Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 Course
Uploaded by
Tejas AdakOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 Course
Uploaded by
Tejas AdakCopyright:
Available Formats
Total No of Questions: [8]
SEAT NO. :
[Total No. of Pages :3]
S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 course
Strength of Materials (Code: 202051)
May 2014 (Semester - II)
Time: 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 50
Instructions to the candidates:
1. Answer four questions out of 8.
2. Solve Q 1 or 2, Q 3 or 4, Q 5 or 6, Q 7 or 8.
3. All the four questions should be solved in one answer book and attach extra supplements if
required.
4. Draw Diagrams wherever necessary.
5. Use of scientific calculator is allowed.
6. Assume suitable data where ever necessary
Q1)
a) A bar of metal 100 mm X 50 mm in cross-section is 250 mm long. It carries a
[6]
tensile load of 400 kN in the direction of its length, a compressive load of 4000
kN on its 100 mm X 250 mm faces and a tensile load of 2000 kN on its 50 mm X
250 mm faces. If E = 2 X 105 N / mm 2 and Poissons ratio is 0.25, find the
change in volume of the bar.
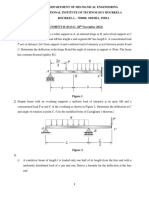
b) A beam AB 10 meters long has supports at its ends A and B. It carries a point
[6]
load of 5 kN at 3 meters from A and a point load of 5 kN at 7 meters from A and
a uniformly distributed load of 1 kN per meter between the point loads. Draw SF
and BM diagrams for the beam.
OR
Q2)
a) A steel rod of 30 mm diameter is enclosed in a brass tube of 42 mm external
[6]
diameter and 32 mm internal diameter. Each is 360 mm long and the assembly is
rigidly held between two stops 360 mm apart. The temperature of the assembly is
then raised by 500C. Determine
(i) Stresses in the tube and the rod.
(ii) stresses in the tube and the rod, if the stops yields by 0.15 mm
Es = 205 GPa;
Eb = 90 GPa
-6
0
s=11 X 10 per C;
b= 19 X 10-6 per 0C
b) Draw SF and BM diagrams for the beam ABCDE shown in following figure
[6]
Page 1 of 3
Q3)
a)
b)
Q4)
Q5)
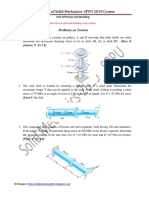
a)
A cast iron pipe of internal diameter 450 mm is 15 mm thick and is supported on
a span of 8 m. Find the maximum bending stress in the pipe when it is full of
water. Take specific weight of cast iron = 71600 N / m3 and that of water = 9810
N / m3 .
Compare the strain energy stored in the two bars of the same material shown in
following figure, if gradually applied load is same.
OR
A horizontal beam of the section shown in following fig. is 3 m long and is
simply supported at the ends. Find the maximum uniformly distributed load it can
carry, if the compressive and tensile stresses must not exceed 55 N / mm 2 and 30
N / mm2 respectively.
[6]
[6]
[6]
b)
Following fig. shows a simply supported beam of uniform section whose moment
of inertia is 4.3 x 108 mm4. For the loading shown, find the position and
magnitude of the maximum deflection. Take E = 200 kN / mm2.
[6]
a)
Compare the weights of equal lengths of a solid and a hollow shaft to transmit a
given torque for the same maximum stress, if the inside diameter of the shaft is
three fourth of the outside.
Determine the buckling load for a strut of tee section, the flange width being 100
mm, overall depth 80 mm and both flange and stem 10 mm thick. The strut is 3 m
long and is hinged at both ends. Take E = 200 GN / m2.
OR
[6]
b)
[7]
Page 2 of 3
Q6)
Q 7)
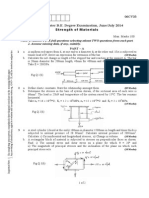
a)
Following fig. shows a stepped steel shaft. It is subjected to a torque T at the
free end and a torque 2T in the opposite direction at the junction of the two
sizes. Determine the total angle of twist, if the maximum shear stress is limited to
80 MPa. Take G = 80 GPa.
[6]
b)
A straight cylindrical bar of 15 mm diameter and 1.2 m long is freely supported
at its two ends in a horizontal position. It is loaded with a concentrated load of
100 N at the centre when the centre deflection is observed to be 5 mm. If placed
in the vertical position and loaded vertically, what load would cause it to buckle?
Also find the ratio of the maximum stress in the two cases.
An axial pull of 20 kN along with a shear force of 15 kN is applied to a circular
bar of 20 mm diameter. The elastic limit of the bar material is 230 MPa and the
Poissons ration, = 0.3.
Determine the factor of safety against failure based on
a) maximum shear stress theory
b) maximum strain energy theory
c) maximum principal strain energy theory
d) maximum shear strain energy theory
In a 2 D stress system, stresses at a point in a material are 50 MPa compression
and 30 MPa shearing in one plane and 20 MPa tensile and a shearing stress in
another plane at 600 to the first one. Determine the value of the shearing stress in
the second plane and the principal stresses and position of their planes.Use
Analytical method.
