Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foot Ankle and Lower Leg Notes
Uploaded by
Andrew OchoaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Foot Ankle and Lower Leg Notes
Uploaded by
Andrew OchoaCopyright:
Available Formats
August 30th foot ankle and lower leg notes
Foot, ankle and lower leg make up 15% of injuries seen.
Feet absorb 3x body weight
3 different arches
o medial longitudinal arch
Arch you think of (even etched into shoes
o Lateral longitudinal arch
Not as large as medial
o Transverse arch
Across the base of each metatarsal
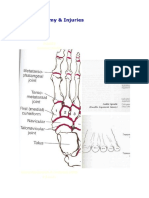
Basic anatomy
o 26 bones in foot (7 tarsals, 5 metatarsals, 14 phalanges)
tibia
fibula
medial malleolus
lateral malleolus
tarsals
talus
o talorcruel
plantar/dorsi flexion joint
top
o subtalor
inversion/eversion joint
bottom
calcaneous
metatarsals
phalanges
o Ligaments
Anterior talofibular ligament (ATF)
Connects talus and fibula
Plantar flexion+ inversion = damage
Calcaneofibular ligament (CF)
Calcaneus and fibula
Inversion damages
Deltoid ligament
Triangle shaped
Medial
Eversion damages
o Articulations of the ankle
Talocrural joint
o Muscles
Intrinsic Muscles
Muscles that originate and insert within ft.
Extrinsic
originate outside ft, insert inside ft.
Gatroc/soleus (calf)
o Ankle sprains
Very common
Mechanism= inversion/ inversion + plantar flexion
Inversion alone=CF
Inversion +plantar flex= CF+ATF
Less common mechanism =eversion
Fibula helps stop eversion
o Special Tests
Anterior drawer test
Testing the integrity of the anterior Talofibular
ligament
Heel in hand, footrests on forearm, pull anteriorly
Talar tilt test
Testing integrity of the Calcaneofibular ligament
(Inversion) and the deltoid (Eversion)
Passively moving athletes foot into inversion or
eversion
o 3 different categories of sprain
1st
swelling, ecchymosis, (least severe)
loss of function tenderness
unable to walk, extreme pain
2nd
3rd
o treatment
R.I.C.E.
ROM/stretching exercises
Strengthening exercises
Functional movement
Proprioception
Skill specific
Return to play
o Arch sprains
Any ligaments can suffer from ligament sprain
When weakened, cannot absorb shock as well
Once ligament is stretched, fail to keep the foot in proper
pos
Mechanism = pronation and supination of the foot
o Blisters
Mechanism
friction
As layers of skin rub, friction causes separation of top layer
Fluid fills the separation area
Treatment
prevent further friction, relieve pain, avoid infection
o Great toe sprain
AKA turf toe
Mechanism
Sliding backwards while plantar flexed
(hyperextension of toe)
Treatment
Provide support c tape, ROM exercises
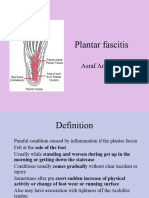
o Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fascia is a wide, nonelastic ligament tissue that
extends from the calcaneus to the distal metatarsals
Mechanism
Chronic
o Overuse, unsupportive footwear, running on
hard surfaces, or tight Achilles
Seen freq. in cross country and track
Treatment
Correct insoles
Arch tape
o Heel bruise
Contusion to calcaneus
Fat pad receives repetitive stress or acute hard blow
o Heel spur
Boney growth on calcaneus that causes painful
inflammation of surrounding soft tissue
Plantar fascia is stretched and pulled overtime at the
attachment site.
