Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jigs and Fixtures
Uploaded by
goldencometCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jigs and Fixtures
Uploaded by
goldencometCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 1 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
WEB CHAPTER 5 - JIGS AND FIXTURES
Jig is a structure to locate and clamp a component for guiding the cutting tool in
operationslikedrilling,reaming,etc.Theyareusedforinspectionalso.
The work is located for machine operations by different types of locating devices.
Clampingforcesduetofrictiononlycannotberelieduponcompletely.Acylindricalpin
is the cheapest and easy locator. Cylindrical bush locators are used for solid work
pieces,butconicallocatorsarepreferred,becausetheyofferselfcentering.Vblockscan
beusedforcylindricalaswellasrectangularobjects
Clamping of the work piece is necessary in addition to location, otherwise it may move
duetocuttingforces.Toreducethewearofclampingdeviceswithcontinuoususe,they
arehardened.Iftherearechancesofdamagingthesurfaceoftheworkpiece,asoftnose
canbeprovidedontheclamp.Thevarioustypesofclampingdevicesare:
Abarclampusesasimplebarhavingaholeinthemiddle.Onesideofthebarisplaced
ontheworkpieceandtheotheronaheel.Astudpassesthroughtheholeofthebar,anda
nutoveritclampstheworkpiece.
Athreadedheelhastheadvantagethatitcanbeadjustedtoanyheightaccordingtothe
heightoftheworkpiece.
Aswingingclampusesanarmwhichishingedononesideandslottedontheotherside.
Theworkpieceislocatedbelowthisarm;aswingingboltisfittedintheslotofthisarmto
clamptheworkpiecewithanut.
In a side clamp, the bar clamps the work piece from one side while the other side rests
againstthebodyofthejig.Anarmhavingapinjointatthemiddleandaboltontheother
endclampstheworkpiece.
Inthesideclamp,theclampingforceisproducedbyrotatinganeccentricwiththehelpof
alever.It pushestheVblockandworkpieceisclampedbetweenthejigbodyandblock.
Clampingforceontheclampingdevicecanbegivenbyanyoneofthefollowingmethod:
Thewingnutorknurledknob,studandnut,camsareusefulwheretheclampingforceis
tobeprovidedjustbyrotatingahandleby90degreesorso.Helicalcamcanalsobeused
asanalternate arrangementtotheeccentric.Hydraulicpistonsareusedwhereaheavy
clampingforceisused.
Guides to the cutting tools for the jigs are called as bushings; generally for drilling and
reaming.
Page 2 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
Jigbodyisthemainbody,whichsupportsthebushings,locatingandclampingdevices..
Therearetwocommontypesofjigbodies:opentypeandclosedtype
TypesofJigsarethefollowing:
PlatejigThejigplateisclampedovertheworkpiece.
SwingingleafjigThejigplatecontainingthebushingisswungaboutapin,justforeasy
placementandwithdrawalofthecomponent.
Indexingjigusesanindexingplatetodillholesinpredefinedangularpositions.
Fixture is an aid for manufacturing which is used to hold and locate the job for some
manufacturingoperationbutdoesnotguidethecuttingtool.Fixturescanbeusedforany
machineandareclassifiedaccordingly.
TurningfixtureAlathefixturemaybetoholdatypicalcomponent,whichmaynotfitin
thejawsofachuckinnormalway.
MillingfixtureItmayholdatypicaljobtogethertoreduceclampingandmanufacturing
time.
WeldingfixtureItistolocatetwostructuralmembersforweldingatspecificpositionto
eachother.
W5.1JIG
JigisastructuretoLOCATEandCLAMPacomponentforGUIDINGthecuttingtoolin
operationslikedrilling,reaming,etc.Theyareusedforinspectionalso.
Suppose ahole is to be drilled inclined at 45 degrees in a cylindrical workpiece (Figure
W5.1).Itmaynotbepossibletodrill thisholewithoutthehelpofajig,becausethedrill
bitwillhaveatendencytoslip.Soajigdoesthreethings:
a.Locateandalignthepartattherequiredposition.
b.Clampthepartsothatitdoesnotmoveduetocuttingforceswhilemachining.
c.Guidethetooltoworkontheobject.
