Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assign Sheet Trig
Uploaded by
Chirag HablaniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assign Sheet Trig
Uploaded by
Chirag HablaniCopyright:
Available Formats
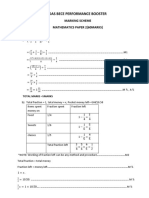
Assignment Sheet Trigonometry
1.
The diagram below shows two straight lines intersecting at O and two circles, each with centre O. The
outer circle has radius R and the inner circle has radius r .
Consider the shaded regions with areas A and B . Given that A: B = 2 :1, find the exact value of the
ratio R : r .
2.
A triangle has sides of length (n2 + n + 1) , (2n +1) and (n2 1) where n > 1.
(a) Explain why the side (n2 + n + 1) must be the longest side of the triangle.
(b) Show that the largest angle, , of the triangle is 120o .
3.
Two non-intersecting circles C1 , containing points M and S , and C2 , containing points N and R, have
centres P and Q where PQ = 50 . The line segments [MN] and [SR] are common tangents to the circles.
The size of the reflex angle MPS is , the size of the obtuse angle NQR is , and the size of the angle
MPQ is . The arc length MS is l1 and the arc length NR is l2 . This information is represented in the
diagram below.
The radius of C1 is x , where x 10 and the radius of C2 is 10.
(a) Explain why x < 40 .
(b) Show that cos = (x 10)/50.
(c) (i) Find an expression for MN in terms of x .
(ii) Find the value of x that maximises MN.
(d) Find an expression in terms of x for
(i) ;
(ii) .
(e) The length of the perimeter is given by l1 + l2 + MN + SR.
(i) Find an expression, b(x), for the length of the perimeter in terms of x .
(ii) Find the maximum value of the length of the perimeter.
(iii) Find the value of x that gives a perimeter of length 200.
4.
In triangle ABC, AB = 9 cm , AC = 12 cm , and angle B is twice the size of angle C .
Find the cosine of angle C.
5.
In the diagram below, AD is perpendicular to BC.
CD = 4, BD = 2 and AD = 3. CAD = and B D A = .
Find the exact value of cos ( ) .
6.
In triangle ABC, BC = a , AC = b , AB = c and [BD] is perpendicular to [AC].
(a) Show that CD = b c cos A.
(b) Hence, by using Pythagoras Theorem in the triangle BCD, prove the cosine rule
for the triangle ABC.
1
3
a b2 a 2
4 .
(c) If AB C = 60o , use the cosine rule to show that c = 2
7.
The above three dimensional diagram shows the points P and Q which are respectively west and southwest of the base R of a vertical flagpole RS on horizontal ground. The angles of elevation of the top S
of the flagpole from P and Q are respectively 35o and 40o , and PQ = 20 m .
Determine the height of the flagpole.
8.
Consider triangle ABC with BAC = 37.8o , AB = 8.75 and BC = 6. Find AC.
9.
The lengths of the sides of a triangle ABC are x 2 , x and x + 2 . The largest angle is 120o .
(a) Find the value of x.
(b) Show that the area of the triangle is 153 / 4.
(c) Find
sin A + sin B + sin C giving your answer in the form pq / r where p, q, r .
10. The diagram below shows a pair of intersecting circles with centres at P and Q with radii of 5 cm and 6
cm respectively. RS is the common chord of both circles and PQ is 7 cm.
Find the area of the shaded region.
11.
Triangle ABC has C = 42o , BC =1.74 cm , and area 1.19 cm2 .
(a) Find AC.
(b) Find AB.
12. The diagram shows a circle centre O and radius 1, with AOB = , 0 . The area of AOB is
three times the shaded area.
Find the value of .
13. The following diagram shows ABC, where BC =105 m, ACB = 40o , ABC = 60o .
Find AB.
14. In the obtuse-angled triangle ABC, AC = 10.9 cm , BC = 8.71 cm and BAC = 50o .
Find the area of triangle ABC.
