbs.
NOTE
You can obtain the installation program of the LMT offline tool from http://support.huawei.com. Log in to
http://support.huawei.com and then search for BTS3900 on the Software tab page. Choose and download
the installation program based on the software version.
Step 2 Select the installation program language and click OK.
The Install HUAWEI Local Maintenance Terminal dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click Next.
The copyright declaration is displayed.
Step 4 Read the software permission terms. If you agree, choose I accept the terms and click Next.
The dialog box for you to specify the installation path is displayed.
Step 5 Use the default installation path or specify another installation path, and click Next.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
21
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
NOTE
The default installation path is D:\HW LMT.
l If the LMT software of another version or for another NE has been installed, the default path is the
installation path of the installed LMT software and cannot be changed.
l If the installation path needs to be changed during this installation, LMT software of other products must
be uninstalled before beginning this installation.
Step 6 Select the required components and click Next. (You are advised to select all components.)
A CD KEY dialog box is displayed.
Step 7 Enter the CD key and click Next.
An installation information confirmation dialog box is displayed.
Step 8 If the installation information is correct, click Next.
A dialog box showing the file copying progress is displayed.
After all files are copied, a dialog box showing the component initializing progress is
displayed. After all components are installed, a dialog box showing that the installation is
complete is displayed.
Step 9 Click Finish.
NOTE
After the LMT offline tool is installed, the system automatically starts the LMT service manager by default.
----End
2.7.2 Operations Related to LMT Offline MML
This section describes how to use the browser to perform MML-related operations when you
have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT) offline. (MML is short for manmachine language.) You can view MML commands, prepare MML scripts, and obtain LMT
online help.
Introduction to the Offline MML Server
This section describes the window of the LMT offline man-machine language (MML) server
and operations on the window of the server.
Startup Operation
To start the LMT offline MML server, choose Start > All Programs > Huawei Local
Maintenance Terminal > LMT Offline MML on the LMT PC.
Window of the LMT Offline MML Server
Figure 2-2 shows the window of the LMT offline MML server. Table 2-8 describes the
components in the window.
NOTE
If you have minimized the window of the LMT offline MML server, you can double-click
right corner of the LMT PC to display the window again.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
at the lower
22
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Figure 2-2 Window of the LMT offline MML server
Table 2-8 Components in the window of the LMT offline MML server
Component
Description
Config
Displays the status of the LMT offline MML server and the
server port.
NOTE
l To minimize the window of the LMT offline MML server, click
Hide.
l To start the LMT offline MML server, click Start.
l To stop the LMT offline MML server, click Stop.
l To log in to the LMT offline MML, click Open Browser.
About
Displays information about the LMT offline MML server.
Introduction to the Offline MML Window
This section describes the offline man-machine language (MML) window.
Figure 2-3 shows the local maintenance terminal (LMT) offline MML window. Table 2-9
describes the components in the window.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
23
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Figure 2-3 LMT offline MML window
NOTE
l The MML navigation tree changes with the RAT, and the above window is specific to a multimode base
station.
l For details about MML commands and their related parameters, see the MML command help.
Table 2-9 Components in the LMT offline MML window
Component
Description
Navigation Tree
Lists all MML commands. If you double-click an MML
command in the navigation tree, the command will be
displayed in the command input text box.
Search
Provides a way for you to search MML commands using the
key word.
Common Maintenance
Displays the output of an MML command.
Operation Records
Displays the information about all the commands that have
been executed.
NOTE
Issued On is the system time of the LMT PC.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Help
Displays the help information about an MML command.
Pane for manual input of
an MML command
Displays the command and parameter values manually entered.
Command History
Records all the commands entered by the user during one
session.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
24
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Component
Description
Command Input
Displays all the MML commands of the system. You can select
an MML command from the drop-down list or directly enter a
command.
Area for settings
parameters of an MML
command
Displays all parameters that can be set in an MML command
entered in the Command Input text box.
NOTE
A parameter in red is mandatory and a parameter in black is optional.
Help
Provides the LMT online help.
About
Provides version information about the LMT offline MML.
Logging In to and Logging Out of the Offline MML
This section describes how to log in to and log out of the local maintenance terminal (LMT)
offline man-machine language (MML).
Prerequisites
You have started the LMT offline MML server.
Procedure
l
Log in to the LMT offline MML.
a.
The LMT offline MML tool is installed on the LMT PC and has been started.
b.
In the address box of the browser, enter http://127.0.0.1:Port. The login window is
displayed.
NOTE
c.
Port is the port number of the LMT offline MML server and the default value is 810.
You can change the port number on the Config tab page of the window of the LMT offline
MML server. The change of the port number takes effect only after the LMT offline MML
server is restarted.
In the login window, specify NE Type and Version, and click Login.
NOTE
Click Reset to restore the default settings.
Log out of the LMT offline MML.
Click Logout at the upper right corner of the window of the LMT offline MML.
----End
Preparing Offline MML Scripts
This section describes how to prepare offline man-machine language (MML) scripts.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT offline MML.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
25
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT offline MML window, enter an MML command in the Command text box and
click Assist to set related parameters.
NOTE
When entering an MML command in the Command text box, you can select the command from the dropdown list.
Step 2 Click Save to save the entered MML command.
NOTE
l When you save an MML command, the command does not overwrite a previously saved command.
l On the Operation Record tab page, you can right-click a command and choose an option from the
shortcut menu to clear the selected or all records.
----End
2.7.3 Traffic Recording Review Tool
This section describes how to use the traffic recording review tool, a component of the local
maintenance terminal (LMT) offline tool, to review tracing and monitoring data.
Startup Operation
On the LMT PC, choose Start > All Programs > Huawei Local Maintenance Terminal >
Traffic Recording Review Tool.
Window of the traffic recording review tool
Figure 2-4 shows the window of the traffic recording review tool. Table 2-10 describes the
components in the window.
Figure 2-4 Window of the traffic recording review tool
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
26
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Table 2-10 Components in the window of the traffic recording review tool
No.
Component
Description
Menu bar
Provides the system menu.
Toolbar
Provides shortcut icons.
Traffic recording review
area
Displays data of a tracing or
monitoring task.
2.7.4 FTP Client
The FTP client is a component of the LMT offline suite and enables the LMT to communicate
with the FTP server according to the FTP or FTPs protocol. You can obtain logs and upload
data configuration files through the FTP client.
Startup
Choose Start > All Programs > HUAWEI Local Maintenance Terminal > FTP Client on
the LMT PC.
Interface
Figure 2-5 shows the FTP client interface.
Figure 2-5 FTP client interface
Table 2-11 describes the components of the FTP client interface.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
27
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Table 2-11 Components of FTP client interface
Number
Component
Description
Menu bar
Provides the menus for the operation of the system.
Tool bar
Provides the shortcut icons for the operation of the
system.
Server input area
Includes the server name, user name, user
password, port number, and mode in this area.
NOTE
To query the port number, run the LST
FTPSCLTDPORT command to query the setting for
Destination Port. If an incorrect port number is used, the
LMT cannot be connected to the FTP server.
Local directory list
window
Displays the directory structure of the current
computer.
Server file list
window
Lists the files and file folders stored in the
connected FTP server.
Local file list window
Lists the files and file folders stored in the current
computer.
Prompt information
window
Displays the information such as the connection
status of the FTP server and the operation
descriptions.
2.8 Configuring an Emergency OM Channel
For a separate-MPT multimode base station, an emergency OM channel is used to maintain a
faulty base station through the OM channel of a normal base station. The maintenance
includes proxy PNP tracing, operations using MML commands, and proxy file transfer for the
faulty base station through the emergency OM channel of the normal base station.
Prerequisites
Ensure that the operator has agreed to the solution of maintaining the target base station using
a proxy base station and that this maintenance mode does not have security risks.
Context
l
In this document, the target base station refers to the faulty base station and the proxy
base station refers to the normal base station.
Ensure that the proxy base station connects to the target base station by using the HTTPS
policy.
Ensure that the emergency OM channel can be established only between one proxy base
station and one target base station.
If the proxy base station or target base station is reset after the emergency OM channel
between them is successfully established, the emergency OM channel needs to be re-
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
28
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
established 5 minutes after the reset. Otherwise, the emergency OM channel cannot be
re-established.
l
When the WMPT serves as the main control board of the proxy base station, the U2000
and the LMT version of the proxy base station must be installed on the same PC.
Otherwise, you cannot log in to the LMT through the remote U2000 proxy.
Procedure
Step 1 Click Configure Emergency OM Channel on the menu bar of the LMT.
The Configure Emergency OM Channel dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 Set related parameters in the Configure Emergency OM Channel dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 2-12.
Table 2-12 Parameters related to the emergency OM channel configuration
Parameter
Description
In Same
Subrack
Indicates whether the proxy base station and target base station are
configured in the same subrack or different subracks.
Main Control
Board Slot No.
Indicates the slot number of the main control board of the target base
station.
User Name
Indicates the user name used for logging in to the LMT of the target
base station.
Password
Indicates the password used for logging in to the LMT of the target base
station.
Step 3 Table 2-13 lists parameters for an emergency OM channel list.
Table 2-13 Parameters for an emergency OM channel list
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
SN
Indicates the sequence number of an
established emergency OM channel.
State
Indicates the status of an emergency OM
channel.
Proxy BTS Index
Indicates the index of the proxy base
station.
Proxy Site Type
Indicates the type of the proxy base station.
Proxy Site Version of Emergency OM
Channel
Indicates the version of the proxy base
station.
Proxy Site Info
Indicates the information about the proxy
base station.
Target Site Type
Indicates the type of the target base station.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
29
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
Parameter
Description
Target Site Version of Emergency OM
Channel
Indicates the version of the target base
station.
Target Site Info
Indicates the information about the target
base station.
Step 4 Click Connect to establish an emergency OM channel between the proxy base station and the
target base station. Emergency OM Channel List displays information of a successfully
established emergency OM channel.
Step 5 Click Disconnect to disconnect the emergency OM channel of the proxy base station from
that of the target base station. Emergency OM Channel List does not display any channel
information.
----End
2.9 Obtain Documentation List
This section describes how to query and obtain documentation packages of the corresponding
product version.
Startup
Click Obtain Documentation List on the menu bar of the LMT to start this function.
GUI
l
Library Name: Name of the document package of the current product version.
Product Version: Current product version number.
Library Version: Version number of the document package of the current product
version.
Available at support.huawei.com: Yes indicates that the document package is released
globally at http://support.huawei.com, and you can obtain it. No indicates that the
document package is not released globally at http://support.huawei.com, and you need to
contact Huawei engineers to obtain it.
Function
You can use either of the following methods to download the documentation packages:
l
Search for the documentation packages at the website http://support.huawei.com and
then download them.
Click Export to export the corresponding .hdxi file. Then double-click the .hdxi file to
search for related product documentation on http://support.huawei.com. The result will
be listed for downloading.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
30
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
2 Introduction to the LMT
NOTE
Before using this function, ensure that:
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
You can visit http://support.huawei.com and have obtained the account.
(For initial use only) You have downloaded the HedEx Lite from the homepage of http://
support.huawei.com to your PC and started it.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
31
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Getting Started with the LMT
About This Chapter
This chapter describes how to manage local maintenance terminal (LMT) rights and how to
log in to and exit the LMT. A minimum of 1 GB free space is required to ensure that the LMT
runs correctly.
3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the LMT
You can log in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT) to manage the base station locally.
After the operation and maintenance (OM) channel between the base station and the U2000
server is established, you can also use the U2000 client to log in to the base station.
3.2 Managing Rights
Managing rights involves managing login accounts, user passwords, and command groups.
3.3 Setting Office Information on the LMT
This section describes how to set IP address information for using the LMT to log in to the
U2000 or base station.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
32
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
3.1 Logging In to and Exiting the LMT
You can log in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT) to manage the base station locally.
After the operation and maintenance (OM) channel between the base station and the U2000
server is established, you can also use the U2000 client to log in to the base station.
Prerequisites
Before using the LMT, install the JAVA Platform Standard Edition Runtime Environment
(JRE) plug-in on the computer where the LMT is installed. The JRE plug-in is a standard Java
runtime environment plug-in, which can be downloaded from http://java.com/.
l
If the plug-in is not installed on the computer, the system displays the message "Java
plug-in is not found. If the Java plug-in is not installed, please download and install
the recommended Java plug-in."
If the installed plug-in is not the compatible version, the system displays the message
"The recommended version of the Java plug-in is x.x.x.xx, but the installed version
is x.x.x.xx now, it may be incompatible with WebLMT. Please download and install
the recommended Java plug-in."
NOTE
l x.x.x.xx indicates the version of the installed JRE plug-in.
l If the LMT of SRAN7.0 and that of a later version are used simultaneously, JRE 1.6.0.27 is
recommended.
l To solve problems about installing or using Java plug-in, follow instructions provided in 9.33 Help
for Installing and Using the Java Plug-in.
If the Java Update Needed dialog box is displayed when you log in to the LMT,
preferentially click Update to install the latest Java version.
If you cannot log in to the LMT after the plug-in is upgraded to the latest version, restart
the browser and then log in.
LMT users are categorized into local users and element management system (EMS)
users. For details, see 3.2.1 Concepts Related to Rights Management.
A maximum of six local users and EMS users can log in to the LMT at the same time.
Context
NOTE
When the BBU3900 is configured with the LMPT, a maximum of four local users and EMS users can
log in to the LMT at the same time.
HTTPS connection is the default policy for logging in to the LMT. Specifically, when
you enter an HTTP URL in a web browser to log in to the LMT, the HTTP request
automatically changes to an HTTPS request.
Login in to the LMT over HTTPS requires configuration of digital certificates.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
The operator-issued certificate, device certificate of a base station, and
preconfigured certificate on the LMT have descending priorities.
The preconfigured certificate on the LMT is used only for initial secure access and
is inadequate to ensure security. The operator-issued certificate is preferred.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
33
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
If an operator has deployed a PKI system on the live network, secure base station
deployment by PnP is recommended and the operator-issued certificate must be
obtained prior to access.
If the colors cannot be displayed in the main window of the LMT, see 9.4 How to
Handle Incorrect Display of Colors of the LMT Main Window.
CAUTION
When the LMT is running, do not change the system time or time zone of an LMT PC.
Otherwise, a critical fault may occur in the system. If the system time or time zone has to be
changed, perform the operation after the LMT exits.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
34
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
NOTICE
l
When the LMT uses the Firefox browser and Block pop-up windows is selected, you
will fail to log in to the LMT. To avoid this problem, open a web page using the Firefox
browser. On the web page, choose Tools > Options from the menu bar. On the Options
window, under Content, clear Block pop-up windows check box.
The refresh function of the browser cannot be used on the LMT. If you use the refresh
function in the LMT main window, the LMT is logged out. If you use the refresh
function on the monitor window, an error occurs in the script.
When the LMT is used in Internet Explorer, do not change the properties of the cache
file folder. Otherwise, Internet Explorer is automatically refreshed, and therefore, an
error occurs in the LMT main window.
If you choose Start > Run to start File Transfer Protocol (FTP) services, the LMT main
window is replaced with the login dialog box of the FTP server. To avoid this problem,
choose Tools > Internet Options from the Internet Explorer menu bar. On the
Advanced tab page, under Browse, clear the Reuse windows for launching shortcuts
check box.
Before you use the LMT to upgrade or roll back a base station, clear the browser's buffer
and cookies.
If you press ALT+<---, the LMT main window may experience an error. In this case,
press ALT+---> to restore the window settings. If the window settings cannot be
restored, close the browser and log in to the LMT again.
The default policy to log in to the LMT can be specified by the WebLMT Login Policy
parameter in the SET WEBLOGINPOLICY command. The parameter can be set to
any of the following values. (1) COMPATIBLE(Compatible): Either HTTP or HTTPS
can be used to log in to the LMT. (2) HTTPS_ONLY(Https_only): Only HTTPS can be
used to log in to the LMT. (3) LOGIN_HTTPS_ONLY(Login_https_only): When
HTTP is used to log in to the LMT, HTTP is changed to HTTPS before login, then
HTTPS returns to HTTP after login. Data over HTTP is transmitted in plaintext and
prone to disclosure. Therefore, the value HTTPS_ONLY(Https_only) is recommended.
If the WebLMT Login Policy parameter is set to HTTPS_ONLY(Https_only) but
login by HTTP is configured on the U2000, login to the LMT in U2000 proxy mode
does not work.
The password status will be checking when you log in to the LMT. You can set whether
the LMT to force the user to change the password on first login by running the SET
PWDPOLICY command.
The TLS/SSL version of the web browser and JRE must be set to the same value as the
TLS/SSL Version configured using the SET SSLCONF command. Otherwise, the
LMT login page cannot be opened using the web browser or the LMT that you have
logged in to cannot work properly.
To use the LMT to log in to the base station, perform the following steps:
Procedure
a.
Connect the LMT to the base station.
n
Wired connection:
The network port on the PC where the LMT application is installed can connect to
the GTMUb, WMPT or LMPT board in the BBU3900 through a crossover cable or
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
35
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
straight-through cable and can connect to the UMPT board in the BBU3900 through
a USB-to-Ethernet adaption cable, as shown in Table 3-1 and Figure 3-1.
Table 3-1 Cable connections
Cable
Port
Crossover cable/
Straight-through cable
ETH port on the GTMUb, LMPT or WMPT
USB-Ethernet adaption
cable
USB port on the UMPT
Figure 3-1 Connection between the computer where the LMT is installed and the
BBU3900
(1) BBU3900 (2) Crossover cable, Straight-through
cable, or USB-to-Ethernet adaption
cable
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
(3) Computer where the
LMT is installed
Wireless connection (applicable only to the BBU3910A)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
36
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
(1) BBU3910A
b.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
(2) Computer where the LMT is installed
If the computer where the LMT is installed is configured with a WLAN
wireless network adapter and the local wireless access point device is enabled
on the base station (by running the SET LOCALWAP command with Switch
set to the default value ON(On)), the computer can be connected to the base
station through the local wireless access point device as long as the base
station transmits WLAN signals:
If the OMCH works properly, the base station by default disables WLAN
signals. To enable the LMT PC to connect the base station through a local
wireless access point device, run the SET LOCALWAPSW command on
the U2000 with Enable Switch set to ENABLE(ENABLE) and Enable
Elapse Time set to an appropriate value. During the time specified by
Enable Elapse Time, the base station transmits WLAN signals so that
the LMT PC can connect the base station through a local wireless access
point device.
If the OMCH is disconnected, the base station automatically transmits
WLAN signals to allow for the connection. After the OMCH is
recovered, the duration in which the base station continues to transmit
WLAN signals is specified by AP auto disable time in the SET
LOCALWAP command.
How to configure a WLAN wireless NIC on a computer, see 9.35 How to
Configure Wireless NIC on a Computer.
The service set identifier (SSID) of the local wireless access point device is in
the format of HID_XXXXXXXXXX, where XXXXXXXXXX indicates the last 10
digits in the ESN.
The initial password of the local wireless access point device is the same as
that of the LMT. The default password is hwbs@com (case-sensitive). The
password can be changed using the SET LOCALWAPPWD command on the
U2000.
To ensure security, only one terminal or user can log in to the local wireless
access point device at a time.
The LMT PC can locally connect to the base station in wireless mode with the
valid line of sight (LOS) being less than 10 m.
In the address box of the browser, enter the IP address of the main control board for
local maintenance. The default maintenance IP address of the base station is
192.168.0.49 in wired login mode and 192.168.1.49 in wireless login mode.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
37
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
NOTE
l For UMTS base stations:
l
If the main control board UMPT is upgraded from V200R014C00 or an earlier
version to V200R015C00 or a later version, use the local maintenance IP address
used before the upgrade.
If the main control board UMPT is newly delivered and the software version is
V200R015C00 or a later version, use the default local maintenance IP address
192.168.0.49.
l If the ACT CFGFILE command is executed to enable minimum configuration, the local
maintenance IP address is restored to 192.168.0.49.
l The local maintenance IP address cannot be the same or on the same network segment as
an existing IP address used on the live network. If such a local maintenance IP address is
used, it must be changed by running the SET LOCALIP command. Otherwise,
information on the U2000, such as traffic statistics and CHR logs are lost when the base
station is maintained both locally and remotely.
c.
Click Go. The Local Maintenance Terminal login window is displayed, as shown
in Figure 3-2.
After the LMT application software is successfully installed, you can log in to the
LMT using either of the following methods. Figure 3-3 shows the LMT login
window.
n
Choose Start > All Programs > HUAWEI Local Maintenance
Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT) > Web Local Maintenance
Terminal(WEBLMT CLIENT). The Local Maintenance Terminal window
is displayed.
In the address box of the browser, enter the IP address http://127.0.0.1:822.
The Local Maintenance Terminal window is displayed.
NOTE
The service port number is 822 by default. If the service port of the local LMT is
changed, the entered port number must be consistent with the changed service port.
Figure 3-2 Local Maintenance Terminal login window
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
38
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
NOTE
l During login, the system checks the Java version and compatibility view settings of the
browser. To use the optimum LMT configurations, perform the operations as prompted.
l In the login window, you can download the default Huawei CA certificate, including the LMT
predefined certificate and the predefined certificate of the U2000 proxy server. If the
predefined certificates have been replaced, the CA certificate downloaded in the login
window is invalid. In this case, import the CA certificate matching the new predefined
certificates.
d.
Enter the user name, password, and verification code in the User name, Password,
and Verification code text boxes, respectively. Set User type to Local.
NOTE
l User name is admin by default. The value of Password varies depending on scenarios:
l
For newly delivered base stations of SRAN7.0SPC200 or later, the default value of
Password is hwbs@com (case-sensitive).
For base stations that are upgraded from a version earlier than SRAN7.0SPC100 to
SRAN7.0SPC200 or later, the password needs to be the same as that used before the
upgrade (case-sensitive).
l User name and Password must be set to those of a local user of the base station.
l Change the password after you have logged in to the LMT. For details, see Changing the
password of a current user account.
l If the verification code is illegible, click Refresh to change the verification code.
e.
Click Login. The LMT main window is displayed.
NOTE
If the login fails because the provided information is incorrect, click Reset and enter the correct
information. If the login failure persists, check the connection between the LMT and the main
control board.
To use the U2000 client to log in to the base station, perform the following steps:
a.
Set proxy server.
If the LMT is used in Internet Explorer, perform the following steps before entering
the IP address:
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
i.
Choose Tools > Internet Options from the menu bar. The Internet Options
dialog box is displayed. On the Connections tab page, click LAN Settings. In
the displayed LAN Settings dialog box, select Use a proxy server for your
LAN in the Proxy server area, set the Address and Port Number of the
U2000 client.
ii.
Choose Tools > Internet Options from the menu bar. The Internet Options
dialog box is displayed. On the Advanced tab page, select Use HTTP1.1
through proxy connections under HTTP 1.1 settings.
b.
Enter the OM IP address of the main control board in the address box of the
browser, enter the user name and password in the User name and Password text
boxes, and then press Enter key. The Local Maintenance Terminal login window
is displayed, as shown in Figure 3-2.
c.
Enter the user name, password, and verification code in the User name, Password,
and Verification code text boxes, respectively. Set User type to EMS.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
39
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
NOTE
l EMS user names and passwords are authorized by the U2000 server. ei*b+@b#6Nh(tS1j is
the default password for user names emscomm and emscommneteco.
l If the verification code is illegible, click Refresh to change the verification code.
l If port 8080 or 8081 is used by the U2000 agent, you need to enter the user name and
password of the agent server when performing the tasks of logging in to the web LMT,
tracing, monitoring, batch processing, and device maintenance. The default user name is
proxyuser and the default password is Changeme_123.
d.
Click Login. The LMT main window is displayed.
NOTE
If the login fails because the provided information is incorrect, click Reset and enter the correct
information. If the login failure persists, check the connection between the LMT and the main
control board.
Exit the LMT.
a.
Click Logout in the toolbar in the LMT main window. The Confirm dialog box is
displayed.
b.
Click Yes. The LMT is disconnected from the base station. A dialog box for logging
in to the LMT is displayed.
c.
Close the browser to exit the LMT.
----End
3.2 Managing Rights
Managing rights involves managing login accounts, user passwords, and command groups.
3.2.1 Concepts Related to Rights Management
This section describes rights control principles, command groups, user types, user rights,
login passwords, and operation time limits.
Table 3-2 describes the concepts related to rights management.
Table 3-2 Concepts related to rights management
Name
Description
Principles for rights
control
The local maintenance terminal (LMT) operation and maintenance
(OM) subsystem enables multiple users to perform operations at
the same time. To ensure system security, user rights are controlled
in the following aspects:
l User identity: A user must enter the correct user name and
password when logging in to the LMT.
l User rights: Users of different levels are allowed to use
different graphical user interface (GUI) operations and manmachine language (MML) operations.
l Operation time limit: It specifies the time during which a user
can perform operations.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
40
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Name
Description
Command groups
The NE provides 32 command groups G_0 to G_31 Command
groups G_22 to G_31 are reserved. The command groups are
described as follows:
l G_0: Basic command.
This command group contains all the basic commands.
l G_1: System command.
This command group contains commands for managing NMS
interfaces and other common services.
l G_2: Alarm query.
This command group contains commands for querying alarms
and faults that cause the alarms.
l G_3: Alarm management.
This command group contains commands for masking alarms
(faults), controlling alarm indicators, clearing alarms, enabling
correlation, checking synchronization, and customizing alarm
environment, as well as commands for configuring and
maintaining alarms.
l G_4: Performance query.
This command group contains commands for querying
performance task files, description files, measurement objects,
and measurement result files.
l G_5: Performance management.
This command group contains commands for download/
uploading performance task files, uploading measurement
description files, adding/deleting measurement objects,
uploading/deleting measurement result object, verifying
services, and other maintenance management commands.
l G_6: Device query.
This command group contains commands for querying
configuration parameters and status for slots/subracks/cabinets,
boards, BBUs, and commands for querying the NE status and
configuration parameters for NE names and other NE basic
information.
l G_7: Device management.
This command group contains commands for managing
configuration parameters for slots/subracks/cabinets, boards,
BBUs, and maintaining the status of such equipment, and
commands for managing NE names and other NE configuration
parameters and maintaining the NE status.
l G_8: Trace query.
This command group contains commands for querying tracing
tasks.
l G_9: Trace management.
This command group contains commands for managing tracing
tasks, for example, creating, deleting, starting, stopping, and
querying tracing tasks, and uploading tracing result files.
l G_10: Wireless query.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
41
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Name
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Description
This command group contains commands for querying
parameter configurations for radio resources, cells, and
neighboring cells, and commands for querying their status.
l G_11: Wireless management.
This command group contains commands for configuring radio
resources, cells, and neighboring cells, and commands for
maintaining their status.
l G_12: Transport query.
This command group contains commands for querying
parameters related to IP and ATM transmission and querying
the transmission status.
l G_13: Transport management.
This command group contains commands for configuring
parameters related to IP and ATM transmission and
maintaining the transmission status.
l G_14: Security query.
This command group contains commands for querying
parameters and status of the security management functions.
l G_15: Security management.
This command group contains commands for configuring
parameters and status of the security management functions
and maintaining the status.
l G_16: Time query.
This command group contains commands for querying clock
and clock reference sources.
l G_17: Time management.
This command group contains commands for configuring clock
and clock reference sources and maintaining their status.
l G_18: Software query.
This command group contains commands for querying the
transmission of files, such as license files, version files, patch
files, and FTP files.
l G_19: Software management.
This command group contains commands for configuring
software management functions for transmission of files, such
as license files, version files, patch files, and FTP files, and
maintaining the software management functions.
l G_20: Test query.
This command group contains commands for querying debugs,
tests, and exceptions.
l G_21: Test management.
This command group contains commands for managing the
debugs, tests, and exceptions.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
42
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Name
Description
User type
LMT users are categorized into local users and element
management system (EMS) users, which are described as follows:
l Local user: Account of local user (including the default admin
user) is managed by the LMT. Local user can use the LMT to
log in to the base station when he is disconnected from the
U2000 server.
l EMS users: Accounts of EMS users are centrally managed by
the U2000 server. EMS user accounts are created, modified,
authenticated, and authorized by the U2000 server. Only
authorized EMS users are permitted to use the LMT to log in to
the base station. Authorized EMS users can also log in to the
U2000 server from the U2000 client to manage the base station.
To directly log in to the base station as an EMS user, ensure
that the base station is connected to the U2000 server.
User rights
LMT user accounts are classified into internal user accounts and
external user accounts. Different accounts have different rights,
which are described as follows:
l The internal user account is a default system account with the
user name being admin and password being hwbs@com. The
internal user accounts are ADMINISTRATOR-level accounts.
l Five levels of external user accounts are provided, and each
level is allocated different rights. The external user accounts are
described as follows:
GUEST: Users with GUEST-level accounts are only
allowed to view data. They can use command groups G_0,
G_2, G_4, G_6, G_8, G_10, G_12, G_16, G_18, and G_20.
USER: Users with USER-level accounts have the rights of
users with GUEST-level accounts and are also allowed to
operate and maintain the system. They can use any
command groups other than G_1, G_9, G_14, or G_15.
OPERATOR: Users with OPERATOR-level accounts have
the rights of users with USER-level accounts and are also
allowed to configure data. They can use any command
groups other than G_1, G_9, G_14, or G_15.
ADMINISTRATOR: Users with ADMINISTRATOR-level
accounts have the rights to run all commands, but cannot
delete the default user admin. The users belong to all
command groups.
CUSTOM: Users with CUSTOM-level accounts can be
allocated any command groups when the accounts are
created. The rights can be changed. Users with different
CUSTOM-level accounts have different rights.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
43
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Name
Description
Login password involves the password policies, initial password,
and password change permissions, which are described as follows:
l Each user account is allocated a login password to ensure
system security. A user must enter the correct user name and
password when logging in to the LMT. The user can operate the
base station only after being verified.
Login password
l The login password of admin user is set when the base station
application software is installed. The user with the
ADMINISTRATOR-level account, and authorized users with
CUSTOM-level accounts are allowed to set the login password
of an external user account when creating the account.
l All users can change their own passwords. The user with the
ADMINISTRATOR-level account, and authorized users with
CUSTOM-level accounts are allowed to change the login
password of any external user account.
The definition, principle, and settings of the operation time limit
are described as follows:
Operation time limit
l The operation time limit specifies the time during which a user
can perform operations. The admin user has no operation time
limit, that is, the admin user can perform operations anytime.
The operation time limit for an external user account is
specified when the account is created. If no time limit is set, the
user can perform operations anytime.
l The operation time limit is represented by a combination of the
date, day, and time.
l Only the admin user, user with the ADMINISTRATOR-level
account, and authorized users with CUSTOM-level accounts
are allowed to set or change the operation time limit for an
external user account.
3.2.2 Managing User Accounts
Managing user accounts involves creating, modifying, and removing external user accounts.
Table 3-3 describes the tasks involved in managing user accounts.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
44
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Table 3-3 Tasks involved in managing user accounts
Task
Description
Creating an external
user account
Functi
on
Creates an external user account and sets the login
password, user level, command group (for users with the
CUSTOM account only), and operation time limit for the
new user account. Only the admin user, user with the
ADMINISTRATOR account, and authorized users with
the CUSTOM account are allowed to create an external
user account.
Proced
ure
Run the ADD OP command to create an external user
account.
Functi
on
Modifies the attributes of an external user account,
including the login password, user level, user rights, and
operation time limit. The new password takes effect upon
the next login. Modifications of other attributes take effect
immediately. Only the admin user, user with the
ADMINISTRATOR account, and authorized users with
the CUSTOM account are allowed to modify the attributes
of an external user account.
Proced
ure
Run the MOD OP command to modify the attributes of
an external user account.
Functi
on
Removes an external user account. Only the admin user,
user with the ADMINISTRATOR account, and authorized
users with the CUSTOM account are allowed to remove
an external user account.
Proced
ure
Run the RMV OP command to remove an external user
account.
Modifying an
external user
account
Removing an
external user
account
NOTE
New user accounts must be different from existing user accounts.
The admin user is internal accounts and cannot be removed.
3.2.3 Managing Login Passwords
Managing login passwords involves setting and viewing password policies and changing the
passwords of current and external user accounts.
Table 3-4 describes the tasks involved in managing login passwords.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
45
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Table 3-4 Tasks involved in managing login passwords
Task
Description
Setting
password
policies
Function
Password policies define how to set login passwords.
NOTE
l Password policies define the minimum password length and
complexity. If a password does not meet the required
minimum password length or complexity, this password
cannot take effect.
l Password policies define the maximum number of times an
incorrect password can be entered. The default number of
attempts is three. If this threshold is exceeded, the LMT will
be locked and then unlocked 30 minutes later. You can specify
the length of this duration in the password policies.
l Only users with the ADMINISTRATOR account are
authorized to set login passwords.
Procedure
Viewing
password
policies
Run the SET PWDPOLICY command to set login
password policies.
Function
Users can view password policies before setting correct
login passwords.
Procedure
Run the LST PWDPOLICY command to view password
policies.
Function
The current user can change its own password after login.
The new password takes effect upon the next login.
1. Click Password on the upper right side of the toolbar in
the LMT main window. A Password dialog box is
displayed.
Changing the
password of a
current user
account
Procedure
2. Fill in the Old Password, New Password, and
Confirm Password text boxes, and click OK.
NOTE
Think carefully before you change a domain account's password.
After this change, all users that have logged in to U2000 clients
using this account will be forcibly logged out.
Changing the
password of an
external user
account
Function
Only the admin user, users with the ADMINISTRATOR
account, and authorized users with the CUSTOM account
are allowed to modify password options to change the
password of an external user account.
Procedure
Run the MOD OP command to change the password of an
external user account.
NOTE
Be cautious when changing the password of the admin user. If you forget the password, you cannot log
in. In this case, contact Huawei technical support.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
46
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
3.2.4 Managing Command Groups
Managing a command group involves viewing and naming a command group and changing
the commands in a command group.
Table 3-5 describes the tasks involved in managing command groups.
Table 3-5 Tasks involved in managing command groups
Task
Description
Viewing a command
group
Function
The base station provides 32 command groups G_0
to G_31. Command groups G_22 to G_31 are
reserved. Only the admin user, user with the
ADMINISTRATOR account, and authorized users
with the CUSTOM account are allowed to view
command groups.
Procedure
Run the LST CCG command.
Function
Only the admin user, user with the
ADMINISTRATOR account, and authorized users
with the CUSTOM account are allowed to name a
command group.
Procedure
l Run the LST CCGN command to view the
name of a command group.
Naming a command
group
l Run the SET CCGN command to name a
command group.
Changing the
commands in a
command group
Function
Only the admin user, user with the
ADMINISTRATOR account, and authorized users
with the CUSTOM account are allowed to change
the commands in a command group.
Procedure
l Run the ADD CCG command to add
commands to a command group.
l Run the RMV CCG command to remove
commands from a command group.
3.3 Setting Office Information on the LMT
This section describes how to set IP address information for using the LMT to log in to the
U2000 or base station.
Context
This setting is required if the LMT application software is installed on the PC.
Generally, an office uses a name to differentiate IP addresses of the U2000 or base stations to
be logged in to. The office information can be set on the LMT so that the LMT can connect to
different U2000 or base stations.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
47
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Procedure
Step 1 Figure 3-3 shows the LMT login window. Click to the right of the Office text box.
An Office Management dialog box is displayed.
Figure 3-3 Local Maintenance Terminal login window
Step 2 In the Office Management dialog box shown in Figure 3-4, set related parameters. For
details about parameter descriptions, see Table 3-6.
Figure 3-4 Office Management dialog box
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
48
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Table 3-6 Descriptions of parameters in the Office Management dialog box
Parameter
Description
Office
Indicates the name of the NE connected to
the LMT. The name is user-defined and
consists of a maximum of 80 single-byte
characters.
IP Address
Indicates the IP address of the NE.
NOTE
l If the main control board WMPT is upgraded
from V200R014C00 or an earlier version to
V200R015C00 or an later version, use the
local maintenance IP address used before the
upgrade.
l If the main control board WMPT is newly
delivered and the software version is
V200R015C00 or an later version, use the
default local maintenance IP address
192.168.0.49.
l If the ACT CFGFILE command is executed
to enable minimum configuration, the local
maintenance IP address is restored to
192.168.0.49.
l The local maintenance IP address cannot be
the same or on the same network segment as
an existing IP address used on the live
network. If such a local maintenance IP
address is used, it must be changed by
running the SET LOCALIP command.
Otherwise, information on the U2000, such
as counter statistics and CHR logs are lost
when the base station is maintained both
locally and remotely.
Connect Type
Indicates the mode of connection between
the LMT and the NE. The LMT and the NE
can be connected in common or SSL mode.
NOTE
Authentication Mode for SSL connection
between the LMT and the base station must not
be set to PEER(Verify Peer Certificate).
Otherwise, you cannot log in to the base station
through the LMT.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Proxy Server
Indicates the proxy server through which
the LMT connects to the NE. The IP address
of the proxy server can be specified.
Protocol Version
Indicates the version of the Secure Sockets
Layer (SSL) protocol. This parameter is set
if the SSL connection mode is used.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
49
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Parameter
Description
Add
If you click this button, an ADD dialog box
is displayed for you to add office
information about another U2000 or base
station.
Modify
If you click this button after choosing an
office, you can modify information about
this office.
Delete
If you click this button after choosing an
office, you can delete information about this
office.
Step 3 Click Add.
An Add dialog box is displayed.
Step 4 Set related parameters in the Add dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions, see
Table 3-7.
Table 3-7 Descriptions parameters in the Add dialog box
Parameter
Description
Office
You can define a name for the NE to be
visited.
IP Address
Indicates the IP address of the NE to be
visited.
Connect Type
Indicates the mode of connection between
the LMT and the NE. This parameter can be
set to NORMAL or SSL.
Proxy Server
If the U2000 is used as the proxy server, set
this parameter to the IP address of the
U2000.
SSL Setting-Protocol Version
Indicates the protocol type and version if the
SSL connection mode is used. This
parameter can be set to TLSv1, TLSv1.1,
TLSv1.2, or SSLv3.
NOTE
The SSL connection mode is recommended to ensure secure communication between the LMT and base
station.
Step 5 Click Submit.
The Office Management dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
50
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
3 Getting Started with the LMT
Step 6 Click Close. The settings are complete.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
51
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
Running MML Commands
About This Chapter
This chapter describes how to run man-machine language (MML) commands on the local
maintenance terminal (LMT) to operate and maintain a base station.
4.1 Basic Concepts Related to MML Commands
The basic concepts related to man-machine language (MML) commands consist of MML
commands and the Graphical User Interface (GUI) of MML commands.
4.2 Running a Single MML Command
You can run man-machine language (MML) commands one at a time to perform routine
operation and maintenance.
4.3 Running MML Commands in Batches
This section describes how to run MML commands in batches to perform a function or
operation.
4.4 Checking the Syntax
The syntax checking function enables you to check the syntax of man-machine language
(MML) commands before you run the commands in batches. This function improves the
maintenance efficiency.
4.5 Setting Parameters
You can set parameters in the MML Settings dialog box.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
52
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
4.1 Basic Concepts Related to MML Commands
The basic concepts related to man-machine language (MML) commands consist of MML
commands and the Graphical User Interface (GUI) of MML commands.
4.1.1 Introduction to MML Commands
This section describes the functions, formats, and types of operations performed using manmachine language (MML) commands.
Functions of MML Commands
You can use MML commands to operate and maintain the base station. Some MML
commands can be used for all radio access technologies (RATs), and some MML commands
are specific to a particular RAT. MML commands enable you to perform the following
operations:
l
System management
Equipment management
Alarm management
Carrier resource management
Transmission management
Formats of MML Commands
The format of an MML command can be "Command Word: Parameter Name=Value;".