Page 3 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5.1Adrillingjig
W5.2LOCATIONDEVICES
Theworkpiecehastobelocatedformachineoperations.Theseoperationsimpartcutting
forces and try to move the work piece from its original position. Clamping forces are
generally due to friction only and cannot be relied upon completely. Hence surfaces to
givethereactiontothecuttingforcesshouldalsoformapartoflocationdevices.Various
typesoflocatingdevicesareshowninFigureW5.2.
Theshape oftheworkpiecedecidesthetypeoflocator to beused.Finishedsurfacesare
generallyusedtolocatetheworkpieceagainstthefinishedsurfaceofthejig.Ifthere isno
finishedsurfaceoftheworkpiece,thenanunfinishedsurfacecanbeused.
Acylindricalpinisthecheapestandeasylocator.Numberofpinscanbeoneormanyfor
accuratelocation.Thesepinsaremadeoftoolsteel,hardenedandground(FigureW5.2A).
Cylindrical bush locators can also be used for solid work pieces (Figure W5.2B), but
conicallocators are preferred,becausethey offer selfcentering (Figure W5.2C). V blocks
canbeused(FigureW5.2D)forcylindricalaswellasrectangularobjects(FigureW5.2E).
Page 4 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5.2Locationdevices
W5.3CLAMPINGDEVICES
As described earlier, clamping of the work piece is necessary in addition to location,
otherwise it may move due to cutting forces. There are a number of clamping devices.
OnlyafewcommonlyusedareshowninFigureW5.3.
Clampingforceshouldbeappliedatapointwhichdoesnotobstructthemanufacturing
process and will offer reaction so as to withstand the forces developed. To reduce the
wearofclampingdeviceswithcontinuoususe,theyarehardened.Iftherearechancesof
damagingthesurfaceofworkpiece,asoftnosecanbeprovidedontheclampwhichcan
bereplaced,whenwornout.Thevarioustypesofclampingdevicesare:
Barclamps(FigureW5.3A)
Adjustablebowclamp(FigureW5.2B)
Swingingbarclamp(FigureW5.3C)
Sideclamp(FigureW5.3D)
Vslide(FigureW5.3E)
Page 5 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5.3Clampingdevices
Barclampusesasimplebarhavingaholeinthemiddle(FigureW5.3A).Onesideofthe
barisplacedontheworkpieceandtheotheronaheelapproximatelyofthesameheight
astheworkpiece.Astudpassesthroughtheholeofthebar.Whenthenutistightened,it
clampstheworkpiece.
Insteadofusingaheeloffixedsize,onecanuseathreadedheel(FigureW5.3B).Ithasthe
advantagethatitcanbeadjustedtoanyheightaccordingtotheheightoftheworkpiece.
Aswingingclamptypejig(FigureW5.3C)usesanarmwhichishingedononesideand
slotted on the other side. The work piece is located below this arm, by lifting it. A
swinging bolt is fitted in the slot of this arm. The nut is tightened over it to clamp the
workpiece.
In a side clamp (Figure W5.3D), the bar clamps the work piece from one side while the
othersiderestsagainstthebodyofthejig.Anarmhavingapinjointatthemiddleanda
Page 6 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
boltonotherendclampstheworkpiecewhentheboltistightened.
FigureW5.3Ealsoshowsasideclamp,buttheclampingforceisproducedbyrotatingan
eccentricwiththehelpofalever.Itclampstheworkpiecequickly.It pushestheVblock
andtheworkpieceisclampedbetweenthejigbodyandblock.
Theforceontheclampingdevicecanbegivenbyanyoneofthefollowingmethods:
Wingnutorknurledknob(FigureW5.4AandB)
Studandnut(FigureW5.4B)
Camsareusefulwheretheclampingforceistobeprovidedjustbyrotatinga
handleby90degreesorso.Useofspiralcamandaneccentricisshowninfigures
W5.4CandW5.4Drespectively.