You might also like
- QB Version 3 Circular Functions and TrigDocument21 pagesQB Version 3 Circular Functions and TrigRowanberry11No ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document5 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Ayush MunotNo ratings yet
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)Document21 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- IB Related RatesDocument8 pagesIB Related RatesVidhiGondaliaNo ratings yet
- Vectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesVectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsJasmine YimNo ratings yet
- All Trig Revision QusDocument11 pagesAll Trig Revision QusAlan WaiNo ratings yet
- EXS 1-2-25v1 HL Exponents LogarithmsDocument2 pagesEXS 1-2-25v1 HL Exponents LogarithmsRaivat ShahNo ratings yet
- IB Maths HL Mini Topic Exam:: AlgebraDocument6 pagesIB Maths HL Mini Topic Exam:: Algebraomar triveñoNo ratings yet
- HL Year 1 Random Trig Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesHL Year 1 Random Trig Practice ProblemslilyNo ratings yet
- Oxford Math AA SL Exam Practise Additional ResourcesDocument172 pagesOxford Math AA SL Exam Practise Additional ResourcesSıla DenizNo ratings yet
- Ib HL Counting Binomial QuestionsDocument2 pagesIb HL Counting Binomial QuestionsMohd Uvais100% (1)
- Transformations of Functions AA SL. WORKSHEET 1Document4 pagesTransformations of Functions AA SL. WORKSHEET 1Azka Hamdah (Yr. 22-24)No ratings yet
- Calculus - Differentiation 1Document69 pagesCalculus - Differentiation 1Amina Rakha HassanNo ratings yet
- Ib Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewDocument46 pagesIb Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewMax HudgenesNo ratings yet
- Paperplainz Com Ib Math Aa SL Practice Exams Paper 1 Practice Exam 1Document5 pagesPaperplainz Com Ib Math Aa SL Practice Exams Paper 1 Practice Exam 1Aung Kyaw HtoonNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory TestDocument8 pagesGas Laws and Kinetic Theory Testmcdaid1888100% (1)
- Dp1 SA Maths Papers For RevisionDocument10 pagesDp1 SA Maths Papers For RevisionDharmik JainNo ratings yet
- IBDP Arithmetic Sequence WorksheetDocument3 pagesIBDP Arithmetic Sequence WorksheetbalajibabutNo ratings yet
- 2012 Probability Past IB QuestionsDocument18 pages2012 Probability Past IB QuestionsVictor O. WijayaNo ratings yet
- Math IB Revision MatricesDocument2 pagesMath IB Revision Matricesmykiri79100% (1)
- Ib Maths HL Markscheme by TopicDocument1,214 pagesIb Maths HL Markscheme by TopicParamtejNo ratings yet
- Possible C3 Questions From Past Papers P1P3Document20 pagesPossible C3 Questions From Past Papers P1P3PXLIV100% (1)
- Ib Maths ST Number HW 1Document6 pagesIb Maths ST Number HW 1Shiny Nivolya100% (2)
- TOPIC1 Quantitative Q&aDocument34 pagesTOPIC1 Quantitative Q&aMike AndersonNo ratings yet
- Math IB Revision Differentiation BasicsDocument3 pagesMath IB Revision Differentiation Basicsmykiri79100% (1)
- MathHL QB3 T2Document25 pagesMathHL QB3 T2Nikola PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Test 7. Statistics - ProbabilityDocument4 pagesTest 7. Statistics - ProbabilityValentina TarabukinaNo ratings yet
- Sample IB Questions ThermalDocument8 pagesSample IB Questions ThermalEthan KangNo ratings yet
- Maths IA SangakuDocument5 pagesMaths IA SangakuKavin RukNo ratings yet
- MockB HL P2 2015v1 Sect A Only PDFDocument11 pagesMockB HL P2 2015v1 Sect A Only PDFYoonseo ChoiNo ratings yet
- IB Maths Worksheet ProbabilityDocument14 pagesIB Maths Worksheet Probabilityhans100% (2)
- HL Topic 7 17 EquilibriumDocument9 pagesHL Topic 7 17 EquilibriumDavid DancerNo ratings yet
- Math IB Revision ProbabilityDocument14 pagesMath IB Revision Probabilitymykiri7950% (2)
- Work Energy and Power Practice WorksheetDocument13 pagesWork Energy and Power Practice Worksheet윤영석No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument1 pageQuadratic EquationEmyRaNo ratings yet
- SL Math Trig Practice Sheet 1Document23 pagesSL Math Trig Practice Sheet 1nora100% (2)
- HL Maths Trig AssignmentDocument7 pagesHL Maths Trig AssignmentTomasNo ratings yet
