Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iso 9001 Sample
Uploaded by
PrialCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iso 9001 Sample
Uploaded by
PrialCopyright:
Available Formats
IS O 9001 2015 TRANS LATED INTO P LAIN ENGLISH
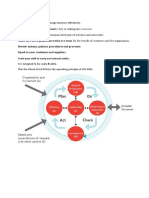
4. CONTEXT
4.1 UNDERSTAND YOUR ORGANIZATION AND ITS UNIQUE CONTEXT
1
An organizations context is its business
environment. It includes all of the internal
and external factors and conditions that
affect its products and services, have an
influence on its QMS, and are relevant
to its purpose and strategic direction.
Identify and understand your organization's context.
Identify and understand your organization's context before
you establish its quality management system (QMS).
Consider the external issues that are relevant to your organization's
purpose and strategic direction and think about the influence these
issues could have on its QMS and the results it intends to achieve.
An organizations external context
includes the needs and expectations of
its interested parties, as well as its social,
cultural, legal, technological, regulatory,
and competitive environment.
Consider your organization's external environment
and think about how it could influence its QMS.
Consider your legal environment and think about
the impact it could have on QMS performance.
"Issues can include positive and
negativ e factors or conditi ons".
Consider your social environment and think about
the impact it could have on QMS performance.
Consider your cultural environment and think about
the impact it could have on QMS performance.
The new standard expects you to
consider your organizations internal
and external context when you define
the scope of its QMS and when you plan
its design and development.
Consider your market environment and think about
the impact it could have on QMS performance.
Consider your economic environment and think
about the impact it could have on QMS performance.
10
Consider your competitive environment and think
about the impact it could have on QMS performance.
11
Consider your technological environment and think
about the impact it could have on QMS performance.
An organizations internal context
includes its values, culture, knowledge,
and performance.
12
Consider the internal issues that are relevant to your organization's
purpose and strategic direction and think about the influence these
issues could have on its QMS and the results it intends to achieve.
13
Consider your organization's values and think about their impact.
14
Consider your organization's culture and think about its impact.
15
Consider your organization's knowledge and think about its impact.
ORGANIZATION:
YOUR LOCATION:
COMPLETED BY:
DATE COMPLETED:
REVIEWED BY:
DATE REVIEWED:
OCT 2015
PART 4
A quality management system (QMS) is a
set of interrelated or interacting elements
that organizations use to formulate quality
policies and quality objectives and to
establish the processes that are needed
to ensure that policies are followed and
objectives are achieved. These elements
include structures, programs, procedures,
practices, plans, rules, roles, responsibilities,
relationships, contracts, agreements,
documents, records, methods, tools,
techniques, technologies, and resources.
PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARD
COPYRIGHT 2015 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
EDITION 1.0
PAGE 38
IS O 9001 2015 TRANS LATED INTO P LAIN ENGLISH
4. CONTEXT
Consider your organization's performance and think about its impact.
16
17
Monitor information about your organization's context.
Consider the impact changes in context could have on
your organization's quality management system (QMS).
18
19
Monitor and review the external issues that could influence your QMS.
20
Monitor and review the internal issues that could influence your QMS.
4.2 CLARIFY THE NEEDS AND EXPECTATIONS OF INTERESTED PARTIES
21
Identify the parties who affect or could affect your QMS.
22
Consider how these interested parties affect or could affect your ability
to provide products and services that meet customer requirements.
23
Consider how these interested parties affect or could affect your ability to provide
products and services that meet all relevant statutory and regulatory requirements.
24
An interested party is anyone who can
affect, be affected by, or believe that
they are affected by a decision or activity.
An interested party is a person, group, or
organization that has an interest or a
stake in a decision or activity.
Clarify and understand their unique needs and expectations.
25
Figure out how their needs, expectations, and requirements
could influence the performance of your organization's QMS.
26
Monitor and review information about your interested parties.
27
Monitor their changing needs, expectations, and requirements.
28
Review their changing needs, expectations, and requirements.
4.3 DEFINE THE SCOPE OF YOUR QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
29
Clarify boundaries and think about what your QMS should apply to.
30
Use boundary and applicability information to define the scope of your QMS.
31
32
33
Consider your organization's context when you define your scope.
Consider the impact your external environment could have.