The command word is mandatory, whereas the parameter name and value are optional.
Examples of MML commands are as follows:
l
An MML command with a command word and parameters: SET ALMSHLD:
AID=25600, SHLDFLG=UNSHIELDED;
An MML command with only a command word: LST VER:;
Types of Operations Performed Using MML Commands
The MML command word format is denoted as Action + Object. Table 4-1 describes the
most commonly used MML commands.
Table 4-1 Most commonly used MML commands
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Action
Meaning
ACT
Activate
ADD
Add
BKP
Backup
BLK
Block
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
53
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
Action
Meaning
DLD
Download
DSP
Display (used for dynamic information)
LST
List (used for static information)
MOD
Modify
RMV
Remove
RST
Reset
SET
Set
STP
Stop or close
STR
Start or open
UBL
Unblock
ULD
Upload
SCN
Scan
CLB
Calibrate
4.1.2 Components of the MML Command Window
This section describes the components of the man-machine language (MML) command
window.
In the LMT main window, click the MML tab. Figure 4-1 shows the MML command
window.
Figure 4-1 MML command window
Table 4-2 describes the components of the MML command window.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
54
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
Table 4-2 Components of the MML command window
No.
Field
Description
Navigation Tree
You can choose Common or a specific RAT.
Common Maintenance tab
Displays the output of an MML command.
Operation Record tab
Displays information about all the commands
that have been executed by the user.
Help tab
Displays the help topics for an MML command.
Command output handling
options
You can click Save Result, Auto Scroll, or
Clear All.
Pane for manual input of an
MML command
Displays the manually entered command and
parameter values.
Command History text box
Records all the commands and parameters a user
enters during one session.
Command text box
Displays all the MML commands of the system.
You can select an MML command from the
drop-down list or enter the command directly.
Select Use Proxy MML. You can log in to the
target base station using the emergency OM
channel on the proxy base station and then
execute related MML commands to maintain the
target base station.
NOTICE
Before Use Proxy MML is enabled, ensure that the
emergency OM channel has been established. For
configurations of an emergency OM channel, see 2.8
Configuring an Emergency OM Channel.
Area for settings parameters of
an MML command
Displays all parameters that can be set in an
MML command entered in the Command text
box. The parameters in red are mandatory, for
example, Cabinet No. in Figure 4-1. The
parameters in black are optional, for example,
Subrack No. in Figure 4-1.
NOTE
The MML navigation tree changes with the RAT selected.
For details about MML commands and their related parameters, see the MML command help.
4.2 Running a Single MML Command
You can run man-machine language (MML) commands one at a time to perform routine
operation and maintenance.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
55
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Context
You can use one of the following four methods to run a single MML command:
l
Enter an MML command in the Command text box.
Select an MML command from the Command History drop-down list box.
Choose an MML command in the MML Command Navigation Tree.
To manually input an MML command, enter or copy it into the pane for manual input of
commands.
Enter an MML command in the Command text box.
Procedure
a.
Enter an MML command in the Command text box. When typing an MML
command, you can select the command from the drop-down list.
b.
Press Enter or click Assist. The parameters related to the command are displayed
in the area for setting the parameters of the command.
c.
Set the related parameters.
d.
Press F9 or click Exec to run the command. The MML command output is
displayed on the Common Maintenance tab page.
Select an MML command from the Command History drop-down list box.
a.
Select a historical command from the Command History drop-down list box. Press
to select the previous command, and press F8 or click
to
F7 or click
select the next command. The parameters related to the command are displayed in
the area for setting the parameters of the command.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
b.
Set the related parameters.
c.
Press F9 or click Exec to run the command. The MML command output is
displayed on the Common Maintenance tab page.
Choose an MML command in the MML Command Navigation Tree.
a.
Choose and double-click an MML command in the MML Command Navigation
Tree.
b.
Set the related parameters.
c.
Press F9 or click Exec to run the command. The MML command output is
displayed on the Common Maintenance tab page.
To manually input an MML command, enter or copy it into the pane for manual input of
commands.
a.
Manually enter or copy an MML command with complete parameter settings into
the pane.
b.
Press F9 or click Exec to run the command. The MML command output is
displayed on the Common Maintenance tab page.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
56
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
NOTE
l The parameters in red are mandatory, and those in black are optional.
l To obtain information about a parameter, move the cursor to the input box of the parameter.
l When you run an MML command with a time parameter, note that the default value of the
time parameter is the base station time. If required, you can change the value.
l If an MML command fails to be executed, the execution result is displayed in red on the
Common Maintenance tab page.
l Setting the browser scaling to 100% is recommended.
----End
4.3 Running MML Commands in Batches
This section describes how to run MML commands in batches to perform a function or
operation.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The batch file is ready.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) of the specified version has been installed.
Context
The batch file (also called data script file) is a text file. It contains a group of man-machine
language (MML) command scripts for a special task. The system automatically runs the
MML command scripts in sequence.
NOTE
The batch processing window is fixed in size and does not change with the web page.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Batch.
Step 2 Copy a group of command scripts with complete parameter values from the batch file to the
pane for entering MML commands, or manually enter a group of MML commands, or click
Open... to select an MML command batch processing file.
NOTE
l Click Open... to select a file whose size is not greater than 4 MB.
l After you click New, a window is displayed indicating whether to save the content in the pane for
entering MML commands.
l You can click Save to save the content in the pane for entering MML commands to a text file.
Step 3 Click Customize. In the displayed Customize dialog box, specify related parameters for
batch processing.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
57
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
NOTE
l Command send interval(s): specifies the interval at which two MML commands are executed.
l Save Failed Commands: specifies a text file for saving MML commands that fail to be executed.
l Save Results: specifies a text file for saving the successful or failed MML command execution
results.
Step 4 Choose an execution type in the Execution Type area. Table 4-3 lists the execution types.
Table 4-3 Execution types
Execution Type
Description
All
The system automatically runs all MML commands one by one.
Step by Step
The system runs one MML command each time you click Go.
Breakpoint
In this mode, you need to click a command before which the
command execution needs to be stopped. Click Go. The system runs
the MML commands from the first one to the one before the
specified command. When you click Go again, the system runs the
MML commands from the specified command to the last command
or another command before which the command execution needs to
be stopped.
Range
The system runs MML commands within a specified range.
Prompt when
error occurs
l Check box selected: If an MML command is delivered to the NE
but no response is returned or the return code for the MML
command is not zero, a dialog box is displayed and the MML
command execution stops.
l Check box deselected: If an MML command is delivered to the
NE but no response is returned or the return code for the MML
command is not zero, the MML command execution continues
until the operation completes and the command is marked with
.
NOTE
l If the return code for an MML command is 0, the MML command is
successfully executed. If the return code for an MML command is not
zero, the MML command fails to be executed.
l Execution of some MML commands takes a long time. After an MML
command is delivered to the NE, the NE directly returns a code zero. It
does not means the command has been successfully executed, and it
indicates that the NE receives the MML commands and starts the
execution.
Step 5 Click Go. The system runs the MML commands.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
58
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
4.4 Checking the Syntax
The syntax checking function enables you to check the syntax of man-machine language
(MML) commands before you run the commands in batches. This function improves the
maintenance efficiency.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The batch file is ready.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) of the specified version has been installed.
Context
The following items are checked: absence of colons and semicolons, incorrect MML
commands, parameter redundancy, and incorrect parameters.
Procedure
Step 1 click New to create a batch file. You can edit MML commands in the command input pane.
NOTE
You can click Open to open a ready batch file.
Step 2 Click Analyze Syntax to check the batch file.
NOTE
l If no error is found, a Information dialog box is displayed to inform you that no error is found. If an error
is found, a dialog box is showing the check result is displayed to inform you of the command line number
and the error cause.
l You can double-click in the Result Information dialog box to locate the erroneous MML command line
in the batch file.
l After the syntax is checked,
mouse over
appears in front of the erroneous MML command line. If you pause the
, the system displays the error information.
l To check the syntax of an MML command line in the batch file, you can right-click the MML command
line and choose Analyze Current Line.
Step 3 In the Result Information dialog box, click Save As to save the check result.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
To clear the syntax check marks in the batch file, right-click in the batch file and choose
Clear Analyze Mark.
4.5 Setting Parameters
You can set parameters in the MML Settings dialog box.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
59
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
4 Running MML Commands
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
Step 1 At the upper right corner of the MML tab page, click Settings.
The Settings dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 Set parameters in the System Settings and Settings areas.
NOTE
The parameter settings in the System Settings and Settings are stored at the server end and client end,
respectively. Therefore, after the base staion resets or restarts, the parameter settings in System Settings
resumes to the default value but the parameter settings in Settings remain unchanged.
Step 3 Click OK. The settings are complete.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
60
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Managing Alarms and Events
About This Chapter
This chapter describes how to manage alarms or events on the local maintenance terminal
(LMT) to analyze, locate, and clear faults.
5.1 Basic Concepts Related to Alarms or Events
Before managing base station alarms or events, you must understand the basic concepts
related to base station alarms or events, including their definitions, logs, severity, and network
management (NM) types.
5.2 Handling Alarms and Events
Handling alarms or events involves the following actions: browsing active alarms or events,
querying alarm or event logs, querying alarm or event configurations, manually clearing
alarms or events, and querying alarm or event handling suggestions.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
61
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
5.1 Basic Concepts Related to Alarms or Events
Before managing base station alarms or events, you must understand the basic concepts
related to base station alarms or events, including their definitions, logs, severity, and network
management (NM) types.
5.1.1 Alarm or Event Categories
This section describes the basic concepts related to alarms and events.
Alarm
An alarm is generated if the hardware is faulty or a major function fails. An alarm has a
higher severity than an event. Based on the status of the faults, alarms can be categorized into
active alarms and clear alarms.
l
If a fault is not cleared, the status of the alarm remains active. This type of alarm is
called an active alarm.
If a fault is cleared, the status of the alarm changes to clear. This type of alarm is called a
clear alarm.
NOTE
l You can search a database for clear alarms.
l Alarms are cleared while you switch from the alarm query page to another page. After you switch
back to the original page, alarms will be updated in the page and the cleared alarms will not be
displayed in the page.
Based on the engineering status of the NE that reported an alarm, the alarm can be an
engineering alarm or a normal alarm.
l
If the NE is being installed, commissioned, upgraded, expanded, or relocated, the NE is
in the engineering state.
The following are engineering alarms: alarms reported by physical or logical equipment
in the engineering state, alarms that are generated by the peer equipment and are
associated with the alarms reported by the equipment in the engineering state, and clear
alarms corresponding to engineering alarms.
Event
An event notifies users of important information when the system is operating correctly. Users
do not need to handle an event.
5.1.2 Alarm Severity
The alarm severity indicates the degree to which an alarm affects system performance. Based
on the severity, all alarms can be categorized into four types: critical, major, minor, and
warning.
Table 5-1 describes alarm severities and provides handling suggestions for each.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
62
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Table 5-1 Alarm severities and handling suggestions
Severit
y
Definition
Handling
Suggestion
Critical
Service-affecting condition. Critical alarms require
immediate attention, and must be cleared
immediately. For example, faulty devices need to be
immediately repaired or unavailable resources need to
be immediately restored.
These alarms must be
cleared immediately.
Otherwise, the system
may fail.
Major
Degradation of service, but not a complete loss of
service. Major alarms must be cleared during working
hours. For example, faults that affect device
performance or resource performance must be fixed
during working hours, and their alarms must be
cleared.
These alarms must be
cleared in a timely
manner. Otherwise,
some important
functions cannot be
implemented.
Minor
Non-service-affecting condition. Minor alarms must
be handled within a certain time period to avoid
severer problems.
These alarms help
maintenance personnel
locate and clear
potential faults before
they become
problems.
Warning
Potential service-affecting condition. Warning alarms
must be handled based on the problems causing the
alarms.
These alarms help
maintenance personnel
learn about the
operating status of the
system.
5.1.3 NM Alarm Type
This section describes alarm types from the perspective of the network management (NM).
Based on NM standards, alarms are categorized as follows:
l
Power alarm: related to the power system
Environment alarm: related to environment of the equipment room
Signaling alarm: related to service signaling
Trunk alarm: related to the transport subsystem
Hardware alarm: related to boards
Software alarm: related to software
Running alarm: related to the running of the system
Communication alarm: related to the communication system
Quality of service (QoS) alarm: related to QoS
Integrity alarm: a type of security alarm, which indicates that information may be
modified, added, or removed without permission.
Operation alarm: a type of security alarm, which indicates that services are unavailable
or unreachable due to factors such as incorrect operations or faults.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
63
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Physical resource alarm: a type of security alarm, which indicates that physical resources
are unavailable due to possible attacks.
Security alarm: a type of security alarm, which indicates that the security service or
security mechanism detects that the system is experiencing attacks.
Time domain alarm: a type of security alarm, which indicates that unexpected events
have occurred.
Processing error alarm: related to processing errors.
5.1.4 Alarm Flags
Four alarm flags are provided: flag indicating whether an alarm is to be reported to the alarm
box, alarm masking flag, alarm modification flag, and alarm clearance flag.
Flag Indicating Whether an Alarm Is to Be Reported to the Alarm Box
This flag controls whether an alarm is to be reported to the alarm box. The flag status is as
follows:
l
Report
In this status, the local maintenance terminal (LMT) instructs the alarm box to generate
audible and visual alarms.
Not report
In this status, the LMT does not instruct the alarm box to generate audible and visual
alarms when alarms are reported or the alarm status is changed.
NOTE
This flag applies only to fault alarms, but not to event alarms.
An alarm can be reported to the alarm box only if this flag is set to Report for the alarm and
the alarm severity is greater than or equal to the severity specified for alarm reporting to the
alarm box.
Alarm Masking Flag
This flag controls whether an alarm is to be masked. The flag status is as follows:
l
Mask
A board does not report an alarm for which this flag is set to Mask to the network
management system (NMS) or the alarm box. The server does not record the alarm log.
Not mask
A board reports an alarm for which this flag is set to Not mask to the NMS and the
alarm box. The server records the alarm log.
Alarm Modification Flag
This flag indicates whether the alarm configuration has been modified, which facilitates the
query and restoration of the configuration. The flag status is as follows:
l
Modified
After an MML command is executed to modify the alarm configuration, this flag is set to
Modified.
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Not modified
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
64
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
If the default alarm configuration is used or an MML command is executed to restore the
default alarm configuration, this flag is set to Not modified.
Alarm Clearance Flag
This flag indicates whether a fault alarm has been cleared. The flag status is as follows:
l
Not cleared
The fault alarm has not been cleared yet.
Cleared
A clear alarm has been reported, indicating that the fault alarm has been cleared.
5.2 Handling Alarms and Events
Handling alarms or events involves the following actions: browsing active alarms or events,
querying alarm or event logs, querying alarm or event configurations, manually clearing
alarms or events, and querying alarm or event handling suggestions.
5.2.1 Setting Alarm or Event Query Properties
Setting alarm or event query properties specifies the settings in an alarm or event display
dialog box. You can customize a color for each alarm or event severity and set alarm or event
display columns.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Alarm/Event.
The Alarm/Event window is displayed.
Step 2 Click Settings in the upper right corner of the Alarm/Event window.
The Settings dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the properties of the Alarm/Event window as required.
NOTE
l To restore the default settings, click Restore Defaults.
l If Enable is selected from the Tips drop-down list, detailed information about an alarm or event is
displayed when you move your cursor over the alarm or event record on the Browse Alarm/Event and
Query Alarm/Event Log tab pages.
Step 4 Click OK.
----End
5.2.2 Browsing Active Alarms or Events
Normal alarms, events, and engineering alarms reported to the local maintenance terminal
(LMT) are displayed on the Browse Alarm/Event tab page in real time. You can view the
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
65
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
detailed information about alarms and events to determine the real-time running status of the
system.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Alarm/Event. In the displayed Alarm/Event window, click
the Browse Alarm/Event tab. The Browse Alarm/Event tab page contains Normal Alarm,
Event, and Engineering Alarm tab pages.
NOTE
On the Normal Alarm tab page, normal alarms generated when the base station is in the common state are
displayed. On the Event tab page, event generated. On the Engineering Alarm tab page, engineering alarms
generated when the base station is in the engineering state are displayed.
Step 2 View the alarm or event information on the Browse Alarm/Event tab page.
Step 3 To view detailed information about an alarm, double-click the alarm record.
The Detailed Information dialog box is displayed.
Step 4 In the Detailed Information dialog box, click Solution to query the description, parameters,
impact on the system, system actions, possible causes, and handling procedure.
NOTE
You can drag the rows in the Browse Alarm/Event tab page to rearrange the row order. The row order
in the Browse Alarm/Event tab page will be the tab page within the Cookie validity period.
----End
5.2.3 Querying Alarm or Event Logs
You can query the historical alarms or events from the alarm or event logs to determine the
previous running status of the equipment.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT.
Procedure
l
GUI mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Alarm/Event, and then click the Query Alarm/
Event Log tab in the Alarm/Event window.
The Query Alarm/Event Log tab page is displayed.
To query the alarms or events generated and cleared within the specified time, click
the Basic tab. Table 5-2 describes the fields on the Basic tab page.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
66
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Table 5-2 Description of the fields on the Basic tab page
Field
Description
Type
Alarm or event type to be selected. By default, all the
types are selected.
Query All Alarms/
Events Raised Within
Time Range
l If you select the Query All Alarms/Events Raised
Within Time Range check box, the alarms or events
generated within the specified time are displayed.
l If you do not select the Query All Alarms/Events
Raised Within Time Range check box, the alarms
or events generated in the following time period are
displayed by default:
Any date as the start date and any time as the start
time
The current date as the end date and the current
time as the end time
Cleared Time
l If you select Cleared Time, the alarms or events
generated within the specified time are displayed.
l If you do not select Cleared Time, the alarms or
events generated in the following time period are
displayed by default:
Any date as the start date and any time as the start
time
The current date as the end date and the current
time as the end time
Severity
Severities of the alarms or events to be selected. All the
severities are selected by default.
Max number of
results
Number of records in the query result. A maximum of
1000 records can be displayed, and the default number
is 64.
To query a type of alarm or event based on the serial number, ID, event type, and
board location, click the Advanced tab. Table 5-3 describes the fields on the
Advanced tab page.
Table 5-3 Description of the fields on the Advanced tab page
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Field
Description
Event Category
Event types of the alarms or events to be selected. All the
types are selected by default.
ID
IDs of the alarms or events to be selected.
Serial No.
Serial numbers of the alarms or events to be selected.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
67
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Field
Description
Maintenance Mode
Flag indicating the engineering status of the base station
that reported an alarm or event.
Board Location
Position of a board that reports an alarm or event, for
example, Cabinet No., Subrack No., and Slot No.
b.
Set the search criteria as required.
c.
Click Query. The query results are displayed in the Result area.
d.
To view the detailed information about an alarm or event, double-click the alarm or
event record.
The Detailed Information dialog box is displayed.
e.
In the Detailed Information dialog box, click Solution to query the description,
parameters, impact on the system, system actions, possible causes, and handling
procedure.
f.
Click Close to exit the dialog box.
NOTE
You can drag the rows in the Browse Alarm/Event tab page to rearrange the row order. The
row order in the Browse Alarm/Event tab page will be the tab page within the Cookie
validity period.
MML mode
Run the LST ALMLOG command.
----End
5.2.4 Querying Alarm or Event Configurations
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Context
The available search criteria are as follows:
l
ID
Severity
Modification Flag
Shield Flag
Return Amount
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Alarm/Event, and then click the Query Alarm/Event
Configuration tab in the displayed Alarm/Event window.
Step 2 Set the search criteria as required.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
68
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Step 3 Click Query. The query results are displayed in the Result area.
----End
5.2.5 Querying Alarm or Event Handling Suggestions
You can query detailed help information about an alarm or event based on alarm or event
handling suggestions.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Context
The detailed help information about an alarm involves the following:
l
Alarm description
Alarm attribute
Alarm parameters
Impact on system
System actions
Possible causes
Handling procedure
Procedure
Step 1 Double-click an alarm on the Browse Alarm/Event or Query Alarm/Event Log tab page.
The Detailed Information dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 In the displayed Detailed Information dialog box, click Solution. The online help of the
alarm or event is displayed.
NOTE
You can also right-click an alarm or event and choose Solution to display the online help of the alarm or
event.
Step 3 View the definition, attribute, parameters, impact on system, system actions, possible causes,
and handling procedure.
Step 4 Click the exit button in the upper right corner of the online help to exit it.
----End
5.2.6 Manually Refreshing Alarms or Events
When browsing or querying alarms or events, you can manually refresh the alarms or events
displayed on the Browse Alarm/Event or Query Alarm/Event Log tab page.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
69
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Procedure
Step 1 Click Refresh or choose Refresh from the shortcut menu on the Browse Alarm/Event,
Query Alarm/Event Log, or Query Alarm/Event Configuration tab page.
NOTE
l The alarms or events are displayed on the Browse Alarm/Event tab page in real time. Therefore, after
you refresh the tab page, the cleared alarms or events are not displayed.
l The alarms or events are not displayed in real time on the Query Alarm/Event Log tab page. Therefore,
after you manually refresh the tab page, the alarms or events are updated and displayed based on the
original search criteria.
----End
5.2.7 Manually Clearing Alarms or Events
If the cause of an alarm or event is identified or the alarm or event can be ignored, you can
manually clear the alarm or event.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Context
Manual alarm clearing applies only to alarms of the ADMC type instead of the ADAC type.
ADMC refers to automatically detected and manually cleared and ADAC refers to
automatically detected and automatically cleared.
Procedure
Step 1 Select an alarm or event to be manually cleared on the Browse Alarm/Event or Query
Alarm/Event Log tab page.
Step 2 Right-click the alarm or event and choose Clear from the shortcut menu or click Clear in the
lower right corner.
The Confirm dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click Yes. The selected alarm or event is cleared, and its color automatically changes to the
color of a cleared alarm or event.
----End
5.2.8 Deleting Cleared Alarms or Events
When browsing active alarms or events or querying alarm or event logs, you can delete the
cleared alarms or events displayed on the Browse Alarm/Event or Query Alarm/Event Log
tab page.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
70
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
5 Managing Alarms and Events
Procedure
Step 1 On the Browse Alarm/Event or Query Alarm/Event Log tab page, click Delete All, Delete
All Cleared Alarms, or Delete Selected Cleared Alarms to clear alarms as required. Table
5-4 describes the functions of these menu items.
Table 5-4 Menu item functions
Item
Description
Delete All
Deletes all the alarms on the Browse Alarm/Event or Query
Alarm/Event Log tab page.
Delete All Cleared
Alarms
Deletes all the cleared alarms on the Query Alarm/Event Log
tab page or on the Normal Alarm and Engineering Alarm tab
pages of the Browse Alarm/Event tab page.
Delete Selected
Cleared Alarms
Deletes all the selected cleared alarms on the Query Alarm/
Event Log tab page.
----End
5.2.9 Saving the Information About Alarms or Events
You can save all or part of the alarm or event records displayed on the Browse Alarm/Event
or Query Alarm/Event Log tab page as files in .csv format for future reference.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Procedure
Step 1 On the Browse Alarm/Event or Query Alarm/Event Log tab page, right-click an alarm or
event record to be saved and choose Save Selected from the shortcut menu. The Save dialog
box is displayed.
Step 2 Enter the file name and specify the save path and file type.
Step 3 Click Save.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
71
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Managing Message Tracing
About This Chapter
By tracing messages, you can verify data and identify faults. After a message tracing task is
created, the traced messages can be browsed and saved.
6.1 Overview of Message Tracing
This section describes message tracing tasks and the internal process of message tracing.
6.2 General Operations Related to Message Tracing
The general message tracing operations involve browsing, querying, and saving traced
messages and suspending, resuming, and closing a tracing task. The operations are applicable
to all message tracing tasks.
6.3 Common Tracing Tasks
This section describes tracing tasks related to common services that are not specific to any
radio access technology (RAT).
6.4 GSM-specific Tracing Tasks
GSM-specific tracing tasks include tracing radio signaling link (RSL) and common signaling
link (CSL) messages over the Abis interface in the circuit switched (CS) domain.
6.5 UMTS-specific Tracing Tasks
After a message tracing task is created, the traced messages can be browsed and saved.
6.6 LTE-specific Tracing Tasks
This section describes LTE-specific tracing tasks.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
72
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
6.1 Overview of Message Tracing
This section describes message tracing tasks and the internal process of message tracing.
Message Tracing Tasks
Message tracing traces interfaces, signaling links, and UEs. It applies to routine equipment
maintenance and fault location.
Only when the OM channel is established between the U2000 and the base station, and the
correct data configuration file is downloaded from the U2000 to the base station, the tracing
task can be performed on the LMT.
On the local maintenance terminal (LMT), common tracing tasks and GSM-, UMTS-, LTEspecific tracing tasks can be performed.
If the message Error returned from NE: Invalid board is displayed when a tracing task is
created during the base station deployment by PnP, run the DSP BRD command to check
whether the board for which the tracing task is created has been configured. If the board is not
configured, run ADD BRD to add the board. Restart the tracing task after the board is
configured successfully.
NOTE
To use the tracing function, you must install the Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in.
The tracing window is fixed in size and does not change with the web page.
It is good practice to use the U2000 instead of the LMT to trace messages in heavy traffic
scenarios. The LMT cannot accommodate processing large amounts of data and may fail to create
tracing tasks in heavy traffic scenarios.
If the sequence of the messages corresponding to the collection time is inconsistent with the actual
message sequence, time deviation occurs in the messages reported by NEs because the time
between the processes for processing the messages is not synchronized.
Common tracing tasks are as follows:
l
PTP Trace
MAC Trace
LACP Trace
PPP Trace
MP Trace
IP Layer Protocol Trace
SCTP Trace
CMPv2 Trace
IKE Trace
PNP Trace
Proxy PNP Trace
ICP Trace
SAAL Trace
HDLC Trace
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
73
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
IUANT Trace
485 Trace
IPMI Trace
RF Link Trace
Process Messages Trace
RF Message Trace
GSM-specific tracing tasks are as follows:
l
Abis Interface CS Trace (RSL)
Abis Interface CS Trace (CSL)
TRX RF Sampling
UMTS-specific tracing tasks are as follows:
l
DSP Trace
Cell Trace
User Trace
Iub Trace
LTE-specific tracing tasks are as follows:
l
S1 Interface Trace
X2 Interface Trace
Uu Interface Trace
IFTS Trace
M2 Interface Trace
Se Interface Trace
EPCInside NAS Interface Trace
EX2 Interface Trace
SO Interface Trace
Internal Process of Message Tracing
The internal process of message tracing involves creating a tracing task on the LMT and
reporting results to the LMT.
1.
2.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Creating a tracing task on the LMT.
a.
After you create a tracing task on the LMT, the LMT sends a binary command to
the base station to create the task.
b.
The base station allocates an ID to the task and forwards the command to the
tracing management module of a specified board.
c.
After receiving the command, the tracing management module records the
parameters for tracing contained in the command in the filter table and sends
messages to the service processing module.
d.
The service processing module updates the local filter table based on the messages
from the tracing management module.
Reporting results to the LMT
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
74
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
a.
After receiving messages from the tracing management module, the service
processing module verifies that the parameters in the local filter table are updated.
Then, it reports the messages meeting filter criteria to the LMT based on the task
IDs contained in the messages.
b.
The LMT analyzes the messages and displays tracing results.
6.2 General Operations Related to Message Tracing
The general message tracing operations involve browsing, querying, and saving traced
messages and suspending, resuming, and closing a tracing task. The operations are applicable
to all message tracing tasks.
6.2.1 Browsing Traced Messages Online
This section describes how to browse traced messages in the real-time message browsing
window online after a message tracing task is created.
Prerequisites
l
The message tracing task has been successfully created.
Traced messages are reported.
Procedure
Step 1 Browse traced messages in the message browsing window in real time. You can right-click a
traced message in the message browsing window and choose an item from the shortcut menu
to perform the associated operation as listed in Table 6-1.
Table 6-1 Operation instructions
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Operation
Description
Stop Trace Task
Suspends a tracing task.
Restart Trace
Task
Resumes a tracing task.
Save All
Messages
Saves all messages in the message browsing window.
Save Selected
Messages
Saves selected messages in the message browsing window.
Auto Scroll
Automatically refreshes messages in the message browsing window in
real time and scrolls up.
Clear Messages
Removes all messages from the message browsing window.
Properties
Views task properties.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
75
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
NOTE
A maximum of 2000 records can be displayed in the message tracing window. If this number is
exceeded, the latest records will replace the earliest ones.
Step 2 Double-click a message to view its details.
The Message Browser dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 6-1.
Figure 6-1 Message Browser dialog box
----End
6.2.2 Viewing Message Details
This section describes how to view the details about a traced message in the message
browsing window after the task is created.
Prerequisites
l
The message tracing task has been successfully created.
Traced messages are reported.
Procedure
Step 1 In the message browsing window, double-click a message to be viewed.
The Message Browser dialog box is displayed, showing the details about the message, as
shown in Figure 6-2.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
76
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Figure 6-2 Message Browser dialog box
Step 2 Click
in the upper right corner of the window to close the window.
----End
6.2.3 Saving Traced Messages
This section describes how to automatically and manually save traced messages. Traced
messages can be automatically saved in files to a local folder after the task is created. All or
some of the traced messages can also be manually saved when a tracing task is in process. A
maximum of 2000 messages can be saved.
Prerequisites
l
The message tracing task has been successfully created.
Traced messages are reported.
The default file name is Base Station IP address_Trace type_Year-Month-Day-HourMinute-Second_key parameters.
Traced messages are saved as files in .tmf format.
If you clear the Save File check box when creating a tracing task, the messages
displayed in the message browsing window are not saved.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
77
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Procedure
l
Automatically Saving Traced Messages
a.
When a tracing task is created, Save File is selected by default. All messages
displayed in the message browsing window are saved automatically.
NOTE
l The LMT saves every 5000 messages as a file. The messages from the 5001st are saved
in other files whose names are added with a sequence number. For example, the 5001st
to 10000th SCTP messages are saved in a file named local maintenance IP address
_SCTPTrace_Year-Month-Day-Hour-Minute-Second_1 by default.
l You can use the Traffic Recording Review Tool to browse files in .tmf format. For
details, see 6.2.4 Browsing Traced Messages Offline.
Manually Saving Traced Messages
a.
Right-click in the message browsing window and choose Save All Messages, or
right-click one or more messages to be saved and choose Save Selected Messages.
The Save dialog box is displayed.
NOTE
l If traced messages are manually saved, all messages are displayed in the window. Currently, a
maximum of 2000 messages can be displayed in the window.
l A maximum of 2000 messages can be displayed in the window, that is, only the latest 2000
messages are displayed. Therefore, it is good practice to automatically save traced messages if
there are a great number of messages.
l You can use the Traffic Recording Review Tool to browse files in .tmf format. For details, see
6.2.4 Browsing Traced Messages Offline.
l To save all traced messages, do not select any message.
l To save some of the traced messages, select the messages first. Otherwise, Save Selected
Messages is unavailable after you right-click the selected messages.
b.
Enter the file name, specify the save path, and click Save.
----End
6.2.4 Browsing Traced Messages Offline
This section describes how to use the Traffic Recording Review Tool to browse saved
message files offline.
Prerequisites
Traced messages have been saved.
The base station Maintenance and Commissioning Tool is installed.
Context
You can double-click a message file in .txt or .csv format to view the messages. A message
file in .tmf format must be opened using the Traffic Recording Review Tool.
Procedure
Step 1 Start the Traffic Recording Review Tool. Choose Start > All Programs > Huawei Local
Maintenance Terminal > Traffic Recording Review Tool.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
78
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
The Open dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 6-3.
Figure 6-3 Open dialog box
Step 2 Locate the folder that contains the message files, and then select the message file to be
viewed. The folder for saving these files is set when the task is started.
Step 3 Click Open. The contents of the message file are displayed, as shown in Figure 6-4.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
79
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Figure 6-4 Traffic Recording Review Tool window
Step 4 View these messages. You can double-click a message to view details, as shown in Figure
6-5.
Figure 6-5 Message Browser dialog box
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
80
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 5 To view other message files, choose File > Open. In the displayed Open dialog box, select
and open the message file to be viewed.
----End
6.3 Common Tracing Tasks
This section describes tracing tasks related to common services that are not specific to any
radio access technology (RAT).
6.3.1 PTP Trace
This section describes how to trace Precision Time Protocol (PTP) messages to locate faults
on PTP links. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the
traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one PTP message tracing task can be created at one time.
The PTP clock links use the IEEE 1588V2 protocol.
NOTE
IEEE 1588V2 is a protocol of precise clock synchronization defined by IEEE. It is called "A Precision
Clock Synchronization Protocol for Networked Measurement and Control Systems" and also referred to
as PTPv2.
IEEE 1588V2 applies to the scenario where all nodes in a distributed network must be
precisely synchronized in terms of reference clocks. It provides a mechanism for
achieving time synchronization among all nodes using the same reference clock.
The IEEE 1588V2 protocol transmits timestamps by means of message exchange to
achieve clock synchronization. If the IEEE 1588V2 protocol does not function properly,
PTP message tracing can be started to view IEEE 1588V2 messages.
If all IEEE 1588V2 messages are traced, check the interval at which packets are
transmitted on the clock link. If packets are transmitted at small intervals, there are a
large number of messages. Therefore, the tracing affects the system performance. You
are advised not to start multiple tracing tasks at the same time.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click PTP Trace.
The PTP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the PTP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 6-2.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
81
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-2 Parameters for PTP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for PTP message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for PTP message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for PTP message
tracing is located.
PTP Clock Link
No.
Specifies the PTP clock link number.
Trace Type
Specifies the type of messages to be traced. The default value is
Signaling/Announce. The signaling and announce messages are used
for PTP clock source negotiation and selection.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Port No.
Specifies the port number. This parameter is valid when PTP Clock
Link No. is set to 2.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
and file type.
to customize the folder, file name,
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-3 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-3 Results of PTP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the
LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
PTP Clock Link
No.
Indicates the PTP clock link number.
Trace Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Address Type
Indicates the address type of the 1588v2 clock source server.
NOTE
The value can be IPV4, MAC, or IPV6. The value IPV6 is specific to LTE.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Server Address
Indicates the address of the 1588v2 clock reference source server.
Message Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
82
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Message Sub
Type
Indicates the subtype of the messages to be traced.
Content
For details, see the IEEE 1588v2 protocol.
----End
6.3.2 MAC Trace
This section describes how to trace Media Access Control (MAC) layer messages to locate
the problems of MAC layer protocol channels.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one MAC message tracing task can be created at one time.
The protocol type, source MAC address, destination MAC address, VLAN tag, VLAN
ID, and VLAN priority are used for identifying messages at the MAC layer.
You can choose one or more items from the protocol type, source MAC address,
destination MAC address, VLAN tag, VLAN ID, and VLAN priority to specify the
scope of messages to be traced. This helps you to trace messages more specific to a fault.
Currently, packet capture at the MAC layer supports the IP, ARP, RARP, LLDP,
ETHOAM, OAM3AH, 802.1x, and SYNCETH protocol types. For details about how
to choose the protocol type, contact Huawei technical support.
The following operations cannot be started simultaneously on one board: the Mac trace,
the IP trace, and the remote loopback that is either applied to all IP addresses or a
specified address.
The WMPT, GTMUb, UTRP2, and UTRP9 boards do not support the IP-layer extended
filtering function of MAC tracing. Specifically, If MAC tracing with Frame Type set to
IP is to be enabled for these boards, Extend Switch cannot be set to ON. Otherwise,
MAC tracing fails to be started.
If the message Error returned from NE: Invalid board is displayed when a tracing
task is created during the base station deployment by PnP, run the DSP BRD command
to check whether the board for which the tracing task is created has been configured. If
the board is not configured, run ADD BRD to add the board. Restart the tracing task
after the board is configured successfully.
In secure networking scenarios, packets are encrypted and decrypted at the IP layer. The
payload in the MAC packet is encrypted. Therefore, IP packets cannot be parsed at the
MAC layer. In this case, the search criteria for the IP layer is invalid for MAC message
tracing.
In secure networking scenarios, TCP packets cannot be identified. As a result, TCP
packets cannot be filtered out during MAC message tracing, leading to packet capture
loops on the U2000. Therefore, remote MAC packet capturing on the U2000 is not
supported. (Remote MAC packet capturing on the WebLMT, to which users log in
through the U2000 proxy, is not included.) In this case, IP message tracing on the U2000
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
83
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
or local MAC message tracing on the LMT can be started. Secure networking scenarios
are as follows:
The OMCH is configured with IPsec protection.
The IPSECBIND MO takes effect on a board. You can run the LST IPSECBIND
command to check whether the IPSECBIND MO takes effect.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click MAC Trace.
The MAC Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the MAC Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-4.
Table 6-4 Parameters for MAC message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for MAC message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for MAC
message tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for MAC message
tracing is located.
Subboard Type
Specifies the type of the subboard for MAC message tracing. This
parameter can be set to:
Eth Cover Board if Slot No. is set to 0 to 5.
Base Board or Eth Cover Board if Slot No. is set to 6 or 7.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Direction
Specifies the direction of MAC messages to be traced. This parameter
can be set to Trace Receiver, Trace Sender, or Trace Both.
Frame Type
Specifies the frame type of the MAC messages to be traced. This
parameter can be set to IP, ARP, RARP, LLDP, ETHOAM,
OAM3AH, 802.1x, SYNCETH, or ALL.
Minimum Frame
Length
Specifies the minimum frame length.
Maximum Frame
Length
Specifies the maximum frame length.
VLAN Tag
Specifies the VLAN tag. This parameter can be set to Tagged, All, or
UnTagged.
VALN Priority
Specifies the VLAN priority. This parameter is valid when VLAN Tag
is set to Tagged.
VALN ID
Specifies the VLAN ID. This parameter is valid when VLAN Tag is
set to Tagged.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
84
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Local MAC
Address
Specifies the local MAC address.
Peer MAC
Address
Specifies the peer MAC address.
FrameFlow
Upper Threshold
Specifies the maximum number of packets to be reported per second.
NOTE
The packets are binary code streams.
Extend Switch
Specifies whether the filtering switch is turned on. This parameter can
be set to ON, or OFF. When the Frame Type is set to IP, this
parameter can be set.
Local IP Address
Specifies the local IP address.
Set this parameter to the source IP address of packets when Direction
is set to Trace Sender, to the destination IP address when Direction is
set to Trace Receiver, and to the source or destination IP address
when Direction is set to Trace Both.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Extend Switch is set to ON.
Peer IP Address
Specifies the peer IP address.
Set this parameter to the destination IP address of packets when
Direction is set to Trace Sender, to the source IP address when
Direction is set to Trace Receiver, and to the source or destination IP
address when Direction is set to Trace Both.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Extend Switch is set to ON.
DSCP
Specifies the DSCP.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Extend Switch is set to ON.
Protocol Type
Indicates the protocol type. This parameter can be set to ALL, ICMP,
TCP, UDP, SCTP, or GTPU.
NOTE
GTPU is only specific to LTE.
Local Port
Specifies the local port.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Protocol Type is set to TCP, or UDP.
Peer Port
Specifies the peer port.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Protocol Type is set to TCP, or UDP.
GTPU TEID
Specifies the GTPU TEID.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Protocol Type is set to GTPU.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
85
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
and file type.
to customize the folder, file name,
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-5 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-5 Results of MAC message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the
LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Message Index
Indicates the message index.
Trace Direction
Indicates the trace direction.
Peer MAC
Address
Indicates the destination MAC address.