- HKExcel Math AI SL NoteDocument60 pagesHKExcel Math AI SL Noteyara hazemNo ratings yet
- MCT MC (T + 273) : IB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1. 5. 9Document16 pagesMCT MC (T + 273) : IB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1. 5. 9MiriamNo ratings yet
- F.3 Chemistry Exercise 3 (Atoms) (Q&A)Document4 pagesF.3 Chemistry Exercise 3 (Atoms) (Q&A)Simon100% (1)
- IB Multiple Choice Past Paper Questions Topic 1 2012Document3 pagesIB Multiple Choice Past Paper Questions Topic 1 2012mamta2111No ratings yet
- Mathematics HL Paper 1 TZ1 PDFDocument15 pagesMathematics HL Paper 1 TZ1 PDFMary LuNo ratings yet
- IB Math SL Arithmetic Geometric Sequences Series ReviewDocument8 pagesIB Math SL Arithmetic Geometric Sequences Series ReviewDiana Oblitas Zanabria100% (1)
- Math IB Revision Vectors SLDocument14 pagesMath IB Revision Vectors SLmykiri79100% (1)
- A Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure MathematicsDocument5 pagesA Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure MathematicsZaka AhmedNo ratings yet
- Trig P2 Mark SchemeDocument21 pagesTrig P2 Mark SchemeMichelle HsiehNo ratings yet
- Specimen Papers 2021 - English PDFDocument122 pagesSpecimen Papers 2021 - English PDFsohamNo ratings yet
- Math IB Revision AlgebraDocument11 pagesMath IB Revision Algebramykiri79No ratings yet
- BearingsDocument15 pagesBearingsJoann NgNo ratings yet
- Ib Practice Integration QuestionsDocument5 pagesIb Practice Integration QuestionsSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year: Diagram of The Undergraduate Programme in EconomicsDocument1 page1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year: Diagram of The Undergraduate Programme in EconomicsLouisDiMariaNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document7 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Fatin Nurina Mohd NazemiNo ratings yet
- Maths H2Document733 pagesMaths H2Weijuan YuenNo ratings yet
- Math IB Revision Functions & EquationsDocument26 pagesMath IB Revision Functions & Equationsmykiri79100% (1)
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Functions)Document17 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Functions)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Bivariate StatisticsDocument6 pagesBivariate StatisticstahsansaminNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry HL Summer AssignmentDocument4 pagesIB Chemistry HL Summer AssignmentVal B100% (1)
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Vectors)Document28 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Vectors)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Le CorbusierDocument10 pagesLe CorbusierChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Thermal Boredom in ARchitectureDocument2 pagesThermal Boredom in ARchitectureChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Evolution of StupasDocument21 pagesEvolution of StupasChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- HPH PDFDocument10 pagesHPH PDFChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Articles: Books: EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesArticles: Books: EntrepreneurshipChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Architecture Books To ReadDocument3 pagesArchitecture Books To ReadChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Liak Teng LitDocument54 pagesLiak Teng LitChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Climate Responsive Architecture Creating Greater Design Awareness Among Architects PDFDocument11 pagesClimate Responsive Architecture Creating Greater Design Awareness Among Architects PDFChirag Hablani100% (1)
- Articles: BackgroundDocument11 pagesArticles: BackgroundChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment Voltaic CellsDocument7 pagesExperiment Voltaic CellsChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Physics HL (Part 1)Document21 pagesPhysics HL (Part 1)Chirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Physics HL (Part 2)Document19 pagesPhysics HL (Part 2)Chirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Logarithms Practice Questions: Attempt These Questions Without A CalculatorDocument1 pageLogarithms Practice Questions: Attempt These Questions Without A CalculatorazrindothmanNo ratings yet