YOUR LOCATION:
COMPLETED BY:
DATE COMPLETED:
REVIEWED BY:
DATE REVIEWED:
PART 4
Your context was discussed in part 4.1.
Consider how external issues could influence your QMS.
ORGANIZATION:
OCT 2015
When we use the word section or clause,
were referring to the original standard;
and when we use the word part, were
referring to our plain English publication.
PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARD
COPYRIGHT 2015 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
EDITION 1.0
PAGE 39
IS O 9001 2015 TRANS LATED INTO P LAIN ENGLISH
4. CONTEXT
34
Consider the impact your legal environment could have.
35
Consider the impact your social environment could have.
36
Consider the impact your cultural environment could have.
37
Consider the impact your market environment could have.
38
Consider the impact your economic environment could have.
39
Consider the impact your competitive environment could have.
40
Consider the impact your technological environment could have.
Consider how internal issues could influence your QMS.
41
42
Consider the impact your organization's values could have.
43
Consider the impact your organization's culture could have.
44
Consider the impact your organization's knowledge could have.
45
Consider the impact your organization's performance could have.
46
Consider interested party requirements when you define your scope.
47
Consider your products and services when you define your scope.
48
Interested parties were discussed in 4.2.
Document the scope of your quality management system (QMS).
49
Use your scope document to describe the boundaries of
your organization's QMS and to explain what it applies to.
50
Consider your products and services when you document your scope.
51
Consider your organization's context when you document your scope.
52
Consider interested party requirements when you document your scope.
53
Use your scope document to identify the types of products
and services that will be included in your organization's QMS.
54
Use your scope document to specify that every ISO 9001 requirement must be
applied unless you can justify and explain why it is not applicable in your case.
ORGANIZATION:
YOUR LOCATION:
COMPLETED BY:
DATE COMPLETED:
REVIEWED BY:
DATE REVIEWED:
OCT 2015
PART 4
PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARD
COPYRIGHT 2015 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
EDITION 1.0
PAGE 40
IS O 9001 2015 TRANS LATED INTO P LAIN ENGLISH
4. CONTEXT
55
Use your scope document to explain that a requirement may be ignored
only if doing so does not compromise your organization's ability or
responsibility to provide compliant products and services that
enhance customer satisfaction.
56
Explain why specified requirements arent applicable in your case.
57
Maintain the document that defines the scope of your QMS.
58
Control the document that defines the scope of your QMS.
ISO 9001 2015 Annex A.5 Applicability says
that organizations may consider things like
size and complexity, risks and opportunities,
and activities and management methods
when they decide which requirements could
be safely classified as "not applicable".
This is documented information. It must
be controlled and retained or maintained.
4.4 DEVELOP A QMS AND ESTABLISH DOCUMENTED INFORMATION
4.4.1 ESTABLISH A QMS THAT COMPLIES WITH THIS STANDARD
59
ISO 9001 section 0.3 makes it clear that an
ISO 9001 QMS must be a process-based QMS.
Develop a process-based quality management system (QMS).
60
Determine the processes that your QMS needs.
Determine process sequences and interactions.
61
62
Identify required inputs for each process.
63
Identify expected outputs for each process.
64
Determine methods needed to manage processes.
65
66
Identify the criteria and methods needed to operate processes.
Identify methods needed to ensure process effectiveness.
67
Identify appropriate process monitoring methods.
68
Identify measurements needed to operate processes.
Identify all necessary process performance indicators.
69
70
Identify the criteria and methods needed to control processes.
71
Identify methods needed to ensure that control is effective.
72
Identify measurements needed to control processes.
ORGANIZATION:
YOUR LOCATION:
COMPLETED BY:
DATE COMPLETED:
REVIEWED BY:
DATE REVIEWED:
OCT 2015
PART 4
A process-based QMS uses a process
approach to manage and control how
its quality policy is implemented and
how its quality objectives are achieved.
A process-based QMS is a network of
interrelated and interconnected processes.
Each process uses resources to transform
inputs into outputs and since the output
of one process becomes the input of
another process, processes interact
and are interrelated by means of such
input-output relationships. These process
interactions create a single integrated
process-based QMS.
PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARD
COPYRIGHT 2015 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
EDITION 1.0
PAGE 41
IS O 9001 2015 TRANS LATED INTO P LAIN ENGLISH
4. CONTEXT
Identify all necessary process control indicators.