Local MAC
Address
Indicates the source MAC address.
VLAN Priority
Indicates the VLAN priority.
VLAN ID
Indicates the VLAN ID.
Protocol Type
Indicates the protocol type of the traced message. The value can be
SYNCETH, IP, ARP, RARP, LLDP, ETHOAM, 802.3ah, 802.1x,
PPPOE Discover, or others.
Protocol
Timestamp
Indicates the message timestamp. Unit: 10 s.
Content
For details, see G.8264 protocols.
----End
6.3.3 LACP Trace
This section describes how to trace the negotiation of the Ethernet trunk protocol. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
86
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one LACP message tracing task can be created at one time.
Unsuccessful negotiation or inconsistent port status may occur during the negotiation of
the Ethernet trunk protocol. In this case, you can locate the problem by tracing messages.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click LACP Trace.
The LACP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the LACP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-6.
Table 6-6 Parameters for LACP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for Link
Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) message tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for LACP message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for LACP message
tracing is located.
Trunk No.
Specifies the Ethernet trunk No. of the board for LACP message tracing.
Direction
Specifies the direction of LACP messages to be traced. This parameter
can be set to Trace Receiver, Trace Sender, or Trace Both.
Subboard Type
Specifies the type of the subboard for LACP message tracing. This
parameter can be set to:
Ethernet Cover Board if Slot No. is set to 0 to 5.
Base Board or Ethernet Cover Board if Slot No. is set to 6 or 7.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-7 describes the message tracing results.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
87
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-7 Results of LACP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Content
For details, see the LACP protocol.
----End
6.3.4 PPP Trace
This section describes how to trace PPP messages to locate problems on the PPP links
between the base station and peer device. Traced messages can be automatically or manually
saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
A PPP link has been established.
Context
A maximum of one PPP message tracing task can be created at one time.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click PPP Trace.
The PPP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the PPP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 6-8.
Table 6-8 Parameters for PPP message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for PPP message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for PPP message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for PPP message tracing
is located.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
88
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Subboard Type
Specifies the type of the subboard for PPP message tracing. This
parameter can be set to:
E1 Cover Board if Slot No. is set to 0 to 5.
Base Board or Back Board if Slot No. is set to 6 or 7.
PPP Link No.
Specifies the number of the PPP link for the message tracing.
Direction
Specifies the direction of PPP messages to be traced. This parameter can
be set to Trace Receiver, Trace Sender, or Trace Both.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-9 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-9 Results of PPP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Protocol Type
Indicates the protocol type.
Content
For details, see the PPP protocol.
----End
6.3.5 MP Trace
This section describes how to trace messages on MP sub-links in an MP group to locate MP
group connection problems between the base station and peer device. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
MP links have been added.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
89
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Context
A maximum of one MP message tracing task can be created at one time.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click MP Trace.
The MP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the MP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 6-10.
Table 6-10 Parameters for MP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board to be traced is
located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board to be traced is
located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board to be traced is located.
Subboard Type
Specifies the type of the subboard for MP message tracing. This
parameter can be set to:
E1 Cover Board if Slot No. is set to 0 to 5.
Base Board if Slot No. is set to 6 or 7.
MpGroup No.
Specifies the number of the MP group.
Direction
Specifies the direction of MP messages to be traced. This parameter can
be set to Trace Receiver, Trace Sender, or Trace Both.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-11 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-11 Results of MP message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
90
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Protocol Type
Indicates the protocol type.
Content
For details, see the MP protocol.
----End
6.3.6 IP Layer Protocol Trace
This section describes how to trace IP layer protocol messages to locate the problems on IP
layer protocol channels. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can
browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one IP message tracing task can be created at one time.
The local IP address, peer IP address, protocol type, IP DSCP, local port number, and
peer port number are used for identifying packets at the IP layer.
You can specify the protocol type or source/destination port No. to limit the scope of
packet capture.
Either the protocol type or port No. must be specified for locating transmission
problems. Otherwise, the packet capture is less useful for problem location.
An IP layer protocol message tracing task cannot trace TCP packets connected to the
LMT itself in the uplink. For a BTS with the GTMUb functioning as the main control
board, the IP layer protocol message tracing task can trace only RSL packets and service
packets in the uplink and cannot trace 1588v2 synchronization packets in the downlink.
The following operations cannot be started simultaneously on one board: the MAC trace,
the IP trace, and the remote loopback that is either applied to all IP addresses or a
specified address.
If the message Error returned from NE: Invalid board is displayed when a tracing
task is created during the base station deployment by PnP, run the DSP BRD command
to check whether the board for which the tracing task is created has been configured. If
the board is not configured, run ADD BRD to add the board. Restart the tracing task
after the board is configured successfully.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click IP Layer Protocol
Trace.
The IP Layer Protocol Trace dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
91
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IP Layer Protocol Trace dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 6-12.
Table 6-12 Parameters for IP layer protocol message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for IP message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for IP message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for IP message
tracing is located.
Frame Flow
Upper Threshold
Specifies the maximum number of packets to be reported per second.
Direction
Specifies the transmission direction of packets to be captured.
Receive Report
Length Option
Specifies the length of received packets. This parameter can be set to
Same, Less, or No Report.
Max.Incoming IP
Packets
Specifies the maximum length of a received packet.
Transmit Report
Length Option
Specifies the length of transmitted packets. This parameter can be set
to Same, Less, or No Report.
Max.Outgoing IP
Packets
Specifies the maximum length of transmitted packets.
Report Type
Specifies the type of packets to be captured. This parameter can be set
to Plaintext or Plaintext and Ciphertext.
IP Address Type
Specifies the IP address type. This parameter can be set to IPV4.
VRF
Specifies the ID of the virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance.
Local IP Address
Specifies the local IP address.
Set this parameter to the source IP address of packets when Direction
is set to Trace Sender, to the destination IP address when Direction is
set to Trace Receiver, and to the source or destination IP address
when Direction is set to Trace Both.
Peer IP Address
Specifies the peer IP address.
Set this parameter to the destination IP address of packets when
Direction is set to Trace Sender, to the source IP address when
Direction is set to Trace Receiver, and to the source or destination IP
address when Direction is set to Trace Both.
DSCP
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Specifies the DSCP.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
92
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Protocol Type
Specifies the protocol type of the packets to be captured. This
parameter can be set to ICMP, UDP, SCTP, GTPU, TCP, , or ALL.
NOTE
GTPU is specific only to LTE.
Local Port No.
Specifies the local port number. This parameter is valid only when
Protocol Type is set to UDP, , or TCP.
Peer Port No.
Specifies the peer port number. This parameter is valid only when
Protocol Type is set to UDP, , or TCP.
GTPU TEID
Specifies the GTPU TEID. This parameter is valid only when
Protocol Type is set to GTPU.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
and file type.
to customize the folder, file name,
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-13 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-13 Results of IP message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the
LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Message Index
Indicates the internal serial number of a traced message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the direction of a traced message.
Header Length
Indicates the IP header length.
Version
Indicates the IP version. The value 4 represents IPv4.
Type Of Service
Indicates the service type of a traced message.
Total Length
Indicates the IP packet length.
Identification
Indicates the tag of a traced message. For details, see the IP protocol.
Fragment Offset
Field
Indicates the fragment offset of a traced message. For details, see the
IP protocol.
Time To Live
Indicates the life time of a traced message. For details, see the IP
protocol.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
93
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Protocol
Indicates the protocol type of a traced message. The value can be
UDP, SCTP, TCP, ICMP, AH, or ESP.
Checksum
Indicates the IP checksum of a traced message. For details, see the IP
protocol.
Source Address
Indicates the source IP address of a traced message.
Dest Address
Indicates the destination IP address of a traced message.
Port Timestamp
Indicates the timestamp (unit: 10 microseconds) of a traced message.
Packet
Sent(Received)
Sequence
Number
A packet has the same sequence number when it is sent or received in
plaintext and ciphertext format. When packets in both plaintext and
ciphertext formats are traced, this parameter specifies the sequence in
which the packets in both plaintext and ciphertext formats are sent or
received.
When only packets in plaintext format are traced, this parameter
specifies the sequence in which the packets in plaintext format are sent
or received.
Packet Type
Indicates the type of the packet that carries a traced message.
Packet Process
Result
Indicates the packet processing result.
Source Port
Indicates the source port No. This parameter is valid for UDP, TCP,
and SCTP packets.
Destination Port
Indicates the destination port No. This parameter is valid for UDP,
TCP, and SCTP packets.
UDP Length
Indicates the Length of a UDP packet. This parameter is valid for UDP
packets.
UDP Checksum
Indicates the checksum of a UDP packet. This parameter is valid for
UDP packets. For details, see the UDP protocol.
TEID
Indicates the TEID of a GTPU packet. This parameter is valid for
GTPU packets. GTPU packets are a type of UDP packets.
SCTP
Verification Flag
Indicates the verification flag for SCTP packets. This parameter is
valid for SCTP packets. For details, see the SCTP protocol.
SCTP Checksum
Indicates the checksum of an SCTP packet. This parameter is valid for
SCTP packets. For details, see the SCTP protocol.
Content
For details, see the IP protocol.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
94
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
6.3.7 SCTP Trace
This section describes how to trace Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) messages
to locate faults on SCTP links. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You
can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of six SCTP message tracing task can be created at one time. In addition,
the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
SCTP tracing affects system performance because SCTP links are busy. Therefore, do
not start multiple SCTP tracing tasks simultaneously.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click SCTP Trace.
The SCTP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the SCTP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-14.
Table 6-14 Parameters for SCTP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for SCTP message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for SCTP message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for SCTP message
tracing is located.
SCTP Link
No.
Specifies the number of the SCTP link to be traced.
Direction
Specifies the direction of SCTP messages to be traced. This parameter can
be set to Trace Receiver, Trace Sender, or Trace Both.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
95
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-15 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-15 Results of SCTP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Chunk Type
Indicates the type of the traced packet.
Chunk Flag
Uniquely indicates the chunk flag.
Chunk Length
Indicates the length of the traced packet.
Content
Indicates the SCTP protocol layer. For details, see the RFC4960 protocol.
----End
6.3.8 CMPV2 Trace
This section describes how to trace Certificate Management Protocol Version 2 (CMPV2)
messages. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the
traced messages online or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display
Information Elements (IEs) contained in the messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one CMPV2 message tracing task can be created at one time.
If the message Error returned from NE: Invalid board is displayed when a tracing
task is created during the base station deployment by PnP, run the DSP BRD command
to check whether the board for which the tracing task is created has been configured. If
the board is not configured, run ADD BRD to add the board. Restart the tracing task
after the board is configured successfully.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click CMPV2 Trace.
The CMPV2 Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the CMPV2 Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-16.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
96
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-16 Parameters for CMPV2 message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for CMPV2 message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for CMPV2 message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for CMPV2 message
tracing is located.
Direction
Specifies the direction of CMPV2 messages to be traced. This parameter
can be set to Trace Receiver, Trace Sender, or Trace Both.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-17 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-17 Results of CMPV2 message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of traced messages.
Trace
Message Type
Indicates the protocol type of traced messages.
Content
Contains only CMPV2 messages. For details, see RFC protocols and
3GPP TS 33.310.
----End
6.3.9 IKE Trace
This section describes how to trace Internet Key Exchange (IKE) messages to locate IKE
negotiation issues or observe the IKE negotiation process. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
97
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Context
l
A maximum of one IKE message tracing task can be created at one time.
In an IKE setup or rekey process, IKE negotiation may fail due to algorithm
inconsistency or certificate errors, packets cannot be encrypted because IKE tunnels are
not successfully established. As a result, packets are lost.
Information such as the message type, request, and response about IKEv1 or IKEv2
message headers can be analyzed.
If the message Error returned from NE: Invalid board is displayed when a tracing
task is created during the base station deployment by PnP, run the DSP BRD command
to check whether the board for which the tracing task is created has been configured. If
the board is not configured, run ADD BRD to add the board. Restart the tracing task
after the board is configured successfully.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click IKE Trace.
The IKE Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IKE Trace dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 6-18.
Table 6-18 Parameters for IKE message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for IKE message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for IKE message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for IKE message
tracing is located.
Direction
Specifies the direction of IKE messages to be traced.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-19 describes the message tracing results.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
98
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-19 Results of IKE message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Content
For details, see the IKE protocol.
----End
6.3.10 PNP Trace
This section describes how to trace the site deployment process. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one PNP message tracing task can be created at one time.
The real-time tracing function for site deployment includes receiving, sending, checking,
and handling of messages. In case of a failure, the failure cause is displayed.
The real-time tracing function can be enabled only by the managing mode of a
multimode base station, only partial deployment information is visible to the nonmanaging mode.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > PNP Trace. Double-click PNP Trace.
The PNP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the PNP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 6-20.
Table 6-20 Parameters for PNP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
99
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-21 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-21 Results of PNP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Cabinet:Subrack
:Slot
Indicates the cabinet, subrack, and slot information about the traced
board.
CPUID
Indicates the ID of the CPU for the traced board.
Message Type
Indicates the type of a message, which can be binary or text.
Content
For details, see the site deployment records.
----End
6.3.11 Proxy PNP Trace
This section describes how to trace and record the deployment procedure of the target base
station that requires emergency maintenance.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The emergency OM channel has been successfully established.
The real-time tracing function for site deployment includes receiving, sending, checking,
and handling of messages. In case of a failure, the failure cause is displayed.
The real-time tracing function can be enabled only by the managing mode of a
multimode base station. During a mode election, the course is visible to the nonmanaging mode. When the transmission board is determined, the deployment
information is invisible to the non-managing mode.
For configurations of an emergency OM channel, see 2.8 Configuring an Emergency
OM Channel.
PNP tracing using the proxy base station applies only to the IP protocol stack.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
100
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Proxy PNP Trace. Double-click Proxy PNP Trace.
The Proxy PNP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Proxy PNP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-22.
Table 6-22 Parameters for proxy PNP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-23 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-23 Results of proxy PNP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Cabinet:Subrack
:Slot
Indicates the cabinet, subrack, and slot information about the traced
board.
CPUID
Indicates the ID of the CPU for the traced board.
Message Type
Indicates the type of a message, which can be binary or text.
Content
For details, see the site deployment records.
----End
6.3.12 ICP Trace
This section describes how to trace IMA Control Protocol (ICP) messages to locate problems
on the IMA link between the base station and peer device. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
101
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Context
l
A maximum of four ICP message tracing task can be created at one time. In addition, the
tasks must differ in parameter settings.
This task is specific only to UMTS.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click ICP Trace.
The ICP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the ICP Trace dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 6-24.
Table 6-24 Parameters for ICP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for ICP message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for ICP message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for ICP message tracing
is located.
Subboard
Type
Specifies the subboard type. This parameter can be set to:
E1 Cover Board if Slot No. is set to 0 to 5.
Base Board if Slot No. is set to 6 or 7.
IMA Group
No.
Specifies the number of the IMA group for ICP message tracing.
Direction
Specifies the direction of ICP messages to be traced. This parameter can
be set to Trace Receiver, Trace Sender, or Trace Both.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-25 describes the message tracing results.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
102
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-25 Results of ICP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Content
For details, see the ICP protocol.
----End
6.3.13 SAAL Trace
This section describes how to trace Signaling ATM Adaptation Layer (SAAL) messages to
locate faults on the SAAL link. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You
can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of four SAAL message tracing task can be created at one time. In addition,
the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
This task is specific only to UMTS.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click SAAL Trace.
The SAAL Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the SAAL Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-26.
Table 6-26 Parameters for SAAL message tracing
Parameter
Description
SAAL Link
No.
Specifies the number of the SAAL link to be traced.
Message Type
Specifies the type of messages to be traced.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
103
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-27 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-27 Results of SAAL message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
SAAL Link
No.
Indicates the link number of the traced SAAL link.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
PDU Message
Type
Indicates the PDU type of the traced message.
Content
For details, see the SAAL protocol.
----End
6.3.14 HDLC Trace
This section describes how to trace High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) messages. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display Information Elements
(IEs) contained in the messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of six HDLC tracing tasks can be created on a main control board. In addition,
the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click HDLC Trace.
The HDLC Trace dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
104
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 3 Set related parameters in the HDLC Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-28.
Table 6-28 Parameters for HDLC message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for HDLC
message tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for HDLC
message tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for HDLC message
tracing is located.
Trace Frame Type
Specifies the frame type for HDLC message tracing. This parameter
can be set to I Frame, S Frame, or U Frame.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
and file type.
to customize the folder, file name,
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-29 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-29 Results of HDLC message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the
LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
HDLC Address
Indicates the address type of traced HDLC messages.
Control Frame
Type
Indicates the type of the traced control frame.
NR
Indicates the value of the traced NR.
NS
Indicates the value of the traced NS.
PF
Indicates the value of the traced PF.
Content
For details, see the HDLC protocol.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
105
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
6.3.15 IUANT Trace
This section describes how to trace IUANT messages. In addition, you can resolve the traced
messages to display information elements (IEs) in the messages. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
The pRRU does not support this function.
Only one IUANT message tracing task can be created on a main control board at one
time, and the parameter settings for each task cannot be identical.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click IUANT Trace.
The IUANT Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IUANT Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-30.
Table 6-30 Parameters for IUANT message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for IUANT message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for IUANT
message tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for IUANT message
tracing is located.
Device No.
Specifies the number of the device for IUANT message tracing.
Node No.
Specifies the number of the node for IUANT message tracing. This
parameter can be set to Application, Driver, or All.
Frame Type
This parameter can be set to I Frame, S Frame, or U Frame.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Node No. is set to Application.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
106
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-31 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-31 Results of IUANT message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence number of the traced message
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Cabinet:Subrac
k:Slot
Indicates the cabinet, subrack, and slot information about the traced
board.
Link ID
Indicates the link ID of the traced message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
HDLC Address
Indicates the traced HDLC type.
HDLC Frame
Type
Indicates the type of the traced control frame.
N(R)
Indicates the value of the traced NR.
N(S)
Indicates the value of the traced NS.
P/F
Indicates the value of the traced PF.
Content
For details, see the IUANT protocol.
----End
6.3.16 485 Trace
This section describes how to trace 485 messages. In addition, the traced messages can be
resolved to display information elements (IEs) in the messages. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
Only one 485 message tracing task can be created on a main control board at one time, and
the parameter settings for each task cannot be identical.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
107
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click 485 Trace.
The 485 Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the 485 Trace dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 6-32.
Table 6-32 Parameters for 485 message tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace Type
Specifies the trace type. This parameter can be set to CSS or Portand
Added.
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for 485 message
tracing is located. This parameter is valid only when Trace Type is set to
CSS.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for 485 message
tracing is located. This parameter is valid only when Trace Type is set to
CSS.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for 485 message tracing
is located. This parameter is valid only when Trace Type is set to CSS.
Manager
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the manager cabinet where the board for 485
message tracing is located. This parameter is valid only when Trace Type
is set to Portand Added.
Manager
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the manager subrack where the board for 485
message tracing is located. This parameter is valid only when Trace Type
is set to Portand Added.
Port No.
Specifies the number of the port for 485 message tracing. This parameter
is valid only when Trace Type is set to Portand Added.
Device
Address
Specifies the address of the device for 485 message tracing. This
parameter is valid only when Trace Type is set to Portand Added.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-33 describes the message tracing results.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
108
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-33 Results of 485 message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Cabinet No.
Indicates the cabinet number.
Subrack No.
Indicates the subrack number.
Slot No.
Indicates the slot number.
Manager
Cabinet No.
Indicates the manager cabinet number.
Manager
Subrack No.
Indicates the manager subrack number.
Port No.
Indicates the port number.
Device
Address
Indicates the device address.
Message
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Content
For details, see the 485 protocol.
----End
6.3.17 IPMI Trace
This section describes how to trace Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI)
messages. In addition, you can resolve the traced messages to display information elements
(IEs) in the messages. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can
browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of three IPMI message tracing task can be created at one time. In addition, the
tasks must differ in parameter settings.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click IPMI Trace.
The IPMI Trace dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
109
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IPMI Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-34.
Table 6-34 Parameters for IPMI message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for IPMI message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for IPMI message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for IPMI message
tracing is located.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-35 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-35 Results of IPMI message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
CabinetNo.:Su
brackNo.:Slot
No.
Indicates the cabinet, subrack, and slot information about the traced
board.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Content
For details, see the IPMI protocol.
----End
6.3.18 RF Link Trace
This section describes how to trace protocol messages over RF links of the base station.
Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced
messages online or offline.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
110
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of four RF link tracing tasks can be created on one main control board.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Trace.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services, and double-click RF Link Trace.
The RF Link Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the RF Link Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-36.
Table 6-36 Parameters for RF link tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for RF link tracing is
located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for RF link tracing is
located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for RF link tracing is
located.
CPU ID
Specifies the ID of the CPU. The value range of this parameter is from 0
to 255.
BUS ID
Specifies the ID of the bus. The value range of this parameter is from 0 to
255.
Device ID
The value range of this parameter is from 0 to 255.
Link Type
Specifies the type of the RF link. This parameter can be set to AISG,
MBUS, HPI, or TCP.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-37 describes the message tracing results.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
111
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-37 Results of the RF link tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
CPUID
Indicates the ID of the CPU in the reported message.
BUS ID
Indicates the ID of the bus in the reported message.
Device ID
Indicates the ID of the device in the reported message.
Link Type
Indicates the type of the RF link in the reported message.
Content
Indicates the content of the reported message.
----End
6.3.19 Process Message Trace
This section describes how to trace protocol messages between processes. Traced messages
can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or
offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display IEs contained in the
messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of 10 internal tracing tasks can be created. In addition, the tasks must differ
in parameter settings.
Message From NBAP/ALCAP to SAAL, and Message From SAAL to NBAP/
ALCAP are applicable to only UMTS.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services. Double-click Process Message
Trace.
The Process Message Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Process Message Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-38.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
112
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-38 Parameters for message tracing over process
Parameter
Description
Mode
Specifies the tracing mode. This parameter can be set to Trace Mode,
Cut Mode, or Both Trace Mode.
Action Side
Specifies the sender or receiver side where messages are to be traced.
This parameter can be set to Sender Side, or Receiver Side.
Sender CPU
ID
Specifies the ID of the sender CPU.
Sender PID
Specifies the ID of the sender process.
Receiver CPU
ID
Specifies the ID of the receiver CPU.
Receiver PID
Specifies the ID of the receiver process.
Report
Message Type
Specifies the message type. This parameter can be set to Measurement
Report, RTWP Report, FP Control Frame, Message From NBAP/
ALCAP to SAAL, or Message From SAAL to NBAP/ALCAP.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Based on the information in the window, you can
view message flows. Table 6-39 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-39 Results of message tracing over process
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Mode
Indicates the tracing mode.
Action Side
Indicates the sender or receiver side where the message is traced.
Sender CPU
ID
Indicates the ID of the sender CPU.
Sender PID
Indicates the ID of the sender process.
Receiver CPU
ID
Indicates the ID of the receiver CPU.
Receiver PID
Indicates the ID of the receiver process.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
113
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Message Type
Indicates the message type.
Content
Indicates the message content.
----End
6.3.20 RF Message Trace
This section describes how to trace protocol messages over RF interfaces of the base station.
Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced
messages online or offline.
Context
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
A maximum of four RF message tracing tasks can be created on one main control board.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Trace.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > Common Services, and double-click RF Message
Trace.
The RF Message Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the RF Message Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-40.
Table 6-40 Parameters for RF message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Indicates the number of the cabinet where the board for RF message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Indicates the number of the subrack where the board for RF message
tracing is located.
Slot No.
Indicates the number of the slot where the board for RF message tracing is
located.
Sender CPU
ID
Specifies the ID of the sender CPU.
Sender PID
Specifies the ID of the sender process.
Receiver CPU
ID
Specifies the ID of the receiver CPU.
Receiver PID
Specifies the ID of the receiver process.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
114
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-41 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-41 Results of the RF message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Sender CPU
ID
Indicates the CPU ID of the sender in the reported message.
Sender PID
Indicates the process ID of the sender in the reported message.
Receiver CPU
ID
Indicates the CPU ID of the receiver in the reported message.
Receiver PID
Indicates the ID of the process ID of the receiver in the reported message.
Content
Indicates the content of the reported message.
----End
6.4 GSM-specific Tracing Tasks
GSM-specific tracing tasks include tracing radio signaling link (RSL) and common signaling
link (CSL) messages over the Abis interface in the circuit switched (CS) domain.
6.4.1 Abis Interface CS Trace (RSL)
This section describes how to use the local maintenance terminal (LMT) to trace radio
signaling link (RSL) messages over the Abis interface. RSL messages are exchanged between
the base station controller (BSC) and base transceiver station (BTS) during call processes.
The message types include measurement reports, channel requests, paging, RLM, and TRXM.
BTSs with the GTMUb functioning as the main control board do not support RSL message
tracing over the Abis interface.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
115
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > GSM Services. Double-click Abis Interface CS
Trace(RSL).
The Abis Interface CS Trace(RSL) dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Abis Interface CS Trace(RSL) dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 6-42.
Table 6-42 Parameters for RSL message tracing over the Abis interface in the CS domain
Parameter
Description
Message
Type
Specifies the type of messages to be traced.
Trace
Target
Specifies the index of the carrier to be traced. The value range is from 0 to
23999.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-43 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-43 Results of RSL message tracing over the Abis interface in the CS domain
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence number of the traced message.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Trx No.
Indicates the number of the carrier where messages are traced.
Trx ID
Indicates the ID of the carrier where messages are traced.
Cell ID
Indicates the ID of the cell where messages are traced.
Message
Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Content
For details, see CS Trace Interface Protocol.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
116
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
6.4.2 Abis Interface CS Trace (CSL)
This section describes how to use the local maintenance terminal (LMT) to trace common
signaling link (CSL) messages over the Abis interface. The CSL messages record the service
configuration and other common signaling interaction between the BSC and the BTS.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > GSM Services. Double-click Abis Interface CS
Trace(CSL).
The Abis Interface CS Trace(CSL) dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Abis Interface CS Trace(CSL) dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 6-44.
Table 6-44 Parameters for CSL message tracing over the Abis interface in the CS domain
Parameter
Description
Message
Type
Specifies the type of messages to be traced.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-45 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-45 Results of CSL message tracing over the Abis interface in the CS domain
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence number of the traced message.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Message
Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
117
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Content
For details, see CS Trace Interface Protocol.
----End
6.4.3 TRX RF Sampling
The section describes how to sample the number of carriers and RF modules on the local
maintenance terminal (LMT). The sampling result is not displayed in the LMT.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > GSM Services. Double-click TRX RF Sampling.
The TRX RF Sampling dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the TRX RF Sampling dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-46.
Table 6-46 Parameters for carriers and RF unit sampling
Parameter
Description
TRX ID
Specifies the index of a carrier. The value range of this parameter is from 0
to 23999.
Sampling
Type
Specifies the sampling type. The value range of this parameter is from 0 to
255.
Sub
Sampling
Type
Specifies the sub-sampling type. The value range of this parameter is from
0 to 255.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Step 4 Click Submit to sample carriers and RF modules.
----End
6.5 UMTS-specific Tracing Tasks
After a message tracing task is created, the traced messages can be browsed and saved.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
118
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
6.5.1 DSP Trace
This section describes how to trace digital signal processor (DSP) service messages. In
addition, you can resolve the traced messages to display information elements (IEs) in the
messages. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the
traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of 4 DSP tracing tasks can be created on a NE at one time. In addition, the tasks
must differ in parameter settings.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > UMTS Services. Double-click DSP Trace.
The DSP Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click the Basic tab page and set the related parameters. Table 6-47 describes parameters on
the Basic tab page.
Table 6-47 Parameters on the Basic tab page for DSP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for DSP message
tracing is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for DSP message tracing
is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for DSP message tracing
is located.
DSP ID
Specifies DSP ID.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click the Uu tab page, set the Uu Message Type. Table 6-48 describes parameters on the Uu
tab page.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
119
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-48 Parameters on the Uu tab page for DSP message tracing
Parameter
Description
Uu Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the Uu interface.
Step 5 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-49 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-49 Results of DSP message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Message No.
Indicates the sequence number of the traced message.
Tracing Entity
ID
Indicates the tracing entity ID.
Message
Category
Indicates the category of the traced message.
Message Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Content
Indicates the content of the traced message.
----End
6.5.2 Cell Trace
This section describes how to trace cell-specific messages to locate cell-specific message
problems. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the
traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of three cell-specific message tracing task can be created at one time. In
addition, the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
The RRU3808, MRFU V1, MRFU V2, RRU3805, and RRU3908 V1 do not support the
following three trace items: (RRU)Channel Information, (RRU)Custom-collection
Datas, and (RRU)Module-collection Datas.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
120
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > UMTS Services. Double-click Cell Trace.
The Cell Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click the Basic tab page and set the related parameters. Table 6-50 describes parameters on
the Basic tab page.
Table 6-50 Parameters on the Basic tab page for cell-specific message tracing
Parameter
Description
Logic Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the cell to be traced.
Trace Type
Specifies the trace type. This parameter can be set to Cell, or All Users.
Information
Level
Specifies the information level of the traced message. This parameter can
be set to Key, or Detail.
Trace Mode
Specifies the information mode of the traced message. This parameter
can be set to Common Message Report, or Compressed Message
Report.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click the Iub tab page or the Uu tab page, select the message type.
l
Table 6-51 describes the parameters on the Iub tab page.
Table 6-51 Parameters on the Iub tab page for cell-specific message tracing
Parameter
Description
Iub Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the Iub interface.
Table 6-52 describes parameters on the Uu tab page.
Table 6-52 Parameters on the Uu tab page for cell-specific message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Uu Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the Uu interface.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
121
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 5 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-53 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-53 Results of cell-specific message tracing
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Message No.
Indicates the sequence number of the traced message.
Tracing Entity
ID
Indicates the tracing entity ID.
Message
Category
Indicates the category of the traced message.
Message Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Content
Indicates the content of the traced message.
----End
6.5.3 User Trace
This section describes how to trace UE-specific messages to locate UE-specific message
problems. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the
traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
This function can be used to quickly locate and resolve problems. Normally there is no
way to avoid that some user data such as International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
will be used during the troubleshooting. However, this function provides an anonymous
data processing method.
You are obligated to take considerable measures, in compliance with the laws of the
countries concerned, to ensure that the personal data of users is fully protected. For
example, you can enable user identity anonymity and delete the tracing files after the
problems are handled.
UE-specific messages can be traced by CRNC ID, Chain Time, IMSI ID, or CELL ID.
If UE-specific messages are to be traced by IMSI ID, determine whether the IMSI data
to be entered must be anonymous by running the LST USERIDANONSWITCH
command and checking the value of User Identity Anonymity Switch in the command
output.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
If User Identity Anonymity Switch is ON, anonymous IMSI data needs to be
entered in IMSI ID. Anonymous IMSI data can be obtained by entering the IMSI
and a key in the anonymization tool HMACUtil.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
122
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
If User Identity Anonymity Switch is OFF, the IMSI can be directly entered in
IMSI ID.
NOTE
l The anonymization switch and the key can be modified on the U2000 by choosing Monitor >
Signaling Trace > Anonymous Policy Management (traditional style), or by choosing Signaling
Trace > Anonymous Policy Management (application style). For details, see U2000 Fault
Management User Guide.
l If the anonymization switch or the key is modified on the U2000 after a UE-specific message
tracing task is started, you need to stop the task and restart it after the modification.
l To obtain the anonymization tool HMACUtil, contact Huawei technical support.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > UMTS Services. Double-click User Trace.
The User Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Click the Basic tab page and set the related parameters. Table 6-54 describes parameters on
the Basic tab page.
Table 6-54 Parameters on the Basic tab page for UE-specific message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Trace Method
Specifies the tracing method.
CRNC ID
Specifies the CRNC ID. This parameter is valid when Trace Method is
set to CRNC ID.
Trace
Time(10s)
Specifies the tracing duration of each user. This parameter is valid when
Trace Method is set to Chain Time.
User Number
Specifies the number of UEs to be traced. This parameter is valid when
Trace Method is set to Chain Time.
Begin Time
Specifies the time when the tracing starts. This parameter is valid when
Trace Method is set to Chain Time.
End Time
Specifies the time when the tracing ends. This parameter is valid when
Trace Method is set to Chain Time.
IMSI ID
Specifies the IMSI. This parameter is valid when Trace Method is set to
IMSI ID.
CELL ID
Specifies the cell ID. This parameter is valid when Trace Method is set to
CELL ID.
Fault Type
Specifies the fault type. This parameter can be set to KPI SRB, KPI
TRB, HSDPA, or HSUPA.
Trace Mode
Specifies the compression flag, indicating whether a packet is compressed.
This parameter can be set to Common Message Report or Compressed
Message Report.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
123
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
NOTE
l After Fault Type is specified, the manually selected message types on the Iub and Uu tab pages are
automatically cleared and the message types of the selected fault type are automatically selected.
l If multiple fault types are selected for Fault Type, all message types of the selected fault types will
be automatically selected on the Iub and Uu tab pages.
Step 4 Click the Iub tab page or the Uu tab page, select the message type.
l
Table 6-55 describes the parameters on the Iub tab page.
Table 6-55 Parameters on the Iub tab page for UE-specific message tracing
Parameter
Description
Iub
Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the Iub interface.
Table 6-56 describes parameters on the Uu tab page.
Table 6-56 Parameters on the Uu tab page for UE-specific message tracing
Parameter
Description
Uu Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the Uu interface.
Step 5 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Based on the information in the window, you can
view message flows. Table 6-57 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-57 Results of UE-specific message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Message No.
Indicates the sequence number of the traced message.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
124
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Tracing Entity
ID
Indicates the tracing entity ID.
Message
Category
Indicates the category of the traced message.
Message Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Content
Indicates the content of the traced message.
----End
6.5.4 Iub Trace
This section describes how to trace messages over the Iub interface. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of four Iub message tracing task can be created at one time. In addition, the
tasks must differ in parameter settings.
If you create the task and is prompted with a message indicating that the system is busy
and the task fails to be created, the central processing unit (CPU) is overloaded. If this
happens, try again 30 seconds after the CPU overload is relieved.
Under heavy traffic, if commands fail to be delivered while Iub tracing starts, the CPU is
overloaded. In this case, deliver the commands again 30 seconds after Iub tracing is
disabled.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > UMTS Services. Double-click Iub Trace.
The Iub Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 6-58.
Table 6-58 Parameters for message tracing over the Iub interface
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
NBAP
Message
Specifies the NodeB application part (NBAP) messages to be traced.
ALCAP
Message
Specifies the Access Link Control Application Part (ALCAP) messages to
be traced.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
125
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-59 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-59 Results of message tracing over the Iub interface
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced message.
Message
Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Content
For details, see the Iub interface protocol.
----End
6.6 LTE-specific Tracing Tasks
This section describes LTE-specific tracing tasks.
6.6.1 S1 Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace control plane messages over the S1 interface. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display Information Elements
(IEs) contained in the messages.
Context
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
A maximum of five message tracing tasks can be created simultaneously over an S1
interface.
This task is specific to LTE.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
126
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click S1 Interface Trace.
The S1 Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the S1 Interface Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-60.
Table 6-60 Parameters for message tracing over the S1 interface
Parameter
Description
Direction
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the S1 interface. This
parameter can be set to Bi-Directional, To MME, or From MME.
Trace object
Specifies the MME for the tracing. This parameter can be set to All
MMEs, Specified MME, or EPCInside MME.
S1 Interface
ID
Specifies the S1 interface ID. After an interface ID is specified, the
messages related to the MME are traced.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Trace object is set to Specified MME.
Message
Type
Specifies the message type. You can select one, multiple, or all message
types. If Select All is selected, all messages are traced. Otherwise, only the
selected types of messages are traced.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save File
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-61 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-61 Results of message tracing over the S1 interface
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Standard
Interface
Message
Type
Indicates the type of the standard interface message.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
127
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Trace
Direction
Indicates the message direction.
S1 Interface
ID
Indicates the ID of the S1 interface.
Call ID
Indicates the ID of the traced call.
PLMN
Indicates the message PLMN.
Local Cell
ID
Indicates the ID of the local cell.
CPU ID
Indicates the ID of the CPU for the traced board.
Content
The version number traced over the S1 interface is 10Q1, and the traced
protocol layer is S1 AP. For details, see 3GPP TS 36.413.
----End
6.6.2 X2 Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace control plane messages over the X2 interface. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display Information Elements
(IEs) contained in the messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of five message tracing tasks can be created simultaneously over an X2 interface.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click X2 Interface Trace.
The X2 Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the X2 Interface Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-62.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
128
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Table 6-62 Parameters for message tracing over the X2 interface
Paramet
er
Description
Direction
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the X2 interface. This
parameter can be set to Bi-Directional, To eNodeB, or From eNodeB.
Trace
object
Specifies the eNodeB to be traced. This parameter can be set to ALL eNodeBs
or Specified eNodeB.
Peer
eNodeB
ID
Specifies the peer eNodeB ID. After an eNodeB ID is specified, the messages
related to the eNodeB are traced.
Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the X2 interface. You can
select one, multiple, or all message types. If Select All is selected, all messages
are traced. Otherwise, only the selected types of messages are traced.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save File
NOTE
This parameter is valid only when Trace object is set to Specified eNodeB.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-63 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-63 Results of message tracing over the X2 interface
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Paramet
er
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Standard
Interface
Message
Type
Indicates the type of the standard interface message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the message direction.
eNodeB
ID
Indicates the peer eNodeB ID.
Call ID
Indicates the ID of the traced call.
PLMN
Indicates the message PLMN.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
129
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Paramet
er
Description
Local
Cell ID
Indicates the ID of the local cell.
CPU ID
Indicates the ID of the CPU for the traced board.
Content
The version number traced over the X2 interface is 10Q1, and the traced
protocol layer is X2 AP. For details, see 3GPP TS 36.423.
----End
6.6.3 Uu Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace all or some of the signaling messages over the Uu
interface of either specified cells or all the cells under an eNodeB. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of five message tracing tasks can be created simultaneously over a Uu interface.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click Uu Interface Trace.
The Uu Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Uu Interface Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-64.
Table 6-64 Parameters for message tracing over the Uu interface
Parameter
Description
Direction
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the Uu interface.
This parameter can be set to Bi-Directional, From UE, or To UE.
Trace object
Specifies the cell or cells to be traced. This parameter can be set to All
cells or Specified cell.
Local Cell ID
Specifies the local cell ID. After a local cell ID is specified, the
messages related to the cell are traced.
NOTE
This parameter is valid only when Trace object is set to Specified cell.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
130
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
Message Type
Specifies the message type. You can select one, multiple, or all message
types. If Select All is selected, all messages are traced. Otherwise, only
the selected types of messages are traced.
Trace Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-65 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-65 Results of message tracing over the Uu interface
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Standard
Interface
Message Type
Indicates the type of the standard interface message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the message direction.
Local Cell ID
Indicates the ID of the local cell.
CPU ID
Indicates the ID of the CPU for the traced board.
Call ID
Indicates the ID of the traced call.
CRNTI
Indicates the cell radio network temporary identifier.
PLMN
Indicates the message PLMN.
Content
The version number traced over the Uu interface is 10Q1, and the
traced protocol layer is RRC. For details, see the 3GPP TS 36.331.
----End
6.6.4 IFTS Trace
This section describes how to trace the messages of a single UE in a specific cell and the
statistical result of data transfer on the user plane based on the causes for the RRC connection
setup so that abnormal UE procedures are detected. The UE messages to be traced include the
control plane messages over the S1, X2, and Uu interfaces. Traced messages can be
automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online or offline.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
131
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
The CPU usage of the board cannot be reported if IFTS tracing is enabled. Therefore,
you are advised to disable IFTS tracing before starting monitoring on the CPU usage of
the board.