- Math IaDocument14 pagesMath IaChirag Hablani100% (3)
- Grade 9 Number SystemDocument19 pagesGrade 9 Number SystemSwetha WariNo ratings yet
- International Competitions IMO Shortlist 2000 17Document6 pagesInternational Competitions IMO Shortlist 2000 17Berce GabrielNo ratings yet
- Personal Data Sheet Application Letter Resume Diplomas: 240 Saint Francis IDocument3 pagesPersonal Data Sheet Application Letter Resume Diplomas: 240 Saint Francis IAngellee MayunoNo ratings yet
- Some Concurrencies From Tucker Hexagons: 1. The Tucker Hexagon and The Tucker CircleDocument9 pagesSome Concurrencies From Tucker Hexagons: 1. The Tucker Hexagon and The Tucker CircleHoang Ngo DangNo ratings yet
- IGCSE TresholdDocument2 pagesIGCSE Tresholds17m0582No ratings yet
- Senior Issue 2012Document13 pagesSenior Issue 2012thewarrioronline_shsNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Derivatives 3Document8 pagesWorksheet On Derivatives 3Darshana Madushanka100% (1)
- CamScanner 10-30-2023 23.31Document4 pagesCamScanner 10-30-2023 23.31joudy2212009No ratings yet
- 12 - Solid Geometry & Mensuration BBADocument5 pages12 - Solid Geometry & Mensuration BBAVeerannaSHiremathNo ratings yet
- Goll Csa ActionplanforhealthDocument8 pagesGoll Csa Actionplanforhealthapi-310210719No ratings yet
- German EducationDocument5 pagesGerman Educationapi-282427998No ratings yet
- Hyderabad Educators Form - 1 (Responses) - Sheet8Document6 pagesHyderabad Educators Form - 1 (Responses) - Sheet8aruna.sharawatNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Maths Book Back and Creative Questions em 219385Document209 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Maths Book Back and Creative Questions em 219385Think BetterNo ratings yet
- The Dallas Post 02-26-2012Document20 pagesThe Dallas Post 02-26-2012The Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Upsr Paper Format Paper Type of Question Type of Number of Time Given Answer QuestionsDocument16 pagesMathematics Upsr Paper Format Paper Type of Question Type of Number of Time Given Answer QuestionsMohd Azri Mohd SidekNo ratings yet
- 2015 SASMO WMTC Intermediate Team Problems and SolutionsDocument13 pages2015 SASMO WMTC Intermediate Team Problems and SolutionsMinh NgôNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Marking SchemeDocument9 pagesMathematics Marking SchemeCharles AlloteyNo ratings yet
- Angles: Polygons: Edexcel GCSEDocument8 pagesAngles: Polygons: Edexcel GCSEAddy The humanNo ratings yet
- MATH2412 Dot ProductDocument7 pagesMATH2412 Dot ProductmjdaleneziNo ratings yet
- Grade I MTAP Math Challenge Questions and ReviewerDocument4 pagesGrade I MTAP Math Challenge Questions and ReviewerRustico Y Jerusalem88% (8)
- Ans and Sol Jee Main 2022 Phase 1-25-06 2022 e Math FinalDocument7 pagesAns and Sol Jee Main 2022 Phase 1-25-06 2022 e Math Finalkrishshukla984No ratings yet
- Term Exam Paper 5B Paper 2 Answers: New Century Mathematics (Second Edition) 5BDocument11 pagesTerm Exam Paper 5B Paper 2 Answers: New Century Mathematics (Second Edition) 5BAlan WongNo ratings yet
- Gagan Video ListDocument10 pagesGagan Video ListTOMNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 MTAP Elimination - 2005 PDFDocument4 pagesGrade 5 MTAP Elimination - 2005 PDFWreigh Paris67% (3)
- Assignment (Ch-Determinants) PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment (Ch-Determinants) PDFManas Ranjan JenaNo ratings yet
- Statements For BOEDocument12 pagesStatements For BOELogan PetersonNo ratings yet
- Predictors of School Affective Engagement During Elementary School A Systematic Reviewanalise PsicologicaDocument16 pagesPredictors of School Affective Engagement During Elementary School A Systematic Reviewanalise Psicologicayeah5795No ratings yet
- G6 - MATH (Fractions)Document10 pagesG6 - MATH (Fractions)Tyas PuspitaningrumNo ratings yet
- Teaching ResumeDocument3 pagesTeaching Resumeapi-222315895No ratings yet
- Differentiated Instruction PresentationDocument16 pagesDifferentiated Instruction Presentationapi-254516641No ratings yet