73
Determine resources needed to support processes.
74
Provide the resources needed to support processes.
75
Determine process responsibilities and authorities.
76
Assign responsibilities and authorities for each process.
77
Determine risks and opportunities for each process.
78
79
Address your organizations risks and opportunities.
80
Determine methods needed to evaluate your processes.
Make sure that processes achieve intended results.
81
82
Actions to address risks and opportunities
will be developed in part 6.1.2, below.
Implement your process-based quality management system.
Apply criteria needed to operate and control your processes.
83
84
Apply monitoring criteria needed to operate and control your processes.
85
Apply measurement criteria needed to operate and control your processes.
Apply methods needed to operate and control your processes.
86
87
Apply monitoring methods needed to operate and control your processes.
88
Apply measurement methods needed to operate and control your processes.
89
Maintain your process-based quality management system.
Evaluate the processes that make up your organizations QMS.
90
Implement changes needed to ensure that they achieve intended results.
91
92
Improve your process-based quality management system.
93
Identify opportunities to improve your organization's QMS.
94
Improvements are discussed in part 10.
Determine opportunities to improve your QMS processes.
ORGANIZATION:
YOUR LOCATION:
COMPLETED BY:
DATE COMPLETED:
REVIEWED BY:
DATE REVIEWED:
OCT 2015
PART 4
Section 6.3 asks you to plan QMS changes.
PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARD
COPYRIGHT 2015 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
EDITION 1.0
PAGE 42
IS O 9001 2015 TRANS LATED INTO P LAIN ENGLISH
4. CONTEXT
4.4.2 MAINTAIN QMS DOCUMENTS AND RETAIN QMS RECORDS
95
This is documented information. It must
be controlled and retained or maintained.
Maintain documents needed to support process operations.
96
Control documents which support process operations.
97
Retain records which show that plans are being followed.
This is documented information. It must
be controlled and retained or maintained.
Control records which show that plans are being followed.
98
For those who wish to use our publication as a checklist, we have provided a column to the right of each task that you
can use to record your response. You could record a DONE, TO DO, or N/A in this column, or you could simply place a
to indicate that the task has been or is being performed or you could record an O/S to indicate that an item is outstanding.
In the spaces below, enter the name and location of your organization, who completed this page, who reviewed it, and the dates.
ORGANIZATION:
YOUR LOCATION:
COMPLETED BY:
DATE COMPLETED:
REVIEWED BY:
DATE REVIEWED:
OCT 2015
PART 4
PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARD
COPYRIGHT 2015 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
EDITION 1.0
PAGE 43
You might also like
- Handout 1-TAI LIEU- DOC HIEU BOI CANH CUA TO CHUCDocument9 pagesHandout 1-TAI LIEU- DOC HIEU BOI CANH CUA TO CHUCdreamteamNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Standard OverviewDocument7 pagesISO 9001 Standard OverviewProject m7070% (1)
- Understanding organizational context and quality management processesDocument5 pagesUnderstanding organizational context and quality management processesSAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- 9001 2015 GuidelinesDocument96 pages9001 2015 GuidelinesYezdi Solaina100% (1)
- Iso 9001 QmsDocument6 pagesIso 9001 QmsMohammad Mahbub AlamNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 2015Document21 pagesIso 9001 2015Sapan Kansara100% (1)
- 29 Sep 2020 Ing AmmDocument37 pages29 Sep 2020 Ing Ammabraham marinNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Internal Audit Checklist GuideDocument22 pagesISO 9001 Internal Audit Checklist GuidePCNo ratings yet
- Checklist - Audit - ISO 9001-2015Document144 pagesChecklist - Audit - ISO 9001-2015pratomo E T100% (1)