Only one intelligent field test system (IFTS) message tracing task can be created in a
cell. After an IFTS message tracing task is started, the UE to be traced is the first UE that
is admitted by, is handed over to, or reestablishes connection with the cell.
NOTICE
After the tracing task starts, lots of data will be reported, which may affect the system
performance. It is recommended that this task be used only in some special scenarios, such as
fault diagnosis.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click IFTS Trace.
The IFTS Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IFTS Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-66.
Table 6-66 Parameters for IFTS message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Ba
sic
Local
Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the local cell to be traced.
Main
eNodeB
ID
Specifies the ID of the eNodeB serving the
monitored cell to be traced.
Trace
User
Type
Specifies the type of UEs to be traced. This
parameter can be set to HOIn User or
RRCReEst User. If you select HOIn User,
the UE handed over to the cell is traced. If you
select RRCReEst User, the UE whose RRC
connection is reestablished is traced.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
132
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Trace
Module
Description
Specifies the module to be traced. This
parameter can be set to L3, L2, or L1. By
default, no items are selected for Trace
Module.
If L3 is selected, items on the L3 Trace Info
tab page can be selected. If L2 is selected,
items on the L2 Trace Info tab page can be
selected. If L1 is selected, items on the L1
Trace Info tab page can be selected.
Save
File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing
results will be automatically saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and
file type.
L3
Trace
Info
L3 Trace Item
S1, Uu, and X2 can be
selected.
L2
Trace
Info
L2 Trace Item
MAC PDCCH, MAC
SRI, MAC MCE, CQI,
ACK, Access, Call
Drop&HO, Traffic,
Voice, and Ping Delay
can be selected.
L2 Trace Extended Item
Specifies the number of
traced extended items.
This parameter is userdefined. The value can
contain a maximum of
32 numbers, two
adjacent numbers of
which are separated by a
slash (/). Each number
must be 255 or less.
Direction
This parameter can be set
to Trace Both, Trace
Sender, or Trace
Receiver.
L1 Trace Item
L1, L1 UP, and L1
DOWN can be selected.
L1
Trace
Info
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
133
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
L1 Trace Extended Item
Trace Reason
Specifies the number of
traced extended items.
This parameter is userdefined. The value can
contain a maximum of
32 numbers, two
adjacent numbers of
which are separated by a
slash (/). Each number
must be 255 or less.
Specifies the reason for message trace. This
parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for
message trace.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-67 describes the message tracing results.
NOTE
For details, send the generated file to Huawei technical support for analysis.
Table 6-67 Results of IFTS message tracing
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced
message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Trace Interface Type
Indicates the interface type of the traced
message.
Trace Message Type
Indicates the type of the traced message.
Direction
Indicates the direction of the traced
message.
CELL Instance
Indicates the cell instance number of the
traced message.
Local CELLID
Indicates the local cell ID of the traced
message.
eNBID
Indicates the eNodeB ID of the traced
message.
PLMN
Indicates the PLMN ID of the traced
message.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
134
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Parameter
Description
S1 Interface ID
Indicates the ID of the S1 interface over
which the traced message is reported. This
parameter is valid only when Trace
Interface Type is S1 Interface.
Message Report Module
Indicates the module that reports the traced
message.
Reserved
Indicates the message extension field.
UEID
Indicates the UE ID of the traced message.
Call ID
Indicates the call ID of the traced message.
CRNTI
Indicates the cell radio network temporary
identifier.
Chip ID
Indicates the chip ID of the reported
message.
Type
Indicates the report type of the reported
message.
Physical Cell ID
Indicates the physical cell ID of the reported
message.
Content
Indicates the content of the reported
message.
----End
6.6.5 M2 Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace control plane messages over the M2 interface. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display Information Elements
(IEs) contained in the messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of five message tracing tasks can be created simultaneously over an M2
interface. In addition, the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click M2 Interface Trace.
The M2 Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
135
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 3 Set related parameters in the M2 Interface Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-68.
Table 6-68 Parameters for message tracing over the M2 interface
Paramet
er
Description
Direction
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the M2 interface. This
parameter can be set to Bi-Directional, To MCE, or From MCE.
Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the M2 interface. You can
select one, multiple, or all message types. If Select All is selected, all messages
are traced. Otherwise, only the selected types of messages are traced.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-69 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-69 Results of message tracing over the M2 interface
Paramet
er
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Standard
Interface
Message
Type
Indicates the type of the standard interface message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the message direction.
Content
Indicates the message content.
----End
6.6.6 Se Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace control plane messages over the Se interface. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display Information Elements
(IEs) contained in the messages.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
136
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of five message tracing tasks can be created simultaneously over an Se interface.
In addition, the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click Se Interface Trace.
The Se Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Se Interface Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-70.
Table 6-70 Parameters for message tracing over the Se interface
Paramet
er
Description
Direction
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the Se interface. This
parameter can be set to Bi-Directional, To ECO, or From ECO.
Protocol
Type
Specifies the protocol type of messages to be traced over the Se interface. This
parameter can be set to SCTP.
Message
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the Se interface. You can
select one, multiple, or all message types. If Select All is selected, all messages
are traced. Otherwise, only the selected types of messages are traced.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
saved. Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-71 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-71 Results of message tracing over the Se interface
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Paramet
er
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
137
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Paramet
er
Description
Standard
Interface
Message
Type
Indicates the type of the standard interface message.
Trace
Direction
Indicates the message direction.
Content
Indicates the message content.
----End
6.6.7 EPCInside NAS Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace control plane messages over the EPCInside NAS
interface. Traced messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the
traced messages online or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display
Information Elements (IEs) contained in the messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one message tracing tasks can be created simultaneously over an
EPCInside NAS interface. In addition, the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
NAS signaling trace belongs to message trace over a Huawei-proprietary EPCInside
NAS interface.
This trace cannot be enabled during base station deployment by PnP.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click EPCInside NAS
Interface Trace.
The EPCInside NAS Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the EPCInside NAS Interface Trace dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 6-72
Table 6-72 Parameters for message tracing over the EPCInside NAS interface
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Param
eter
Description
Report
Type
This parameter can be set to Message Report.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
138
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Param
eter
Description
Trace
Directi
on
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the EPCInside NAS
interface. This parameter can be set to Bi-Directional, To MME, or From
MME.
Trace
Inclusi
on
Specifies the UE to be traced. This parameter can be set to All UE or Special
UE.
Trace
UE
numbe
r
Specifies the number of UEs to be traced.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Trace Inclusion is set to Special UE.
Local
Subscr
iber ID
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Trace Inclusion is set to Special UE.
Specifies the ID of the local subscriber to be traced.
Messa
ge
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the EPCInside NAS interface.
You can select one, multiple, or all message types. If Select All is selected, all
messages are traced. Otherwise, only the selected types of messages are traced.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save
File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically saved.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-73 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-73 Results of message tracing over the EPCInside NAS interface
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced
message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Interface Message Type
Indicates the type of the interface message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the message direction.
Call ID
Indicates the ID of the traced call.
Local Subscriber ID
Indicates the unique ID of a call initiated by
a UE served by the base station.
Content
Indicates the message content.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
139
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
----End
6.6.8 EX2 Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace control plane messages over the EX2 interface. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display Information Elements
(IEs) contained in the messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
A maximum of five message tracing tasks can be created simultaneously over an EX2
interface. In addition, the tasks must differ in parameter settings.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click EX2 Interface Trace.
The EX2 Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the EX2 Interface Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-74
Table 6-74 Parameters for message tracing over the EX2 interface
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Param
eter
Description
Directi
on
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the EX2 interface.
Trace
object
Specifies the eNodeB to be traced.
Peer
eNode
B ID
Specifies the peer eNodeB ID. After an eNodeB ID is specified, the messages
related to the eNodeB are traced.
Messa
ge
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the EX2 interface.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when Trace object is set to Specified eNodeB.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
140
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Param
eter
Description
Save
File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically saved.
Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-75 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-75 Results of message tracing over the EX2 interface
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced
message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Interface Message Type
Indicates the type of the interface message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the message direction.
eNodeB ID
Indicates the peer eNodeB ID.
Content
The version number traced over the EX2
interface is 10Q1, and the traced protocol
layer is EX2 AP. For details, see 3GPP TS
36.423.
----End
6.6.9 SO Interface Trace
This section describes how to trace control plane messages over the SO interface. Traced
messages can be automatically or manually saved. You can browse the traced messages online
or offline. In addition, the traced messages can be resolved to display Information Elements
(IEs) contained in the messages.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
A maximum of one SO message tracing task can be created at one time.
SO interface trace applies only to LampSite base stations (DBS3900).
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click the Trace tab.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
141
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
6 Managing Message Tracing
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Trace > LTE Services. Double-click SO Interface Trace.
The SO Interface Trace dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the SO Interface Trace dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 6-76
Table 6-76 Parameters for message tracing over the SO interface
Param
eter
Description
Report
Type
Specifies the report type of the message.
Trace
Directi
on
Specifies the direction of messages to be traced over the SO interface.
Messa
ge
Type
Specifies the types of messages to be traced over the SO interface.
Trace
Reason
Specifies the reason for message trace. This parameter is mandatory.
Save
File
If you select the Save File check box, tracing results will be automatically saved.
NOTE
Operation logs record the reason specified for message trace.
Click
to customize the folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A message browsing window is displayed. Table 6-77 describes the message tracing results.
Table 6-77 Results of message tracing over the SO interface
Parameter
Description
No.
Indicates the sequence of the traced
message that received by the LMT.
Time
Indicates the time of the traced message.
Interface Message Type
Indicates the type of the interface message.
Trace Direction
Indicates the message direction.
Content
Indicates the content of the reported
message.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
142
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Managing Performance Monitoring
About This Chapter
This chapter describes how to perform real-time performance monitoring. Real-time
performance monitoring allows you to track the base station performance in real time.
7.1 Overview of Real-time Performance Monitoring
This section describes the functions of real-time performance monitoring and the internal
process of real-time performance monitoring.
7.2 General Operations Related to Real-time Performance Monitoring
This section describes how to browse, edit, and save monitoring results.
7.3 Common Monitoring Tasks
This section describes the common monitoring tasks.
7.4 GSM-Specific Monitoring Tasks
This section describes GSM-specific monitoring tasks.
7.5 UMTS-specific Monitoring Tasks
This section describes UMTS-specific monitoring tasks.
7.6 LTE-specific Monitoring Tasks
This section describes LTE-specific monitoring tasks.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
143
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.1 Overview of Real-time Performance Monitoring
This section describes the functions of real-time performance monitoring and the internal
process of real-time performance monitoring.
Functions of Common Monitoring
Common monitoring tasks are as follows:
l
Transport Port Traffic Monitoring
Transport Link Traffic Monitoring
IP Performance Monitoring
IPsec Performance Monitoring
Local Pass-By Traffic Monitoring
IP Clock Data Collection Monitoring
Clock Quality Test Monitor
CPU/DSP Usage Monitoring
Board Temperature Monitoring
RRU/RFU Output Power Monitoring
Rx Frequency Scanning
DTF Test
FFT Frequency Scanning
Board RTWP
Antenna Radiation Pattern
Transport OAM Monitoring
Transport Auto Setup User Plane Monitoring
DTP Test
NOTE
To use the monitoring function, you must install the Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in.
The monitoring window is fixed in size and does not change with the web page.
A monitoring task is a monitoring instance, which consists of monitoring items, monitoring
objects, and monitoring parameters.
Real-time performance monitoring functions display monitoring results in lists and charts,
which enables you to monitor the running status of services and equipment.
You can analyze exceptions based on the monitoring results to maintain devices and rectify
faults.
GSM-specific monitoring tasks are as follows:
l
Offline Spectrum Scan Monitoring
Online Spectrum Scan Monitoring
Codec Mode Test
UMTS-specific monitoring tasks are as follows:
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
144
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
HSPA Monitoring
Sector Equipment Group RTWP
Cell Throughput Statistic
Cell Service Resource Query
Cell RTWP
Frequency Scan Monitoring
Repeater Interfere Frequency Scan Monitoring
LTE-specific monitoring tasks are as follows:
l
Sector Performance Detect
Cell Performance Monitoring
Internal Process of Real-time Performance Monitoring
The internal process of CPU usage monitoring is different from that of other real-time
performance monitoring functions.
Internal process of CPU usage monitoring
1.
After a CPU usage monitoring task is created on the LMT, the LMT sends a binary CPU
usage query command to the maintenance module of the base station every other
monitoring period.
2.
The maintenance module of the base station sends the command to the maintenance
module of a specified board.
3.
The board collects and reports related data to the maintenance module of the base
station.
4.
The maintenance module of the base station forwards the data to the LMT.
Internal process of other real-time performance monitoring functions
l
Creating a monitoring task on the LMT
a.
After you create a monitoring task on the LMT, the LMT sends a binary command
to the base station to create the task.
b.
The base station allocates an ID to the task and forwards the command to the
monitoring management module of a specified board.
c.
After receiving the command, the monitoring management module informs the
service processing module of the command. Then, the service processing module
starts performance monitoring.
Reporting monitoring results to the LMT
a.
After performance monitoring is started, the service processing module reports
monitoring results to the LMT.
b.
The LMT resolves the monitoring results and displays them in the window.
7.2 General Operations Related to Real-time Performance
Monitoring
This section describes how to browse, edit, and save monitoring results.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
145
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.2.1 Browsing Performance Monitoring Results Online
This section describes how to browse monitoring results in the real-time monitoring window
after a real-time performance monitoring task is started.
Prerequisites
l
The real-time performance monitoring task has been started.
Monitoring results are reported.
Procedure
Step 1 In the real-time monitoring window, click the List tab. Right-click on the List tab page and
choose Auto Scroll from the shortcut menu.
Step 2 Click the Chart tab. Right-click on the Chart tab page and choose one of the following items
from the shortcut menu:
l
Auto Scroll
Show Grid
Switch Display Mode
NOTE
When the number of real-time monitoring tasks is greater than 60, right-click on the Chart tab
page and choose Switch Display Mode from the shortcut menu:
If the bar chart has been displayed, you can switch it to the sequence diagram.
If the sequence diagram has been displayed, you cannot switch it to the bar chart.
Auto Adjust
Step 3 Right-click in the task information pane at the bottom of the real-time monitoring window.
Then, choose List Detailed Task Info from the shortcut menu.
----End
7.2.2 Setting the Chart Display Mode
This section describes how to customize the appearance of a real-time monitoring window
after a monitoring task is created and started. At the bottom of the Chart tab page in the
window, you can set the display mode, such as the line color and line type.
Prerequisites
l
The real-time performance monitoring task has been started.
Monitoring results are reported.
Procedure
Step 1 Click Line Color or Line Type of a monitoring task at the bottom of the box.
Step 2 Select a value from the corresponding drop-down list.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
146
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
NOTE
l The attributes of the chart display mode take effect only for the real-time monitoring window of the
existing monitoring task.
l During real-time performance monitoring, if data is displayed on the List tab page but no chart is
displayed on the Chart tab page, you can change the line color and line type.
l If the data reported for a monitoring task has two more types of units, the units are not displayed on
the Y axis. In this case, the units are displayed on the monitoring task attribute list at the bottom of
the real-time monitoring window. On the LMT, you can also manually set the Y axis display range
so that a figure for data items of different units can be displayed on the GUI. The procedure is
detailed as follows: Right-click in the chart display window, clear Auto Adjust. Then right-click the
chart display window, and select Set Y Axis Display Range > Both Axis. The Set Y Axis Display
Range window is displayed. Enter the maximum and minimum displayed values for the Y axis, and
click OK.
l If a certain task at the bottom of the box cannot be selected and its attributes cannot be edited, this
task is displayed only on the List tab page rather than the Chart tab page or is saved in a file and
can be viewed in offline mode.
----End
7.2.3 Saving Performance Monitoring Results
This section describes how to save the monitoring results as files for future reference.
Context
The files are automatically saved in .csv or .mmf format.
Procedure
Step 1 When creating a monitoring task, select the Save File check box in the dialog box.
Step 2 Click ....
The Save dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the save folder, file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Save.
The monitoring results are saved in the specified folder.
----End
7.2.4 Browsing Performance Monitoring Results Offline
This section describes how to browse the monitoring results offline to locate faults and obtain
historical information about the system running status.
Prerequisites
You have installed the Huawei maintenance and commissioning tool.
Monitoring results are saved as files in .csv or .mmf format.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
147
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Procedure
l
To save monitoring results as files in .csv format, perform the following steps:
a.
Open the folder containing the monitoring result files to obtain the real-time
performance monitoring file in .csv format.
b.
Double-click the file to open it and browse the file to obtain the required
information.
To save monitoring results as files in .mmf format, perform the following steps:
a.
Choose Start > All Programs > HUAWEI Local Maintenance Terminal >
Traffic Recording Review Tool.
The Open dialog box is displayed.
b.
Select a real-time performance monitoring file in .mmf format, and click Open.
The Traffic Recording Review Tool dialog box is displayed.
c.
View monitoring results.
----End
7.3 Common Monitoring Tasks
This section describes the common monitoring tasks.
7.3.1 Transport Port Traffic Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the transport port traffic to obtain information about the
port bandwidth usage. The transmission/reception traffic rate and amount are monitored. The
ports to be monitored include MP, PPP, ETH, IMAGRP, UNI, FRAATM, ETHTRUNK,
IMALINK, BACKETH, and TUNNEL ports.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
A maximum of eight monitoring tasks of the same type can be started simultaneously on
a base station.
If Protocol Type is set to IP, only one monitoring task can be started on a port.
If Protocol Type is set to ATM, only one monitoring task can be started on a port with
the same unit. ATM related services are specific to UMTS.
When Protocol Type is set to IP and Port Type is set to PHYSICAL_PORT, the
transmission and reception rates at different layer are calculated for IP ports depending
on the setting of Physical Port Type.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
If Physical Port Type is set to TUNNEL, transmission and reception rates at the
network layer are calculated for IP ports.
If Physical Port Type is set to other values, transmission and reception rates at the
link layer are calculated for IP ports.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
148
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Transport
Port Traffic Monitoring.
The Transport Port Traffic Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Transport Port Traffic Monitoring dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-1.
Table 7-1 Parameters for transport port traffic monitoring
Parameter
Description
Protocol
Type
Specifies the protocol type. This parameter can be set to IP or ATM.
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the board.
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of the board.
Slot No.
Specifies the slot number of the board.
Subboard
Type
When Slot No. is set to 6 or 7, Subboard Type can be set to
BASE_BOARD, BACK_BOARD or ETH_COVERBOARD.
When Slot No. is set to other value, Subboard Type can be set to :
l E1_COVERBOARD or ETH_COVERBOARD if Protocol Type is
set to IP.
l E1_COVERBOARD or UNCHANNELLED_COVERBOARD if
Protocol Type is set to ATM.
Port Type
l PHYSICAL_PORT
l RSCGRP
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
149
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Physical
Port Type
l If Protocol Type is set to IP, this parameter can be set to:
EthPort, EthTrunk, or BACKETH when Subboard Type is
ETH_COVERBOARD.
PPP, MPGroup, or BACKETH when Subboard Type is
E1_COVERBOARD.
PPP, MPGroup, EthPort, EthTrunk, or BACKETH when
Subboard Type is BASE_BOARD.
PPP, or TUNNEL when Subboard Type is BACK_BOARD.
l If Protocol Type is set to ATM, this parameter can be set to:
IMA, UNI, FRAATM, or IMALINK when Subboard Type is
E1_COVERBOARD.
STM-1 when Subboard Type is
UNCHANNELLED_COVERBOARD .
IMA, UNI, FRAATM, or IMALINK when Subboard Type is
BASE_BOARD.
UNI, FRAATM, or IMALINK when Subboard Type is
BACK_BOARD.
Port No.
l IMA: 0 to 3
l UNI: 0 to 7
l FRAATM: 0 to 7
l IMALINK: 0 to 7
l PPP: 0 to 15
l MPGroup: 0 to 3
l STM-1: 0
l EthPort: 0 to 5
l EthTrunk: 0 to 2
l TUNNEL: 0 to 14
l BACKETH: 0
Unit
l If Protocol Type is set to ATM, Unit can be set to cps or bps.
l If Protocol Type is set to IP, Unit cannot be set.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Report
Period
Specifies the interval at which the monitoring results are reported. This
parameter is set to 1s and cannot be changed.
Include IP
Discard
Packet's
Information
This parameter is valid only when Protocol Type is set to IP.
When this parameter is selected, the RX and the TX Packet Discard Rate on
the IP layer is exported in the monitoring result. The unit of Packet Discard
Rate is .
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
150
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Include
Link
Discard
Packet's
Information
This parameter is valid only when Protocol Type is set to IP.
Monitor
Type
This parameter can be set to Flow Stat or Load Stat.This parameter is valid
only when Port Type is set to RSCGRP.
Rate Config
Mode
This parameter can be set to Single Rate or Dual Rate. This parameter is
valid only when Port Type is set to RSCGRP, and Monitor Type is set to
Load Stat.
Resource
Group No.
The number of resource group. Value range: 0 to 15, or DEFAULTPORT.
This parameter is valid only when Port Type is set to RSCGRP.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
When this parameter is selected, the RX and the TX Packet Discard Rate on
the link layer is exported in the monitoring result. The unit of Packet
Discard Rate is .
automatically saved. Click
type.
to customize the folder, file name, and file
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the transport port
flux stat monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
NOTE
In the monitoring results, the IP-layer reception packet loss rate and transmission packet loss rate indicate the
reception and transmission packet loss rates over the Versatile IP and Security Platform (VISP) protocol stack
on the internal modules of the base station. The packets are discarded due to invalid IP headers, packet
reassembly failures, or processing failures for selected IP options.
----End
7.3.2 Transport Link Traffic Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the transport link traffic. You can monitor the traffic of
each data flow from or to the base station to obtain information about the bandwidth usage by
each service.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
A maximum of eight transport link traffic monitoring tasks can be started simultaneously
on a base station.
If Protocol Type is set to IP, only one monitoring task can be started on a link.
If Protocol Type is set to ATM, only one monitoring task can be started on a link with
the same unit. ATM related services are specific to UMTS.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
151
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
In an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) link traffic monitoring task, a maximum of six
PVCs can be started for the monitoring. This task is specific to UMTS.
An IP link traffic monitoring task can cover one maintenance channel (TCP link), two
SCTP links, three IP paths, and three GPM links.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Transport
Link Traffic Monitoring.
The Transport Link Traffic Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Transport Link Traffic Monitoring dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-2.
Table 7-2 Parameters for transport link traffic monitoring
Parameter
Description
Protocol Type
Specifies the protocol type. This parameter can be set to IP or ATM.
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the board.
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of the board.
Slot No.
Specifies the slot number of the board.
Subboard Type
This parameter is valid when Protocol Type is set to ATM.
When Slot No. is set to 6, or 7, this parameter can be set to
BASE_BOARD or BACK_BOARD.
When Slot No. is set to other value, this parameter can be set to
UNCHANNELLED_COVERBOARD or E1_COVERBOARD.
Physical Port
Type
This parameter is valid when Protocol Type is set to ATM. It can be set
to:
STM-1 if Subboard Type is set to
UNCHANNELLED_COVERBOARD.
IMAGRP, UNI, or FRAATM if Subboard Type is set to
E1_COVERBOARD.
IMAGRP, UNI or FRAATM if Subboard Type is set to
BASE_BOARD.
UNI or FRAATM if Subboard Type is set to BACK_BOARD.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
152
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Port No.
This parameter is valid when Protocol Type is set to ATM.
l When Subboard Type is set to
UNCHANNELLED_COVERBOARD, this parameter can be set to:
0 if Physical Port Type is set to STM-1.
l When Subboard Type is set to E1_COVERBOARD, this parameter
can be set to:
0 to 3 if Physical Port Type is set to IMAGRP.
0 to 7 if Physical Port Type is set to UNI.
0 to 7 if Physical Port Type is set to FRAATM.
l When Subboard Type is set to BASE_BOARD, this parameter can
be set to:
0 to 1 if Physical Port Type is set to IMAGRP.
0 to 3 if Physical Port Type is set to UNI.
0 to 3 if Physical Port Type is set to FRAATM.
l When Subboard Type is set to BACK_BOARD, this parameter can
be set to:
0 to 3 if Physical Port Type is set to UNI.
0 to 3 if Physical Port Type is set to FRAATM.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Unit
If Protocol Type is set to ATM, Unit can be set to cps or bps.
Report Period
Specifies the interval at which the monitoring results are reported. This
parameter is set to 1s and cannot be changed.
ATM
Parameter
You can select a maximum of six PVCs.
OM(TCP)
If Protocol Type is set to IP, OM(TCP) can be set.
Local IP
If Protocol Type is set to IP, this parameter specifies the local IP
address.
Remote IP
If Protocol Type is set to IP, this parameter specifies the peer IP address.
DSCP
If Protocol Type is set to IP, this parameter specifies the differentiated
services code point. The value range is from 0 to 63,or 255.
Include IPPM
Statistic
If Protocol Type is set to IP, only one IPPM statistics task is supported.
IPPath
If Protocol Type is set to IP, a maximum of three IP paths are supported.
SCTP
If Protocol Type is set to IP, a maximum of two SCTP links are
supported.
GPM
If Protocol Type is set to IP, a maximum of three GPM links are
supported.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
153
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the transport link
flux stat monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.3 IP Performance Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the IP link performance.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Context
The IP layer traffic amount and quality of each board are monitored.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click IP
Performance Monitoring.
The IP Performance Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IP Performance Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-3.
Table 7-3 Parameters for IP performance monitoring
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for IP online
performance monitoring is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for IP online
performance monitoring is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for IP online
performance monitoring is located.
VRF
Specifies the ID of the virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance for
IP online performance monitoring is located.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
154
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the IP performance
monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.4 IPsec Performance Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the IPsec traffic over the transmission security output
port on the base station.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
The IPsec tunnel has been configured on the transmission output port of the base station.
Context
The transmit rate, receive rate, and packet loss rate during reception in an IPsec tunnel are
calculated on each board.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring, and double-click IPsec
Performance Monitoring.
The IPsec Performance Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IPsec Performance Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-4.
Table 7-4 Parameters for IPsec Performance Monitoring
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for IPsec
performance monitoring is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for IPsec
performance monitoring is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for IPsec performance
monitoring is located.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
155
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the IPsec
performance monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.5 Local Pass-By Traffic Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the local traffic volume of a base station and the
volume of traffic forwarded by the base station. The monitoring result helps determine the
traffic volume of the base station and the proportion of forwarded traffic so that the proportion
is appropriate.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Local traffic and passby traffic constitute the total traffic of a base station.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Local Pass-By
Traffic Monitoring.
The Local Pass-By Traffic Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Local Pass-By Traffic Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-5.
Table 7-5 Parameters for local and pass-by traffic monitoring
Paramete
r
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
type.
to customize the folder, file name, and file
Step 4 Click Submit.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
156
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view traffic monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.6 IP Clock Data Collection Monitoring
This section describes how to collect IP clock data to obtain information about IP packet jitter.
The data to be collected includes frequency discrimination data and phase discrimination data.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click IP Clock Data
Collection Monitoring.
The IP Clock Data Collection Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IP Clock Data Collection Monitoring dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-6.
Table 7-6 Parameters for IP clock data collection
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for IP clock data
collection is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for IP clock data
collection is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for IP clock data
collection is located.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
type.
to customize the folder, file name, and file
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.7 Clock Quality Test Monitoring
This task describes how to monitor the clock quality. The reference clock quality is crucial for
the system operation. If the clock module generates an alarm, the alarm must be promptly
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
157
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
handled. You can test the reference clock first. A clock test does not affect the system or
services.
Prerequisites
l
The reference clock for the base station has been set.
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
If IP clock+Synchronous Ethernet or IP clock is used as the clock source, clock quality
monitoring results with Test Type set to Frequency Discrimination cannot be provided
on the Chart tab page.
The period for reporting phase discrimination is 1s.
In normal situations, the value of the phase discrimination falls within the range from -10
to +10. In abnormal situations where excessive frequency deviation occurs, the value of
phase discrimination falls within the range from -128 to +127.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Clock Quality
Test Monitoring.
The Clock Quality Test Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Clock Quality Test Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-7.
Table 7-7 Parameters for clock quality monitoring
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Indicates the cabinet number of the board.
Subrack No.
Indicates the subrack number of the board.
Slot No.
Indicates the slot number of the board.
Test Type
Including:
l Frequency Discrimination
l Phase Discrimination
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
type.
to customize the folder, file name, and file
Step 4 Click Submit.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
158
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.8 CPU/DSP Usage Monitoring
This task describes how to monitor the CPU/DSP usage of the base station to obtain
information about system resource usage.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click CPU/DSP
Usage Monitoring.
The CPU/DSP Usage Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the CPU/DSP Usage Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-8.
Table 7-8 Parameters for CPU/DSP usage monitoring
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for CPU/DSP usage
monitoring is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for CPU/DSP usage
monitoring is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for CPU/DSP usage
monitoring is located.
Monitor
Period (s)
Specifies the interval at which the LMT delivers the query command.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the CPU/DSP usage
monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
159
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.3.9 Board Temperature Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the temperatures of a board and the power amplifier in
the board.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Context
After a board temperature monitoring task is started, the system reports the detected
temperatures of the WMPT, UMPT, LMPT, UTRP, WRFU, RRU, and power amplifiers in the
WMPT, UMPT, LMPT, UTRP, WRFU, and RRU at specified intervals. When the working
temperature of a power amplifier exceeds the normal range, an alarm will be reported.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Board
Temperature Monitoring.
The Board Temperature Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Board Temperature Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-9.
The Board Temperature Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Table 7-9 Parameters for board temperature monitoring
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for temperature
monitoring is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for temperature
monitoring is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for temperature
monitoring is located.
Monitor
Period (ms)
This parameter can be set to 1000, 2000, or 3000.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
160
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the board
temperature monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.10 RRU/RFU Output Power Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the output power, including the channel output power
and output power of each carrier.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
After an output power monitoring task is started, the system reports the detected channel
output power and output power of each carrier at specified intervals.
Context
NOTE
The output power of a base station is related to the configuration and services.
When the RF module reports an invalid value for the output power, N/A is displayed on the list
tab page and the figure table page is not displayed.
Table 7-10 lists the pilot power and typical power of the RRU, WRFU, and pRRU.
Table 7-10 Power configuration table
Board
Pilot Power (dBm)
Typical Power (dBm)
RRU
33
43
WRFU
33
43
pRRU
1 carrier
13
1 carrier
23
2 carriers
10
2 carriers
20
When the base station is not carrying services, the difference between the output power
and pilot power of a WRFU, RRU, or pRRU is 3 dBm. If the output power is much
lower than the pilot power, the output power is abnormal.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click RRU/RFU
Output Power Monitoring.
The RRU/RFU Output Power Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the RRU/RFU Output Power Monitoring dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-11.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
161
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Table 7-11 Parameters for RRU/RFU output power monitoring
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the WRFU or RRU is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the WRFU or RRU is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the WRFU or RRU is located.
Monitor
Period (ms)
This parameter can be set to 1000, 2000, or 3000.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the RRU/RFU
output power monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.11 Rx Frequency Scanning
This section describes how to perform RX frequency scan. Uplink frequency scan helps to
check the electromagnetic environment around a base station and detects internal interference
in the base station. The RRU or WRFU scans its frequency or frequencies, calculates the
received signal strength, and reports the calculation result. You are advised to perform the
scan before configuring the cell.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Before you start an uplink frequency scan task, block the corresponding board.
This task is specific only to UMTS and LTE.
The following are reference results of uplink frequency scan:
Context
If the antenna is disconnected and the scan result shows a sharp increase reaching a
value greater than -108 dBm, there is internal interference in the base station.
There is external interference to the base station if the scan result shows a sharp
increase greater than -105 dBm under the following conditions: (1) The antenna is
connected and the tower-mounted amplifier (TMA) is turned on. (2) The radio
channel attenuation has been properly set to compensate for TMA gains and feeder
loss.
The increase varies with interference characteristics:
n
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
If the increase appears in the shape of a triangle or trapezoid, the monophony
interference occurs and the peak indicates the center frequency of the
interference.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
162
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
n
If the increase appears in the shape of a rectangle or overlaps with a rectangle,
wideband interference occurs and the center of the rectangle indicates the
interfering frequency.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Rx Frequency
Scanning.
The Rx Frequency Scanning dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the RX Frequency Scanning dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-12.
Table 7-12 Parameters for RX frequency Scanning
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the WRFU or RRU.
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of the WRFU or RRU.
Slot No.
Specifies the slot number of the WRFU or RRU.
Start RF
Frequency(20
0kHz)
Specifies the start frequency.
End RF
Frequency(20
0kHz)
Specifies the end frequency.
Scanning
Frequency
Inteval(200kH
z)
Value range: 1 to 25.
Scanning
Time
Inteval(0.1s)
Value range: 2 to 600.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the scan results on
the Chart or List tab page.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
163
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.3.12 DTF Test
This section describes how to monitor the distance to fault (DTF).
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Context
l
This task is used to locate the connection faults between the RRU/RFU and the antenna
in the following scenarios:
A voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) alarm is generated. In this situation, you can
perform this task on a specified transmit channel of the RRU or RFU that reported
the alarm on the local or remote maintenance terminal. This task cannot be created
on the U2000.
In routine maintenance, a VSWR exception is detected on the local or remote
maintenance terminal. In this situation, you can perform this task to further locate
the fault. The U2000 does not support this task.
The test frequency used by the base station varies as follows:
If you specify the test frequency, the base station uses the specified test frequency.
If you do not specify the test frequency, the base station chooses a test frequency
that is supported by its RF boards from the predefined authorized downlink
frequency band (which can be added using the ADD AUTHDLFREQRANGE
command).
If no test frequency or authorized downlink frequency band is specified, the base
station chooses a test frequency only based on the capability of its RF boards. In
this case, UEs may transmit power outside the authorized downlink frequency band.
The DTF test monitoring-enabled RF module can be the RRU3926, RRU3936,
RRU3962, RRU3952, RRU3952m, RRU3959w, RRU3826, RRU3824, MRFU V2a,
RRU3838, RRU3832, RRU3269,RRU3261,RRU3249, RRU3262, LRFUe, or RRU3839.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree of the Monitor window, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring.
Double-click DTF Test.
The DTF Test dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the DTF Test dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 7-13.
Table 7-13 Parameters for a DTF test
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the RRU or RFU.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
164
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of the RRU or RFU.
Slot No.
Specifies the slot number of the RRU or RFU.
TX Channel No.
Specifies the transmit channel number of the RRU or RFU.
Cable Type
Specifies the feeder model. This parameter can be set to 1/4 Cable,
3/8 Cable, 1/2 Cable, 5/8 Cable, 7/8 Cable, 7/8 Low-loss Cable,
11/4 Cable, 15/8 Cable, or Ideal Transmission Line.
Display Range Of
Feeder Test
Results(m)
Specifies the feeder length (measuring from the cabinet top).
Start
Frequency(0.1MH
Z)
Specifies the low frequency of the external filter.
Stop
Frequency(0.1MH
Z)
Specifies the high frequency of the external filter.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
NOTE
When the base station uses the unit of metric system, this field is valid.
NOTE
If no external filter is installed, use the default value of this parameter. The
default value is 0.
NOTE
If no external filter is installed, use the default value of this parameter. The
default value is 65535.
automatically saved. Click
and file type.
to customize the folder, file name,
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.13 FFT Frequency Scan
This section describes how to check the spectrum status. You can check interference in the
frequency and time domains by analyzing the sampled spectrum and power distribution.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
GSM does not support FFT frequency scan monitoring.
Starting an offline FFT frequency scan on an RF unit shared by all modes of a
multimode base station interrupts services of all modes.
An offline FFT frequency scan automatically deactivates cells or carriers.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
165
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
The RRU3801C does not support this function.
The RRU3804, RRU3801E, RRU3806 and WRFU support broadband offline frequency
scanning. They do not support high-resolution online frequency scanning or wideband
online frequency scanning.
High-resolution online frequency scanning scans cell frequencies in current use for
interference, including a small number of frequency sidebands. Wideband online
frequency scanning scans a continuous frequency spectrum within a certain range,
including all frequencies in current use and the frequency spectrum between the
frequencies. Wideband offline frequency scanning scans offline an entire frequency
spectrum that an RF can work on.
Before performing FFT frequency scan on an RF module, query the frequency band
range supported by this RF module in a specified mode by following instructions
provided in 3900 Series Base Station Technical Description. Then, run the DSP
RXBRANCH command to query the band number mapping the supported frequency
band range and perform FFT frequency scan based on the band number.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring, and double-click FFT
Frequency Scan.
The FFT Frequency Scan dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the FFT Frequency Scan dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 7-14.
Table 7-14 Parameters for FFT frequency scan
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board for FFT frequency
scan is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board for FFT frequency
scan is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board for FFT frequency
scan is located.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
166
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Scan Mode
Specifies the scan mode in which signals on a carrier or receive (RX)
channel are monitored for interference identification. This parameter
can be set to High-Resolution Online Frequency, Broadband Online
Frequency, or Broadband Offline Frequency.
l High-resolution Online Frequency: An online carrier-level scan.
Signals in specified channels within a specified frequency band are
scanned for all established cells on a carrier of a specified radio
access technology (RAT).
l Broadband Online Frequency: An online channel-level scan.
Signals in specified channels within a specified frequency band are
scanned for all established cells.
l Broadband Offline Frequency: An offline channel-level scan.
Signals within the bandwidth of the duplexer in specified channels
within a specified frequency band are scanned.
RBW(kHz)
Specifies the time frequency to perform the FFT frequency scan.
l High-Resolution Online Frequency:
Value range: 15 to 200. Default value: 100. As stipulated by
protocols, the minimum accuracy is 100 kHz. You are advised to
retain the default value 100 kHz for this parameter.
l Broadband Online Frequency and Broadband Offline Frequency:
Value range: 100 to 5000. Default value: 200.
Index of RX
Channel 1
Specifies RX channel 1 where signals are scanned.
Index of RX
Channel 2
Specifies RX channel 2 where signals are scanned.
Mode
You can select WCDMA, LTE-TDD, or LTE-FDD.
NOTE
When it's a UMTS single-mode base station, this field is unavailable on the
WebUI. This parameter is set to WCDMA by default.
Band No.
Number of the supported band in a Mode.
NOTE
Run the DSP RXBRANCH command to query the band number. For example, if
Band 1 Minimum frequency(0.1MHz) = 8900 is displayed in the command
output after you run the DSP RXBRANCH command with RX Channel No.
specified, the band number is 1.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the FFT frequency
scanning results on the Chart tab page.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
167
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.3.14 Board RTWP
This section describes how to measure the received total wideband power (RTWP) of a
UTRAN uplink channel. Based on the RTWP, the uplink radio channel can be adjusted. This
task does not affect services.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Context
This function is available only to the UMTS and supports the RF modules only in UMTS
mode.
The following are reference results of board-level RTWP monitoring:
l
If the antenna is disconnected or the board is not loaded, the RTWP is about -108 dBm.
If the antenna is connected and the tower-mounted amplifier (TMA) is turned on, or the
board is loaded, the RTWP is about -105 dBm.
The RTWP value varies depending on the pRRU deployment scenarios.
By default, the RTWP is -102 dBm.
If the sector equipment groups in a cell have different numbers of pRRUs, the
RTWP will increase by up to 12 dBm.
Compared with the RTWP when no service is running, the RTWP increases about 6 dB when
services are running normally and the uplink load reaches 75%.