OR
A solid circular shaft is subjected to a bending moment of 40 kN-m and a torque
of 10 kN-m. Design the diameter of the shaft according to
i)
Maximum principal stress theory
ii)
Maximum shear stress theory
iii)
Maximum strain energy theory.
Take = 0.25, Stress at elastic limit = 200 N / mm2and factor of safety = 2.
The stresses on two perpendicular planes through a point in a body are 30 MPa
and 15 MPa both tensile along with shear stress of 25 MPa. Find
(i)
magnitude and direction of principal stresses
(ii)
maximum shear stress and their planes
(iii) normal and shear stresses on the planes of maximum shearing stress
Use Mohrs Circle method.
[7]
a)
b)
Q8)
a)
b)
[6]
[7]
[6]
[7]
Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Ilm College of Engineering & Technology: Model Exam - Novenber-2015Document2 pagesIlm College of Engineering & Technology: Model Exam - Novenber-2015Deepak V DasNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesMechanics of SolidsKhaista RahmanNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Assgn-1Document6 pagesB.Tech Assgn-1K Pushpendu PrashantNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- SM Model Exam QuestionDocument5 pagesSM Model Exam QuestionAravind PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Me2254 SM QBDocument15 pagesMe2254 SM QBhodvmkvecautoNo ratings yet
- Me2254 - Strength of Materials 2008 PDFDocument4 pagesMe2254 - Strength of Materials 2008 PDFAndrew CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Me2254 QBDocument18 pagesMe2254 QBAinnar Kesavan0% (1)
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocument8 pages9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PapersDocument23 pagesMechanical PapersSachin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Sample Question PaperDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineering Sample Question PaperManiVijayNo ratings yet
- Queastion Bank MOM 22 26Document5 pagesQueastion Bank MOM 22 26karvaminNo ratings yet
- G For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of TheDocument6 pagesG For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of Theክበር ተመስጌንNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SOM Question Bank For RevisionDocument11 pagesSOM Question Bank For RevisiongoldencometNo ratings yet
- PartDocument9 pagesPartMahendranath Ramakrishnan0% (2)
- CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS PART-B TOPICSDocument8 pagesCE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS PART-B TOPICSnkchandruNo ratings yet
- Mechanicsofsolids Dec 2010Document10 pagesMechanicsofsolids Dec 2010simalaraviNo ratings yet
- MOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23Document6 pagesMOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23PankajNo ratings yet
- SOM3601 Assignment 2Document3 pagesSOM3601 Assignment 2Elendu Emmanuel ChigozieNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. EXAMINATION, 2020: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Document5 pagesB. Tech. EXAMINATION, 2020: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Gopu KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNo ratings yet
- Som TutorialsDocument22 pagesSom TutorialsbaizubirajiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids exam questionsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Solids exam questionsgalehNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameavinashNo ratings yet
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Be Arch Am 401 A 2006Document3 pagesBe Arch Am 401 A 2006James WallNo ratings yet
- TUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignDocument8 pagesTUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignCharles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material 2Document6 pagesStrength of Material 2viv_1971No ratings yet
- Ce 6306 Som QBDocument11 pagesCe 6306 Som QBHODMECHANICAL AKTMCETNo ratings yet
- SOM Question BankDocument8 pagesSOM Question BankprakashmenmoliNo ratings yet
- 7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsDocument5 pages7 - MOS-I Assignment QuestionsSrikant Potluri100% (1)
- Som Strength of Material Question BankDocument16 pagesSom Strength of Material Question BankarindamckbtNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Solids Exam QuestionsNandu Sreekumar SNo ratings yet
- r13 Mos Old Q PapersDocument21 pagesr13 Mos Old Q PapersSrinu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Trichy Engineering College Department of Mechanical Engineering Me-2254-Strength of Materials Model ExamDocument4 pagesTrichy Engineering College Department of Mechanical Engineering Me-2254-Strength of Materials Model Examgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- CE8301-Strength of Materials IDocument4 pagesCE8301-Strength of Materials Isyed1188No ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Prelim 2022 SMDocument4 pagesPrelim 2022 SMARJUNANo ratings yet
- Som I Iat Ques 2019Document3 pagesSom I Iat Ques 2019Siva RamanNo ratings yet
- SoM Assignment 1 23Document2 pagesSoM Assignment 1 23balajimeieNo ratings yet