- Quality Manual Rev 31Document42 pagesQuality Manual Rev 31Er Pajapati YashNo ratings yet
- QMS Audit Report Sample IatfDocument39 pagesQMS Audit Report Sample IatfMANGESH100% (2)
- TQM ProjctDocument25 pagesTQM ProjctTehreem IjazNo ratings yet
- Determining The Scope of The Quality Management SystemDocument6 pagesDetermining The Scope of The Quality Management SystemNaeemNo ratings yet
- Iso 13485 2016 Bab 4Document131 pagesIso 13485 2016 Bab 4ode iskandar100% (1)
- Technical Guide - IsO 9001 2015Document12 pagesTechnical Guide - IsO 9001 2015Anonymous A2jnZ5MNPxNo ratings yet
- 9001 Training Module 3 - Cl1 To Cl7 in DetailDocument41 pages9001 Training Module 3 - Cl1 To Cl7 in Detailzack2008No ratings yet
- Draft QMSDocument4 pagesDraft QMSChandra RaoNo ratings yet
- F103-12-QMS-2015 ISO 9001 2015 Checklist GuidanceDocument42 pagesF103-12-QMS-2015 ISO 9001 2015 Checklist GuidanceAnand Dubey96% (25)
- ISO 9001 Checklist GuidanceDocument42 pagesISO 9001 Checklist GuidanceHelton75% (4)
- Some of The Core Concepts of ISO 9001Document4 pagesSome of The Core Concepts of ISO 9001gayathrisrk001No ratings yet
- Scorecard Best Practices: Design, Implementation, and EvaluationFrom EverandScorecard Best Practices: Design, Implementation, and EvaluationNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management System (Ims) Iso 90012015, Iso 140012015 & Iso 450012018 Awareness Training Clause 4Document20 pagesIntegrated Management System (Ims) Iso 90012015, Iso 140012015 & Iso 450012018 Awareness Training Clause 4AHMAD AIZUDDINNo ratings yet
- ISO9001 2015 Checklist GuidanceDocument42 pagesISO9001 2015 Checklist GuidanceVictoria100% (1)
- ISO 9001 2015 Audit QuestionsDocument8 pagesISO 9001 2015 Audit Questionsanup sharmaNo ratings yet
- Apendix ADocument1 pageApendix ASadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Iso9001 2015Document9 pagesIso9001 2015VIVEK VARMANo ratings yet
- Beyond Compliance Design of a Quality System: Tools and Templates for Integrating Auditing PerspectivesFrom EverandBeyond Compliance Design of a Quality System: Tools and Templates for Integrating Auditing PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Internal Quality Management System Audit Checklist (ISO9001:2015)Document35 pagesInternal Quality Management System Audit Checklist (ISO9001:2015)Medan MedanNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide Applying Quality Control: LO1: Assess Own WorkDocument49 pagesLearning Guide Applying Quality Control: LO1: Assess Own WorkNigussie BerhanuNo ratings yet
- 3 Auditable ClauseDocument13 pages3 Auditable Clauseajee doNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Checklist ISO 9001-2015Document22 pagesInternal Audit Checklist ISO 9001-2015Emad100% (3)
- Internal Quality Management System Audit ChecklistDocument37 pagesInternal Quality Management System Audit ChecklistSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Internal Audit ChecklistDocument26 pagesISO 9001 Internal Audit Checklistsajid waqas100% (1)
- What Are The Elements of A System of Quality Control? Identify and Explain EachDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Elements of A System of Quality Control? Identify and Explain Eachits me keiNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Learning GuideDocument54 pagesQuality Control Learning Guidenigus100% (1)
- Apply Quality StandardDocument29 pagesApply Quality StandardJaleto sunkemo100% (1)
- Iso 9001Document27 pagesIso 9001Sagar DaundNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 - 2015 Audit Checklist - SafetyCultureDocument56 pagesISO 9001 - 2015 Audit Checklist - SafetyCulturebhavesh_balasNo ratings yet
- Quality Process ManagementDocument11 pagesQuality Process Managementselinasimpson2001No ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Quality Management System FrameworkDocument5 pagesISO 9001 Quality Management System FrameworkA KumarNo ratings yet