Helicalcamcanalsobeusedasanalternate arrangementtotheeccentric(Figure
W5.4E).
Hydraulic pistons are used where a heavy clamping force is required
(FigureW5.4F).
Page 7 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5.4Clampingforcemethods
W5.4GUIDES
Guides to the cutting tools for the jigs are called BUSHINGS; generally for drilling and
reaming.Bushesareusedtoguide thecuttingtool.Thesebushesarepressedinto a plate
whichisscrewedtothebodyofthejig.Various typesofbushingsareusedasshownin
FigureW5.5.
FigureW5.5Bushingsforjigs
Page 8 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
Basically bushes are of two types: headless and head type. If the centre between the
adjacent holes is small, then a headless bushing is preferred. Sometimes a liner
is used inside thebushing, whichcanbereplacedwhenthebushiswornandone hasnot
toreplacethecompletebush.
Slip busingisused,ifitistobereplacedfordifferentsizesofdrillsorreamingoperations
afterdrilling.
W5.5JIGBODY
It is the main body, which supports the bushings, locating and clamping devices. There
aretwocommontypesofjigbodies:
Opentype(FigureW5.6A)
Closedtype(FigureW5.6B)
Ifdrillingistobedoneinoneplaneonly,anopentypeofbodycanbeused,butifthejig
is to be used from different directions and planes, a closed type of the body is to be
provided. Figure W5.6 shows two such types of the jig bodies; one open type and the
other,closedtype.
FigureW5.6Jigbodies
Ajigbodyismadeofcastironorsometimesfabricatedbyweldingsteelparts.Thebody
hastoberigidformaintainingtheaccuracy.Sharpcornersandedgesshouldbeavoided
forthesafetyoftheoperator.Smallsizeofthejigscanbefixed onthetable,butlargejigs
shouldbeprovidedbymeansoffixingonthemachinesecurely.
Page 9 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
Opentypeofjigscanbefurtherclassifiedas:
A.PlatejigThejigplateisclampedovertheworkpiece(FigureW5.7A)
B.SwingingleafjigThejigplatecontainingthebushingcanbeswungaboutapin,just
foreasyplacementandwithdrawalofthecomponent(FigureW5.7B).
C. Indexing jig It uses an indexing plate to dill holes in predefined angular positions
(FigureW5.7C).Theindexingplate iskeptinpositionbyaspringloadedplunger.
FigureW5.7Typesofjigs
Page 10 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
W5.6FIXTURES
It is an aid for manufacturing which is used to HOLD and LOCATE the job for some
manufacturingoperationbutdoesNOTGUIDEthecuttingtool.Fixturescanbeusedfor
anymachineandareclassifiedas:
Lathefixture
Millingfixture
Weldingfixture
W5.6.1LATHEFIXTURE
A lathe fixture may be to hold a typical component, which may not fit in the jaws of a
chuckinthenormalway.Turningfixturescanbeheldinthejawsofthechuckorcanbe
mountedonthefaceplateofthelathe.
A bracket is shown in Figure W5.8 in which two holes are to be drilled at the position
indicated in the figure. It can be seen, that this component cannot be put on a lathe
chuck easily. A special fixture to hold it is shown in Figure W5.8B. An angled block is
bolted on the front side of the face plate and then the work piece is clamped on it. A
balanceweightismounted to avoidunbalancedforcesonthelathespindle.
Page 11 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5.8Alathefixture.
W5.6.2MILLINGFIXTURE
A milling fixture may hold a typical job together to reduce clamping nda manufacturing
time. A setting block is used in conjunction with the holding device to achieve correct
alignment of the tool with respect to the component and accuracy of machining. Figure
W5.9 shows a milling fixture to make slots on a component as shown in Figure W5.9A.
Fourpiecescanbe positionedsimultaneouslytomilladiagonalslot.
Page 12 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5.9Amillingfixture
W5.6.3WELDINGFIXTURE
FigureW5.10showsaweldingfixturetolocatetwostructuralmembers(angleirons)for
weldingat30toeachothertoagussetplate.