o Muscle cramps
Sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle
Fatigue
Fracture
Dehydration
Lack of nutrients
Poor flexibility
Improper equipment
Treatment
Stretching and fluid replacement
o Achilles tendonitis
Inflammation of the Achilles tendon
Where the gastroc and soleous meet at keel
Swelling caused by the gradual onset or single
incident of overtstressing the Achilles
Treatment
Stretching, correcting gait, and taking ibuprofen
o Achilles tendon rupture
Tendon completely tears
Muscle will ball up towards knee
Overextension or sudden force while dorsiflexed
Treatment
Surgery + 1 year rehab
o Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS)
Shin splint
Doing too much too soon
Causes
Strain
Microfx
Tight calf
Improper ft. wear/gait
Uneven or hard surfaces
Treatment
Ice
Reduce activity
Stretching
o Stress fx
Incomplete crack in bone
Sharp localized pain
o Compartmental syndrome
Serious condition that may develop when swelling exists in
1+ of the compartments in the lower leg
Swelling caused from contusion, fx, or infection
Causes increased pressure cutting off blood flow/
nerve signals
Can lead to loss off appendages/ phalanges or
serious damage
Must be treated within 72 hours
You might also like
- AnkleDocument6 pagesAnkleitoolNo ratings yet
- Plantar Fasciitis Exercises and Home TreatmentFrom EverandPlantar Fasciitis Exercises and Home TreatmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Foot Anatomy Tendons and LigamentsDocument3 pagesFoot Anatomy Tendons and Ligamentsanak_kost_aji_baungNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heel Spur, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heel Spur, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Ankle Power PointDocument36 pagesAnkle Power PointjermaineNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Bones and JointsDocument43 pagesFoot and Ankle Bones and Jointshannah murphyNo ratings yet
- Ankle Anatomy & InjuriesDocument13 pagesAnkle Anatomy & Injuriesvictormusonda78No ratings yet
- ANKLE JOINT &joints of FootDocument35 pagesANKLE JOINT &joints of Foothhaanniiss3870No ratings yet
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus FinalDocument28 pagesCongenital Talipes Equinovarus FinalLakshmi Narayan R100% (2)
- Foot Anatomy: Muhammad AzamDocument30 pagesFoot Anatomy: Muhammad AzamMuhammad AzamNo ratings yet
- Written Report of The Lower Limb (Lower Leg)Document16 pagesWritten Report of The Lower Limb (Lower Leg)Christi EspinosaNo ratings yet
- 30.ankle & Foot DiseasesDocument46 pages30.ankle & Foot DiseasesDuha HamidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologySarah CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- FeetDocument47 pagesFeetChandradatNo ratings yet
- Joints: DR Sendhi TristantiDocument50 pagesJoints: DR Sendhi TristantiNafis Edi YahyanaNo ratings yet
- Lower Leg and FootDocument40 pagesLower Leg and Footapi-295870055No ratings yet
- Plantas Fascitis FinalDocument23 pagesPlantas Fascitis Finalasraf amirullahNo ratings yet
- Knee AnatomyDocument44 pagesKnee AnatomyYanti WijayaNo ratings yet
- Study Case OT (Fracture Mid Shaft of Tibia)Document28 pagesStudy Case OT (Fracture Mid Shaft of Tibia)radicalmpNo ratings yet
- Lec 18 THE ANKLE JOINTDocument12 pagesLec 18 THE ANKLE JOINTMaheen IrfanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The FootDocument26 pagesAnatomy of The FootKumar BalramNo ratings yet
- 4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingDocument53 pages4-Conservative Treatment FX, CastingMuhammad TaqwaNo ratings yet
- Knee Sport Injury - Martinus VTDocument62 pagesKnee Sport Injury - Martinus VTIcha NathaniaNo ratings yet
- (10 F) FOOT - Bones, Ligaments, TendosDocument6 pages(10 F) FOOT - Bones, Ligaments, TendosJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Foot and AnkleDocument4 pagesFoot and AnkleDonna EnyNo ratings yet
- Foot Ankle AnatomyDocument26 pagesFoot Ankle AnatomyBrad HunkinsNo ratings yet
- Foot and AnkleDocument58 pagesFoot and Anklekyliever100% (1)
- Bones of The FootDocument3 pagesBones of The FootHaris ImranNo ratings yet
- Origin and Insertion MusclesDocument5 pagesOrigin and Insertion MusclesStephenMontoyaNo ratings yet
- Ankle & Foot MechanicsDocument47 pagesAnkle & Foot MechanicsAhmed El goharyNo ratings yet
- Knee InjuryDocument44 pagesKnee Injuryvamshi reddyNo ratings yet
- Total Knee ReplacementDocument35 pagesTotal Knee ReplacementYumi Kaito100% (3)
- Triple Arthrodesis: DR Chirag Patel Department of Orthopaedics ST Stephen's HospitalDocument41 pagesTriple Arthrodesis: DR Chirag Patel Department of Orthopaedics ST Stephen's HospitalImam SulemanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of FeetDocument22 pagesAnatomy of FeetsherysheryyNo ratings yet
- AnkleDocument54 pagesAnkleUmi ShakiraNo ratings yet
- 21 - MSK8 Carpal TunnelDocument51 pages21 - MSK8 Carpal TunnelNTRisforthinkersNo ratings yet
- 7 CavigliaDocument24 pages7 CavigliaFrancesco AgostiniNo ratings yet