- Checklist ISO 9001-2015Document37 pagesChecklist ISO 9001-2015indri100% (2)
- MALA, A. - QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesMALA, A. - QuestionnaireAmina Beth MalaNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit QuestionsDocument22 pagesInternal Audit QuestionsAshiq Maan100% (2)
- Iso Qbest - Abdul RazakDocument48 pagesIso Qbest - Abdul RazakBunga TerataiNo ratings yet
- ISO9001 Internal Audit ChecklistDocument24 pagesISO9001 Internal Audit ChecklistFatimaezzahraa BouaalamNo ratings yet
- ISO-9001 & 14001 - 2015-TrainingDocument24 pagesISO-9001 & 14001 - 2015-TrainingKranti Crank100% (1)
- Audit Iso9001 2015 ChecklistDocument23 pagesAudit Iso9001 2015 ChecklistLa Metalurgica100% (5)
- Module 2Document31 pagesModule 2ChristianieAnnNo ratings yet
- ISO9001 Implementation Guide Final April2016Document12 pagesISO9001 Implementation Guide Final April2016udomsak.suntithikavongNo ratings yet
- Checklist IQA 9001-2015Document38 pagesChecklist IQA 9001-2015Adhi GunantoNo ratings yet
- InternalAuditChecklistISO9001 2015Document21 pagesInternalAuditChecklistISO9001 2015Seven FungNo ratings yet
- Apply Quality Control TTLM Final TvetDocument14 pagesApply Quality Control TTLM Final Tvetmohammed ahmed100% (3)
- ISO 9001-2015 Checklist PDFDocument37 pagesISO 9001-2015 Checklist PDFHomero Januncio100% (1)
- Internal Quality Management System Audit Checklist (ISO9001:2015Document37 pagesInternal Quality Management System Audit Checklist (ISO9001:2015MohamedNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Manual of Internal Audit Practice and Guide: The Most Practical Guide to Internal Auditing PracticeFrom EverandComprehensive Manual of Internal Audit Practice and Guide: The Most Practical Guide to Internal Auditing PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quality Management Iso9001:2015 Changes: A Guide to ImplementationFrom EverandQuality Management Iso9001:2015 Changes: A Guide to ImplementationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rules And Policy Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandRules And Policy Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Global Supply Chain Governance A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandGlobal Supply Chain Governance A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Common Project RiskDocument15 pagesCommon Project RiskPrialNo ratings yet
- Project Document StructureDocument1 pageProject Document StructurePrialNo ratings yet
- CSI Masterformat DivisionsDocument1 pageCSI Masterformat DivisionsPrialNo ratings yet
- Vlookup SampleDocument2 pagesVlookup SamplePrialNo ratings yet
- WBS Various StructureDocument6 pagesWBS Various StructurePrialNo ratings yet
- Matrix of Common Project RisksDocument3 pagesMatrix of Common Project RisksPrialNo ratings yet
- Excel DashboardsDocument13 pagesExcel DashboardsPrial100% (1)
- Crew TableDocument1 pageCrew TablePrialNo ratings yet
- Visio Non Conformance Process MapsDocument1 pageVisio Non Conformance Process MapsPrialNo ratings yet
- FIDIC 6 BooksDocument4 pagesFIDIC 6 BooksPrial100% (1)
- Earned ValueDocument8 pagesEarned ValuePrialNo ratings yet
- Oracle p6.8 Exam TopicsDocument4 pagesOracle p6.8 Exam TopicsPrialNo ratings yet
- Course ContentsDocument2 pagesCourse ContentsPrialNo ratings yet
- Was-Grp Pipe Execution - Process MapDocument1 pageWas-Grp Pipe Execution - Process MapPrialNo ratings yet
- Long Range Pipeline MonitoringDocument9 pagesLong Range Pipeline MonitoringPrialNo ratings yet
- Area QTY Kilometer Surge Tank 4 Pumping Station 6 Piping 1 198 Piping 2 246 Storage Tank 3 5 Polishing Plant 4 1 WWTP 5&6 3Document11 pagesArea QTY Kilometer Surge Tank 4 Pumping Station 6 Piping 1 198 Piping 2 246 Storage Tank 3 5 Polishing Plant 4 1 WWTP 5&6 3PrialNo ratings yet
- Transformational StoryDocument2 pagesTransformational StoryPrialNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Blue OceanDocument1 pageHealthcare Blue OceanPrialNo ratings yet