FigureW5.10AWeldingfixture
Page 13 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
THEORYQUESTIONS
Q.1.Differentiatebetweenajigandfixture.
Q.2.Whatistheimportanceofalocator? Describedifferenttypesoflocators.
Q.3.Whyisclampingnecessaryinajig?Explainanyfourtypesofclampingdevices.
Q.4.Whatisthefunctionofabushinajig?Discussvarioustypesofbushesusedinajig.
Q.5.Explainthedifferenttypesofjigbodies.Givethetypicaluseofeach.
Q.6.Sketchanyturningfixtureandexplainitsconstruction.
Q.7.Explaintheconstructionanduseofamillingfixture.
Q.8.Describeandsketchaweldingfixtureforanytypicalwork.
FILLUPTHEBLANKQUESTIONS
Q1 Ajigisusedfor__________._____________and___________.
Q2. Fixtures__________tofixajob.
Q3. Swingingbarisa______________device.
Q4. ____________areusedwhereaheavyclampingforceisrequired.
Q5. Aneccentriccanbeusedasaclampingdevicefor____________clamping.
Q6. Bushingsareusedas____________injigs.
Q7. ____________isusedifitistobereplacedfordifferentoperations.
Q8. Twoimportantjigbodiesare:____________and____________.
Q9. ____________jigisusedtolocateangularpositions.
Q10.Fixtureholdsandlocatesthejobbutdoesnot____________.
Q11. Millingfixturecanbeusedtohold____________simultaneously.
Q12. Weldingfixturehelpsto____________thepartstobewelded.
MULTIPLECHOICEQUESTIONS
Q1Ajigisusedto
a.drillahole
b.locateandclampaworkpiece
c.locate,clamptheworkpieceandguidethecuttingtool
d.settheworkpieceformeasurement
Q2.Commonfeaturebetweenjigandfixtureisthatbothareusedfor
a.cuttingtheworkpiece
b.holdingtheworkpiece
c.locatingtheworkpiece
d.testingandinspectionoftheworkpiece
Page 14 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
Q3.Slipbushisusedinjigwhere
a.thedrillbitcanslipontheworkpiece
b.holesaretooclose
c.thebushistobereplacedeverytime
d.alinerisusedalongwithbush
Q4Linerinabushofajig
a.savesthebushfromwear
b.strengthensthebush
c.offerslubrication
d.alignsthebushinahole
Q5Acamisusedinajigto
a.locatetheworkpiece
b.liftaheavyworkpiece
c.movetheworkpiecefrequently
d.toclamptheworkpiece
Q6Aturningfixtureisusedonthelathe
a.toturnanonsymmetricjob
b.sothatthesurfacefinishoftheworkpieceisnotspoiled
c.toturntheworkpiecewhichotherwisecannotbefittedonthelathe
d.toturnlongjobs
Q7Anindexingjigisusedto
a.planesurfaces
b.oneangularsettings
c.multiangularsettings
d.multiplanesettings
Q8Afixtureisusedto
a.savetime
b.fixoddshapedjobs
c.easymachining
d.noneofabove
Page 15 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
Q9Thequickestclampingdeviceisa
a.wingnut
b.knurlednut
c.cam/eccentric
d.Conventionalnut
Q10Aconicallocaterhastheadvantageof
a.easylocation
b.selfcentering
c.easylocationandselfcentering
d.offersgoodgrid
AnswerstoFilluptheblankquestions
1Locate,fix,andguidethetool 2helps
5quick
6toolguide
8Open,closed9Indexing
12locate
Answerstomultiplechoicequestions
1c
2a
3c
4a
8b
9c
10c
3clamping 4Hydraulicpistons
7Slipbushings
10guidethetool 11many
5d
6c
7c
Page 16 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
PROBLEMSFORPRACTICE
Q15SketchasuitablejigtodrillaholeintheworkpiecesasshowninfiguresW5P.1to
W5P.5.
.
