Professional Documents
Culture Documents
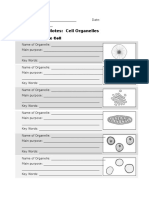
Cell Organelles
Uploaded by
api-3277577450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views2 pagesProkaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and are therefore smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells contain specialized organelles that perform complex tasks to help the cell survive. The mitochondria generates energy in the form of ATP, earning it the name the "powerhouse of the cell". The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus produce and modify proteins and lipids. The nucleus contains DNA and acts as the control center. Other organelles include vesicles, ribosomes, vacuoles, and the cell membrane.
Original Description:
Original Title
cell organelles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProkaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and are therefore smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells contain specialized organelles that perform complex tasks to help the cell survive. The mitochondria generates energy in the form of ATP, earning it the name the "powerhouse of the cell". The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus produce and modify proteins and lipids. The nucleus contains DNA and acts as the control center. Other organelles include vesicles, ribosomes, vacuoles, and the cell membrane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views2 pagesCell Organelles
Uploaded by
api-327757745Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and are therefore smaller than eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells contain specialized organelles that perform complex tasks to help the cell survive. The mitochondria generates energy in the form of ATP, earning it the name the "powerhouse of the cell". The endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus produce and modify proteins and lipids. The nucleus contains DNA and acts as the control center. Other organelles include vesicles, ribosomes, vacuoles, and the cell membrane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
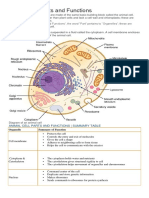
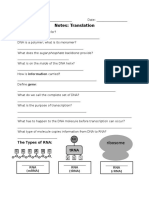
Cell Organelles
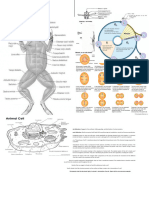
Prokaryotic cells are cells that do NOT contain any
membrane-bound organelles. They do still contain some
organelles, such as ribosomes and cell walls. Because they do
not contain individual compartments, they are much smaller than
eukaryotes.
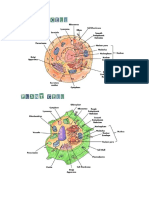
Eukaryotic cells are complex cells that contain many
specialized parts known as organelles. These organelles often
have their own membrane, and they help the cell perform the
complex tasks needed for survival.
The cells mitochondria perform the energy conversions
necessary to transfer the bulk of the energy taken from food
molecules into the energy molecule called ATP. This is why the
mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell.
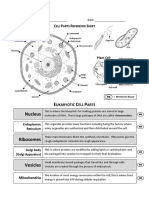
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the location where many
important molecules are created and metabolized. The rough ER
is where proteins are translated. It is the ribosomes that give the
rough ER its bumpy appearance. The smooth ER is where lipids
and steroids are synthesized. The endoplasmic reticulum also
distributes these new molecules throughout the cell.
The nucleus contains the genetic material of the cell in the
form of DNA. This DNA is packaged into large structures known
as chromosomes. The DNA contains the instructions or blueprint
for the cell, which is why the nucleus is often referred to as the
control center of the eukaryotic cell.
Vesicles are small membrane bound sacs that are used to
transport molecules into, out of and through the eukaryotic cell.
The primary function of the Golgi apparatus is to modify and
package large molecules, primarily proteins and lipids. This is
especially important for proteins that will eventually leave the
cell. Sugars and lipid molecules are added to the proteins in the
Golgi so that they can perform specific functions.
The cell membrane provides a barrier for the cell. The main
job of the cell membrane is to maintain the steady balance of
nutrients and energy in the cell we call homeostasis. It does this
by regulating which molecules enter and leave the cell. The cell
membrane also helps the cell communicate with other cells.
Cyto- means cell, and the cytoskeleton is made up of the
long, strong proteins that helps the cell keep its shape and
structure. It also helps the cell divide into two cells as it
reproduces.
Ribosomes are made mostly of rRNA, and they are found in
the cytoplasm of the cell. They are the molecular machines that
organize the translation of proteins. Ribosomes are found in high
numbers in the rough endoplasmic reticulum where much of the
cells translation of proteins occurs.
Vacuoles are membrane bound organelles which contain
water and other molecules. Vacuoles can serve many purposes
including storing nutrients and isolating wastes. The central
vacuole in plant cells helps the plant maintain turgor pressure
which keeps the cell rigid and stiff.