- Adding A Proxy (Unifier)Document1 pageAdding A Proxy (Unifier)PrialNo ratings yet
- Project Change RequestDocument1 pageProject Change RequestPrialNo ratings yet
- Tracking SheetsDocument23 pagesTracking SheetsPrialNo ratings yet
- Project Change RequestDocument1 pageProject Change RequestPrialNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Creating WBSDocument10 pagesA Guide To Creating WBSPrialNo ratings yet
- ISO 9000 Jcia: StandardsDocument1 pageISO 9000 Jcia: StandardsPrialNo ratings yet
- JZMH aXKBJ3TwcVIkazQwapfCMfeHvtqxB xBJ1YDocument84 pagesJZMH aXKBJ3TwcVIkazQwapfCMfeHvtqxB xBJ1YReinbrandt malikiyano cahyonoNo ratings yet
- Revision Module 1,2,3Document129 pagesRevision Module 1,2,3jitamitra88No ratings yet
- Drive Test For BeginnerDocument88 pagesDrive Test For Beginnerahwaz96100% (1)
- 611k01 Kicatalog C Ka Us 1Document8 pages611k01 Kicatalog C Ka Us 1Ean LeeNo ratings yet
- Be Circular Fibre Reinforced ConcreteDocument4 pagesBe Circular Fibre Reinforced ConcreteLim Kang HaiNo ratings yet
- Chem 361 Separation Methods IntroDocument8 pagesChem 361 Separation Methods IntroTwum SomoahNo ratings yet
- Advance Distributed ComputingDocument2 pagesAdvance Distributed ComputingValia Centre of ExcellenceNo ratings yet
- 10 ExtSpringsDocument27 pages10 ExtSpringsresh27No ratings yet
- Evolution of The Fire SprinklerDocument11 pagesEvolution of The Fire SprinklerPedro DudesonNo ratings yet
- Advances in X-Ray Analysis - Volume 33 - 1989Document685 pagesAdvances in X-Ray Analysis - Volume 33 - 1989CVNo ratings yet
- Anie Altamirano Learning For Life HandoutDocument4 pagesAnie Altamirano Learning For Life HandoutAnnapurna VNo ratings yet
- Acer Veriton S480G Service ManualDocument90 pagesAcer Veriton S480G Service ManualAndreea Georgiana ChirilaNo ratings yet
- 2. Green finance and sustainable development in EuropeDocument15 pages2. Green finance and sustainable development in Europengocanhhlee.11No ratings yet
- CitationCJ4-CB Checklists B v1.2Document4 pagesCitationCJ4-CB Checklists B v1.2Joao Vitor RojasNo ratings yet
- Finimpianti Power EngDocument2 pagesFinimpianti Power EngJosip GrlicaNo ratings yet
- Foundation ProblemsDocument71 pagesFoundation Problemsيقين يقين0% (1)
- Veiga Et Al. 2015 - Composition, Structure and Floristic Diversity in Dense Rain Forest inDocument8 pagesVeiga Et Al. 2015 - Composition, Structure and Floristic Diversity in Dense Rain Forest inYakov Mario QuinterosNo ratings yet
- The Machine-Room-Less Elevator: Kone E MonospaceDocument8 pagesThe Machine-Room-Less Elevator: Kone E MonospaceAbdelmuneimNo ratings yet
- T38N/T48N: Suffix Code Instruction ManualDocument1 pageT38N/T48N: Suffix Code Instruction ManualaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Fanning EquationDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Fanning EquationFaisal AyyazNo ratings yet
- Manhattan Project SummaryDocument5 pagesManhattan Project Summaryapi-302406762No ratings yet
- Creative WritingDocument2 pagesCreative WritingSharmaine AsoyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Financial Performance of Small and MediumDocument9 pagesA Study On Financial Performance of Small and Mediumtakele petrosNo ratings yet
- Capacitor BanksDocument49 pagesCapacitor BanksAmal P RaviNo ratings yet
- Sist-En-6101-2016 .Document9 pagesSist-En-6101-2016 .lokelooksNo ratings yet
- Physics Semiconductor Device MCQDocument3 pagesPhysics Semiconductor Device MCQAsim Ali0% (1)
- Sri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1Document11 pagesSri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1sri dwi mutiaraNo ratings yet
- Verb-Particle Constructions in Romance. A Lexical-Syntactic AccountDocument29 pagesVerb-Particle Constructions in Romance. A Lexical-Syntactic AccountWagaJabalNo ratings yet
- Đề Minh Họa 2020 Số 23 - GV Trang Anh - Moon.vnDocument22 pagesĐề Minh Họa 2020 Số 23 - GV Trang Anh - Moon.vnLily LeeNo ratings yet
- PLC SCADA ASSIGNMENT SsDocument10 pagesPLC SCADA ASSIGNMENT SsShadab AhmadNo ratings yet