- Mechanical engineering problems on stress, strain, modulus of elasticityDocument2 pagesMechanical engineering problems on stress, strain, modulus of elasticityMariz Ellaine BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Instructionsharnishtanna21285No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.karthikeyankv.mech DscetNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materialsgirish_deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)Document4 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)aryansorout1612No ratings yet
- Som Model QP N SchemeDocument2 pagesSom Model QP N Schemesihefer203No ratings yet
- Mom AssignmentDocument8 pagesMom AssignmentfrogNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNDocument12 pagesFoundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNLata SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ashok Dmm1Document4 pagesAshok Dmm1Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIDocument4 pages9A01401 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Strength of Materials Question PaperDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineering Strength of Materials Question PaperKkNo ratings yet
- Strength WorksheetDocument9 pagesStrength WorksheetHabtamu GetaNo ratings yet
- Mehcanics of Solids May2004 RR 220304Document8 pagesMehcanics of Solids May2004 RR 220304Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: 2. Assume Missing Data, If Any, SuitablyDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials: 2. Assume Missing Data, If Any, SuitablynvnrevNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsFrom EverandCyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldDocument110 pagesScaffoldJuantoro Puspo WiryolukitoNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: Effect of Subcritical Annealing Temperature On Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Scm435 SteelDocument6 pagesSciencedirect: Effect of Subcritical Annealing Temperature On Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Scm435 SteelShyam VsNo ratings yet
- The Behaviour of Composite BeamsDocument19 pagesThe Behaviour of Composite BeamssvnNo ratings yet
- Forces and Stresses On Ships (Compatibility Mode)Document44 pagesForces and Stresses On Ships (Compatibility Mode)Htin Lin Aung100% (1)
- Drillstring Design ManualDocument23 pagesDrillstring Design ManualAdil Aytekin93% (14)
- AISI 1045 Carbon Steel (UNS G10450)Document3 pagesAISI 1045 Carbon Steel (UNS G10450)AndresNo ratings yet
- Circular Plate HODocument6 pagesCircular Plate HOnrnakNo ratings yet
- MD Elements1Document22 pagesMD Elements1Ben LopezNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet Developed by Hazim Dwairi for Concrete Beam DesignDocument7 pagesSpreadsheet Developed by Hazim Dwairi for Concrete Beam DesignJD HemaNo ratings yet
- MSC Marc WP Nonlinear FEA Elastomers PDFDocument75 pagesMSC Marc WP Nonlinear FEA Elastomers PDFPradeep SarodeNo ratings yet
- Fall 2017 MD Rashidul Hasib MECH 991 Seminar ReportDocument2 pagesFall 2017 MD Rashidul Hasib MECH 991 Seminar Reporthasib_07No ratings yet
- Friction: Reference: Theory of Machines by R.S. Khurmi & J.K.GuptaDocument17 pagesFriction: Reference: Theory of Machines by R.S. Khurmi & J.K.GuptaSaad AliKhan100% (2)
- Paper 11 13986 1037Document12 pagesPaper 11 13986 1037initbashNo ratings yet
- Practical Aspects of PSCDocument73 pagesPractical Aspects of PSCAnde BhanuNo ratings yet
- Design With Polymers - Tools and Process by Kartik Srinivas, CEO, AdvanSESDocument4 pagesDesign With Polymers - Tools and Process by Kartik Srinivas, CEO, AdvanSESRaasik JainNo ratings yet
- Avesta Welding ManualDocument300 pagesAvesta Welding Manual66apenlullenNo ratings yet
- Pak 37 17 18Document39 pagesPak 37 17 18Lift carry LapsittingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document186 pagesChapter 7mgualdiNo ratings yet
- AntonPaar White PaperDocument4 pagesAntonPaar White PaperPablo AntezanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document91 pagesLecture 01usman cheemaNo ratings yet
- IPE Sections To Euronorm 89: Dimensions and PropertiesDocument2 pagesIPE Sections To Euronorm 89: Dimensions and PropertiesLodewijk ClausNo ratings yet
- Grain Growth in Phosphorus-Doped PolysiliconDocument5 pagesGrain Growth in Phosphorus-Doped PolysiliconPk dataNo ratings yet
- Bill Mosley John Bungey & Ray Hulse: Reinforced Concrete Design To EC2Document33 pagesBill Mosley John Bungey & Ray Hulse: Reinforced Concrete Design To EC2RyanWongJiaHanNo ratings yet
- Kumaran PDFDocument46 pagesKumaran PDFmitthu23No ratings yet
- Bending Test For SteelDocument2 pagesBending Test For SteelDeku50% (2)
- Concrete Industrial Ground Floor Slab Design (TR34)Document3 pagesConcrete Industrial Ground Floor Slab Design (TR34)Nihar ShahNo ratings yet
- Ugur ErsoyDocument16 pagesUgur ErsoyTeknomdepo TeknomdepoNo ratings yet
- Study of Microstructural Degradation of A Failed Pinion Gear at A Cement PlantDocument10 pagesStudy of Microstructural Degradation of A Failed Pinion Gear at A Cement Planttheerapat patkaewNo ratings yet
- Creep and Shrinkage SpreadsheetDocument33 pagesCreep and Shrinkage SpreadsheetpedjaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingDocument33 pagesChapter 18-Fundamentals of Metal FormingMuhammad Qasim QureshiNo ratings yet