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus FinalDocument28 pagesCongenital Talipes Equinovarus FinalTibin Kavumkal ThomasNo ratings yet
- Foot Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesFoot Anatomy and PhysiologyMarta BłaszczykNo ratings yet
- Ankle InjuriesDocument32 pagesAnkle InjuriesArefa PandorNo ratings yet
- L12Document45 pagesL12Ahmed El goharyNo ratings yet
- 1 Lower Limb Skeleton 2013Document20 pages1 Lower Limb Skeleton 2013Ayu FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Cat Muscles!Document5 pagesCat Muscles!Heather UyNo ratings yet
- EQS 370 Equine Evaluation and SelectionDocument29 pagesEQS 370 Equine Evaluation and Selectionrmlinares9328No ratings yet
- 2008 Case Files AnatomyDocument4 pages2008 Case Files AnatomyPJHGNo ratings yet
- Presented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KDocument81 pagesPresented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Apps To Functional Anatomy Lecture 6Document9 pagesApps To Functional Anatomy Lecture 6jenNo ratings yet
- Amputation of ExtremitiesDocument51 pagesAmputation of ExtremitiesKiyasweet HaniNo ratings yet
- The Foot and Ankle1Document20 pagesThe Foot and Ankle1Ágúst Aðalsteinn ÓlafssonNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Injuries of The AthleteDocument24 pagesFoot and Ankle Injuries of The AthleteSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- Club FootDocument104 pagesClub FootKittipong PoolketkitNo ratings yet
- 1 Articulating Surfaces 2 Ligaments: The Ankle JointDocument6 pages1 Articulating Surfaces 2 Ligaments: The Ankle JointHassan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Skeletal SystemPauline JoyceNo ratings yet
- The Ankle Joint: Articulating BonesDocument5 pagesThe Ankle Joint: Articulating BonesJoe SpencerNo ratings yet
- Meniscal TearDocument6 pagesMeniscal TearAdrian Diago TevesNo ratings yet
- MUSCULOSKELETALDocument27 pagesMUSCULOSKELETALCassandra Mae PerochoNo ratings yet
- Ankle Instability: Dr. Syarif Hidayatullah, SP - OT, M.KesDocument75 pagesAnkle Instability: Dr. Syarif Hidayatullah, SP - OT, M.Kesahmad zakyNo ratings yet
- (9F) Ankle - Bones, Joints, Tendons and LigamentsDocument4 pages(9F) Ankle - Bones, Joints, Tendons and LigamentsJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- KneeDocument29 pagesKneedoctoradeeb18No ratings yet
- Tsoukaki 2012Document8 pagesTsoukaki 2012Marina JoelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety in HealthcareDocument2 pagesElectrical Safety in HealthcareNur Aqilah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lüscher Colour TestDocument1 pageLüscher Colour TestVicente Sebastián Márquez LecarosNo ratings yet
- Satvik DietDocument3 pagesSatvik DietDisha TNo ratings yet
- Biodata Format FinalDocument5 pagesBiodata Format FinalCharles Saurus PacomaNo ratings yet
- Excerpt From Treating Trauma-Related DissociationDocument14 pagesExcerpt From Treating Trauma-Related DissociationNortonMentalHealth100% (3)
- ID Virus Avian Influenza h5n1 Biologi Molek PDFDocument13 pagesID Virus Avian Influenza h5n1 Biologi Molek PDFArsienda UlmafemaNo ratings yet
- SDS N 7330 NorwayDocument15 pagesSDS N 7330 NorwaytimbulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Coaching: Confidential Page 1 of 52 5/1/2009Document52 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Coaching: Confidential Page 1 of 52 5/1/2009James ZacharyNo ratings yet
- Study On Consumer Behavior For Pest Control Management Services in LucknowDocument45 pagesStudy On Consumer Behavior For Pest Control Management Services in LucknowavnishNo ratings yet
- EO Supporting The Immunization Activities - EditedDocument2 pagesEO Supporting The Immunization Activities - EditedDem SalazarNo ratings yet
- DM 2020-0187 - Must Know Covid IssuancesDocument18 pagesDM 2020-0187 - Must Know Covid IssuancesFranchise AlienNo ratings yet
- 13fk10 Hav Igg-Igm (D) Ins (En) CeDocument2 pages13fk10 Hav Igg-Igm (D) Ins (En) CeCrcrjhjh RcrcjhjhNo ratings yet
- School Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersDocument4 pagesSchool Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersRyan A. CabalidaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: General Biology 2 (Quarter IV-Week 3)Document4 pagesActivity 2: General Biology 2 (Quarter IV-Week 3)KatsumiJ AkiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ParuDocument31 pagesJurnal Parudr. syah sembung wasisoNo ratings yet
- 3.3.2.4 Love AnimalDocument8 pages3.3.2.4 Love AnimalRina ErnawatiNo ratings yet
- Boracay Rehabilitation: A Case StudyDocument9 pagesBoracay Rehabilitation: A Case StudyHib Atty TalaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 DQ 2.Document3 pagesTopic 5 DQ 2.Emmanuel OpiyoNo ratings yet
- Biocontrol in Disease SugarcaneDocument11 pagesBiocontrol in Disease SugarcaneAlbar ConejoNo ratings yet
- ErpDocument31 pagesErpNurul Badriah Anwar AliNo ratings yet
- PNF 8th EditionDocument7 pagesPNF 8th EditionDanisaWajeNo ratings yet
- Msds Uq160 enDocument5 pagesMsds Uq160 enAnnalisa GiammòNo ratings yet