DNA is wound and wound into very compact structures
called chromosomes. Each chromosome contains a large amount
of DNA. DNA is the molecule that contains the blueprint for the
cell. DNA is wound and wound into very compact structures called
chromosomes. DNA is the molecule that contains the blueprint for
the cell. In prokaryotes, there is only one, circular chromosome.
One main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that
prokaryotes do NOT have a nucleus to store DNA inside of.
Some prokaryotic cells have a cell wall. This cell wall is
usually made of peptidoglycan and it provides the cell with
additional protection and structural support.
You might also like
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Cell FunctionDocument2 pagesCell Functionvuminhtut66No ratings yet
- Animal Cell PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell PDFPerry Sin67% (3)
- Assignment II: Macaranas, Mar SDocument7 pagesAssignment II: Macaranas, Mar SMar MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument37 pagesNotesDaideepya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- JetDocument14 pagesJetAnnie Lyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- Only Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The CytoplasmDocument14 pagesOnly Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The Cytoplasmrakan ilyasNo ratings yet
- Life Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologyDocument16 pagesLife Processes and Cells: Chapter 1:-Longman GCSE BiologynkllaeNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- Gen BioCell TheoryDocument18 pagesGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNo ratings yet
- CellDocument11 pagesCellNicole ArangurenNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument10 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionAngelique VeteNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- Basic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"Document12 pagesBasic Structural and Functional Units of Living Organisms"cbseiscNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDocument34 pagesChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellJayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsDocument15 pagesPlant Cells Cristae Mitochondria Chloroplasts: The Following Is A Glossary of Plant Cell Anatomy TermsanyoyoyNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument2 pagesZoologygabrf.pascualNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document10 pagesCell Organelles 2Hardik tyagiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 General BiologyDocument93 pagesLESSON 1 General Biologygelisan haruhiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsKarren Ferrer-Mora Handayan100% (1)
- CELLSDocument6 pagesCELLSFenny May SebonNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument7 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionJoanne AlindayoNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Pes5 6.umaliDocument4 pagesPes5 6.umaliJenny Shane UmaliNo ratings yet
- THE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaDocument16 pagesTHE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaJoshua DorisNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Parts Reference SheetDocument2 pages2 Cell Parts Reference Sheetapi-3268559130% (1)
- Phospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreDocument7 pagesPhospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreCmae VidadNo ratings yet
- Name: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDocument5 pagesName: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 pagesPlant Cell - LayoutMahiNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument4 pagesCell BiologyasadzamanchathaNo ratings yet
- "Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology IDocument23 pages"Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology ITeacher Ella MorillaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (2.1)Document13 pagesChapter 2 (2.1)mrtheunknownNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- BiotechDocument2 pagesBiotechKristel Faye Cortez SubiaNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- 11a Revision Pack T1Document36 pages11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument108 pagesBiochemJangNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellssalahuddin_md5935100% (1)
- The CellDocument36 pagesThe CellSam MumoNo ratings yet
- Foundation - 1 RecapDocument15 pagesFoundation - 1 RecapSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- 2013 Body Systems NotesDocument5 pages2013 Body Systems Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- 2 Transcription NotesDocument3 pages2 Transcription Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- North Mesquite High School Ms. Taylor's Biology ClassDocument51 pagesNorth Mesquite High School Ms. Taylor's Biology Classapi-3277577450% (1)
- 3 Translation NotesDocument3 pages3 Translation Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- 1 Vocabulary Reference SheetDocument5 pages1 Vocabulary Reference Sheetapi-327757745No ratings yet