NOTE
l A normal curve is displayed if the reported board-level RTWP is valid. The vertical axis shows the
measurement value and the unit is 0.1 dBm.
l An abnormal curve is displayed if the reported board-level RTWP is invalid. The RTWP measurement
results of the receive channels An and Bn are at the level of -1200, that is, -120 dBm. The problem may
be that the RF module is disconnected or cannot be detected, or the RF channels are faulty. You need to
locate and rectify the problem.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Board
RTWP.
The Board RTWP dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Board RTWP dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 7-15.
Table 7-15 Parameters for board-level RTWP monitoring
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the RRU or RFU.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
168
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of the RRU or RFU.
Slot No.
Specifies the slot number of the RRU or RFU.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.15 Antenna Radiation Pattern
This section describes how to view the horizontal and vertical directed graph of the active
antenna system (AAS) in polar coordinates system based on the data received from the RU
module.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Context
The active antenna system (AAS) sends the LMT 360 values about radiation intensity from
both horizontal and vertical directions. The LMT generates a polar diagram in both horizontal
and vertical directions based on the values.
NOTE
Only the AAS supports this function. The remote radio unit (RRU) and radio frequency unit (RFU) do not
support this function.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring, and double-click Antenna
Radiation Pattern.
The Antenna Radiation Pattern dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Antenna Radiation Pattern dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-16.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
169
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Table 7-16 Parameters for antenna radiation pattern querying
Parameter
Description
AARU
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the active antenna radio unit.
AARU
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of active antenna radio unit.
AARU Slot
No.
Specifies the slot number of the active antenna radio unit.
Frequency
Specifies the frequency of a carrier, which is measured in the unit of 100
kHz. Uplink or downlink data transmitted on an RU module can be
determined based on frequencies.
Antenna Port
No.
Specifies the port No. of the virtual antenna.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the AAS monitoring
results on the Chart tab page.
----End
7.3.16 Transport OAM Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the transport network quality based on the Y1731-LM
and Y1731-DM sessions.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
The Y1731-LM and Y1731-DM sessions have been configured.
The packet loss rate, delay, and jitter transport network are calculated based on the
Y1731-LM and Y1731-DM sessions.
The ETHDM and ETHLM functions have been enabled and are running correctly. If the
NodeB experiences a power-off reset or an upgrade, the two functions will be
unavailable. The two functions need to be reactivated.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
170
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring, and double-click Transport
OAM Monitoring.
The Transport OAM Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Transport OAM Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-17.
Table 7-17 Parameters for Transport OAM Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Test Type
You can select Y1731-LM or Y1731-DM.
NOTE
l If this parameter is set to Y1731-LM, packet loss rate of Y.1731 is monitored.
l If this parameter is set to Y1731-DM, delay and jitter of Y.1731 is monitored.
Session ID
Specifies the ID of the Y1731-LM and Y1731-DM sessions.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the OAM monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.17 Transport Auto Setup User Plane Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the performance of user plane in transport interface
self-setup scenarios.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
IPPM Flag can be set to User Plane Link or User Plane Link + IPPM. If IPPM Flag
is set to User Plane Link + IPPM, the values of the IP PM parameters, including
Average RTT Delay, Transmit Time Jitter, Receive Packet Discard Rate, Receive
Time Jitter, Transmit lost packet, and Transmit packet, are reported.
If quadbit-based IP PM is used and IPPM Flag is set to User Plane Link + IPPM,
DSCP must be specified.
If IPPM Flag is set to User Plane Link + IPPM and the DSCP value is specified, the
values of the parameters Recieve Rate (pps), Transmit Rate (pps), Recieve Rate (bps)
and Transmit Rate (bps) are not reported. The parameters Recieve Rate (pps),
Transmit Rate (pps), Recieve Rate (bps) and Transmit Rate (bps) are set to 0 by
default.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
171
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring. Double-click Transport
Auto Setup User Plane Monitoring.
The Transport Auto Setup User Plane Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Transport Auto Setup User Plane Monitoring dialog box. For
details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-18.
Table 7-18 Parameters for transport auto setup user plane monitoring
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Indicates the cabinet number of the board for transport interface selfsetup.
Subrack No.
Indicates the subrack number of the board for transport interface selfsetup.
Slot No.
Indicates the slot number of the board for transport interface self-setup.
IPPM Flag
Indicates whether IP performance monitoring (PM) results need to be
reported. This parameter can be set to User Plane Link or User Plane
Link + IPPM.
VRF
Indicates the ID of the virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance for
transport interface self-setup.
Source IP
Indicates the local IP address for transport interface self-setup.
Destination IP
Indicates the destination IP address for transport interface self-setup.
DSCP
Indicates the DSCP. This parameter is valid only when IPPM Flag is set
to User Plane Link + IPPM.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the transport auto
setup user plane monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.3.18 DTP Test
This section describes how to check the distance to PIM (DPIM) test results. The DTP test is
used to locate a passive intermodulation (PIM) fault of the antenna system.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
172
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
The DTP test is applicable only to the RRU3952 working on the 1800 MHz frequency
band.
When the antenna system experiences a PIM fault, users can locate the fault point based
on the DTP test results, which eliminates the need of repeated tower climbing for fault
point location and therefore reduces the maintenance cost.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree of the Monitor window, choose Monitor > Common Monitoring.
Double-click DTP Test.
The DTP Test dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the DTF Test dialog box. For details about parameter descriptions,
see Table 7-19.
Table 7-19 Parameters for a DTP test
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the RRU or RFU.
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of the RRU or RFU.
Slot No.
Specifies the slot number of the RRU or RFU.
Tx No.
Specifies the transmitter number of the RRU or RFU.
Cable Type
Specifies the feeder model. This parameter can be set to 1/4 Cable, 3/8
Cable, 1/2 Cable, 5/8 Cable, 7/8 Cable, 7/8 Low-loss Cable, 11/4
Cable, 15/8 Cable, or Ideal Transmission Line.
Cable Length
Specifies the feeder length (measuring from the cabinet top).
Start
Frequency
Specifies the start frequency for a DTP test. The default value is 0.
Stop
Frequency
Specifies the stop frequency for a DTP test. The default value is 65535.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
173
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.4 GSM-Specific Monitoring Tasks
This section describes GSM-specific monitoring tasks.
7.4.1 Offline Spectrum Scan Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the spectrum scan of a specific band in a carrier in the
cell. Based on received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values reported to the LMT PC, a
frequency spectrum graph is generated. You can log in to the local maintenance terminal
(LMT) and remotely obtain the frequency spectrum graph to preliminarily troubleshoot the
interference during interference localization.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
This test cannot be performed together with any of the following tests, including the
online spectrum scan, CDMA interference network test, online and offline passive
intermodulation test, and TRX RF self-loopback test. You must stop these tests before
monitoring offline spectrum scan.
Only one offline spectrum scan test can be performed at a time in a cell, and a maximum
of eight test tasks can be started at the same time for one base station.
The offline spectrum scan consists of the channel-level spectrum scan and carrier-level
spectrum scan. When the spectrum of a channel is scanned, channels of all carriers in the
same cell with the same timeslot number as that of the channel are blocked, and the
carrier carrying the channel is also blocked. When the spectrum of the carrier is scanned,
all carriers in the same cell except the active BCCH carrier are blocked.
The maximum spectrum can be scanned each time does not exceed 25 MHz.
In a carrier-level spectrum scan test, the carrier to be scanned must be a non-activeBCCH carrier. In a channel-level test, the test channel No. must be different from the
BCCH No., CCCH No., or CBCH No. More than one SDCCH must be involved in the
test.
The carrier to be scanned must be a non-active-BCCH carrier.
In a channel-level test, the test channel No. must be different from the BCCH No.,
CCCH No., or CBCH No. More than one SDCCH must be involved in the test.
The frequency band to be scanned cannot exceed the frequency band supported by the
carrier.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
174
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > GSM Monitoring. Double-click Offline Spectrum
Scan Monitoring.
The Offline Spectrum Scan Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Offline Spectrum Scan Monitoring dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-20.
Table 7-20 Parameters for offline spectrum scan monitoring
Parameter
Description
Test Type
Channel Type Test or Trx Type Test can be selected.
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely specifies a
local cell in a base station.
TRX ID
Specifies the index of the carrier to be tested. This parameter uniquely
specifies a carrier under a BSC.
Channel No.
Specifies the number of the channel to be tested.
Duration(Minut
e)
Specifies the duration of the test.
Begin
Frequency(0.1
M)
Specifies the lowest frequency in the test.
End
Frequency(0.1
M)
Specifies the highest frequency in the test.
Show Working
Frequency
If you select the Show Working Frequency check box, the working
frequencies scanned in the test will be automatically queried and you
can view the working frequencies on the Chart or List tab page.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.4.2 Online Spectrum Scan Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the online spectrum of a carrier in the cell. Based on
received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values reported to the base station, a frequency
spectrum graph is generated. You can log in to the local maintenance terminal (LMT) and
remotely obtain the frequency spectrum graph to preliminarily troubleshoot the interference
during interference localization.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
175
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
This test cannot be performed together with any of the following tests, including the
offline spectrum scan, CDMA interference network test, online and offline passive
intermodulation test, and TRX RF self-loopback test. You must stop these tests before
monitoring online spectrum scan.
Only one online spectrum scan test can be performed at a time in a cell, and a maximum
of eight test tasks can be started at the same time for one base station.
During the test, the specified test channel is blocked.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > GSM Monitoring. Double-click Online Spectrum
Scan Monitoring.
The Online Spectrum Scan Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Online Spectrum Scan Monitoring dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-21.
Table 7-21 Parameters for Online Spectrum Scan Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely specifies a
local cell in a base station.
TRX ID
Specifies the index of the carrier to be tested. This parameter uniquely
specifies a carrier under a BSC.
Channel No.
Specifies the number of the channel to be tested.
Duration(Minut
e)
Specifies the duration of the test.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
176
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.4.3 Codec Mode Test
This section describes how to perform a voice test, and record the uplink signal noise ratio
(SNR), downlink frame type, and DTX indicator during the test. The test result is reported by
the BTS to the local maintenance terminal (LMT) PC.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > GSM Monitoring. Double-click Codec Mode Test.
The Codec Mode Test dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Codec Mode Test dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 7-22.
Table 7-22 Parameters for voice coding and decoding
Parameter
Description
Local Cell
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely specifies a local
cell in a base station.
TRX ID
Specifies the index of the carrier to be tested. This parameter uniquely
specifies a carrier under a BSC.
Channel
Specifies the number of the channel in a carrier.
Sub-channel
Specifies the number of the subchannel.
Duration
Specifies the duration of the test.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.5 UMTS-specific Monitoring Tasks
This section describes UMTS-specific monitoring tasks.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
177
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.5.1 HSPA Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the single-user High Speed Packet Access (HSPA)
performance. Based on the monitoring results, you can efficiently commission the HSPA rate
by modifying parameters or adjust the UE location. This task includes High Speed Uplink
Packet Access (HSUPA) monitoring and High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA)
monitoring.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Only one HSUPA and HSDPA monitoring task of the same UE can be started on a base
station.
This function can be used to quickly locate and resolve problems. Normally there is no
way to avoid that some user data such as International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
will be used during the troubleshooting. However, this function provides an anonymous
data processing method.
You are obligated to take considerable measures, in compliance with the laws of the
countries concerned, to ensure that the personal data of users is fully protected. For
example, you can enable user identity anonymity and delete the tracing files after the
problems are handled.
When entering IMSI, check whether IMSI data to be entered must be anonymous by
running the LST USERIDANONSWITCH command and querying User Identity
Anonymity Switch.
Context
If User Identity Anonymity Switch is ON, anonymous IMSI data needs to be
entered in IMSI ID. Anonymous IMSI data can be obtained by entering the IMSI
and a key in the anonymization tool HMACUtil.
If User Identity Anonymity Switch is OFF, the IMSI can be directly entered in
IMSI ID.
NOTE
l The anonymization switch and the key can be modified on the U2000 by choosing Monitor >
Signaling Trace > Anonymous Policy Management (traditional style), or by choosing Signaling
Trace > Anonymous Policy Management (application style). For details, see U2000 Fault
Management User Guide.
l If you change the anonymous policy or cipher key of a started monitoring task, you need to restart
the monitoring task. Otherwise, the monitoring task becomes invalid.
l To obtain the anonymization tool HMACUtil, contact Huawei technical support.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > UMTS Monitoring. Double-click HSPA
Monitoring.
The HSPA Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-23.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
178
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Table 7-23 Parameters for single-user HSPA monitoring
Parameter
Description
IMSI ID
Specifies the IMSI for HSPA monitoring.
Report Type
This parameter can be set to HSUPA or HSDPA.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
type.
to customize the folder, file name, and file
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.5.2 Sector Equipment Group RTWP
This section describes how to measure the received total wideband power (RTWP) of a
UTRAN uplink channel. Based on the RTWP, the uplink radio channel can be adjusted. This
task does not affect services.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
RTWP measurement results for sector equipment groups are reported only when logic
cells exist.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > UMTS Monitoring. Double-click Sector
Equipment Group RTWP.
The Sector Equipment Group RTWP dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-24.
Table 7-24 Parameters for sector equipment group RTWP
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the local cell.
Sector
Equipment
Group Index
Specifies the index of the sector equipment group.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
179
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.5.3 Cell Throughput Statistic
This section describes how to monitor uplink and downlink throughput of a cell. Based on the
monitoring results, you can know the distribution of users in the cell.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Context
Downlink HSPA service throughput monitoring is not supported in cells with downlink
baseband resources established on the WBBPa board.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > UMTS Monitoring. Double-click Cell
Throughput Statistic.
The Cell Throughput Statistic dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-25.
Table 7-25 Parameters for cell throughput statistic
Parameter
Description
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the local cell.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
180
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.5.4 Cell Service Resource Query
This section describes how to query service resources of a cell, including the number of users,
the number of channel elements (CEs) used in the uplink, and the number of CEs used in the
downlink.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
A logical cell has been set up.
Uplink resources include uplink demodulation resources and decoding resources. The
unit is number.
Downlink resources include downlink demodulation resources and decoding resources.
The unit is number.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > UMTS Monitoring. Double-click Cell Service
Resource Query.
The Cell Service Resource Query dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-26.
Table 7-26 Parameters for querying cell service resources
Parameter
Description
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the local cell.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the query results on
the Chart or List tab page.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
181
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
7.5.5 Cell RTWP
This section describes how to measure the received total wideband power (RTWP) of a
UTRAN uplink channel. Based on the RTWP, the uplink radio channel can be adjusted. This
task does not affect services.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > UMTS Monitoring. Double-click Cell RTWP.
The Cell RTWP dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-27.
Table 7-27 Parameters for cell-level RTWP monitoring
Parameter
Description
Logic Cell ID
Specifies the ID of the cell to be monitored.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
to customize the folder, file name, and
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.5.6 Frequency Scan Monitoring
By analyzing the spectral and power distribution of sampled data, you can monitor the
interference in the frequency and time domains in radio environments.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
If a logical cell has been activated, the frequency must be consistent with the uplink
frequency configured for the logical cell.
If a logical cell does not exist or is not activated, the start frequency and end frequency
must be within the frequency band supported by the RRU.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
182
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Interference detection is performed on RF modules. To perform NodeB offline
interference detection on a SDR-based RF module of a multi-mode base station, perform
the following steps:
For a GSM+UMTS (GU) base station
i.
On the NodeB, run the BLK BRD command to block the RF module.
ii.
On the BSC, run the DEA BTS command to deactivate the base station on the
GSM side.
iii. Wait 30 minutes and perform NodeB offline interference detection.
For a UMTS+LTE (UL) base station
i.
On the NodeB, run the BLK BRD command to block the RF module.
ii.
On the eNodeB, run the DEA CELL command to deactivate the base station
on the GSM side.
iii. Perform NodeB offline interference detection.
For a GSM+UMTS+LTE (GUL) base station
i.
On the NodeB, run the BLK BRD command to block the RF module.
ii.
On the BSC, run the DEA BTS command to deactivate the base station on the
GSM side.
iii. On the eNodeB, run the DEA CELL command to deactivate the base station
on the GSM side.
iv.
Wait 30 minutes and perform NodeB offline interference detection.
After NodeB offline interference detection is performed, unblock the RF module and
activate the cell and base station.
l
Only the RF modules RRU3804, RRU3806, RRU3801E, RRU3808, and WRFU support
this function. FFT Frequency Scanning is recommended for the modules that do not
support this function.
Monitoring frequency scan require that the FTP server be used to upload files from the
base station. Therefore, this operation is available when you log in to the base station
using the LMT rather than the U2000 proxy.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > UMTS Monitoring. Double-click Frequency Scan
Monitoring.
The Frequency Scan Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-28.
Table 7-28 Parameters for monitoring frequency scan
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Specifies the cabinet number of the RRU or RFU.
Subrack No.
Specifies the subrack number of the RRU or RFU.
Slot No.
Specifies the slot number of the RRU or RFU.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
183
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Band
Band 1 to Band 9 can be selected.
Start Frequency No.
Start frequency number for the detection.
End Frequency No.
End frequency number for the detection.
Start Freq(MHz)
Start frequency that the system automatically calculates according
to the start frequency No.
End Freq(MHz)
End frequency that the system automatically calculates according to
the end frequency No.
Module
Type[Compensator]
Module type for the detection
FTP File Path
Path to the directory where the sampling files are saved. Two
sampling files are downloaded each time.
FTPServer IP
Address
Specifies the IP address of the LMT PC.
FTPServer User
FTPServer user name.
User Password
FTPServer password. The default password is hwbs@com.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
In the Chart, the horizontal axis represents the frequency (MHz), and the vertical axis
represents the amplitude (dBm).
NOTE
l The detection result can have an acceptable error within 5 dB.
l You can select Show Power Graph to open a window that shows the power data in a graph. In the graph,
the horizontal axis represents the relative time (ms), and the vertical axis represents the amplitude (dBm).
----End
7.5.7 Repeater Interfere Frequency Scan Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the interference caused by repeaters to RRUs. You can
monitor the interference caused by repeaters based on spectrum analysis.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
You have verified the following before enabling the repeater interference monitoring
function:
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
184
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
The RRU is a V3 KUNLUN module running on the 900 MHz band and is not an
active antenna system (AAS) module, as indicated in the DSP BRDMFRINFO
command output.
The RF desensitization value is 0, as indicated in the DSP RRU command output.
No intermodulation interference exists, as indicated in the STR RFTEST command
output.
The repeater interference monitoring function can be enabled only when all the
preceding conditions apply.
Context
l
The repeater interference monitoring function can be used to monitor the stable repeater
interference that causes the RTWP to increase by higher than 10 dBm in the uplink band
from 890 MHz to 915 MHz on which the spectral power rises.
It is good practice to perform this function during off-peak hours for high monitoring
accuracy.
If the monitoring result displays "suspected repeater interference", manually check for
the following points: spectrum resources fully occupied, blocking interference, and other
unstable wideband interference (probably intermodulation interference caused by other
components).
An RRU supports one repeater interference monitoring task at a time.
Repeater interference monitoring and FFT spectrum scanning are mutually exclusive on
the same RRU.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor. The Monitor tab is displayed.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > UMTS Monitoring. Double-click Repeater
Interfere Frequency Scan Monitoring.
The Repeater Interfere Frequency Scan Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set the related parameters. For details about parameter descriptions, see Table 7-29.
Table 7-29 Parameters for repeater interference monitoring
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Cabinet No.
Cabinet number of the board implementing repeater
interference monitoring
Subrack No.
Subrack number of the board implementing repeater
interference monitoring
Slot No.
Slot number of the board implementing repeater
interference monitoring
Band No.
The band number corresponds to the 900 MHz band,
which can be queried using the DSP RXBRANCH
command.
Mode
WCDMA
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
185
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Index of RX Channel 1
RX channel 1 for data sampling.
NOTE
If this parameter is set to 255, repeater interference monitoring
is not performed on the channel.
Index of RX Channel 2
RX channel 2 for data sampling.
NOTE
If this parameter is set to 255, repeater interference monitoring
is not performed on the channel.
Smooth Frame Count
Number of frames for the smoothing process to calculate
the average value on the spectrum.
Tested Total Frame Count
Total number of sample frames for spectrum analysis.
Interference Energy
Threshold(dB)
The interference is identified when the energy variation
caused by the interference is greater than this threshold
value.
Interference Probability
Threshold
Probability threshold for interference detection.
Start Frequency(MHz)
Start frequency for interference detection.
End Frequency(MHz)
End frequency for interference detection.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results
will be automatically saved. Click
save path, file name, and file type.
to customize the
Step 4 Click Submit. A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the
monitoring results on the Chart tab.
----End
7.6 LTE-specific Monitoring Tasks
This section describes LTE-specific monitoring tasks.
7.6.1 Sector Performance Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor the sector performance by performing a uplink
frequency scan. In a frequency scan, the frequency information is scanned to detect
interference. An uplink frequency scan is used to detect uplink interference.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
The cell in the monitored sector must be in the non-activated state.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
186
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Context
A Task ID on the List tab page in the monitoring window represents a point for one frame
shown on the monitoring figure on the Chart tab page. Each point indicates the signal
strength for a specified frequency. Task ID displayed in the task information pane at the
bottom of the real-time monitoring window indicates the running task of the frame.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > LTE Monitoring. Double-click Sector
Performance Monitoring.
The Sector Performance Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Sector Performance Monitoring dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 7-30.
Table 7-30 Parameters for sector performance monitoring
Parameter
Description
Monitor Item
It can be set to UL Widefreq Scan.
Monitor Period
(ms)
Specifies the interval at which monitoring results are reported. This
parameter can be set to 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, or 2000.
You are advised to set Monitor Period (ms) to 1000 or a larger value. If
Monitor Period (ms) is set to 50, 100, 200, or 500, the precision may not
meet the requirements. As a result, the monitoring result is inaccurate.
Sector
Equipment ID
Specifies the sector ID.
Frequency
Band
Specifies the frequency band supported by the sector.
UL EARFCN
Specifies the uplink EARFCN of a cell.
NOTE
The uplink EARFCN must fall in the frequency range supported by the RRU that
serves the sector. If this parameter is set to an EARFCN beyond the frequency
range, the monitoring will fail.
UL Bandwidth
Specifies the uplink bandwidth of the cell. This parameter can be set to
1.4M, 3M, 5M, 10M, 15M, or 20M.
NOTE
l pRRU only support 5M, 10M, 15M, 20M.
l The uplink bandwidth must fall in the frequency range supported by the RRU
that serves the sector. If this parameter is set to a bandwidth beyond the
frequency range, the monitoring will fail.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
file type.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
to customize the folder, file name, and
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
187
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the monitoring
results on the Chart or List tab page.
----End
7.6.2 Cell Performance Monitoring
This section describes how to monitor common measurement values and the number of users
over common channels.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The Java runtime environment (JRE) plug-in has been installed.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Monitor.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose Monitor > LTE Monitoring. Double-click Cell Performance
Monitoring.
The Cell Performance Monitoring dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Cell Performance Monitoring dialog box. The following tables
list the parameter descriptions.
Table 7-31 Parameters for Interference Detection
Parameter
Description
Monitor Item
Detect Interference.
NOTE
l If there is a local cell. The frequency to be checked must be the uplink frequency
of the local cell.
l If there is not a local cell, the start frequency number and end frequency number
must be in one frequency band.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Main
eNodeB ID
Specifies the main eNodeB ID.
Monitor
Period (ms)
Specifies the interval at which monitoring results are reported. This
parameter can be set to 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, or 2000.
Local Cell
ID
Specifies the ID of a local cell.
Cell Type
Specifies the cell type. This parameter can be set to Single RRU Cell,
Multi-RRU cell: Cell Sector Equipment, or Multi-RRU cell: Cell
Sector Equipment Group.
Cell Sector
Equipment
ID
Specifies the ID of a cell sector equipment. This parameter is valid only
when Cell Type is set to Multi-RRU cell: Cell Sector Equipment.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
188
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Cell Sector
Equipment
Group ID
Specifies the ID of a cell sector equipment group. This parameter is valid
only when Cell Type is set to Multi-RRU cell: Cell Sector Equipment
Group.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box, monitoring results will be
automatically saved. Click
type.
to customize the folder, file name, and file
Table 7-32 Parameters for PIM Interference Detection
Parameter
Description
Monitor Item
PIM Interference Detect.
Main eNodeB ID
Specifies the main eNodeB ID.
Monitor Period (ms)
Specifies the interval at which monitoring
results are reported. This parameter can be
set to 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, or 2000.
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of a local cell.
Cell Type
Specifies the cell type. This parameter can
be set to Single RRU Cell, or Multi-RRU
cell: Cell Sector Equipment.
Cell Sector Equipment ID
Specifies the ID of a cell sector equipment.
This parameter is valid only when Cell
Type is set to Multi-RRU cell: Cell Sector
Equipment.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box,
monitoring results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder,
file name, and file type.
Table 7-33 Parameters for General Throughout Monitoring
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Monitor Item
General Throughout.
Monitor Period (ms)
Specifies the interval at which monitoring
results are reported. This parameter can be
set to 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, or 2000.
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of a local cell.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
189
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Test Items to Monitor
You can select the Overall RLC
Throughput, RLC Throughput of GBR
Service, or RLC Throughput of NONGBR Service check box.
Test Items to Monitor
You can select the CN Operator ID0, CN
Operator ID1, CN Operator ID2, CN
Operator ID3, CN Operator ID4, or CN
Operator ID5 check box.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box,
monitoring results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder,
file name, and file type.
Table 7-34 Parameters for User Statistics Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Monitor Item
User Statistics.
Monitor Period (ms)
Specifies the interval at which monitoring
results are reported. This parameter can be
set to 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, or 2000.
Local Cell ID
Specifies the ID of a local cell.
Test Items to Monitor
You can select the General Users Number,
NO-Activated Users Number, or Keep UL
Synch Users Number check box.
Test Items to Monitor
You can select the CN Operator ID0, CN
Operator ID1, CN Operator ID2, CN
Operator ID3, CN Operator ID4, or CN
Operator ID5 check box.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box,
monitoring results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder,
file name, and file type.
Table 7-35 Parameters for MA Scheduling Statistic Monitoring
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Monitor Item
MA Scheduling Statistic.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
190
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
7 Managing Performance Monitoring
Parameter
Description
Monitor Period (ms)
Specifies the interval at which monitoring
results are reported. This parameter can be
set to 1280, or 5120.
MBSFN Area ID
Specifies the ID of a MBSFN area.
Special TMGI
This parameter can be set to ALL TMGI,
Special TMGI.
MCC
Specifies the mobile country code.
MNC
Specifies the mobile network code.
Service ID
Specifies the ID of service.
This parameter is valid only when Special
TMGI is set to Special TMGI.
Save File
If you select the Save File check box,
monitoring results will be automatically
saved. Click
to customize the folder,
file name, and file type.
Step 4 Click Submit.
A real-time performance monitoring window is displayed. You can view the cell performance
monitoring results on the Chart or List tab page.
NOTE
l In the cell performance monitoring results, the values of the RRU Cabinet No., RRU Subrack No.,
and RRU Slot No. parameters under the Interference Detect item are displayed as the actual values
when the SFN or cell combination feature is enabled and displayed as N/A in other scenarios.
l You are advised to set Monitor Period (ms) to 1000 or a larger value. If Monitor Period (ms) is set
to 50, 100, 200, or 500, the precision may not meet the requirements. As a result, the monitoring
result is inaccurate.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
191
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Maintaining the Base Station
About This Chapter
This chapter describes how to operate the device panel, manage software and files and
maintain base station equipment.
8.1 Device Panel Operations
This section describes the operations of the BTS device panel, including how to start and use
it to maintain the base station.
8.2 Common Maintenance Tasks
This section describes how to manage software and files and use the IP transfer self-test
function. Managing software and files involves upgrading the software and data configuration
file using the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server.
8.3 Maintaining the GSM Base Station
This section describes how to maintain the cells and carriers of a GSM base station.
8.4 Maintaining the LTE Base Station
This section describes how to check whether the eNodeB is installed correctly.
8.5 BTS Self-test
This section describes how to use the base station self-test function. The base station self-test
function helps check the version of the base station software, running status of cells and
RRUs, and alarms.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
192
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
8.1 Device Panel Operations
This section describes the operations of the BTS device panel, including how to start and use
it to maintain the base station.
8.1.1 Introduction to the Device Panel
Man-machine language (MML) commands and graphical device panels can be used on the
local maintenance terminal (LMT) to maintain devices.
Context
A device panel is a graphical user interface (GUI) that shows components of a base station.
Procedure
Step 1 On the device panel, you can right-click an installed board and perform related operations.
Figure 8-1 and Table 8-1 show a device panel and parameters on the device panel.
Figure 8-1 Interface of a device panel
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
193
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
NOTE
l The device panel automatically refreshes with the board status of the base station. Device panels vary
with the base station type and configuration.
l The board maintenance menu varies with the board type.
l Overflow Information: Due to the no restrictions on component configurations, the cabinet configuration
may be beyond the capability of the cabinet panel. To avoid GUI element display in disorder, a table is
provided to display detailed overflow information when the cabinet configuration may be beyond the
capability of the cabinet panel. For example, right-click the Empty/Uninstalled status area in area 2 and
the Overflow Information item is displayed. If Overflow Information is not gray, click Overflow
Information and a table will be displayed to show the detailed overflow information.
Table 8-1 Parameters on the device panel
No.
Parameter
Description
Legend
A color is used to indicate the status of each board.
Device Panel
Based on information reported by the base station, the
device panel displays the boards configured in the
cabinet and the real-time status of each board. On the
device panel, you can perform board-specific
operations.
----End
8.1.2 Starting the Device Panel
This section describes how to start the device panel to maintain installed boards.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
Before operating and managing a base station, you must start the device panel.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
Step 2 In the device maintenance navigation tree, double-click the BTS under Cabinet, and the
corresponding BTS device panel is displayed in the Device Panel tab page on the right.
Step 3 Right-click a board and choose a maintenance item.
----End
8.1.3 Querying the Board Version Information
This section describes how to query the board version information of a base station.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
194
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
You can check whether the current version of a board matches that of the base station based
on the query result. The version information about a board includes the cabinet number,
subrack number, slot number, software version, hardware version, and the BootROM version.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Display Board Version
Information. A Display Board Version Information dialog box is displayed,
showing the board version information.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the DSP BRDVER command.
----End
8.1.4 Listing Active Alarms
This section describes how to list active alarms about a board.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose List Active Alarms.
A List Active Alarms dialog box is displayed, showing the active alarms about the
board.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the LST ALMAF command.
----End
8.1.5 Resetting a Board
This section describes how to reset a faulty board.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
195
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Reset Board.
A confirmation dialog box is displayed.
c.
In the confirmation dialog box, click OK.
NOTE
l The result will be displayed and the color indicating the board status will be updated
accordingly.
l The UPEU and USCU cannot be reset.
l The reset interrupts the services on the board.
l The reset board cannot be used before it is reinitialized.
l If you reset the active main control board, the base station is reset.
l The common device of a dual-mode base station can be reset. However, the reset interrupts
services on the common device and therefore affects the services of the peer mode.
l If a base station is configured with multi-mode radio frequency (RF) modules, the reset of the
RF modules interrupts the services of the peer modes.
l If a base station works in CPRI MUX mode and one mode is the convergence end, the reset of
the baseband board providing the convergence function or the main control board of this
mode interrupts services of the peer modes.
l If a multimode base station supports co-transmission and the shared ports for co-transmission
are located on a board working in UMTS mode, the reset of the board interrupts services of
the peer modes.
l If a multimode base station supports co-transmission and the shared ports for co-transmission
are located on a board working in LTE mode, the reset of the board interrupts services of the
peer modes.
l The reset of a multi-mode RF module of a multimode base station interrupts the services of
the peer modes. The reset of UMPT, LMPT, WMPT, or UTRP interrupts the services of the
peer modes.
l The reset of an uninstalled board fails.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the RST BRD command.
----End
8.1.6 Querying the Current Version Information of the Base
Station
This section describes how to query the current version information about the base station.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
The version information includes the current software version, and software version status.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
196
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click the active board and choose List Current Software
Version.
A dialog box is displayed, showing the current version information about the base
station.
NOTE
This step applies to the active main control board (including WMPT, UMPT, or LMPT board) of a
base station.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the LST VER command.
----End
8.1.7 Blocking a Board
This section describes how to block a board to maintain the board without affecting services.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Block Board.
A Confirm dialog box is displayed.
c.
In the Confirm dialog box, click OK.
NOTE
l The result will be displayed and the color indicating the board status will be updated
accordingly.
l After a board is blocked, the resources of the board are unavailable logically.
l After a BBP, RRU, or RFU is blocked, if links cannot be set up for the associated RRUs or
RFUs or links cannot work at the highest CPRI line rate, you need to run the STR
CPRILBRNEG command to initiate a negotiation.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the BLK BRD command.
----End
8.1.8 Unblocking a Board
This section describes how to unblock a board to maintain the board without affecting
services.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
197
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Unblock Board.
A Confirm dialog box is displayed.
c.
In the Confirm dialog box, click OK.
NOTE
l The result will be displayed and the color indicating the board status will be updated
accordingly.
l If a board is functional, the resources of the board are available logically after it is unblocked.
l After a BBP, RRU, or RFU is unblocked, if links cannot be set up for the associated RRUs or
RFUs or links cannot work at the highest CPRI line rate, you need to run the STR
CPRILBRNEG command to initiate a negotiation.
l A board can be unblocked for a consecutive number of times.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the UBL BRD command.
----End
8.1.9 Querying the Clock Status
This section describes how to query the current clock status of a base station.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
By checking the running status and modification settings of the clock, you can maintain and
adjust the clock status.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Display Clock Status.
A Display Clock Status dialog box is displayed, showing the clock information.
NOTE
You can maintain the clock based on the query result of the base station clock status, clock
reference status, clock working mode, and clock synchronization mode.
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
198
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Run the DSP CLKSTAT command.
----End
8.1.10 Querying the Board Status
This section describes how to query the board status of a base station.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Display Board Status.
The Display Board Status dialog box is displayed, showing the current status of
the board.
n
Table 8-2 lists the board status.
Table 8-2 Board status
Status Type
Description
Management
Indicates the administrative state of the board.
Active or
standby
A board is either in the active status or in the standby status.
Functionality
Indicates the operational state of the board.
Alarms
Alarms indicate alarms of the highest class on the board.
Availability
Availability indicates the physical status of a board.
By checking the board status, you can know about the running status of a base
station.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the DSP BRD command.
----End
8.1.11 Querying the Software Version of the Base Station
This section describes how to query the software version of a macro or distributed base
station.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
199
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Context
The software version information includes the storage position, software version, and
software version status.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose List Software Version.
The List Software Version dialog box is displayed, showing the software version
information and patch version information.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the LST SOFTWARE command.
----End
8.1.12 Querying the CPU/DSP Usage
This section describes how to query the central processing unit (CPU) and digital signal
processor (DSP) usage of a base station.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
By checking the usage of all CPUs and digital signal processors (DSPs) on a specified board,
you can determine whether the system is overloaded.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Display CPU/DSP
Occupancy.
The Display CPU/DSP Occupancy dialog box is displayed, showing the CPU and
DSP usage of the board.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the DSP CPUUSAGE command.
----End
8.1.13 Querying the Manufacturing Information of a Board
This section describes how to query the manufacturing information of a board.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
200
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Context
l
The manufacturing formation about a board includes the board type, bar code,
description, manufacturing date, manufacturer, and version number.
Only the baseband unit (BBU) has backplane manufacturing information. To query the
backplane manufacturing information, the slot number 255 must be specified.
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
Procedure
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Display Board Manufacturing
Information.
The Display Board Manufacturing Information dialog box is displayed, showing
the board manufacturing information.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the DSP BRDMFRINFO command.
----End
8.1.14 Querying the E1/T1 Port Status
This section describes how to query the E1 or T1 port status.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
If base station cascading mode does not match the E1 or T1 clock mode, the link running
status may be reported as abnormal.
In T1 clock mode, if the frame format is T1 superframe, the physical loopback status
cannot be correctly detected.
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
Procedure
a.
Start the device panel of the base station.
b.
On the device panel, right-click a board and choose Display E1T1 Port Status.
The Display E1T1 Port Status dialog box is displayed, showing the E1 or T1 port
status.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the DSP E1T1 command.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
201
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
8.2 Common Maintenance Tasks
This section describes how to manage software and files and use the IP transfer self-test
function. Managing software and files involves upgrading the software and data configuration
file using the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server.
8.2.1 Concepts Related to Software and Files
This section describes software and file types, and methods of obtaining files.
Software Types
There are different types of software.
l
BootROM
All the boards on the base station is equipped with the BootROM. The BootROM refers
to the software bound with hardware. It provides basic device drive function and can be
started and updated manually.
The BootROM is a re-writable storage medium, which is used to store binary data, that
is, the machine codes.
BTS software
The BTS software is the version software of a base station.
Cold patch
The BTS cold patch is also known as the patch. It can upgrade a specific board or
module to improve functions or to fix some problems.
Hot patch
The hot patch is also known as the online patch. It supports the upgrade without
disrupting the system operation and rectify some function defects.
File Types
There are different types of files, and operations on the files vary with the types.
l
Data configuration file
A data configuration file contains parameter settings for each module of the base station.
This file is an .xml file. You can upload and download the file.
Maintenance and operation log
A maintenance and operation log file records the information about the maintenance and
operation of the base station.
This file is a text file. You can upload the file.
Main control log
A main control log file is a collection of logs including the original, commissioning, or
user alarm log, running log, call log, cell log, maintenance log, and operation log.
This file is a binary file. You can upload the file.
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Board log
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
202
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
A board log file is a collection of logs including the log of active and standby central
processing unit (CPU) breakdown, the detailed breakdown log, and the digital signal
processor (DSP) memory log.
This file is a binary file. You can upload the file.
NOTE
Board log files vary with boards because some boards do not have a standby CPU and other boards do
not have a DSP.
Routine received total wideband power (RTWP) test log
After a routine RTWP test is started, the system keeps a real-time RTWP log.
This file is a binary file. You can upload the file.
Device archive file
A device archive file records information about each board of the BTS such as the
manufacturing information and running time.
This file is an .xml file. You can upload the file.
Methods of Obtaining the Files
After obtaining a file, you can browse it.
There are two methods of obtaining and browsing a file:
l
You can upload a file to the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server and log in to the FTP
server to browse the file.
You can browse an operation log file on the U2000 client.
8.2.2 Configuring the FTP Server
You can download the base station software, data configuration file, and license from an File
Transfer Protocol (FTP) server to the local maintenance terminal (LMT).
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
Because the base station software, data configuration file, and license are downloaded from
the FTP server, ensure that the FTP server has been configured before the download.
Procedure
Step 1 Download the FTP server software. (Optional. Perform this step only when there is no FTP
server at the LMT computer.)
1.
In the upper right corner of the LMT main window, click FTP Tool. The File
Download-Security Warning dialog box is displayed.
2.
Click Save to save the FTP server software SFTPServer.exe to the LMT computer.
Step 2 Double-click SFTPServer.exe. SFTPServer.exe is decompressed into an SFTPServer
folder.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
203
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Step 3 Open SFTPServer. Double-click SFTPServer.exe to start the FTP server. The
displayed on the right side of the taskbar after the FTP server is started.
l
If the FTP server runs for the first time, go to Step 4.
Otherwise, go to Step 5.
icon is
Step 4 If the FTP server starts for the first time, an FTP password config dialog box is prompted,
indicating to modify the password of the FTP server, as shown in Figure 8-2. In the dialog
box, enter the initial password hwbs@com, and enter and confirm the new password. Then,
click OK.
Figure 8-2 FTP password config dialog box
Step 5 Configure the FTP server.