- 7 Contoh Analytical Exposition Pendek Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pages7 Contoh Analytical Exposition Pendek Bahasa InggrisDarsi YujiwatiNo ratings yet
- Sps8 Q1mod1 Skill Related Parameters Noel Rullan Bgo v2Document20 pagesSps8 Q1mod1 Skill Related Parameters Noel Rullan Bgo v2RandyNo ratings yet
- Code of Conduct Shell Vs PetronasDocument4 pagesCode of Conduct Shell Vs PetronasSharulNizamAkilayni100% (1)
- The Role of Women in Trade Unions and Nation BuildingDocument18 pagesThe Role of Women in Trade Unions and Nation BuildingSneha KanitCar Kango100% (1)
- Top 10 Regulatory Challenges in The Healthcare EnvironmentDocument3 pagesTop 10 Regulatory Challenges in The Healthcare EnvironmentNicki BombezaNo ratings yet
- Mosh RoomDocument21 pagesMosh RoomBrandon DishmanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards Healtth Care ProductsDocument46 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards Healtth Care ProductsJayesh Makwana50% (2)
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsFrom EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (97)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessFrom EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Relentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableFrom EverandRelentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (788)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayFrom EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayNo ratings yet
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouFrom EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerFrom EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingFrom EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (67)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionFrom EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindFrom EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- Yin Yoga: How to Enhance Your Modern Yoga Practice With Yin Yoga to Achieve an Optimal Mind-Body Connection: Yoga Mastery SeriesFrom EverandYin Yoga: How to Enhance Your Modern Yoga Practice With Yin Yoga to Achieve an Optimal Mind-Body Connection: Yoga Mastery SeriesNo ratings yet
- Pranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingFrom EverandPranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Muscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!From EverandMuscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- True Yoga: Practicing With the Yoga Sutras for Happiness & Spiritual FulfillmentFrom EverandTrue Yoga: Practicing With the Yoga Sutras for Happiness & Spiritual FulfillmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.From EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (124)
- Strength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymFrom EverandStrength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Tibetan Yoga: Magical Movements of Body, Breath, and MindFrom EverandTibetan Yoga: Magical Movements of Body, Breath, and MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (133)
- Fascial Training: With Easy Exercises To More Mobility And Less Pain (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)From EverandFascial Training: With Easy Exercises To More Mobility And Less Pain (10 Minutes Fascia Workout For Home)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Which Comes First, Cardio or Weights?: Fitness Myths, Training Truths, and Other Surprising Discoveries from the Science of ExerciseFrom EverandWhich Comes First, Cardio or Weights?: Fitness Myths, Training Truths, and Other Surprising Discoveries from the Science of ExerciseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (47)
- Easy Strength: How to Get a Lot Stronger Than Your Competition-And Dominate in Your SportFrom EverandEasy Strength: How to Get a Lot Stronger Than Your Competition-And Dominate in Your SportRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.From EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Wheels of Life: A User's Guide to the Chakra SystemFrom EverandWheels of Life: A User's Guide to the Chakra SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- Music For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicFrom EverandMusic For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 5-Minute Yoga: A More Energetic, Focused, and Balanced You in Just 5 Minutes a DayFrom Everand5-Minute Yoga: A More Energetic, Focused, and Balanced You in Just 5 Minutes a DayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceFrom EverandEndure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Mind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeFrom EverandMind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Calisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesFrom EverandCalisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Somatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindFrom EverandSomatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindNo ratings yet