FigureW5P.1
FigureW5P.2
FigureW5P.3
Page 17 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5P.4
FigureW5P.5
Q68SketchafixtureforlathefortheworkpiecesshowninfiguresW5P.6toW5.P8.
Page 18 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
FigureW5P.6
FigureW5P.7
FigureW5P.8
FigureW5P.5FigureW5P.6Partsarematingwitheachother
Page 19 of WEB CHAPTER 5- JIGS AND FIXTURES
Q9 Draw a milling fixture for the work pieces (shown in Figure W5.P9) to a suitable
scale.
FigureW5P.9
Q 10 Draw a suitable jig for welding the steel sections to the gusset plate as shown in
FigureW5P.10.
FigureW5P.10
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- MG6863 Engineering Economics April May 2018Document2 pagesMG6863 Engineering Economics April May 2018goldencometNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Cama Lab 10mel68 PDFDocument63 pagesCama Lab 10mel68 PDFshreedharkolekar50% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- MG6863 Engineering Economics TopicsDocument2 pagesMG6863 Engineering Economics TopicsgoldencometNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
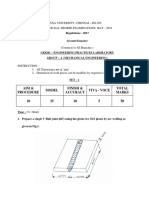
- Engineering Practices Lab Regulation 2017 AU Sample Question PaperDocument4 pagesEngineering Practices Lab Regulation 2017 AU Sample Question Papergoldencomet100% (3)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- MG2404 CASA Record PDFDocument56 pagesMG2404 CASA Record PDFgoldencometNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- CAD/CAM Viva-Voce Questions (SVSCE Edition)Document4 pagesCAD/CAM Viva-Voce Questions (SVSCE Edition)goldencometNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Engineering Practices Laboratory Sample Question PaperDocument1 pageEngineering Practices Laboratory Sample Question PapergoldencometNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- FEA Project Proposal Technical DetailsDocument8 pagesFEA Project Proposal Technical DetailsgoldencometNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Friction Stir Welding Effect On Aluminum AlloyDocument8 pagesFriction Stir Welding Effect On Aluminum AlloygoldencometNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Unit-1: Production Planning and ControlDocument20 pagesUnit-1: Production Planning and ControlbabuNo ratings yet
- Design Presentation: Virtual Baja Saeindia 2015Document12 pagesDesign Presentation: Virtual Baja Saeindia 2015goldencomet100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- 5112Document3 pages5112goldencometNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Ultrasonic Metal Welding PrimerDocument15 pagesUltrasonic Metal Welding PrimergoldencometNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ultrasonics For MetalsDocument4 pagesUltrasonics For MetalsgoldencometNo ratings yet
- Meterology Lab PDFDocument7 pagesMeterology Lab PDFVivek AnandanNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Phase DiagramsDocument30 pagesPhase DiagramsjerfmosNo ratings yet
- FEA Question Bank Mechanical EngineeringDocument15 pagesFEA Question Bank Mechanical Engineeringgoldencomet0% (1)
- Linear Vs Non-Linear Contact Analysis 082207Document9 pagesLinear Vs Non-Linear Contact Analysis 082207Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- I C DiagramDocument26 pagesI C DiagramNaman DaveNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- CE6306-Strength of Materials Part-A EditDocument15 pagesCE6306-Strength of Materials Part-A EditgoldencometNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sample Paper IDocument4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sample Paper IBaskar RamrajNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Introduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)Document22 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Method (FEM)goldencomet100% (1)