1.
Double-click
Figure 8-3.
. The FTP server configuration dialog box is displayed, as shown in
Figure 8-3 FTP server configuration dialog box
2.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Set User name, Password, Working directory, the default user name is admin. Set
Working directory to the root directory of the FTP server, which is D:\FTP, and retain
default values for other parameters.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
204
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
NOTE
3.
The user name, password, and other parameters displayed in the FTP server configuration
dialog box can be modified as required.
n
The method for modifying the password of the FTP server is as follows: Enter a new
password in Password and click OK. The FTP password authentication dialog box is
displayed. In FTP password authentication, enter the old password and the new
password that needs to be authenticated, and then click OK. The password is
successfully modified and the new password takes effect.
The method for modifying the FTP user name and other parameters displayed in the
FTP server configuration dialog box is as follows: Enter the changed value in the text
boxes of parameters and click OK. The FTP password authentication dialog box is
displayed. In the FTP password authentication dialog box, enter the valid password
and click OK. The parameters are successfully modified.
If you forget the password of the FTP server, delete the FTP server applications, and then
download and reinstall them. Then, the user name and password of the FTP server are restored
to the default ones.
Working directory must be set to a specified path for storing software and data configuration
files because the FTP server cannot access the files not stored in Working directory. Do not
set Working directory to a value containing sensitive information or to the father path of the
FTP server installation path.
Plain text indicates that data is transmitted in plaintext format. Encrypted indicates that data
is transmitted in ciphertext format. Both indicates data can be transmitted in the format of
plaintext or ciphertext as required.
To enable encryption transmission, the FTP server can run TLSv1.0, TLSv1.1, or TLSv1.2,
and the FTP client must run the same TLS version as the FTP server to properly connect the
FTP server.
Click SSL Settings, and configure parameters used for data encryption and transmission using
the FTP server on the displayed SSL Settings dialog box. These parameters include Root
Certificate FIle Name, Certificate FIle Name, Private Key File Name, and Private Key
Password. Ensure that the root certificate file, certificate file, and private key file must be
stored in the same directory as SFTPServer.exe.
During an upgrade of the LMT, if LmtView Common component under Select Software
Components is selected, the password of the FTP tool is restored to the default password
hwbs@com after an upgrade.
If the running FTP tool is SingleRAN V100R007C00, NodeB V200R015C00, LTE
V100R005C01, or an earlier version, the changes on the parameters of the FTP server take
effect, without entering the password.
To implement data or file transfer between the FTP server and base station, you must log in to
the base station using the LMT, not the remote U2000 proxy.
Click OK. The FTP server is successfully configured.
----End
8.2.3 Software Management
To add functions or correct defects during base station operation, you may need to upgrade
the version software, install the license file, or activate the data configuration file.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The FTP server has been configured.
The FTP server is running properly. The IP address of the FTP server is on the same
network segment as the IP address of the base station, and the FTP server is properly
connected to the base station.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
205
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
There is no firewall between the FTP server and the base station.
The user of the FTP server has the permission to read files in specified paths.
Context
The base station software consists of the version software, license file, and data configuration
file.
NOTICE
If the base station restarts, all services carried on the base station are interrupted.
l
The license file applies only to LTE.
Downloading and activating the data configuration file do not cause the base station to
restart. The updated configuration data automatically takes effect next time the base
station restarts.
Installing the license file does not cause the base station to restart. The license file takes
effect immediately after the installation.
After the version software is successfully activated, the base station automatically
restarts.
NOTE
l In special scenarios such as base station deployment or upgrade, select the Download version software
check box and set Delay Download Flag to Yes (Delay download) to reduce the time required. In delay
download mode, only the minimum LMT package is downloaded, and the complete LMT package can be
automatically downloaded about four hours later. This mode has no impact on the base station software. If
the functions of the complete LMT package are required before the complete package is automatically
downloaded, you can run the SPL SOFTWARE command to download the complete package to the base
station.
l If the Install license check box is selected and Force flag is set to Yes, the license file is forcibly installed
despite of any errors. If Force flag is set to No, which is recommended, error information is displayed
during the license file installation. For details, see the section "Troubleshooting" in License Management
Feature Parameter Description.
Procedure
l
GUI mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance >
Software Management. Double-click Software Management.
The Software Management tab page is displayed.
n
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Figure 8-4 shows the directory structure of the software package.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
206
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Figure 8-4 Directory structure of the software package
c.
Figure 8-4 shows the directory structure of the software package of a
multimode base station. To download the version software of a single-mode
base station, you only need to download a single-mode software package, for
example, BTS3900 V100R00xCxxSPCxxx_NodeB.
To download the BootROM, configuration data file, and license file, choose
the folder where the the BootROM, configuration data file, and license file are
saved.
Set parameters related to FTP Server Configuration on the Software
Management tab page. Table 8-3 lists the parameters that need to be set.
Table 8-3 FTP Server Configuration
Parameter
Description
FTP Server IP
Specifies the IP address of the LMT
PC. The IP address must be on the
same network segment as the IP
address of the base station.
User name
Specifies the user name for logging in
to the FTP server.
NOTE
The value of this parameter must be the
same as that of User name in Configuring
the FTP Server.
Password
Specifies the password for logging in
to the FTP server.
NOTE
The value of this parameter must be the
same as that of Password in Configuring
the FTP Server.
d.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Select tasks based on scenarios. Table 8-4 describes the scenarios and
corresponding tasks.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
207
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-4 Scenarios and corresponding tasks
e.
Scenario
Recommended Task
Only version software upgrade is
required. The data configuration file
does not need to be downloaded and
activated, and the license file does not
need to be installed.
Download version software and
Activate version software
Version software upgrade and license
file installation are required. The data
configuration file does not need to be
downloaded and activated.
Download version software, Install
license, and Activate version
software
Version software upgrade and data
configuration file download and
activation are required. The license file
does not need to be installed.
Download version software,
Download configuration file,
Activate configuration file, and
Activate version software
Version software upgrade, data
configuration file download and
activation, and license file installation
are required.
All
Only license file installation is required.
Install license
Only BootROM upgrade is required.
Upgrade BootROM
Only supply software upgrade is
required.
Supply software
Only cold patch upgrade is required.
Upgrade Patch
Only hot patch upgrade is required.
Upgrade Hot Patch
Version software upgrade, data
configuration file download and
activation, and license file installation
are required.
Upgrade
Only board activate is required.
Activate Board
Click Execute. The base station performs the selected tasks from top to bottom as
required. The operation results are displayed in Information.
NOTE
l If all tasks are selected, the base station performs the tasks one by one. A progress bar is
displayed under Execute to indicate the progress of each task.
l If a check box is not selected, the base station skips this task and proceeds with the next task.
l If a task fails, the base station stops this task and following tasks.
l If the base station software is successfully activated, the base station automatically restarts
and the new software takes effect.
l If the base station software fails to be activated, the base station rolls back to the source
version.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
208
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
f.
l
Clear Clear Message to clear all contents displayed in Information.
MML mode
a.
Run the DLD SOFTWARE command to download the software and BootROM.
n
If you want to run the MML command to operate and maintain the base station
after being restarted, Delay Download Flag must be set to NO(Not Delay
Download).
To ensure that the base station can download software of all target RATs, select
all target options for Application Type List.
b.
Run the DLD CFGFILE command to download the configuration file.
c.
Run the ACT CFGFILE command to activate the configuration file. If EFT is set
to AFTER_RESET, the operation takes effect only after the base station restarts.
In this case, software activation by running the ACT SOFTWARE command fails
before the base station restarts.
d.
Run the ACT SOFTWARE command to activate the software and BootROM.
To ensure that the base station can download software of all target RATs, select all
target options for Application Type List.
e.
Run the INS LICENSE command to download and install the license file.
----End
8.2.4 Extra Configuration File Transfer
This section describes how to download the BTS extra configuration file from the FTP server
to the base station. The downloaded extra configuration files take effect after activating.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server has been configured.
The FTP server is running properly. The IP address of the FTP server is on the same
network segment as the IP address of the base station, and the FTP server is properly
connected to the base station.
There is no firewall between the FTP server and the base station.
The user of the FTP server has the permission to read files in specified paths.
Downloading the extra configuration file requires that the FTP server be used to
download files to the base station. Therefore, this operation is available when you log in
to the base station using the LMT rather than the U2000 proxy.
The extra configuration files downloaded using the LMT can be in plaintext or encrypted
format. If the extra configuration files are encrypted, enter the encryption password to
download them.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance. Double-click
Extra Configuration File Transfer.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
209
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
The Extra Configuration File Transfer tab page is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters on the Extra Configuration File Transfer tab page. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 8-5.
Table 8-5 Parameter description
Parameter
Description
FTP Server
IP
Specifies the IP address of the LMT PC. The IP address must be on the
same network segment as the IP address of the base station.
User Name
Specifies the user name for logging in to the FTP server.
Password
Specifies the password for logging in to the FTP server.The default
password is hwbs@com.
Destination
File Name
Specifies the local batch configuration file.
NOTE
If the extra configuration file is encrypted, click Browse. The Encrypt Password
dialog box is displayed for you to enter the encryption password.
Step 4 Click Activate or Preactivate. The operation results are displayed in the message area.
NOTE
To enable the configuration data to take effect on the base station, click Activate. To only check the
correctness of the configuration data, click Preactivate.
----End
8.2.5 Device Archive Transfer
This section describes how to generate a BTS device archive file and upload the BTS device
archive file to the FTP server.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The FTP server has been configured.
The FTP server is running properly. The IP address of the FTP server is on the same
network segment as the IP address of the base station, and the FTP server is properly
connected to the base station.
There is no firewall between the FTP server and the base station.
The user of the FTP server has the permission to read files in specified paths.
Context
Transferring the device archive file requires that the FTP server be used to upload and
download files to and from the base station. Therefore, this operation is available when you
log in to the base station using the LMT rather than the U2000 proxy.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
210
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Procedure
l
GUI mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance.
Double-click Device Archive Transfer.
The Device Archive Transfer tab page is displayed.
c.
Set related parameters on the Device Archive Transfer tab page. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 8-6.
Table 8-6 Parameter description
Paramet
er
Description
FTP
Server IP
Specifies the IP address of the computer used as the LMT. The IP
address must be on the same network segment as the IP address of
the base station.
User
Name
Specifies the user name for logging in to the FTP server.
Password
Specifies the password for logging in to the FTP server. The default
password is hwbs@com.
Destinatio
n File
Name
Specifies the file to be uploaded to the FTP server.
Transfer
Type
Specifies the transfer type. This parameter can be set to Export
Device File or Upload Device File.
If this parameter is set to Export Device File, a device archive file
is generated on the base station. If this parameter is set to Upload
Device File, the generated device archive file is uploaded to the FTP
server.
Transfer
Status
d.
l
A progress bar is displayed to indicate the progress of file transfer.
Click Start.
MML mode
a.
Run the EXP DEVFILE command to generate the device archive file.
b.
Run the ULD DEVFILE command to upload the file from the base station to the
FTP server.
----End
8.2.6 Data Configuration File Transfer
This section describes how to download the data configuration file from the File Transfer
Protocol (FTP) server to the base station, or upload the data configuration file from the base
station to the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server. The downloaded data configuration file
takes effect after the base station restarts.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
211
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The FTP server has been configured.
The FTP server is running properly. The IP address of the FTP server is on the same
network segment as the IP address of the base station, and the FTP server is properly
connected to the base station.
There is no firewall between the FTP server and the base station.
The user of the FTP server has the permission to read files in specified paths.
Transferring the data configuration file requires that the FTP server be used to upload
and download files to and from the base station. Therefore, this operation is available
when you log in to the base station using the LMT rather than the U2000 proxy.
When encrypting configuration files to be uploaded from the base station to the FTP
server, you must set the password for encryption to a string of 6 to 32 characters.
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
Context
Procedure
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance.
Double-click Data Configuration File Transfer.
The Data Configuration File Transfer tab page is displayed.
c.
Set related parameters on the Data Configuration File Transfer tab page. For
details about parameter descriptions, see Table 8-7.
Table 8-7 Parameter description
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Paramet
er
Description
FTP
Server IP
Specifies the IP address of the computer used as the LMT. The IP
address must be on the same network segment as the IP address of
the base station.
User
Name
Specifies the user name for logging in to the FTP server.
Password
Specifies the password for logging in to the FTP server. The default
password is hwbs@com.
Destinatio
n File
Name
Specifies the file to be uploaded to the FTP server.
Transfer
Type
Specifies the transfer type. This parameter can be set to Upload
(Site to FTP server), Download (FTP server to site), Make data
configuration file take effect, Reset immediately, or Reset later.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
212
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
d.
l
Paramet
er
Description
Transfer
Status
A progress bar is displayed to indicate the progress of file transfer.
Click Start.
Man-machine language (MML) mode
Upload (Site to FTP server)
a.
Run the BKP CFGFILE command to back up the data configuration file.
b.
Run the ULD CFGFILE command to upload the file from the base station to the
FTP server.
Download (FTP server to site)
a.
Run the DLD CFGFILE command to download the file from the FTP server to the
base station.
b.
Run the ACT CFGFILE command to activate the data configuration file.
----End
8.2.7 Other File Transfer
This section describes how to upload base station files to the FTP server. After the base
station files are uploaded, you can save, browse, and modify the files.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The FTP server has been configured.
The FTP server is running properly. The IP address of the FTP server is on the same
network segment as the IP address of the base station, and the FTP server is properly
connected to the base station.
There is no firewall between the FTP server and the base station.
The user of the FTP server has the permission to read files in specified paths.
Context
Uploading other files require that the FTP server be used to upload files from the base station.
Therefore, this operation is available when you log in to the base station using the LMT rather
than the U2000 proxy.
Procedure
l
GUI mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance.
Double-click Other File Transfer.
The Other File Transfer tab page is displayed.
c.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Set related parameters on the Other File Transfer tab page. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 8-8.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
213
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-8 Parameter description
Parameter
Description
FTP Server IP
Specifies the IP address of the computer used as the LMT.
The IP address must be on the same network segment as
the IP address of the base station.
User name
Specifies the user name for logging in to the FTP server.
Password
Specifies the password for logging in to the FTP server.
The default password is hwbs@com.
Destination File
Name
Specifies the file to be uploaded to the FTP server.
Transfer Type
Upload(Site to FTP server) is selected by default.
NOTE
This parameter can be set to only Upload(Site to FTP server).
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Function Type
Selects ALL or the system that the base station supports.
IP Mode
Specifies the IP mode of the FTP server.
File Type
Specifies the type of the file to be uploaded. Different
Function Type correspond to different File Type. For
details, see Table 8-9.
Flow Control
Option
Specifies whether to perform flow control during file
upload.
Upload Mode
Compressed is selected by default.
Cabinet No.
Specifies the number of the cabinet where the board or
RRU is located.
Subrack No.
Specifies the number of the subrack where the board or
RRU is located.
Slot No.
Specifies the number of the slot where the board or RRU
is located.
Transfer Status
A progress bar is displayed to indicate the progress of file
transfer.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
214
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-9 File type description
d.
l
Function Type
File Type
ALL
ALMLOG(Alarm Log),
BAKOTHER(Abnormal Configured
File), BRDLOG(Compositive Log),
BSPLOG(BSP Log), CFLTLOG(NE
Fault Log), DBGLOG(NODE
Commissioning Log),
EXPT(Exception-Recording Log),
GPSMSG(GPS Message Trace),
OPRLOG(Operation Log),
PERILOG(Monitoring Board Log),
RFSTUFF(RF Test Log),
RRULOG(RRU Log).
ENODEB
BRDLOG-ENODEB(ENODEB
Compositive Log),
CALDPOWERFILE(Antenna
Coefficient File), CHRLOG(Call
History Record Log), DBGLOGENODEB(ENODEB Commissioning
Log).
NODEB
BRDLOG-NODEB(NODEB
Compositive Log), DBGLOGNODEB(NODEB Commissioning
Log), DSPEXPT(DSP Exceptional
Log), DSPRUNLOG(DSP Running
Log), RRUIQDATA(RRU Interference
Detection file), RRURXPOWER(RRU
Interference Detection power file),
RTWPTEST(RTWP Routine Test
Result Log).
GBTS
BRDLOG-GBTS(GBTS Compositive
Log), DBGLOG-GBTS(GBTS
Commissioning Log),
FRQLOG(Frequency Scan Record
Log), GSMBBLOG(GSM BB Log),
RFTST(RF Test Record File),
TODMSG(TOD Message Trace).
Click Start.
MML mode
a.
Run the ULD FILE command to upload the file from the base station to the FTP
server.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
215
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
8.2.8 Proxy GBTS Transmission Maintenance
Ping and Tracert are two basic functions of Proxy GBTS Transmission Maintenance. The
Ping function tests whether the IP layer is pingable from the source to the destination to check
for network connection faults. The Tracert function tests the gateways through which data
packets travel from the host to the destination to check whether network connections are
reachable and locate the fault point.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The emergency OM channel has been successfully established. For configurations of an
emergency OM channel, see 2.8 Configuring an Emergency OM Channel.
The base station has been configured with transmission data. If no data configuration file
is available on the GBTS, follow instructions provided in 8.2.9 Proxy File Transfer to
download the GBTS data configuration file to the GBTS.
The Abis over IP transmission is in use. This function does not work in Abis over TDM/
HDLC transmission mode.
This function can be used only by a single user at a time.
If the emergency maintenance channel is disabled and then restarted, close the Proxy
GBTS Transmission Maintenance window and navigate to the window again.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance. Double-click
Proxy GBTS Transmission Maintenance.
The Proxy GBTS Transmission Maintenance tab page is displayed.
Step 3 Click Switch to IP Mode.
Step 4 Set Operation to Ping or Tracert.
l
Table 8-10 describes the parameters to be configured for the Ping operation.
Table 8-11 describes the parameters to be configured for the Tracert operation.
Table 8-10 Parameters for the Ping operation
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Source IP
Specifies a local IP address. This IP address must have
been configured locally. If this parameter is not
specified, the IP address of the base station is used as the
source IP address by default.
Destination IP
Specifies the destination IP address.
Packet Size(byte)
Specifies the payload length of ping packets. The length
does not contain the ICMP header.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
216
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Parameter
Description
Packet Number
Specifies the number of sent ping packets.
DFSwitch
Specifies whether a packet is fragmented. If this switch
is turned on, the base station does not fragment ping
packets to be sent. In this case, if the length of a ping
packet exceeds the maximum transmission unit of the
base station, the packet fails to be sent.
DSCP
Specifies the priorities of differentiated services.
Timeout(ms)
Specifies the timeout duration.
Table 8-11 Parameters for the Tracert operation
Parameter
Description
Source IP
Specifies the local IP address. This IP address must have
been configured locally. If this parameter is not
specified or is set to 255.255.255.255, the outbound IP
address on the routing table that approximates most to
the destination IP address in the same routing domain is
used as the source IP address.
Destination IP
Specifies the destination IP address.
First TTL
Specifies the initial Time to Live (TTL) of a Tracert
packet.
Maximal TTL
Specifies the maximum TTL of a Tracert packet.
UDP Port No.
Specifies the destination port of the UDP packet
specified by the sent Tracert packet.
Timeout(ms)
Specifies the timeout length for waiting for a response to
a Tracert packet.
DFSwitch
Specifies whether a packet is fragmented. If this switch
is turned on, the detection of path maximum
transmission unit (PMTU) can be used.
DSCP
Specifies the priorities of differentiated services.
Path DSCP Display Switch
Specifies the DSCP display switch. If this switch is
turned on, the DSCP value in the IP header in the
payload of a received ICMP packet can be displayed.
Step 5 Click Start. The operation results are displayed in the Response Result area.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
217
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
8.2.9 Proxy File Transfer
The emergency OM channel helps obtain log files and certificate request files of the target
base station and transfer configuration files and certificate files to the main control board on
the target base station. This function requires an FTP server deployed locally or on the U2000.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The emergency OM channel has been successfully established.
The FTP server (deployed locally or on the U2000) has been started. If a local FTP
server is used, the OM IP address of the proxy base station and the IP address of this
FTP server must be mutually reachable.
When the GBTS is the target base station:
Context
The emergency OM channel can be successfully enabled only when local or remote
OM channel is faulty.
The base station is automatically restarted after obtaining configuration files to
make the configuration take effect.
Certificate file transfer are not allowed.
In V100R010C00, the base station supports uploading NODE Commissioning
Log, BSP Log, and NE Fault Log.
In V100R010C10, the base station supports uploading NODE Commissioning
Log, BSP Log, NE Fault Log, and Run Log.
When the GTMUa or WMPT serves as the main control board of the proxy base station,
the size of files that can be transferred depends on the available flash memory.
Only ASCII characters are allowed in file name and file path specified on the Proxy File
Transfer page.
If the FTP server on the U2000 is used, files downloaded and uploaded by the base
station (as the FTP client) are saved in default paths on the FTP server, which are as
follows:
a.
Default save path for files that the base station uploads to the FTP server on the
U2000: /export/home/sysm/ftproot/MBTSProxyFileDownload/
b.
Default save path for files that the base station downloads from the FTP server on
the U2000: /export/home/sysm/ftproot/MBTSProxyFileUpload/
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance, Double-click
Proxy File Transfer.
The Proxy File Transfer page is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters on the Proxy File Transfer page. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 8-12.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
218
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-12 Parameter description
Parameter
Description
FTP Server IP
Specifies the IP address of the FTP server deployed
locally or on the U2000.
User Name
Specifies the user name of the FTP server deployed
locally or on the U2000.
Password
Specifies the user password of the FTP server deployed
locally or on the U2000.
File Transfer Type
Specifies the types for FTP transfer. The value can be
Obtain logs of the target BTS, Download
configuration file to the target BTS, Download
certificate file to the target BTS, or Obtain
certificate request file of the target BTS.
Obtain logs of the target BTS
Specifies that the target base station uploads logs to the
FTP server.
The logs to be transferred can be NODE
Commissioning Log, BSP Log, NE Fault Log, Run
Log, or Operation Log.
Destination File Name specifies the name of a file
that the target base station uploads to the FTP server.
l If the FTP server on the U2000 is used:
If Download Path of U2000 FTP Server: /
export/home/sysm/ftproot/
MBTSProxyFileDownload/ is selected, you do
not need to enter the default save path of a file
in the Destination File Name text box.
If Download Path of U2000 FTP Server: /
export/home/sysm/ftproot/
MBTSProxyFileDownload/ is deselected, you
need to enter the default save path of a file in the
Destination File Name text box.
l If a local FTP server is used, the value of
Destination File Name can contain the absolute
path, relative path, or default path of the FTP
server.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when File Transfer Type is set to
Obtain logs of the target BTS.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
219
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Parameter
Description
Download configuration file to
the target BTS
Specifies that the target base station downloads
configuration files from the FTP server.
Configure File Name specifies the name of a
configuration file and cannot contain path information.
Server Path specifies the save path of files on the FTP
server.
l If the FTP server on the U2000 is used:
If Upload Path of U2000 FTP Server: /export/
home/sysm/ftproot/MBTSProxyFileUpload/
is selected, you do not need to enter the default
save path of a file in the Server Path text box.
If Upload Path of U2000 FTP Server: /export/
home/sysm/ftproot/MBTSProxyFileUpload/
is deselected, you need to enter the default save
path of a file in the Server Path text box.
l If a local FTP server is used, the value of Server
Path can contain the absolute path, relative path, or
default path of the FTP server.
Encrypted Mode specifies the encryption mode of a
file. The value can be UNENCRYPTED or
PWD_ENCRYPTED.
File Encryption Password specifies the password for
encrypting a file. This option is valid only when
Encrypted Mode is set to PWD_ENCRYPTED.
NOTE
l This parameter is valid when File Transfer Type is set to
Download configuration file to the target BTS.
l If a configuration file to be downloaded is encrypted, but
Encrypted Mode is set to UNENCRYPTED, the file
cannot be activated after being downloaded.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
220
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Parameter
Description
Download certificate file to the
target BTS
Specifies that the target base station downloads
certificate files from the FTP server.
Destination File Name specifies the name of a target
certificate file and cannot contain path information.
Source File Name specifies the name of a source
certificate file.
l If the FTP server on the U2000 is used:
If Upload Path of U2000 FTP Server: /export/
home/sysm/ftproot/MBTSProxyFileUpload/
is selected, you do not need to enter the default
save path of a file in the Source File Name text
box.
If Upload Path of U2000 FTP Server: /export/
home/sysm/ftproot/MBTSProxyFileUpload/
is deselected, you need to enter the default save
path of a file in the Source File Name text box.
l If a local FTP server is used, the value of Source
File Name can contain the absolute path, relative
path, or default path of the FTP server.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when File Transfer Type is set to
Download certificate file to the target BTS.
Obtain certificate request file of
the target BTS
Specifies that the target base station uploads certificate
files to the FTP server.
Destination File Name specifies the name of a target
certificate file.
l If the FTP server on the U2000 is used:
If Download Path of U2000 FTP Server: /
export/home/sysm/ftproot/
MBTSProxyFileDownload/ is selected, you do
not need to enter the default save path of a file
in the Destination File Name text box.
If Download Path of U2000 FTP Server: /
export/home/sysm/ftproot/
MBTSProxyFileDownload/ is deselected, you
need to enter the default save path of a file in the
Destination File Name text box.
l If a local FTP server is used, the value of
Destination File Name can contain the absolute
path, relative path, or default path of the FTP
server.
Source File Name specifies the name of a source
certificate file and cannot contain path information.
NOTE
This parameter is valid when File Transfer Type is set to
Obtain certificate request file of the target BTS.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
221
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Parameter
Description
Transfer Status
A progress bar is displayed to indicate the progress of
file transfer.
Step 4 Click Start.
NOTE
To terminate a file transfer, click Stop.
Step 5 Click View Details. The displayed table detailed information about file transfer success and
failures.
----End
8.2.10 IP Transport Selftest
This section describes how to use the IP transport self test function. The IP transport self test
function helps check the local transmission failure.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > Common Maintenance. Double-click IP
Transport Selftest.
The IP Transport Selftest tab page is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the IP Transport Selftest dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 8-13.
Table 8-13 Parameters for IP transport selftest
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Detection Item
IP transfer detection item. This parameter
can be set to OM, SCTP, IP Path, or IP
Clock.
Master/Slave flag
This parameter can be set to MASTER or
SLAVE. This parameter is valid when
Detection Item is set to OM.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
222
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Parameter
Description
SCTP Link/ENDPoint Mode
This parameter is set to SCTP Link by
default. This parameter is valid when
Detection Item is set to SCTP.
l If this parameter is set to SCTP Link,
SCTP Link No. needs to be specified.
l If this parameter is set to ENDPoint
Mode, Local IP and Peer IP need to be
specified.
IP Path/ENDPoint Mode
This parameter is set to IP Path by default.
This parameter is valid when Detection
Item is set to IP Path.
l If this parameter is set to IP Path, IP
Path ID needs to be specified.
l If this parameter is set to ENDPoint
Mode, Local IP and Peer IP need to be
specified.
IP Clock ID
ID of the detected IP clock. This parameter
is valid when Detection Item is set to IP
Clock.
Step 4 Click Start.
----End
8.3 Maintaining the GSM Base Station
This section describes how to maintain the cells and carriers of a GSM base station.
8.3.1 Querying Frequency Scan
This section describes how to query the maximum and average of the main level and diversity
level. You can perform this task to evaluate the interference condition on the uplink
frequency.y.
Prerequisites
l
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
The task of 8.3.2 Configuring Frequency Scan has been started.
This task is specific to GSM.
Each carrier has two receive channels. One is the main receive channel and the other is
the diversity receive channel. The main level is the uplink signal level on the main
receive channel, and the diversity level is the uplink signal level on the diversity receive
channel.
Context
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
223
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > GSM Maintenance. Double-click Query
Frequency Scan.
The Query Frequency Scan tab page is displayed.
Step 3 Set related parameters in the Query Frequency Scan dialog box. For details about parameter
descriptions, see Table 8-14.
Table 8-14 Parameters for query frequency scan
Parameter
Description
Local Cell
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely specifies a
local cell in a base station.
Sector ID
Specifies the ID of a sector. This parameter uniquely specifies a sector in
a base station.
Step 4 Click Start.
----End
8.3.2 Configuring Frequency Scan
This section describes how to set the start time and period for scanning frequencies of a cell.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
This task is specific to GSM.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > GSM Maintenance. Doubleclick Configure Frequency Scan.
The Configure Frequency Scan dialog box is displayed.
c.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Set related parameters in the Configure Frequency Scan dialog box. For details
about parameter descriptions, see Table 8-15.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
224
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-15 Parameters for configure frequency scan
d.
Parameter
Description
Local Cell
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely
specifies a local cell in a base station.
Sector ID
Specifies the ID of a sector. This parameter uniquely specifies a
sector in a base station.
Start Time
Specifies the start time of the scan.
Duration
Specifies the duration of the scan.
Frequency
Specifies the frequency to be scanned, which is dynamically
displayed based on base station configurations.
Click Start.
NOTE
After the configured frequencies are scanned, you can query the scanning results by using
the Querying Frequency Scan function.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the SET GCELLFREQSCAN command.
----End
8.3.3 Monitoring Channel Status
This section describes how to monitor the channel status.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
This task is specific to GSM.
NOTICE
PS channel status cannot be monitored and queried on the BTS LMT. Query the channel
status on the BSC LMT if channels of the type PBCCH+PDTCH, PCCCH+PDTCH, or
PDTCH are configured on a TRX.
Procedure
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > GSM Maintenance. Doubleclick Monitor Channel Status.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
225
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
The Monitor Channel Status tab page is displayed.
c.
Set related parameters on the Monitor Channel Status tab page.
d.
Click Start.
NOTE
l A dot under a channel indicates a sub-channel.
l The * mark to the upper right side of a carrier number indicates that the carrier works in
mutual-aid mode.
l The channel status monitoring window is fixed in size and does not change with the web
page.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the DSP GTRXCHNSTAT command.
----End
8.3.4 Testing Channel Loopback
This section describes how to test the transmission capability of the voice channel.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
This task is specific to GSM.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > GSM Maintenance. Doubleclick Test Channel Loopback.
The Test Channel Loopback tab page is displayed.
c.
Set related parameters on the Test Channel Loopback tab page. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 8-16.
Table 8-16 Parameters for test channel loopback
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Parameter
Description
Local Cell
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely
specifies a local cell in a base station.
TRX ID
Specifies the ID of the TRX to be tested. This parameter uniquely
specifies a TRX under a BSC.
Channel
Specifies the number of the channel in a carrier.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
226
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
d.
Parameter
Description
Sub-channel
Specifies the number of the sub-channel. When Test Project is
set to TRX RF Self-Loop Test or BIU Loop Test, Sub-channel
is set to All by default, and the parameter value cannot be
modified. When Test Project is set to BTS Voice Loop Test or
TRX Voice Loop Test, Sub-channel is set to All by default, and
the parameter value can be modified.
Test Project
TRX RF Self-Loop Test, BIU Loop Test, BTS Voice Loop Test
or TRX Voice Loop Test can be selected.
Duration
Specifies the duration of the test.
Power Level
Specifies the power level of the test.
Click Start.
NOTE
The test result is displayed in the Test Report area.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the following commands to perform a channel loopback test:
Run the STR GBTSTST command to start the test.
Run the STP GBTSTST command to stop the test.
----End
8.3.5 Testing TRX Loopback
This section describes how to perform a transceiver (TRX) loopback test to learn about the
TRX performance and channel transmission status. The test helps you locate voice service
problems.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
This task is specific to GSM.
Procedure
l
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > GSM Maintenance. Doubleclick Test TRX Loopback.
The Test TRX Loopback dialog box is displayed.
c.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Set related parameters in the Test TRX Loopback dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 8-17.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
227
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-17 Parameters for testing TRX loopback
d.
Parameter
Description
Local Cell
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely
specifies a local cell in a base station.
TRX ID
Specifies the ID of the TRX to be tested. This parameter uniquely
specifies a TRX under a BSC.
Test Item
BIU Loop Test can be selected.
Duration (s)
Specifies the duration of the test.
Click Start.
NOTE
The test result is displayed in the Test Report area.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the following commands to perform a TRX loopback test:
Run the STR GBTSTST command to start the test.
Run the STP GBTSTST command to stop the test.
----End
8.3.6 Modifying the Cell Management Status
This section describes how to block or unblock a local cell.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
This task is specific to GSM.
After a local cell is blocked, the corresponding logical cell is unavailable.
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
Procedure
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > GSM Maintenance. Doubleclick Modify Cell Management Status.
The Modify Cell Management Status tab page is displayed.
c.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Set related parameters on the Modify Cell Management Status tab page. For
details about parameter descriptions, see Table 8-18.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
228
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-18 Parameters for modify cell management status
d.
Parameter
Description
Local Cell
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely
specifies a local cell in a base station.
Modified
Status
Lock or Unlock can be selected.
Current
Status
Specifies the current status of the selected local cell. Lock or
Unlock can be selected.
Click Apply.
NOTE
The test result is displayed in the Operation Result area.
MML mode
The administrative status of a cell can be modified by running MML commands.
To block a local cell, run the BLK GLOCELL command.
To unblock a local cell, run the UBL GLOCELL command.
----End
8.3.7 Testing Idle Timeslot
This section describes how to test idle timeslots in the network to maximize interference in
the network.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
This task is specific to GSM.
To obtain information about the maximum interference level in the network during
network optimization phase, transmit bursts on downlink idle channels to simulate
downlink signal transmitting under the condition that services are not affected. This
maximizes the uplink interference stimulated by downlink signals and therefore enables
the evaluation of intra-network interference.
Graphical user interface (GUI) mode
Procedure
a.
In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
b.
In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > GSM Maintenance. Doubleclick Test Idle Timeslot.
The Test Idle Timeslot dialog box is displayed.
c.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Set related parameters in the Test Idle Timeslot dialog box. For details about
parameter descriptions, see Table 8-19.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
229
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Table 8-19 Parameters for test idle timeslot
d.
Paramet
er
Description
Local
Cell
Specifies the ID of the local cell. This parameter uniquely specifies a
local cell in a base station.
Sector ID
Specifies the ID of a sector. This parameter uniquely specifies a
sector in a base station.
TRX ID
Specifies the ID of the TRX to be tested. This parameter uniquely
specifies a TRX under a BSC.
Duration
(h)
Specifies hours that a test lasts.
Click Start.
NOTE
The test result is displayed in the Test Result area.
Man-machine language (MML) command mode
Run the following commands to test idle timeslots:
Run the STR GBTSTST command to start the test.
Run the STP GBTSTST command to stop the test.
----End
8.4 Maintaining the LTE Base Station
This section describes how to check whether the eNodeB is installed correctly.
8.4.1 Engineering Quality Check
This section describes how to check whether the installation meets the requirement by
executing specified check scripts.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Context
l
The check scripts are displayed in a table. They are executed one by one and the check
results are displayed.
Engineering quality check is designed to locally check device status. Exercise caution
while performing the check item Checking VSWR Status because the operation will
interrupt ongoing services.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
230
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Device Maintenance.
Step 2 In the navigation tree, choose BTS Maintenance > LTE Maintenance. Double-click
Engineering Quality Check.
The Engineering Quality Check tab page is displayed.
Step 3 Click Go. The check scripts are executed one by one and the result for each check item is
displayed.
NOTE
The result for each check item is Pass, Failed, Error, or Ignore. Pass indicates that the check
result meets the expected requirement. Failed indicates that the check result does not meet the
expected requirement. Error indicates that the check fails due to an error during the check
process. Ignore indicates that the check item does not meet corresponding prerequisites.
Step 4 Click Export Self-test Report. The self-test report is saved in an HTML file. You can
double-click the saved file to view the check result on a browser.
----End
8.5 BTS Self-test
This section describes how to use the base station self-test function. The base station self-test
function helps check the version of the base station software, running status of cells and
RRUs, and alarms.
Prerequisites
You have logged in to the LMT using an account with the required operation rights.
Procedure
Step 1 In the LMT main window, click Self Test.
The Self Test window is displayed, as shown in Figure 8-5.
Figure 8-5 Self Test tab page
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
231
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
8 Maintaining the Base Station
Step 2 Set the command execution mode. For details, see 4.3 Running MML Commands in
Batches.
NOTE
In common mode, you can change a man-machine language (MML) command in the command input pane.
1. Click Open. In the displayed Open dialog box, select an MML script file and import the MML
commands in the file.
2. Click Save. All the MML commands are saved.
Step 3 Click Go. The MML commands are executed in sequence to check the status of base station
equipment. The command execution results are displayed in Current Execute Command.
Step 4 Click Clear Results to clear all contents displayed in Current Execute Command.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
232
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
FAQ
About This Chapter
This chapter provides the answers to frequently asked questions (FAQs) during the LMT use.
9.1 How to Switch a Minimum LMT Package to a Complete LMT Package
The postponement download mode is used by default when the local maintenance terminal
(LMT) software package is downloaded during a base station upgrade. A minimum LMT
package is downloaded first, and then a complete LMT package is downloaded based on the
requirement. If the base station is upgraded on the U2000 and a complete LMT package
(Software.csp) of the same version as the minimum LMT package is available on the U2000,
the complete LMT package can be automatically downloaded to the base station four hours
after the upgrade. If the base station is upgraded on the LMT, the base station is properly
connected to the U2000, and a complete LMT package (Software.csp) of the same version as
the minimum LMT package is available on the U2000, the complete LMT package can be
automatically downloaded to the base station four hours after the upgrade. If the base station
is upgraded on the LMT or a complete LMT package is required immediately, you can
download the complete LMT package manually. This section describes the procedure for
switching a minimum LMT package to a complete LMT package.
9.2 Functions of the LMT Become Abnormal After an LMT Version Upgrade or Rollback
You need to clear the cache, cookies, and java applets in the browser if any of the following
scenarios apply: (a) The local maintenance terminal (LMT) does not display the target version
after the LMT upgrade or rollback. (b) The The MML configuration file parsed failed.
message is displayed when you run a man-machine language (MML) command. (c) Login to
the LMT succeeds and the tracing or monitoring interface is displayed, but the functions are
unavailable. For example, the reported message cannot be displayed, or is not fully displayed,
or is displayed out of sequence, or is incompletely saved, or cannot be saved. (d) Device
Panel fails to be opened for the first time after the upgrade.
9.3 How to Increase the LMT Response Speed During the Use of the Firefox Browser
When the Firefox browser is used on the local maintenance terminal (LMT), the LMT
response is slow. For example, after you click Monitor, it takes about 30 seconds to
maximize the window. In this case, check that the add-on extension Live Margins is installed.
9.4 How to Handle Incorrect Display of Colors of the LMT Main Window
When the LMT uses the Internet Explorer, the colors of the LMT main window are not
correctly displayed. For example, the colors indicating the status of boards and alarms are not
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
233
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
displayed, or the background color of the LMT main window is the same as that of the
Internet Explorer. In this case, check the color settings of the browser.
9.5 How to Handle Failed Display of the Verify Code in the LMT Login Dialog Box
When the LMT uses the Internet Explorer in the Microsoft Windows 2003, Microsoft
Windows 2008, or Microsoft Windows Vista operating system, the verify code in the LMT
login dialog box cannot be displayed. In this case, check the settings related to the protection
mode of the browser.
9.6 How to Handle No Responses to the Operations Performed on the Menu of the LMT Main
Window
When the LMT uses an Internet Explorer, there are no responses to the operations performed
on the menu of the LMT main window or the script error occurs. For example, when you click
the menu bar or buttons in the window or right-click in the window, there is no response or a
script error is displayed, indicating that you are rejected or have no right to access the LMT.