- 2016 RulesandproceduresDocument3 pages2016 Rulesandproceduresapi-327757745No ratings yet
- 2 Cell Parts Reference SheetDocument2 pages2 Cell Parts Reference Sheetapi-327757745No ratings yet
- SynthesisDocument3 pagesSynthesisapi-327757745No ratings yet
- North Mesquite High School Ms. Taylor's Biology ClassDocument2 pagesNorth Mesquite High School Ms. Taylor's Biology Classapi-327757745No ratings yet
- RubricfirstsixweeksDocument2 pagesRubricfirstsixweeksapi-327757745No ratings yet
- DnanotesDocument3 pagesDnanotesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- 4 Energy Conversions NotesDocument4 pages4 Energy Conversions Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- Energy Conversions1Document3 pagesEnergy Conversions1api-327757745No ratings yet
- 2 Cell Organelles NotesDocument3 pages2 Cell Organelles Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- 1 Comparing Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes NotesDocument2 pages1 Comparing Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Reading Sample FunctionDocument3 pagesBiomolecules Reading Sample Functionapi-327757745No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Reading Sample Part 1-Edited For NotesDocument2 pagesBiomolecules Reading Sample Part 1-Edited For Notesapi-327757745No ratings yet
- Calendar 16-17ljDocument2 pagesCalendar 16-17ljapi-327757745No ratings yet
- ITA 2001 Warm Up Session MasterclassDocument2 pagesITA 2001 Warm Up Session MasterclassMauricio EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of NeuronsDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of NeuronsVan Jasper Pimentel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test-G8-Quarter-4Document13 pagesSummative Test-G8-Quarter-4Charmaine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy For The Thorax - A Biomechanical Approach - D. Lee (DOPC, 1994) WW PDFDocument156 pagesManual Therapy For The Thorax - A Biomechanical Approach - D. Lee (DOPC, 1994) WW PDFEliMihaela100% (2)
- Inhaled Anesthesia For BirdsDocument18 pagesInhaled Anesthesia For BirdsBianca PaludetoNo ratings yet
- Zabrina Joana DDocument4 pagesZabrina Joana DEmman BalidoNo ratings yet
- A&p Lab Ex 38Document6 pagesA&p Lab Ex 38Alex Lee95% (19)
- Management Organizational Behavior: Individuals in Organizations: Perception, Personality, and Cultural DifferencesDocument37 pagesManagement Organizational Behavior: Individuals in Organizations: Perception, Personality, and Cultural DifferencestesfalemNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ModulesDocument37 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ModulesAllan IgbuhayNo ratings yet
- Inhs PDFDocument34 pagesInhs PDFKrupa RaoNo ratings yet
- 1 Rep MassDocument97 pages1 Rep MassIt's Just Me100% (3)
- Worksheets-Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument8 pagesWorksheets-Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsCarlos GuardadoNo ratings yet
- MIO MediumDocument2 pagesMIO MediumIntan Farida YasminNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument40 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosiscmillica1176No ratings yet
- Adult Health Final Study GuideDocument5 pagesAdult Health Final Study GuideNurseNancy93100% (1)
- Circadian RhythmsDocument4 pagesCircadian Rhythmsapi-642709499No ratings yet
- What Is Ghrelin? Results Ghrelin Effecting Fat ScoresDocument1 pageWhat Is Ghrelin? Results Ghrelin Effecting Fat ScoresJihad Abou Ali WakedNo ratings yet
- The Real TabataDocument11 pagesThe Real TabataJason TiongcoNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument3 pagesVital SignsNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Brigada EskwelaDocument35 pagesBrigada EskwelaRichard Panaguiton CanlasNo ratings yet
- Skeletal StructureDocument58 pagesSkeletal StructureCsd AutoprimNo ratings yet
- U.S. Army Survival Manual FM 21-76 (June 1992)Document572 pagesU.S. Army Survival Manual FM 21-76 (June 1992)explorer_ebook100% (1)
- Puntos Craneometricos CompressDocument13 pagesPuntos Craneometricos CompressLaura PNo ratings yet
- As Biology With Stafford Unit 3 Workbook Answers PDFDocument21 pagesAs Biology With Stafford Unit 3 Workbook Answers PDFFatma ZorluNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Organs 2004Document323 pagesEndocrine Organs 2004Game TesterNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Tanpa Bab PembahasanDocument67 pagesSkripsi Tanpa Bab PembahasanUpitFlowNo ratings yet
- Department of Pathology: Mrs. Malyala SujathaDocument6 pagesDepartment of Pathology: Mrs. Malyala Sujathasanath kumarNo ratings yet
- Updates in The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCDocument7 pagesUpdates in The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Kathryn Evans Kreider, DNP, FNP-BCLenin Zavaleta RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic DrugsDocument19 pagesAnticholinergic DrugseashshankarNo ratings yet
- Taller 8Document2 pagesTaller 8monchito83hotmailesNo ratings yet