- SOM Question Bank For RevisionDocument11 pagesSOM Question Bank For RevisiongoldencometNo ratings yet
- Updated MQC ManualDocument29 pagesUpdated MQC ManualssselvaNo ratings yet
- Nba Sar MeDocument314 pagesNba Sar MegoldencometNo ratings yet
- Capgemini Paper On 14Th May: Section ADocument9 pagesCapgemini Paper On 14Th May: Section AgoldencometNo ratings yet
- CH 140203085002 Phpapp02Document58 pagesCH 140203085002 Phpapp02Adrian ReyesNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare The SarDocument107 pagesHow To Prepare The Sargoldencomet100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- FEM QuizDocument3 pagesFEM Quizmkdev2004No ratings yet
- MPR RitikDocument20 pagesMPR RitikRavan bhoyeNo ratings yet
- Cutting ToolsDocument5 pagesCutting ToolsBhavdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Fatal Accident in LatheDocument3 pagesFatal Accident in Lathe4gen_7No ratings yet
- Lock Nut WasherDocument3 pagesLock Nut WasherParmasamy SubramaniNo ratings yet
- EURODIMA Catalogue - 3-3Document1 pageEURODIMA Catalogue - 3-3Music NetNo ratings yet
- Threads PDFDocument5 pagesThreads PDFAnoj pahathkumburaNo ratings yet
- Through Holes Steam Oxide External Cooling: Series 4402Document8 pagesThrough Holes Steam Oxide External Cooling: Series 4402TungstenCarbideNo ratings yet
- ToolingDocument52 pagesToolingcmgankl0% (1)
- LatheDocument39 pagesLatheDominador Lozano Jr.No ratings yet
- 1792 Brochure LPKF Drilling Milling Routing Tools en PDFDocument4 pages1792 Brochure LPKF Drilling Milling Routing Tools en PDFperiodoNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CNC Milling BasicsDocument10 pagesCNC Milling Basicsjsrplc7952No ratings yet
- DJFPT MCQDocument9 pagesDJFPT MCQBappi ChamuaNo ratings yet
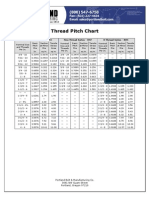
- Thread Pitch ChartDocument1 pageThread Pitch Chartyu7468No ratings yet
- Lathe - Exercise 2014Document8 pagesLathe - Exercise 2014Ramesh VajramNo ratings yet
- Jigs and FixturesDocument8 pagesJigs and FixturesHafizuddin NasirNo ratings yet
- ReamersDocument2 pagesReamersPuneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Dial Indicator and Dial Test Indicator Using PDFDocument1 pageDial Indicator and Dial Test Indicator Using PDFjames.anitNo ratings yet
- Catalogues Maktec PDFDocument24 pagesCatalogues Maktec PDFDương Viết CươngNo ratings yet
- Jigs FixuresDocument36 pagesJigs FixuresThulasi RamNo ratings yet
- By Group 7: Maintenance of CNC MachinesDocument27 pagesBy Group 7: Maintenance of CNC MachinesFerdian Gamalea DelastaNo ratings yet
- GegasDocument18 pagesGegasPiraven Casanova II50% (2)
- Tle-Ia-Smaw: Quarter 0 - Module 1 Use Basic Hand Tools and EquipmentDocument25 pagesTle-Ia-Smaw: Quarter 0 - Module 1 Use Basic Hand Tools and EquipmentAnalyn Taguran BermudezNo ratings yet
- CNC G-Code and M-Code Reference For CNC MachinesDocument8 pagesCNC G-Code and M-Code Reference For CNC MachinesShashank PathakNo ratings yet
- Mill Keyways On LatheDocument1 pageMill Keyways On LatheJim100% (3)
- SC4 Bench Lathe: User 'S Guide and Installation ManualDocument50 pagesSC4 Bench Lathe: User 'S Guide and Installation Manualmariza razuri cordovaNo ratings yet
- Lohia Corps Limited ReportDocument23 pagesLohia Corps Limited ReportAnkit Patel100% (1)
- Homework Solution# 3 I&ME 471 Due 3/31: Hint: You Will Need To Calculate The NDocument4 pagesHomework Solution# 3 I&ME 471 Due 3/31: Hint: You Will Need To Calculate The NBizuayehu TadesseNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Manufacturing TechnologyDocument79 pagesLab Manual - Manufacturing Technologyvelumani2003No ratings yet
- Stamping ToolsDocument40 pagesStamping ToolsJoris De VreeseNo ratings yet
- Study of Grinding MachinesDocument10 pagesStudy of Grinding Machinesdeepa82ece100% (1)