In this case, check the proxy settings of the browser.
9.7 How to Clear Garbled Characters That Occurred in a CSV File
If a CSV file containing non-English charactersis saved on the LMT and the CSV file is
opened in Excel format using the regular method, all non-English characters are displayed as
garbled characters. In this case, import the CSV file to Excel to open the file.
9.8 How to Set a Correct SSL Security Certificate
If a browser such as the Internet Explorer or Firefox uses the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
protocol to connect to the local maintenance terminal (LMT), a message indicating an
incorrect certificate may be displayed. As a result, you may fail to log in to the LMT.
9.9 How to Rectify Errors That Occurr While Saving a File
If the function of saving operation results is configured when you first log in to the LMT, the
system may display an error message during result file saving. In this case, the file size is zero
bytes.
9.10 How to Avoid the Failure to Log In to the LMT Due to a High Default Internet Explorer
Security Level
In Windows Server 2003 or Windows Server 2008, the Internet Explorer blocks Web
programs on sites that are not in the trusted site list to improve system security. As a result,
you may fail to log in to the LMT.
9.11 How to Handle the Slow Redirection After Logging in to the LMT
When the LMT uses the Internet Explorer, the redirection is slow after you log in to the LMT,
that is, the explorer remains blank for more than 15 seconds after you enter the base station IP
address in the address box of the Internet Explorer and before the explorer displays a security
warning. This section describes how to solve the problem.
9.12 How to Handle the LMT Interface Disorder
When the LMT uses Internet Explorer 8 or 9, the LMT interface may be displayed in disorder.
In this case, manually set the compatibility views of the Internet Explorer before logging in to
the LMT. This section describes the setting method.
9.13 How to Handle the Unknown Error Occurrs on LMT Interface or MML Command
Execution Failure After a Browser Upgrade
After Internet Explorer 6 is upgraded to Internet Explorer 8 or 9, some cached files cannot be
cleared. If an unknown error occurrs on LMT interface, or a man-machine language (MML)
command is executed, the system displays The MML configuration file parsed failed.. To
solve the problem, manually clear the cache and cookies in the Internet Explorer.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
234
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.14 How to Handle Error Message Displayed on the LMT or No Responses to Operations
Performed on the LMT Login Window
The error message Problems with this Web page might prevent it from being displayed
properly or functioning properly. is displayed in the Internet Explorer, or there is no
response to the operations performed on the LMT login window during the logging in of the
LMT.
9.15 How to Install OS Patches
If the LMT runs the Microsoft Windows 2003 operating system (OS), the security patch
KB938397 must be installed.
9.16 What Do I Do if Tracing, Monitoring or Other Functions Cannot Be Used?
Tracing, monitoring or other functions cannot be used after a successful login to the LMT, and
an error message is displayed.
9.17 What Do I Do If There Is No Response or Any Error Message After a Tracing,
Monitoring or Other Task Is Created
Some time after a successful login to the LMT, you may suddenly find that batch processing
fails with no error message. Alternatively, after a tracing or monitoring task is created, the
task page is not opened. There is no response or any error message. The NE task list shows
that this task has been successfully created. Or right-click in the message browsing window
and choose save messages, the Save dialog box is not displayed. If you open a new browser
and log in to the LMT again, the task nevertheless can be successfully created. If either of the
previous problems occurs, perform the following operations.
9.18 How to Handle the Problem That Only the Error Code Is Displayed in an Error Message
After a Tracing or Monitoring Task Is Created
Messages related to base station errors have been configured. However, the local maintenance
terminal (LMT) displays only the error code rather than the error message when a base station
error occurs. If the previous problem occurs, perform the following operations:
9.19 Any Further Operation Performed When Some LMT Web Pages Fail to Update Causes
the Web Pages to Turn Blank
Some LMT Web pages fail to update when batch processing, tracing, or monitoring is in use.
Any further operation causes the Web pages to turn blank. If you restart the function, the Web
page returns to normal. To prevent this problem, perform the following operations to add an
environment variable.
9.20 How to Handle the LMT Exit After Clicking Trace, Monitor, or Device Maintenance Tab
in Window 7
When you have successfully logged in to the LMT, the interface is redirected to the other
interface if you click the Trace, Monitor, or Device Maintenance tab. A few seconds after
the redirection, the interface is automatically redirected to the login window of the LMT and a
login failure message is prompted.
9.21 How to Handle the Disconnection Between the LMT and Base Station After the Device
Digital Certificate Is Replaced
During base station deployment using Plug and Play (PnP), device digital certificate addition
or deletion, the local maintenance terminal (LMT) is disconnected from the base station.
9.22 How to Handle Exceptions in the LMT Due to Insufficient PC Memory
If the memory space for the local maintenance terminal (LMT) PC is insufficient, exceptions
occur when the LMT runs on the PC.
9.23 Error Message "This user session already exists" Upon Login to LMT
The interface displays an error message this user session already exists upon login to LMT.
Solve the problem by using the method described in the procedure part.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
235
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.24 Interfaces for Performing Tracing or Monitoring Tasks Blinking
Interfaces for performing tracing or monitoring tasks blink.
9.25 The web site's certificate cannot be verified.Do you want to continue? Is Displayed
During Tracing or Monitoring
During initialization of a task such as tracing or monitoring on the LMT, "The web site's
certificate cannot be verified.Do you want to continue?" is displayed.
9.26 Batch Execution of MML Commands Fails Because Some MML Commands Contain
Invisible Carriage Returns or Line Feeds
After line feeds (LF) are deleted from MML command scripts copied to Batch, command
execution fails.
9.27 How to Handle Shortcut Key Invalidation
Shortcut keys are defined on the LMT. When logging in to the LMT through a web page, you
may fail to use the corresponding function by pressing a shortcut key. In this case, the shortcut
key becomes invalid. For example, you cannot stop pinging by pressing Ctrl+Q in the MML
Command window. This is because the same shortcut key is preferentially used by another
running program on the PC, which leads to a shortcut key conflict.
9.28 What Do I Do If A Message "Stop running this script?" Is Displayed?
This section describes how to solve the problem that a message "Stop running this script?" is
displayed during script execution on the LMT.
9.29 The Internet Explorer Fails to Respond or the Login Window Is Displayed After the
LMT Is Running for a While or Multiple Functions Are Concurrently Enabled on the LMT
The Internet Explorer fails to respond or the login window is displayed after the LMT is
running for a while or multiple functions are concurrently enabled on the LMT. Solve the
problem by using the method described in the procedure part.
9.30 A Message checking client environment... Is Displayed on the Login Window and the
browser Does Not Respond
During the login to the WebLMT, a message "checking client environment..." is displayed
on the login window and the browser does not respond and has to be forcibly closed. In this
case, solve the problem by using the method described in the procedure part.
9.31 LMT Login Window Being Stopped by the Browser
The LMT login window is stopped by the browse, and the login stills fails even though the
user selects Allow popups. To solve the problem, perform the following steps:
9.32 The Application Blocked by Security Settings Dialog Box Is Displayed When Batch
Processing, Tracing, Monitoring, or Device Maintenance Is Enabled
After the JRE is installed or upgraded, the Application Blocked by Security Settings dialog
box is displayed when the tab page related to batch processing, tracing, monitoring, or device
maintenance is open. Click OK, and the The application cannot be run dialog box is
displayed, indicating that the batch processing, tracing, monitoring, or device maintenance
function is unavailable.
9.33 Help for Installing and Using the Java Plug-in
The Java plug-in used by LMT modules, including Batch, Trace, Monitor, and Device
Maintenance, is the Java runtime environment(JRE). You need to install the Java plug-in
before using these modules. You can try the following methods to solve problems about
installing or using Java plug-in.
9.34 What Do I Do If the Message Your Java version is out of date Is Displayed?
If you are prompted that Your Java version is out of date when logging in to the WebLMT,
follow the instructions provided in this session.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
236
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.35 How to Configure Wireless NIC on a Computer
To connect a computer to a local wireless access point device, ensure that the computer is
configured with a WLAN wireless network interface card (NIC). Before connecting the
computer to a local wireless access point device, configure WLAN wireless NIC by following
the instructions below.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
237
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.1 How to Switch a Minimum LMT Package to a
Complete LMT Package
The postponement download mode is used by default when the local maintenance terminal
(LMT) software package is downloaded during a base station upgrade. A minimum LMT
package is downloaded first, and then a complete LMT package is downloaded based on the
requirement. If the base station is upgraded on the U2000 and a complete LMT package
(Software.csp) of the same version as the minimum LMT package is available on the U2000,
the complete LMT package can be automatically downloaded to the base station four hours
after the upgrade. If the base station is upgraded on the LMT, the base station is properly
connected to the U2000, and a complete LMT package (Software.csp) of the same version as
the minimum LMT package is available on the U2000, the complete LMT package can be
automatically downloaded to the base station four hours after the upgrade. If the base station
is upgraded on the LMT or a complete LMT package is required immediately, you can
download the complete LMT package manually. This section describes the procedure for
switching a minimum LMT package to a complete LMT package.
Prerequisites
l
The LMT directly communicates with the base station, and direct File Transfer Protocol
(FTP) download is enabled between them. Ports 20 and 21 are enabled.
The minimum LMT package can be used normally.
The minimum LMT package provides only some functions that involve the download of
the FTP server software and some MML commands.
The complete LMT package provides complete LMT functions, including MML
command running, batch processing, alarm management, tracing management,
performance monitoring, equipment maintenance, and self-test.
Context
NOTE
l The file name of the complete LMT package must be Software.csp. If the package is in compressed
format, you need to manually decompress the package and download the Software.csp file to the
base station using the FTP server.
l After the minimum LMT package is switched to the complete LMT package, boards do not reset.
You can use the functions of the complete LMT package after you log in to the LMT again.
l Except for local operation and maintenance (OM) services, the switch process does not interrupt
other services carried by the base station.
Procedure
Step 1 Download the FTP server software. (Optional. Perform this step only when there is no FTP
server at the LMT computer.)
1.
In the upper right corner of the LMT main window, click FTP Tool. The File
Download-Security Warning dialog box is displayed.
2.
Click Save to save the FTP server software SFTPServer.exe to the LMT computer.
Step 2 Double-click SFTPServer.exe. SFTPServer.exe is decompressed into an SFTPServer
folder.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
238
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Step 3 Open SFTPServer. Double-click SFTPServer.exe to start the FTP server. The
displayed on the right side of the taskbar after the FTP server is started.
l
If the FTP server runs for the first time, go to Step 4.
Otherwise, go to Step 5.
icon is
Step 4 If the FTP server starts for the first time, an FTP password config dialog box is prompted,
indicating to modify the password of the FTP server, as shown in Figure 9-1. In the dialog
box, enter the initial password hwbs@com, and enter and confirm the new password. Then,
click OK.
Figure 9-1 FTP password config dialog box
Step 5 Configure the FTP server.
1.
Double-click
Figure 9-2.
. The FTP server configuration dialog box is displayed, as shown in
Figure 9-2 FTP server configuration dialog box
2.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Set User name, Password, Working directory, the default user name is admin. Set
Working directory to the root directory of the FTP server, which is D:\FTP, and retain
default values for other parameters.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
239
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
NOTE
3.
The user name, password, and other parameters displayed in the FTP server configuration
dialog box can be modified as required.
n
The method for modifying the password of the FTP server is as follows: Enter a new
password in Password and click OK. The FTP password authentication dialog box is
displayed. In FTP password authentication, enter the old password and the new
password that needs to be authenticated, and then click OK. The password is
successfully modified and the new password takes effect.
The method for modifying the FTP user name and other parameters displayed in the
FTP server configuration dialog box is as follows: Enter the changed value in the text
boxes of parameters and click OK. The FTP password authentication dialog box is
displayed. In the FTP password authentication dialog box, enter the valid password
and click OK. The parameters are successfully modified.
If you forget the password of the FTP server, delete the FTP server applications, and then
download and reinstall them. Then, the user name and password of the FTP server are restored
to the default ones.
Working directory must be set to a specified path for storing software and data configuration
files because the FTP server cannot access the files not stored in Working directory. Do not
set Working directory to a value containing sensitive information or to the father path of the
FTP server installation path.
Plain text indicates that data is transmitted in plaintext format. Encrypted indicates that data
is transmitted in ciphertext format. Both indicates data can be transmitted in the format of
plaintext or ciphertext as required.
To enable encryption transmission, the FTP server can run TLSv1.0, TLSv1.1, or TLSv1.2,
and the FTP client must run the same TLS version as the FTP server to properly connect the
FTP server.
Click SSL Settings, and configure parameters used for data encryption and transmission using
the FTP server on the displayed SSL Settings dialog box. These parameters include Root
Certificate FIle Name, Certificate FIle Name, Private Key File Name, and Private Key
Password. Ensure that the root certificate file, certificate file, and private key file must be
stored in the same directory as SFTPServer.exe.
During an upgrade of the LMT, if LmtView Common component under Select Software
Components is selected, the password of the FTP tool is restored to the default password
hwbs@com after an upgrade.
If the running FTP tool is SingleRAN V100R007C00, NodeB V200R015C00, LTE
V100R005C01, or an earlier version, the changes on the parameters of the FTP server take
effect, without entering the password.
To implement data or file transfer between the FTP server and base station, you must log in to
the base station using the LMT, not the remote U2000 proxy.
Click OK. The FTP server is successfully configured.
Step 6 Run the SPL SOFTWARE command to download the complete LMT package to the base
station using the FTP server.
NOTE
You must enter the IP address, user name, and password for logging in to the FTP server correctly and set
Delay Download File Supply Flag to YES (Supply File that Support Delay).
Step 7 Log in to the LMT again to use the functions of the complete LMT package.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
240
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.2 Functions of the LMT Become Abnormal After an LMT
Version Upgrade or Rollback
You need to clear the cache, cookies, and java applets in the browser if any of the following
scenarios apply: (a) The local maintenance terminal (LMT) does not display the target version
after the LMT upgrade or rollback. (b) The The MML configuration file parsed failed.
message is displayed when you run a man-machine language (MML) command. (c) Login to
the LMT succeeds and the tracing or monitoring interface is displayed, but the functions are
unavailable. For example, the reported message cannot be displayed, or is not fully displayed,
or is displayed out of sequence, or is incompletely saved, or cannot be saved. (d) Device
Panel fails to be opened for the first time after the upgrade.
Procedure
l
To clear the cache and cookies in the browser, perform the steps shown in the following
table.
Browse
r Type
Handling Procedure
Firefox
1. Open the Firefox browser, and choose Tools > Clear Private Data
from the menu bar.
2. In the displayed Clear Private Data dialog box, select the Cache,
Cookies, and Offline Website Data check boxes, and click Clear
Private Data Now.
Internet
Explore
r 7.0
1. Open the Internet Explorer, and choose Tools > Internet Options from
the menu bar. The Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
2. On the General tab page, click Delete. The Delete Browsing History
dialog box is displayed.
3. To delete the files, click Delete Files and then click OK in the
displayed dialog box. To delete the cookies, click Delete Cookies and
then click OK in the displayed dialog box.
4. In the Delete Browsing History dialog box, click OK and close the
Internet Options dialog box.
Internet
Explore
r 8.0 or
9.0
1. Open the Internet Explorer, and choose Tools > Internet Options from
the menu bar. The Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
2. On the General tab page, click Delete. The Delete Browsing History
dialog box is displayed.
3. Clear the Preserve Favorites website data check box and select the
Cookies and Temporary Internet files check boxes. Then, click
Delete and close the Internet Options dialog box.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
241
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Browse
r Type
Handling Procedure
Internet
Explore
r 10.0
1. Open the Internet Explorer, and choose Tools > Internet Options from
the menu bar. The Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
2. On the General tab page, click Delete. The Delete Browsing History
dialog box is displayed.
3. Clear the Preserve Favorites website data check box and select the
Cookies and Website data and Temporary Internet files and
Website Files check boxes. Then, click Delete and close the Internet
Options dialog box.
To clear the Java Applet, perform the following steps:
NOTICE
Before you clear the Java Applet, exit the LMT. Otherwise, some loaded data will be lost
and unexpected errors will occur.
The procedure for clearing the Java Applet is slightly different among different operating
systems. The following uses Windows 7 as an example.
a.
Choose Start > Control Panel.
b.
Double-click Java in the displayed window. The JAVA Control Panel is displayed.
c.
On the General tab page, click Settings. The Temporary Files Settings dialog box
is displayed.
d.
Click Delete Files. In the displayed Delete Temporary Files dialog box, select the
Applications and Applets and Trace and Log Files check boxes, and click OK.
e.
In Java Control Panel, click OK.
f.
The operations take effect after the browser restarts.
----End
9.3 How to Increase the LMT Response Speed During the
Use of the Firefox Browser
When the Firefox browser is used on the local maintenance terminal (LMT), the LMT
response is slow. For example, after you click Monitor, it takes about 30 seconds to
maximize the window. In this case, check that the add-on extension Live Margins is installed.
Procedure
Step 1 Open the Firefox browser, and choose Tools > Add-ons from the menu bar. The Add-ons
window is displayed.
Step 2 On the Extensions tab page, select Live Margins, and click Disable. A message is displayed,
indicating that the changes will take effect after the Firefox browser restarts.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
242
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Step 3 Click Restart Firefox to make the changes take effect.
----End
9.4 How to Handle Incorrect Display of Colors of the LMT
Main Window
When the LMT uses the Internet Explorer, the colors of the LMT main window are not
correctly displayed. For example, the colors indicating the status of boards and alarms are not
displayed, or the background color of the LMT main window is the same as that of the
Internet Explorer. In this case, check the color settings of the browser.
Procedure
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer, and choose Tools > Internet Options from the menu bar. The
Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 On the General tab page, click Accessibility. The Accessibility dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 In the Formatting area, select Ignore colors specified on Web pages, and click OK.
Step 4 In the Internet Options dialog box, click OK to exit the dialog box.
----End
9.5 How to Handle Failed Display of the Verify Code in
the LMT Login Dialog Box
When the LMT uses the Internet Explorer in the Microsoft Windows 2003, Microsoft
Windows 2008, or Microsoft Windows Vista operating system, the verify code in the LMT
login dialog box cannot be displayed. In this case, check the settings related to the protection
mode of the browser.
Context
If the protection mode is enabled in the Microsoft Windows 2003, Microsoft Windows 2008,
or Microsoft Windows Vista operating system, many security restrictions are imposed. For
example, neither JavaScript nor Applet can be run. Therefore, you must disable the protection
mode. If the protection mode is enabled, the LMT main window cannot be normally
displayed.
Procedure
Step 1 In the address box of the Internet Explorer, enter the IP address of the base station for local
maintenance. The default IP address is 192.168.0.49.
Step 2 Click Go next to the address box. The Local Maintenance Terminal dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Check whether the message "Internet|Protected Mode: Off" is displayed in the lower right
corner of the window.
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
If the message is displayed, contact Huawei technical support.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
243
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
If the message is not displayed, go to Step 4.
Step 4 Open the Internet Explorer, and choose Tools > Internet Options from the menu bar. The
Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
Step 5 On the Security tab page, select Trusted sites in the Select a Web content zone to specify
its security settings area.
Step 6 Under Zone Security Level, clear Enable Protected Mode, and then click Sites. The
Trusted sites dialog box is displayed.
Step 7 Enter the IP address of the base station for local maintenance in the Add this Web site to the
zone text box. The default IP address is 192.168.0.49. Then, click Add. The site is added to
the Trusted sites list.
Step 8 In the Internet Options dialog box, click OK to exit the dialog box.
Step 9 The verify code can be displayed after the Internet Explorer restarts.
----End
9.6 How to Handle No Responses to the Operations
Performed on the Menu of the LMT Main Window
When the LMT uses an Internet Explorer, there are no responses to the operations performed
on the menu of the LMT main window or the script error occurs. For example, when you click
the menu bar or buttons in the window or right-click in the window, there is no response or a
script error is displayed, indicating that you are rejected or have no right to access the LMT.
In this case, check the proxy settings of the browser.
Context
Do not change the settings of the Internet Explorer when the LMT is in use. Set the proxy
server before you log in to the LMT.
Procedure
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer, and choose Tools > Internet Options from the menu bar. The
Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 On the Connections tab page, click LAN Settings. The LAN Settings dialog box is
displayed.
Step 3 In the Proxy server area, select Use a proxy server for your LAN (These settings will not
apply to dial-up or VPN connections). Enter the IP address and port number of the proxy
server in the corresponding boxes, and then click Advanced. The Proxy settings dialog box
is displayed.
Step 4 In the Exceptions area, enter the IP address of the base station for local maintenance in the
text box. The default IP address is 192.168.0.49. Then, click OK and close the Internet
Options dialog box.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
244
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.7 How to Clear Garbled Characters That Occurred in a
CSV File
If a CSV file containing non-English charactersis saved on the LMT and the CSV file is
opened in Excel format using the regular method, all non-English characters are displayed as
garbled characters. In this case, import the CSV file to Excel to open the file.
Procedure
l
Office2003
a.
On the menu bar of Excel, choose Data > Import External Data > Import Data.
The Select Data Source dialog box is displayed.
b.
In the Select Data Source dialog box, select the CSV file. The Text Import
Wizard - Step 1 of 3 dialog box is displayed. Then, select Delimited under
Original data type, and select 936: Chinese Simplifed(GB2312) from the File
origin drop-down list. Click Next.
The Text Import Wizard - Step 2 of 3 dialog box is displayed.
c.
Select Comma under Delimiters. Click Finish.
The Import Data dialog box is displayed.
d.
l
click OK. The file will be normally displayed.
Office 2007 or later
a.
On the menu bar of Excel, choose Data > From Text. The Import Text File dialog
box is displayed.
b.
In the Import Text File dialog box, select the CSV file. The Text Import Wizard Step 1 of 3 dialog box is displayed. Then, select Delimited under Original data
type, and select 936: Chinese Simplifed(GB2312) from the File origin drop-down
list. Click Next.
The Text Import Wizard - Step 2 of 3 dialog box is displayed.
c.
Select Comma under Delimiters. Click Finish.
The Import Data dialog box is displayed.
d.
click OK. The file will be normally displayed.
----End
9.8 How to Set a Correct SSL Security Certificate
If a browser such as the Internet Explorer or Firefox uses the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
protocol to connect to the local maintenance terminal (LMT), a message indicating an
incorrect certificate may be displayed. As a result, you may fail to log in to the LMT.
Context
l
Internet Explorer (Internet Explorer 8 as an example.)
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
The Certificate Invalid alarm is displayed when you log in to the LMT in HTTPS
mode.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
245
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
i.
Enter https://IP address of the base station (for example, https://
10.141.115.219) in the address box of the Internet Explorer. The There is a
problem of this website's security certificate. dialog box is displayed.
ii.
Click Continue to this website (not recommended). in the There is a
problem of this website's security certificate. dialog box to enter the LMT
login page. However, a Certificate error warning is displayed in the address
box.
iii. Click Certificate error. The Certificate Invalid dialog box is displayed.
The Mismatched Address alarm is displayed when you log in to the LMT in
HTTPS mode.
i.
Enter https://a virtual external IP address (for example, https://
10.141.115.219) in the address box of the Internet Explorer. A There is a
problem of this website's security certificate. dialog box is displayed.
ii.
Click Continue to this website (not recommended). in the There is a
problem of this website's security certificate. dialog box to enter the LMT
login page. However, a Certificate error warning is displayed in the address
box.
iii. Click Certificate error. A Mismatched Address dialog box is displayed.
l
Firefox browser (Firefox 3 as an example)
Enter https://a virtual external IP address (for example, https://10.148.63.106) in the
address box of the browser. A This connection is Untrusted dialog box is displayed.
Procedure
l
In the Internet Explorer, the Certificate Invalid alarm is displayed when you log in to
the LMT in HTTPS mode.
If the SSL application certificate uses the WebLMT predefined certificate, perform
the following steps:
a.
On the login interface, click Download CA Certificate. In the displayed dialog
box, click Save. After the download is complete, the ca.zip file is saved.
b.
Decompress the ca.zip file.
NOTE
The ca.zip file is decompressed into two files: ne.cer and oss.cer. The ne.cer file is the root
certificate of Huawei certificate predefined for the LMT and the oss.cer file is the root
certificate predefined for the U2000 proxy server.
c.
Double-click ne.cer or oss.cer.
A Certificate Import Wizard dialog box is displayed.
d.
Click Next, choose the Place all certificates in the following store option button,
and click Browse.
A Select Certificate Store dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
e.
Choose Trusted Root Certification Authorities and click OK.
f.
Click Next, then click Finish and confirm that the ne.cer file has been imported.
g.
Repeat steps 3 to 6 to import the oss.cer file.
If the SSL application certificate uses the digital certificate issued by the customer's
PKI system, perform the following steps:
a.
Start Internet browser, and choose Tools > Internet Options. The Internet
Options dialog box is displayed.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
246
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
b.
Click the Content tab, and click Certificates. The Certificates dialog box is
displayed.
c.
Click the Trusted Root Certification Authorities tab, and then click Import.
The Certificate Import Wizard dialog box is displayed.
d.
Click Next, and click Browse in the displayed dialog box. Select the target root
certificate.
e.
Click Next, choose Place all certificates in the following store and click Browse.
A Select Certificate Store dialog box is displayed.
f.
Choose Trusted Root Certification Authorities and click OK.
g.
Click Next, then click Finish and confirm that the certificate import is complete.
In the Internet Explorer, the Mismatched Address alarm is displayed when you log in to
the LMT in HTTPS mode.
a.
Choose Internet Options from Tools on the toolbar.
b.
In the Internet Options dialog box, click the Advanced tab.
c.
In the Internet Options group box, clear the Warn about certificate address
mismatched* check box and click OK.
NOTE
Restart the Internet Explorer to make the modification take effect.
Firefox browser
a.
Click Add Exception in the This connection is Untrusted dialog box. An Add
Security Exception dialog box is displayed.
b.
Click Get Certificate.
NOTE
Firefox 10 obtains the certificate only in HTTP mode. Therefore, modify the server address
prefix to http before you use Firefox 10 to obtain the certificate.
c.
Click Confirm Security Exception. After the website is successfully added as a
security exception, no more security alarms will be displayed when the Firefox
browser is used to connect to the LMT in the future.
----End
9.9 How to Rectify Errors That Occurr While Saving a File
If the function of saving operation results is configured when you first log in to the LMT, the
system may display an error message during result file saving. In this case, the file size is zero
bytes.
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Start > Control Panel. In Control Panel, click Java. The JAVA Control Panel is
displayed.
NOTE
If you do not see the Java item in Control Panel, switch to another view.
Step 2 In Java Control Panel, click the Advanced tab. On the displayed tab page, choose Java
Plug-in > Enable the next-generation Java Plug-in (requires browser restart) in the
Settings navigation tree, and then click OK.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
247
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Step 3 Restart the LMT.
----End
9.10 How to Avoid the Failure to Log In to the LMT Due to
a High Default Internet Explorer Security Level
In Windows Server 2003 or Windows Server 2008, the Internet Explorer blocks Web
programs on sites that are not in the trusted site list to improve system security. As a result,
you may fail to log in to the LMT.
Context
According to acceptable Internet Explorer security levels, there are the following two
solutions:
l
If lowering the Internet Explorer security level on the Windows server is unacceptable,
you can add the LMT site to the trusted site list of the Internet Explorer using a
configuration startup script. The system automatically loads the script and configures the
Internet Explorer after a user logs in.
If lowering the Internet Explorer security level on the Windows server is acceptable, you
can remove Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration, a Windows component.
To set a configuration startup script, perform the following steps:
Procedure
a.
Create a configuration startup script.
Enter the following script contents in a notepad and save it as an IE-unset.bat file.
@echo off
setlocal ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
set uu="HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
\Internet Settings"
reg add %uu% /v EnableHttp1_1 /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f >nul
reg add %uu% /v ProxyHttp1.1 /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f >nul
setlocal ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
set uu="HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\EscRanges\Trust"
reg add %uu% /v :Range /t REG_SZ /d "10.141.149.193" /f >nul
reg add %uu% /v http /t REG_DWORD /d "2" /f >nul
reg add %uu% /v https /t REG_DWORD /d "2" /f >nul
NOTE
l The IE-unset.bat script file enables the system to automatically add a site to the trusted site
list of the Internet Explorer.
l You can modify the file when required, for example, change 10.141.149.193 in reg add %uu
% /v :Range REG_SZ /d "10.141.149.193" /f >nul to the IP address of the network element
to be visited.
l The Trust field in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows
\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\ZoneMap\EscRanges\Trust can be named as required.
b.
Load the startup script.
n
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
If the LMT runs on a Windows server, perform the following steps to set the
script:
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
248
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
1)
Log in to the Windows server with an administrator account, and choose
Start > Run.
2)
Enter gpedit.msc in the displayed dialog box, and click OK. The Group
Policy Object Editor dialog box is displayed.
3)
In the displayed dialog box, choose User Configuration > Windows
Settings > Scripts(Logon/Logoff), and double-click Logon.
The Logon Properties dialog box is displayed.
4)
Click Show Files and copy the created script to the displayed folder.
Then, close the dialog box displaying the folder.
5)
Click Add.
The Add a Script dialog box is displayed.
6)
Click Browse to select the created script and click OK.
7)
Click Apply and verify that the script is loaded successfully.
If the LMT runs on a Citrix Farm network, perform the following steps to set
the script:
1)
Log in to the primary or secondary Citrix domain control server with an
administrator account, and choose Start > Programs > Administrative
Tools > Active Directory Users and Computer. Select an organization
unit such as OSS and right-click Properties. Click the Group Policy tab
in the displayed dialog box, and click New on the displayed tab page to
create a group policy object.
NOTE
You can rename the group policy object as required.
2)
Select the created group policy object and click Edit. In the displayed
dialog box, choose User Configuration > Windows Settings >
Scripts(Logon/Logoff), and double-click Logon.
The Logon Properties dialog box is displayed.
3)
Click Show Files and copy the created script to the displayed folder.
Then, close the dialog box displaying the folder.
4)
Click Add.
The Add a Script dialog box is displayed.
5)
Click Browse to select the created script and click OK.
6)
Click Apply and verify that the script is loaded successfully.
To remove Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration, perform the following
steps:
a.
Choose Start > Control Panel > Add or Remove Programs. In the displayed
dialog box, select Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration.
b.
Click Details. In the displayed dialog box, clear For administrator groups and
For all other user groups.
c.
Click OK and then Next to remove Internet Explorer Enhanced Security
Configuration. After the removal is completed, click Finish.
d.
Restart the Internet Explorer to make the settings take effect.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
249
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.11 How to Handle the Slow Redirection After Logging in
to the LMT
When the LMT uses the Internet Explorer, the redirection is slow after you log in to the LMT,
that is, the explorer remains blank for more than 15 seconds after you enter the base station IP
address in the address box of the Internet Explorer and before the explorer displays a security
warning. This section describes how to solve the problem.
Prerequisites
l
The LMT directly communicates with the base station.
You log in to the LMT in HTTPS mode.
The operating system is Microsoft Windows 2003.
Context
In HTTPS mode, the interface will be redirected to HTTPS after you enter the IP address in
the address box of the Internet Explorer. After you log in to the LMT in HTTPS mode,
Windows visits the Microsoft website and updates the trusted root certification list until the
update succeeds or expires. In this period, the certification authentication in HPPTS mode is
slow. Generally, if you can visit the base station on the LMT, you can access the Intranet but
not the Internet. You can accelerate the visit to the LMT by disabling this function.
Procedure
Step 1 Click Start > Control Panel. The Control Panel is displayed.
Step 2 In Control Panel, click Add or Remove Programs. The Add or Remove Programs
window is displayed.
Step 3 In the Add or Remove Programs window, click Add/Remove Windows Components. The
Windows Components Wizard window is displayed.
Step 4 In the Components area of the Windows Components Wizard window, clear the Update
Root Certificates check box.
Step 5 Click Next. The system automatically performs the configuration.
Step 6 After the configuration is complete, click Finish.
----End
9.12 How to Handle the LMT Interface Disorder
When the LMT uses Internet Explorer 8 or 9, the LMT interface may be displayed in disorder.
In this case, manually set the compatibility views of the Internet Explorer before logging in to
the LMT. This section describes the setting method.
Prerequisites
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Internet Explorer 8 or 9 is used.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
250
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
The LMT interface is displayed in disorder.
Procedure
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer. Choose Tools > Compatibility View Settings.
The Compatibility View Settings dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 In the Add this website text box, enter the IP address of the network element (NE), for
example, 10.147.212.161. Click Add. Select the Display all websites in compatibility view
check box and click Close.
Step 3 The LMT interface is displayed in order after you log in to the LMT again.
----End
9.13 How to Handle the Unknown Error Occurrs on LMT
Interface or MML Command Execution Failure After a
Browser Upgrade
After Internet Explorer 6 is upgraded to Internet Explorer 8 or 9, some cached files cannot be
cleared. If an unknown error occurrs on LMT interface, or a man-machine language (MML)
command is executed, the system displays The MML configuration file parsed failed.. To
solve the problem, manually clear the cache and cookies in the Internet Explorer.
Procedure
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer 8 or 9, and choose Tools > Internet Options from the menu bar.
The Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 On the General tab page, click Delete in the Browsing history area. The Delete Browsing
History dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Clear the Preserve Favorites website data check box, select the Cookie and Temporary
Internet files check boxes, and click Delete.
Step 4 Close the Delete Browsing History dialog box.
Step 5 On the General tab page, click Settings in the Browsing history area. The Temporary
Internet Files and History Settings dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 Click View objects and delete all displayed files.
Step 7 Close the displayed window and the Internet Options dialog box.
----End
9.14 How to Handle Error Message Displayed on the LMT
or No Responses to Operations Performed on the LMT
Login Window
The error message Problems with this Web page might prevent it from being displayed
properly or functioning properly. is displayed in the Internet Explorer, or there is no
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
251
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
response to the operations performed on the LMT login window during the logging in of the
LMT.
Context
If the Internet Explorer has insufficient buffer or is upgraded, the Internet Explorer cannot
obtain new files from a base station after the base station is upgraded. The Internet Explorer
obtains files about the base station in the original version from the buffer, which is
inconsistent with the information about the base station in the current version.
Procedure
l
Internet Explorer Browser
a.
Open the Internet Explorer, and choose Tools > Internet Options from the menu
bar. The Internet Options dialog box is displayed.
b.
On the General tab page, click Delete in the Browsing history area. The Delete
Browsing History dialog box is displayed.
c.
Clear the Preserve Favorites website data check box, select the Cookie and
Temporary Internet files check boxes, and click Delete.
d.
Close the Delete Browsing History dialog box.
e.
On the General tab page, click Settings in the Browsing history area. The
Temporary Internet Files and History Settings dialog box is displayed.
f.
Click View objects and delete all displayed files.
g.
Close the displayed window and the Internet Options dialog box.
Firefox Browser
a.
Open the Firefox browser, and choose Tools > Clear Private Data from the menu
bar.
b.
In the displayed Clear Private Data dialog box, select the Cache, Cookies, and
Offline Website Data check boxes, and click Clear Private Data Now.
----End
9.15 How to Install OS Patches
If the LMT runs the Microsoft Windows 2003 operating system (OS), the security patch
KB938397 must be installed.
Context
Patch KB938397 rectifies the problem that the Windows operating system does not support
SHA256.
Procedure
Step 1 Choose Start > Control Panel. The Control Panel is displayed. Double-click Add or
Remove Programs in the displayed window. The Add or Remove Programs dialog box is
displayed.
Step 2 In the displayed Add or Remove Programs dialog box, select Show updates. Check whether
patch KB938397 is present in the list of Currently installed programs.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
252
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
If the patch is present in the list, contact Huawei technical support.
If the patch is not present in the list, go to Step 3.
Step 3 Download the security patch.
NOTE
To download the patch KB938397, visit http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=938397.
----End
9.16 What Do I Do if Tracing, Monitoring or Other
Functions Cannot Be Used?
Tracing, monitoring or other functions cannot be used after a successful login to the LMT, and
an error message is displayed.
Context
The error message is shown in Figure 9-3. After clicking Details, detailed error information
is displayed. You need to correct the error based on the error type.
Figure 9-3 The error message dialog box
If the java.lang.ClassNotFoundException error is displayed, perform steps 1 and 2.
Figure 9-4 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException error
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
If the netscape.javascript.JSException error is displayed, perform Step 3.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
253
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Figure 9-5 netscape.javascript.JSException error
If this problem occurs in Citrix Farm networking, you need to perform related steps on
the Citrix Farm server rather than on the local PC. If you have no permission to log in to
the Citrix Farm server, you cannot directly access Windows Control Panel on the Citrix
Farm server. To access it, right-click the Java icon on Windows system tray on the local
PC and choose Open Control Panel from the short-cut menu. The following figure
shows the window:
Figure 9-6 Opening control panel
This problem is caused by a Java defect. For details about this defect, visit http://
bugs.sun.com/bugdatabase/view_bug.do?bug_id=6967414.
Procedure
Step 1 Enable the next-generation Java plug-in again.
1.
Open Control Panel in the Windows operating system and double-click Java. The Java
Control Panel dialog box is displayed. In the Java Control Panel dialog box, click the
Advanced tab, clear Enable the next-generation Java Plug-in (requires browser
restart) under Java Plug-in and click OK.
2.
Select Enable the next-generation Java Plug-in (requires browser restart) by
referring to Step 1.1 and click OK.
3.
Restart the browser to enable the new setting to take effect.
Step 2 Delete temporary Java files.
If this problem persists after performing Step 1, delete temporary Java files.
1.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Open Control Panel in the Windows operating system and double-click Java. The Java
Control Panel dialog box is displayed.In the displayed Java Control Panel dialog box,
click Setting, as shown in Figure 9-7.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
254
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Figure 9-7 Checking the amount of disk space set for storing temporary files
2.
Check the amount of disk space used for storing temporary Java files in the directory
where temporary Java files are saved. If this amount is greater than the preset one, delete
folders in this directory manually or by clicking Delete Files shown in the figure above.
NOTE
Before deleting folders in this directory, close all running LMT clients.
3.
Log in to the LMT again to check whether this problem is solved.
Step 3 Install Windows operating system patch KB960714, for more details please see 9.15 How to
Install OS Patches.
If this problem cannot be solved by performing the above steps, uninstall and reinstall Java.
----End
9.17 What Do I Do If There Is No Response or Any Error
Message After a Tracing, Monitoring or Other Task Is
Created
Some time after a successful login to the LMT, you may suddenly find that batch processing
fails with no error message. Alternatively, after a tracing or monitoring task is created, the
task page is not opened. There is no response or any error message. The NE task list shows
that this task has been successfully created. Or right-click in the message browsing window
and choose save messages, the Save dialog box is not displayed. If you open a new browser
and log in to the LMT again, the task nevertheless can be successfully created. If either of the
previous problems occurs, perform the following operations.
Procedure
Step 1 Open Control Panel in the Windows operating system and double-click Java. The Java
Control Panel dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
255
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Step 2 In the displayed Java Control Panel dialog box, click the Advanced tab.
l
If the Java plug-in of version 1.6 is installed, choose Security > SecurityMixed code
(sandboxed vs. trusted) security verification, and select Disable verification (not
recommended).
If the Java plug-in of version 1.7 or 1.8 is installed, choose SecurityMixed code
(sandboxed vs. trusted) security verification, and select Disable verification (not
recommended).
Step 3 Close all browsers and log in to the LMT again.
----End
9.18 How to Handle the Problem That Only the Error Code
Is Displayed in an Error Message After a Tracing or
Monitoring Task Is Created
Messages related to base station errors have been configured. However, the local maintenance
terminal (LMT) displays only the error code rather than the error message when a base station
error occurs. If the previous problem occurs, perform the following operations:
Procedure
Step 1 Open Control Panel in the Windows operating system and double-click Java. The Java
Control Panel dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 In the displayed Java Control Panel dialog box, click the Advanced tab, choose
SecurityMixed code (sandboxed vs. trusted) security verification , and select Disable
verification (not recommended).
Step 3 Close all browsers and log in to the LMT again.
----End
9.19 Any Further Operation Performed When Some LMT
Web Pages Fail to Update Causes the Web Pages to Turn
Blank
Some LMT Web pages fail to update when batch processing, tracing, or monitoring is in use.
Any further operation causes the Web pages to turn blank. If you restart the function, the Web
page returns to normal. To prevent this problem, perform the following operations to add an
environment variable.
Procedure
Step 1 On the LMT PC, select My Computer and right-click Properties from the shortcut menu.
The System Properties dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 In the System Properties dialog box, click the Advanced tab and click Environment
Variables. The Environment Variables dialog box is displayed.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
256
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Step 3 In the Environment Variables dialog box, click New. The New User Variable dialog box is
displayed. In the New User Variable dialog box, set Variable name to
JPI_PLUGIN2_NO_HEARTBEAT and Variable value to 1. Then click OK.
Step 4 In the Environment Variables dialog box, click OK.
Step 5 In the System Properties dialog box, click OK to finish adding the environment variable.
----End
9.20 How to Handle the LMT Exit After Clicking Trace,
Monitor, or Device Maintenance Tab in Window 7
When you have successfully logged in to the LMT, the interface is redirected to the other
interface if you click the Trace, Monitor, or Device Maintenance tab. A few seconds after
the redirection, the interface is automatically redirected to the login window of the LMT and a
login failure message is prompted.
Context
The IERationalEnabler Class plug-in is installed in Internet Explorer when test tools, such as
IBM Rational Functional Tester (RTF), are installed in the PC. The problem can be resolved
by disabling the plug-in.
Procedure
Step 1 Choose ToolsInternet from the menu bar of Internet Explorer.
The Internet dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 Click Manage Add-ons on the Programs tab page.
The Manage Add-ons dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Choose Toolbras and Extensions in the Add-Ins navigation tree. Click IERationalEnabler
Class on the right of the dialog box and disable the plug-in.
Step 4 Close all the opened Internet Explorer and log in to the LMT again.
----End
9.21 How to Handle the Disconnection Between the LMT
and Base Station After the Device Digital Certificate Is
Replaced
During base station deployment using Plug and Play (PnP), device digital certificate addition
or deletion, the local maintenance terminal (LMT) is disconnected from the base station.
Context
In the Internet Explorer, when you log in to the LMT in HTTPS mode, the root certificate of
the new device digital certificate is not imported into the browser when the the device digital
certificate is replaced. Therefore, the browser does not trust the new certificate, and the
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
257
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
security socket layer (SSL) authentication fails. As a result, the connection between the
website and the base station is disconnected.
NOTE
The Firefox browser is not recommended to use in this scene.
Procedure
Step 1 Open the Internet Explorer. Import the root certificate of the new device digital certificate to
the browser before the device digital certificate is replaced. For details, see 9.8 How to Set a
Correct SSL Security Certificate.
Step 2 Close the browser and log in to the LMT again.
----End
9.22 How to Handle Exceptions in the LMT Due to
Insufficient PC Memory
If the memory space for the local maintenance terminal (LMT) PC is insufficient, exceptions
occur when the LMT runs on the PC.
Context
When a PC has been running for a long time or multiple programs occupying huge memory
space are running on the PC, memory usage of the PC almost reaches 100%. In this case, if
the LMT starts, the PC cannot allocate sufficient memory space to the LMT, and exceptions
occur, such as slower user interface (UI) response and unavailability of tracing and
monitoring functions.
Mappings between the PC memory and the number of LMT clients that can simultaneously
start on the PC are as follows:
l
On a PC of 4 GHz memory, 32 LMT clients can simultaneously start.
On a PC of 2 GHz memory, 16 LMT clients can simultaneously start.
On a PC of 1 GHz memory, eight LMT clients can simultaneously start.
On a PC of 512 MHz memory, four LMT clients can simultaneously start.
NOTE
The preceding mappings are obtained when no other software is running on the PC and only basic
functions, such as MML, alarm, and device panel, are used on the LMT. When other functions are
running on an LMT such as tracing, monitoring, and batch processing, the LMT will consume over 50
MHz memory on the PC. Therefore, fewer LMT clients can simultaneously start on the PC.
Procedure
Step 1 Log off or restart the PC, or stop programs occupying huge memory space.
Step 2 Log in to the LMT again.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
258
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.23 Error Message "This user session already exists" Upon
Login to LMT
The interface displays an error message this user session already exists upon login to LMT.
Solve the problem by using the method described in the procedure part.
Context
To enhance system security, the client browser uses Cookie to store the session information of
users who have successfully logged in. Due to the session Cookie mechanism, the user
encounters the following problems when using LMT:
l
Problem 1: For the same NE, the user desires to log in to multiple LMTs. After
successfully logging in to the first LMT, the user logs in to the second LMT of the NE,
and the interface displays This user session already exists. This is because all browser
windows opened by the same user share the same session under the session sharing
mechanism of IE8 or IE9 and Firefox enabled by default. As a result, when the user
attempts to repeatedly log in to the LMTs of the same NE, the system determines a
repeated login of the same user session. For the IE6/7 browser in which each browser
window uses independent sessions, this problem does not arise.
Problem 2: The LMT interface displays the error This user session already exists, while
the user has not carried out the operation described in Problem 1. This is because the
previous session information remains valid due to an abnormal exit from LMT. As a
result, the LMT determines a repeated login attempt when the same user tries to login to
the LMT. This problem arises when the browser automatically recovers from breaking
down during use of the LMT, or when the pop-up LMT window is blocked by the
browser pop-up blocker enabled.
Problem 3: After you use the Internet Explorer (IE) to log in to the LMT, and then enter
the IP address of the eNodeB into the Windows Explorer to open the IE, the message
This user session already exists is displayed. This problem is caused by the conflict of
the IE sessions created in both manners. This problem exists on all IE browsers.
For Problem 1, the following method is used:
Procedure
In the menu bar of the IE browser, click File > New Session, to start a new IE browser
window and log in to the LMT.
NOTE
This method applies only to the IE8 or IE9 browser, not Firefox. Users of the Firefox browser can log in
to only one LMT of a single NE.
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
For Problem 2, the following method is used:
a.
Close all currently opened browser windows to make the previous session
information invalid.
b.
If the pop-up blocker is enabled for the browser, disable it.
c.
Restart the browser and log in to LMT.
For Problem 3, the following method is used:
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
259
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
The IE8/9 browser user needs to click File > New Session in the menu bar of the
browser, to start a new IE browser window and log in to the LMT.
----End
9.24 Interfaces for Performing Tracing or Monitoring
Tasks Blinking
Interfaces for performing tracing or monitoring tasks blink.
Context
Java Applet in the IE browser is incompatible with HTML elements when they are stacked
together. As a result, interfaces (stacked in the Java Applet) for performing tracing and
monitoring tasks blink. This problem does not affect the function but deteriorates user
experience.
Procedure
l
To avoid this problem, use the following methods:
a.
This problem occurs only on the IE browser. Use the Firefox browser to avoid this
problem.
b.
This problem occurs only on Java later than the version of 1.6.21. Visit
www.oracle.com and download Java SE Runtime Environment 6u21 or an earlier
version to avoid this problem.
----End
9.25 The web site's certificate cannot be verified.Do you
want to continue? Is Displayed During Tracing or
Monitoring
During initialization of a task such as tracing or monitoring on the LMT, "The web site's
certificate cannot be verified.Do you want to continue?" is displayed.
Context
If the certificate of the U2000 proxy server or base station is not Java authenticated,
verification on the website fails. In this case, the dialog box is displayed when the Java Virtual
Machine (JVM) requests the verification for the website from which the Java archive (JAR)
file is downloaded.
Procedure
Step 1 Select Always trust content from this publisher., and then click Yes.
Step 2 Import the CA certificate by referring to 9.8 How to Set a Correct SSL Security Certificate.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
260
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
NOTE
Log in to the base station through the U2000 proxy server, and click Logout at the upper right to switch
to the LMT login interface for downloading or importing the CA certificate.
----End
9.26 Batch Execution of MML Commands Fails Because
Some MML Commands Contain Invisible Carriage
Returns or Line Feeds
After line feeds (LF) are deleted from MML command scripts copied to Batch, command
execution fails.
Context
Copy the MML commands failing to be executed to an UltraEdit file. It is found that these
to view these MML
MML commands are displayed in two lines. In UltraEdit, click
commands in the binary format. A redundant carriage return (CR) 0x0D stays at the LF
location of the MML command each. See Figure 9-8.
Figure 9-8 Viewing an MML command in the binary format using UltraEdit
In the Windows operating system (OS), the CR 0x0D and LF 0x0A must be used pairwise.
The unpaired CRs or LFs cannot be deleted. As a result, the MML commands fail to be
executed.
Procedure
Step 1 Copy the MML commands failing to the executed to an UltraEdit or notepad file and delete
all LFs and CRs. Then, copy these commands back to Batch and execute them again.
----End
9.27 How to Handle Shortcut Key Invalidation
Shortcut keys are defined on the LMT. When logging in to the LMT through a web page, you
may fail to use the corresponding function by pressing a shortcut key. In this case, the shortcut
key becomes invalid. For example, you cannot stop pinging by pressing Ctrl+Q in the MML
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
261
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Command window. This is because the same shortcut key is preferentially used by another
running program on the PC, which leads to a shortcut key conflict.
Procedure
Step 1 Check all running programs on the PC. Find the program using the same shortcut key settings
as the LMT.
Step 2 Modify the program shortcut key settings which are the same as those on the LMT or stop the
program when you use the LMT.
----End
9.28 What Do I Do If A Message "Stop running this
script?" Is Displayed?
This section describes how to solve the problem that a message "Stop running this script?" is
displayed during script execution on the LMT.
Context
When it takes a long time to execute certain scripts, you are prompted with the message "Stop
running this script?", indicating whether to continue the script execution.
To solve this problem, download the file at http://download.microsoft.com/download/
5/9/5/595D11B8-A0FD-4EA0-BF0D-F113258FC28A/MicrosoftFixit50403.msi.
Procedure
Step 1 Install the downloaded file.
Step 2 Restart the computer, and then log in to the LMT to check whether this problem has been
solved.
----End
9.29 The Internet Explorer Fails to Respond or the Login
Window Is Displayed After the LMT Is Running for a
While or Multiple Functions Are Concurrently Enabled on
the LMT
The Internet Explorer fails to respond or the login window is displayed after the LMT is
running for a while or multiple functions are concurrently enabled on the LMT. Solve the
problem by using the method described in the procedure part.
Context
If the LMT installed with multiple network adapters, the problem mentioned above may
occur. For Internet Explorer's failing to respond, the check result of the task manager shows
that the virtual memory occupied by the Internet Explorer process exceeds 1 GHz. For the
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
262
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
displayed login window, the check result of the task manager shows the Internet Explorer
progress for the LMT window has been abnormally closed. In this case, the automatic
recovery mechanism of the Internet Explorer displays the last access webpage when you open
the Internet Explorer again.
Procedure
l
Log in to the LMT through a Firefox browser. The Firefox browser versions 10.x, 17.x,
and 24.x are supported.
If the LMT is running Windows 7, log in to the LMT through Internet Explorer 9.0.
----End
9.30 A Message checking client environment... Is
Displayed on the Login Window and the browser Does
Not Respond
During the login to the WebLMT, a message "checking client environment..." is displayed
on the login window and the browser does not respond and has to be forcibly closed. In this
case, solve the problem by using the method described in the procedure part.
Context
After the WebLMT is started, the software environment of the client is checked, including the
versions and basic settings of Java applications, Adobe Flash Player, and browser. If the
browser does not respond, faults occur on the software.
Procedure
Step 1 If all the preceding software settings are correct, uninstall all Java applications on the client
by performing the following steps:
1.
Choose Start > Control Panel. The Control Panel is displayed. Double-click Add or
Remove Programs in the displayed window. The Add or Remove Programs dialog
box is displayed.
2.
Right-click the Java application and choose Uninstall.
3.
Remove the registry entry HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\JavaSoft and
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\JavaSoft.
4.
Remove files under the C:\Program Files\Java directory.
5.
Install the Java application of the recommended version that can be obtained from http://
java.com/.
Step 2 After Java applications are successfully installed, log in to the WebLMT again.
Step 3 If the problem persists, download and then reinstall Adobe Flash Player of the latest version.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
263
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
9.31 LMT Login Window Being Stopped by the Browser
The LMT login window is stopped by the browse, and the login stills fails even though the
user selects Allow popups. To solve the problem, perform the following steps:
Procedure
l
IE browser
a.
Choose Tool > Internet Options on the tool bar of the IE browser. The Internet
Options dialog box is displayed.
b.
On the Privacy tab page, clear Turn on Pop-up Blocker in the Pop-up Blocker
pane. Or, select Turn on Pop-up Blocker, and click Settings to add allowed
websites.
c.
Click OK. Close the browser and log in to the LMT again.
FireFox browser
a.
Choose Tool > Options on the tool bar of the FireFox browser. The Options dialog
box is displayed.
b.
On the Content tab page, clear Block popup windows. Or, select Turn on Pop-up
Blocker, and click Exceptions to add allowed websites.
c.
Click OK. Close the browser and log in to the LMT again.
----End
9.32 The Application Blocked by Security Settings Dialog
Box Is Displayed When Batch Processing, Tracing,
Monitoring, or Device Maintenance Is Enabled
After the JRE is installed or upgraded, the Application Blocked by Security Settings dialog
box is displayed when the tab page related to batch processing, tracing, monitoring, or device
maintenance is open. Click OK, and the The application cannot be run dialog box is
displayed, indicating that the batch processing, tracing, monitoring, or device maintenance
function is unavailable.
Context
A function is introduced to the JRE later than Java 1.7. 10 to control when and how to run
untrusted Java applications contained in a web page. The untrusted Java application refers to
an application with digital signature applied by an unknown issuer or without a certificate
issued by a trusted certificate authority. The default security level is set to High, indicating
that the untrusted Java applications will be blocked.
Procedure
Step 1 Reconfigure the Java security level or add Exception Site List.
l
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
On the Control Panel page, click Java. In the displayed Java Control Panel dialog
box, click Security. On the displayed Security tab page, select Enable Java content in
the browser, set Security Level to Medium, and then click Apply.
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
264
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
NOTE
The step applies only to the JRE 1.7 or an earlier version.
Alternatively, click Edit Site List on the Security tab page in the Java Control Panel
dialog box to add the sites accessing the LMT to the site list. If this method is used, the
Java security level does not need to be reconfigured. For the sites added in the site list,
mark whether the access to the LMT through HTTPS or HTTP. For example, https://
10.20.198.33 or http://10.30.192.60.
Step 2 Specify Enable the next-generation Java Plug-in(requires browser restart).
1.
In the Java Control Panel dialog box, click Advanced. On the displayed Advanced tab
page, select Java Plug-in, clear Enable the next-generation Java Plug-in(requires
browser restart), and then click OK.
2.
Select Enable the next-generation Java Plug-in(requires browser restart) according
to operations in step 2.a, and click OK.
3.
Restart the browser to make the settings take effect.
Step 3 Delete temporary Java files.
1.
In the Java Control Panel dialog box, click General. On the displayed General tab
page, click Settings. The Temporary Files Settings dialog box is displayed.
2.
Close all running LMT windows and click Delete Files.
Step 4 Log in to the LMT again. When enabling any of the batch processing, tracing, monitoring,
and device maintenance functions, select I accept the risk and want run this application on
the displayed Do you want run this application? dialog box and click Run. If the Allow
access to the following application from this web site? dialog box is displayed, click Allow.
----End
9.33 Help for Installing and Using the Java Plug-in
The Java plug-in used by LMT modules, including Batch, Trace, Monitor, and Device
Maintenance, is the Java runtime environment(JRE). You need to install the Java plug-in
before using these modules. You can try the following methods to solve problems about
installing or using Java plug-in.
Context
When a user logs in to the LMT, it checks the version of the installed java plug-in. The
following problems may occur when a user logs in to or use the LMT:
1.
A tooltip with the message "java plug-in is not found" is displayed on the login interface.
2.
A tooltip with the message "please download and install the recommended Java plug-in"
is displayed on the login interface.
3.
LMT modules, including Batch, Trace, Monitor, and Device Maintenance, cannot be
used even after the java plug-in of a recommend version is installed.
For the first problem, perform the following steps to check whether the java plug-in is
successfully installed:
Procedure
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
265
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
a.
On the windows system, click StartRun, enter CMD in the text box, and press the
Enter key. Enter java -version in the run window and press the Enter key to view the
current java plug-in version.
NOTE
You can log in to the LMT even if the Java plug-in is not installed, but LMT modules, including
Batch, Trace, Monitor, and Device Maintenance cannot be used. You can obtain the Java plug-in
from the official website of Java.
b.
If Java plug-ins of multiple versions are installed on the computer, the current active
Java plug-in version can be viewed on the Java control panel. Select Control
PanelJava, and click the Java icon to display the Java control panel. Select the
Java tab page, click View, and click the User tab page in the displayed window to
view and select the Java plug-in version.
NOTE
You may view the Java plug-in version on the Java control panel even when this plug-in has been
uninstalled. Therefore, ensure that the selected Java plug-in version is available.
When Java plug-ins of more than one version are installed on the computer, they may be
incompatible. You are advised to uninstall the java plug-ins of versions that are not required and
use the recommend version. You can install or uninstall Java plug-ins on the Windows control
panel.
c.
If the Java plug-in is successfully installed and you are using the IE browser, you
can ignore the tooltips and continue using the LMT. You can also try to clear the
tooltips using the following methods:
n
If you are using IE browser, choose ToolsManage Add-ons. In the displayed
window, click Toolbars and Extensions, select All add-ons in the Show
combo box and ensure that the plug-ins Deployment Toolkit and isInstalled
Class are enabled.
If you are using Firefox browser, open the Add-ons window, select the
Plugins tab page, and ensure that the installed Java plug-in is enabled.
Restart the browser, and log in to the LMT again.
NOTE
If the Java plug-in is enabled in the IE browser and the tooltips still exist, choose ToolsInternet
Options , select the Advanced tab page, and click Reset.
The second problem indicates that you have installed a Java plug-in not supported by the
LMT. You can continue using the LMT, but some modules, including Batch, Trace,
Monitor, and Device Maintenance, may become abnormal. You are advised to install the
Java plug-in of a recommended version.
NOTE
The Java plug-in of version 1.7.0.55 is recommended for the SRAN9.0 LMT, the Java plug-in of
version 1.7.0.65 is recommended for the SRAN10.0 or SRAN10.1 LMT, and the Java plug-in of version
1.8.0.45 is recommended for the SRAN11.0 LMT. The SRAN9.0 and that of a later version also
supports JRE 1.6. If the LMT of SRAN7.0 and that of a later version are used simultaneously, JRE
1.6.0.27 is recommended.
When a Java plug-in of a later version has been installed, a java plug-in of an earlier version installed
afterward will not be activated. Tooltips with the message "please download and install the
recommended Java plug-in" will also be displayed on the login interface even if the earlier version is
supported by the LMT. If you need to activate the Java plug-in version of the earlier version, first
uninstall the one of the later version.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
As for the third problem, the Java applet is forbidden by default because the security is
enhanced in JRE 1.7. Some tooltips will also be displayed before the applet is executed.
You can try the following methods to solve this problem:
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
266
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Click the Java icon in the Windows control panel and select the Security tab page
in the Java control panel. Set Security Level to Medium or add the current website
to Exception Site List.
If JRE 1.6 and JRE 1.7 are installed simultaneously on the computer. A dialog box
may be displayed for selecting the appropriate Java plug-in version to execute the
applet.
If the Application Blocked by Security Settings dialog box is displayed, or an
error message is displayed on the LMT interface, you can reconfigure Java
security level or Exception Site List.
When other exceptions occur, you can try to delete temporary java files. Open the
Java Control Panel dialog box, select the General tab page, and click Settings.
The Temporary Files Settings dialog box is displayed. Close all running LMT
windows and click Delete Files.
----End
9.34 What Do I Do If the Message Your Java version is out
of date Is Displayed?
If you are prompted that Your Java version is out of date when logging in to the WebLMT,
follow the instructions provided in this session.
Context
The JRE installed on the computer is not up-to-date and an update to the latest version is
recommended by Java. To ensure that the WebLMT works properly, it is good practice to
perform the procedure described below.
Procedure
Step 1 In the Your Java version is out of date dialog box, select the Do not ask again until the
next update is available check box.
Step 2 Click Later.
----End
9.35 How to Configure Wireless NIC on a Computer
To connect a computer to a local wireless access point device, ensure that the computer is
configured with a WLAN wireless network interface card (NIC). Before connecting the
computer to a local wireless access point device, configure WLAN wireless NIC by following
the instructions below.
Context
This section uses a laptop configured with a wireless NIC and running Window 7 as an
example.
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
267
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
9 FAQ
Procedure
Step 1 Click Start, select Control Panel.
Step 2 Perform the following operations according to the value of View by:
l
If Category is selected, click Network and Internet. In the displayed window, click
Network and Sharing Center.
If Large icons or Small icons is selected, click Network and Sharing Center.
Step 3 Click Change adapter settings.
Step 4 In the display windows, right-click wireless and choose Properties.
A wireless Properties dialog box is displayed.
Step 5 On the Networking tab page, double-click Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4).
The Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4) Properties dialog box is displayed.
Step 6 On the General tab page, choose Use the following IP address. In IP address, enter an IP
address, which is in the same network segment together with the default maintenance IP
address of the base station. For example, 192.168.1.2. In Subnet mask, enter 255.255.255.0,
In default gateway, enter 192.168.1.1.
NOTE
l For the purpose of security, the IP address of the wireless NIC must be manually configured in this
step.
l The default maintenance IP address of the base station is 192.168.1.49.
l IP address mentioned in step 5 cannot be set to 192.168.1.49.
Step 7 On the wireless tab page, check for the SSID. If the SSID is not found, click
side.
on the right
Step 8 Choose the SSID, such as HID_9TAB198910, and then click Connect on the bottom.
NOTE
The SSID of the local wireless access point device is in the format of HID_XXXXXXXXXX.
Step 9 If the status of the wireless network is Connected, and the ping 192.168.1.49 command is
successfully executed, the terminal successfully connects to the wireless network.
----End
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
268
3900 Series Base Station
LMT User Guide
Index
Index
Issue 05 (2015-12-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
269
You might also like
- 3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide (V100R009C00 11) (PDF) - enDocument263 pages3900 Series Base Station LMT User Guide (V100R009C00 11) (PDF) - enmirs67% (3)
- WebLMT HelpDocument12 pagesWebLMT HelpJoão LopesNo ratings yet
- BBU3900 User Guide (V200 - 05)Document88 pagesBBU3900 User Guide (V200 - 05)Lovasoa Ralaivao100% (1)
- BBU3900 Hardware Description (V100R008C00 - 05) (PDF) - enDocument132 pagesBBU3900 Hardware Description (V100R008C00 - 05) (PDF) - enIbrahim Al-Taie100% (3)
- Web LCT Installation Guide: 4 Step ProcessDocument10 pagesWeb LCT Installation Guide: 4 Step ProcessJennis Sherano FernandoNo ratings yet
- Huawei BTS Field Commissioning GuideDocument78 pagesHuawei BTS Field Commissioning GuideKumar Yuv100% (6)
- 3900 Series Base Station Configuration Principles (SRAN9.0 - 13) (PDF) - enDocument236 pages3900 Series Base Station Configuration Principles (SRAN9.0 - 13) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (2)
- RRU3829 DescriptionDocument10 pagesRRU3829 DescriptionMarco MatteucciNo ratings yet
- BBU3900 User Guide (V200 - 04)Document72 pagesBBU3900 User Guide (V200 - 04)Anuradha ThilakarathnaNo ratings yet
- Downgrade UMPT Software From R13 To R12Document8 pagesDowngrade UMPT Software From R13 To R12JunedyNo ratings yet
- Description For UMPTe and UBBPe BoardDocument16 pagesDescription For UMPTe and UBBPe BoardHasnain Muhammad100% (4)
- Base Station Cabinets and Subracks (Including The BBU Subrack) Configuration (SRAN12.1 - 02)Document81 pagesBase Station Cabinets and Subracks (Including The BBU Subrack) Configuration (SRAN12.1 - 02)anthony100% (1)
- UMPT and All Boards Huawei QuipDocument88 pagesUMPT and All Boards Huawei QuipdragosNo ratings yet
- ALU FDD LTE eNB Commissioning ProcedureDocument11 pagesALU FDD LTE eNB Commissioning Procedurenoelcnl100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Flexi Zone Micro BTSDocument51 pagesTroubleshooting Flexi Zone Micro BTSDidier Sepulveda100% (1)
- RRU3824&RRU3826 Installation Guide (07) (PDF) - enDocument129 pagesRRU3824&RRU3826 Installation Guide (07) (PDF) - enTiffany Young100% (1)
- BBU3900 Description PDFDocument20 pagesBBU3900 Description PDFbinoNo ratings yet
- SJ-20200606171511-001-ZXMW NR8250 (V3.05.02) System Description - 980966Document119 pagesSJ-20200606171511-001-ZXMW NR8250 (V3.05.02) System Description - 980966مهدي مهديNo ratings yet
- Install Web LMTDocument6 pagesInstall Web LMTpr3m4nNo ratings yet
- BBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 01) (PDF) - enDocument196 pagesBBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 01) (PDF) - enMyce Elu100% (3)
- Guide To Configuration File Upload & Download Using Web LMT For BTS3900Document8 pagesGuide To Configuration File Upload & Download Using Web LMT For BTS3900Abouelhassan GalalNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 V100R010C00 Commissioning Guide 02Document218 pagesRTN 950 V100R010C00 Commissioning Guide 02Anonymous 8RFzObvNo ratings yet
- ATN 910&910I&910B&950B V200R003C10 Configuration Guide 01 (U2000) PDFDocument636 pagesATN 910&910I&910B&950B V200R003C10 Configuration Guide 01 (U2000) PDFMiky CCis100% (1)
- Huawei OptiX PTN 950 Commissioning Guide (V100R005)Document106 pagesHuawei OptiX PTN 950 Commissioning Guide (V100R005)Thunder-Link.com100% (1)
- MTS9300A V100R002C00 Telecom Power Installation GuideDocument129 pagesMTS9300A V100R002C00 Telecom Power Installation GuideJames Mota.No ratings yet
- ZXMW NR8000 SplitDocument2 pagesZXMW NR8000 SplitМөнхзаяа ЛхайжавNo ratings yet
- Nodeb LMT User Guide (v200r013 - 04) (PDF) - enDocument205 pagesNodeb LMT User Guide (v200r013 - 04) (PDF) - enpr3m4n100% (5)
- ICC500 Power Cube ManualDocument47 pagesICC500 Power Cube Manualmukaram1128100% (1)
- Huawei NodeB Commission Procedure GuidelineDocument22 pagesHuawei NodeB Commission Procedure GuidelinesamNo ratings yet
- MPT Boards (WMPT & Umpt) Configuration StepsDocument14 pagesMPT Boards (WMPT & Umpt) Configuration StepsEniafe S. B.100% (1)
- Backup Configuration Alfoplus80hd Ags-20 Alfoplus2 - r1Document9 pagesBackup Configuration Alfoplus80hd Ags-20 Alfoplus2 - r1mahdimecarniNo ratings yet
- Guide To UMPT Board Replacement ForDocument23 pagesGuide To UMPT Board Replacement ForPhilip Saunders100% (1)
- Smu02b User Manual v200r001c00 02 PDFDocument209 pagesSmu02b User Manual v200r001c00 02 PDFHUyNo ratings yet
- Enodeb LMT User Guide (v100r004c00 - 01) (PDF) - enDocument139 pagesEnodeb LMT User Guide (v100r004c00 - 01) (PDF) - enala_a_silawiNo ratings yet
- BBU Interconnection (SRAN15.1 02)Document49 pagesBBU Interconnection (SRAN15.1 02)VVL1959No ratings yet
- SJ-20201130103457-003-ZXMW (V3.05.03) Maintenance Guide - 1013679Document68 pagesSJ-20201130103457-003-ZXMW (V3.05.03) Maintenance Guide - 1013679مهدي مهديNo ratings yet
- Huawei Imanager U2000 Web LCT V200R018C60 User Guide 03Document181 pagesHuawei Imanager U2000 Web LCT V200R018C60 User Guide 03julu paezNo ratings yet
- ENodeB Commissioning Guide LMT ERAN3.0SPC340 Version1.1 For South Africa Telkom Project 20121112Document13 pagesENodeB Commissioning Guide LMT ERAN3.0SPC340 Version1.1 For South Africa Telkom Project 20121112Sedjali Ali-MustaphaNo ratings yet
- 3900 Series Multi-Mode Base Station Commissioning Guide (PDF) - ENDocument280 pages3900 Series Multi-Mode Base Station Commissioning Guide (PDF) - ENadramat1085No ratings yet
- 19-Inch Rack Installation Guide (01) (PDF) - enDocument164 pages19-Inch Rack Installation Guide (01) (PDF) - enюрий ермошенкоNo ratings yet
- BTS3900 External Alarm MonitoringDocument16 pagesBTS3900 External Alarm MonitoringkikirnNo ratings yet
- Microwave-bc-En-zxmw Nr8250 v1.00 Commissioning GuideDocument105 pagesMicrowave-bc-En-zxmw Nr8250 v1.00 Commissioning GuideOmingo Kingi100% (1)
- 9500 MPR R6 1 0 Release NoticeDocument76 pages9500 MPR R6 1 0 Release NoticeddNo ratings yet
- MANUAL Web LCTDocument18 pagesMANUAL Web LCTpr3m4nNo ratings yet
- BTS3900 (Ver.D) Installation Guide (V100R009C00 - 03) (PDF) - enDocument175 pagesBTS3900 (Ver.D) Installation Guide (V100R009C00 - 03) (PDF) - enEugeneNo ratings yet
- WDT Introdution: Wireless Deployment Tool OverviewDocument41 pagesWDT Introdution: Wireless Deployment Tool Overviewquykiem02No ratings yet
- LTE eNodeB V2 1 CommissioningDocument26 pagesLTE eNodeB V2 1 CommissioningFerry KurniawanNo ratings yet
- ZTE LMT-Installing LMT and Upgrade VersionDocument18 pagesZTE LMT-Installing LMT and Upgrade VersionMuhammad Kashif100% (8)
- RRU5909&RRU5309&RRU5309w&RRU3959a Installation GuideDocument123 pagesRRU5909&RRU5309&RRU5309w&RRU3959a Installation GuideDmitry059No ratings yet
- BTS Antenna System Installation Guide RET V300R009 01Document143 pagesBTS Antenna System Installation Guide RET V300R009 01Moo Ping100% (1)
- RTN 950 V100R003C03 Maintenance Guide 05 (U2000)Document834 pagesRTN 950 V100R003C03 Maintenance Guide 05 (U2000)Alvaro Avila Sanchez100% (1)
- HUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware Structure GuideDocument64 pagesHUAWEI BTS3900 Hardware Structure GuideHamid Qazii100% (1)
- RTN 905Document189 pagesRTN 905mabvieira100% (3)
- Hsu PapdDocument41 pagesHsu PapdEfosa AigbeNo ratings yet
- Atm&Ip Dual Stack (Ran16.0 - 01)Document54 pagesAtm&Ip Dual Stack (Ran16.0 - 01)hekriNo ratings yet
- Base Station Cabinets and Subracks (Including The BBU Subrack) Configuration (SingleRAN - 05) PDFDocument75 pagesBase Station Cabinets and Subracks (Including The BBU Subrack) Configuration (SingleRAN - 05) PDFsamuraial100% (1)
- 3900 Series Base Station LMT User GuideV100R009C00 11PDF enDocument263 pages3900 Series Base Station LMT User GuideV100R009C00 11PDF enTibalt INo ratings yet
- 3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (V100R009C00 - 14) (PDF) - enDocument851 pages3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (V100R009C00 - 14) (PDF) - enMd AtaullaNo ratings yet
- Bts3900b GSM User Guide - (v600r009 - 01)Document30 pagesBts3900b GSM User Guide - (v600r009 - 01)Serkan KılınçarslanNo ratings yet
- BTS3900 GSM Hardware Description - (V300R008&009 - 03)Document143 pagesBTS3900 GSM Hardware Description - (V300R008&009 - 03)Eng Amr ElorbanyNo ratings yet
- Concept of Pre-NumberDocument1 pageConcept of Pre-NumberchennileNo ratings yet
- LTE eNB Alarm Manual For PKG 3.1.0 - Ver.1.0 - RIL PDFDocument95 pagesLTE eNB Alarm Manual For PKG 3.1.0 - Ver.1.0 - RIL PDFMd Ataulla100% (1)
- 3900 Series Base Station NodeBFunction Performance Counter Reference (V100R009C00 - 11) (PDF) - enDocument491 pages3900 Series Base Station NodeBFunction Performance Counter Reference (V100R009C00 - 11) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (1)
- 3900 Series Base Station GBTSFunction Performance Counter Reference (V100R009C00 - 11) (PDF) - enDocument22 pages3900 Series Base Station GBTSFunction Performance Counter Reference (V100R009C00 - 11) (PDF) - enMd AtaullaNo ratings yet
- AAU3911 Hardware Description (04) (PDF) - enDocument64 pagesAAU3911 Hardware Description (04) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla64% (11)
- AAU3940 Hardware Description (03) (PDF) - enDocument28 pagesAAU3940 Hardware Description (03) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (5)
- BBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 08) (PDF) - enDocument202 pagesBBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 08) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (1)
- 3900 Series Base Station Node Performance Counter Reference (V100R009C00 - 11) (PDF) - enDocument343 pages3900 Series Base Station Node Performance Counter Reference (V100R009C00 - 11) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (1)
- AAU3920 Hardware Description (02) (PDF) - enDocument38 pagesAAU3920 Hardware Description (02) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (3)
- AAU3910 Hardware Description (07) (PDF) - enDocument46 pagesAAU3910 Hardware Description (07) (PDF) - enMd AtaullaNo ratings yet
- 3900 Series Base Station Hardware Description (02) (PDF) - enDocument863 pages3900 Series Base Station Hardware Description (02) (PDF) - enMd AtaullaNo ratings yet
- 3900 Series Base Station Configuration Principles (SRAN9.0 - 13) (PDF) - enDocument236 pages3900 Series Base Station Configuration Principles (SRAN9.0 - 13) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (2)
- AAU3902 Hardware DescriptionDocument37 pagesAAU3902 Hardware Descriptionestebanarca75% (4)
- 3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (V100R009C00 - 14) (PDF) - enDocument851 pages3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (V100R009C00 - 14) (PDF) - enMd AtaullaNo ratings yet
- 3900 Series Base Station Cables (V100R009C00 - 04) (PDF) - enDocument712 pages3900 Series Base Station Cables (V100R009C00 - 04) (PDF) - enMd AtaullaNo ratings yet
- 3900 Series Base Station eNodeBFunction Parameter Reference (V100R009C00 11) (XLS) - ENDocument7,758 pages3900 Series Base Station eNodeBFunction Parameter Reference (V100R009C00 11) (XLS) - ENMd AtaullaNo ratings yet
- SiemensDocument9 pagesSiemensGhassen Khalil100% (2)
- Closed Source DocumentationDocument12 pagesClosed Source Documentation이즈르엘No ratings yet
- 0 Delphi Labs DataSnap XE CallbacksDocument7 pages0 Delphi Labs DataSnap XE Callbacksduna tarimaNo ratings yet
- Performance Adjustment On Me Engine 20130415Document24 pagesPerformance Adjustment On Me Engine 20130415NAGENDRA KUMAR DONTULANo ratings yet
- Deep Cycle Batteries Solar EbookDocument27 pagesDeep Cycle Batteries Solar Ebookanakraja11No ratings yet
- Haynes 230 Alloy: Principal FeaturesDocument28 pagesHaynes 230 Alloy: Principal FeaturesMatheus DominguesNo ratings yet
- SRM-RMPM Registration Report For EvDocument3 pagesSRM-RMPM Registration Report For EvAAKASH J (RA2111043020035)No ratings yet
- IaaS Product Line Architecture Fabric Architecture GuideDocument112 pagesIaaS Product Line Architecture Fabric Architecture GuideChalks Dreaner Alvino VelaNo ratings yet
- Custom Storage ClassesDocument2 pagesCustom Storage ClassesSameer KumthekarNo ratings yet
- Arkaprava Bhattacharya Civil Engineering Portfolio: Email IDDocument9 pagesArkaprava Bhattacharya Civil Engineering Portfolio: Email IDArkaprava BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Metco®73F-NS-1 (-2) 10-058 PDFDocument7 pagesMetco®73F-NS-1 (-2) 10-058 PDF張政雄No ratings yet
- Wartsila O E W 50DF PG Product GuideDocument180 pagesWartsila O E W 50DF PG Product GuideFábio Almeida100% (1)
- RICOH Streamline NX Guia de UsuarioDocument107 pagesRICOH Streamline NX Guia de UsuarioMaria Elena AvilaNo ratings yet
- Manual VISSIM 540 e PDFDocument763 pagesManual VISSIM 540 e PDFEze KA100% (1)
- Analysis of Non-Salient Pole Synchronous Generator Using Phasor DiagramsDocument19 pagesAnalysis of Non-Salient Pole Synchronous Generator Using Phasor DiagramsNavitha RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Notification Part-3Document35 pagesNotification Part-3sks65No ratings yet
- PDFDocument76 pagesPDFRavishankarNo ratings yet
- A - Buch PL120106Document84 pagesA - Buch PL120106Cristian Piñeros100% (1)
- Resistance in The Fluid System PDFDocument21 pagesResistance in The Fluid System PDFDyo MandeNo ratings yet
- Zero Escape Virtues Last Reward PDFDocument33 pagesZero Escape Virtues Last Reward PDFfcaicedo7239No ratings yet
- Engineer'S Stamp: Contractor'S Stamp:: Al Qunfudhah New City Feeder Water Transmission SystemDocument7 pagesEngineer'S Stamp: Contractor'S Stamp:: Al Qunfudhah New City Feeder Water Transmission SystemLouis ClarkNo ratings yet
- WindowsITPro Magazine 2013-05Document88 pagesWindowsITPro Magazine 2013-05kflimNo ratings yet
- Pro Line FusionDocument8 pagesPro Line FusionГригорий Омельченко50% (2)
- Sullair AWFDocument4 pagesSullair AWFOscar BedregalNo ratings yet
- IOM Fire Pump & ControllerDocument123 pagesIOM Fire Pump & ControllerPrasanth foustin pereiraNo ratings yet
- Online Treasure Hunt TitleDocument3 pagesOnline Treasure Hunt TitleqoufwsjelmkNo ratings yet
- The Aesthetics of Interactive Music Systems: Robert RoweDocument5 pagesThe Aesthetics of Interactive Music Systems: Robert Rowesertimone0% (1)
- NPD1 - Small Planetary Catalogue - Apr 2020Document39 pagesNPD1 - Small Planetary Catalogue - Apr 2020Shyam J VyasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineer Skill SetDocument2 pagesChemical Engineer Skill SetJunaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Army C-sUAS Systems AssessmentDocument4 pagesArmy C-sUAS Systems AssessmentArthur WongNo ratings yet