Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Contents: Design Note On Level Crossing Inlet
Uploaded by
suranga dadallageOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Contents: Design Note On Level Crossing Inlet
Uploaded by
suranga dadallageCopyright:
Available Formats
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
1 Contents
1.
Introduction and Background ......................................................................................................... 2
1.1
Reference Standards and Documents .................................................................................... 2
1.2
Design Summary ..................................................................................................................... 2
Design Calculations ......................................................................................................................... 3
2.1
Design Parameters .................................................................................................................. 3
2.2
Hydraulic force calculation ..................................................................................................... 3
2.3
No.of beams and spaces between beams .............................................................................. 4
2.4
Forces on beams and stress calculations................................................................................ 5
2.5
Beam Deflection...................................................................................................................... 8
2.6
Skin Plate................................................................................................................................. 9
Gate Lifting Forces Calculation .....................................................................................................10
3.1
Gate weight...........................................................................................................................10
3.2
Buoyancy of submerged parts ..............................................................................................10
3.3
Friction forces on sliding surfaces.........................................................................................11
3.4
Combined operating load .....................................................................................................11
3.5
Selected Lifting Apparatus technical details ........................................................................12
3.6
Arrangement of the Gate......................................................................................................12
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
1. Introduction and Background
The purpose of this document is to present calculations and conclusions of design phase of Level
Crossing Inlet at Wavulewa to Upper Mediyawa Route. This inlet gate set can be considered as
Low Head Vertical Slide Gates.
1.1 Reference Standards and Documents
IS 9349 (2006): Recommendations for structural design of medium and high head slide
gates.
IS 6938 (2005): Design of rope drum and chain hoists for hydraulic gates.
Design of Hydraulic Gates- Erbisti P.C.F
IS 5620 (1985): Recommendations for Structural Design Criteria for Low Head Slide Gates.
Engineer Manual EM 1110-2-2701- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 203141000
1.2 Design Summary
Structure Name
Location
Type of Structure
No.of Structures
Operating Mechanism
Sealing method
Level Crossing Inlet
Wavulewa to Upper Mediyawa Route
Low head vertical slide gate
02
Electrical motor and manual
Metallic strip
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
2 Design Calculations
2.1 Design Parameters
Canal full supply level
Design head
Clear span
Seal span
Clear height
Materials
1.45m
2.2m
2.4m
2.7m
2.2m
ASTM A36
2.2 Hydraulic force calculation
Specific weight of water
span of side seals
Maximum headwater on sill
Total force
9.807
2.7
2.2
64.07
kN/m3
m
m
kN
Total Hydraulic force on the gate = 64.07 kN
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
2.3 No.of beams and spaces between beams
According to above methodology beams are loaded equally to withstand the hydrostatic force
acting on the gate.
1
Max. Head
water sill m
2.2
No
beams
3
2.2
2.2
Area No
hk (depth) Yk(depth of
m
1.27
beams) m
0.85
1.80
1.55
2.20
2.00
Then the pressures acting on the beam centres, which are spaced according to above Yk,
P = . Yk,
P = Pressure kN/m2
= Specific weight of water 9.807 kN/m3
Yk = Depth of beams m
Depth
arrangements
of beams m
0.00
Pressure at relevant
points kN/m2
0.000
0.85
8.336
1.55
15.201
2.00
19.614
2.20
21.575
Point
2.4
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
Forces on beams and stress calculations
Hydro static force acting on beams of the gate is given by,
In above equations,
Ra, Rb = Reaction forces kN
B = Seal span 2.7 m
bi = space between two beams, m
Pa, Pb = Pressure kN/m2
Index
Total Force
Beam1
3.188 kN
Beam2
16.407 kN
Beam3
19.81 kN
Beam4
24.65 kN
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
Then calculated forces will be applied to determine the maimum bending moment and
shear forces acting on beams.
Maimum bending moment and shear force given by,
M = Maimum bending moment kNm
L = supporting span 2.4m
S = F/2
S = Shar Force kN
B = seal span 2.7m
F = Load on the beam kN
Max. Bending
Moment kNm
Shearing
force
kN
2.7
2.4
1.20
1.594
16.407
2.7
2.4
6.15
8.2035
19.81
2.7
2.4
7.43
9.905
24.65
2.7
2.4
9.24
12.325
Beam No
Design Load
kN
3.188
According to above values now need to select a steel profile as beams which is satisfy
the allowable bending stress and shear stress for such design.
Allowable bending stress = 0.68 x (minimum yield stress)
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
Allowable shear stress = 0.39 x (minimum yield stress)
Bending stress = (Bending moment)/(section modulus)
Shear Stress = (Shear force)/ (Sectional Area)
Below mentioned tapered flange C-Channel 150x75x9mm section properties satisfied
the design requirements.
Beam No
Max. Bending
Moment kNm
Section Modulus
m3
Bending Stress
MPa
Allowable bending
stress MPa
0.2275
6.018519
168.64
1.17075
1.41 X 10-4
1.41 X 10-4
30.97222
168.64
1.41225
37.36111
168.64
1.757525
46.49537
168.64
1.41 X 10-4
1.41 X 10-4
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
Beam No
Shearing force
kN
Area of the Section
cm2
Shear Stress
MPa
Allowable shear
stress MPA
1.594
30.5
0.523
99
8.2035
30.5
2.69
99
9.905
30.5
3.248
99
12.325
30.5
4.041
99
2.5 Beam Deflection
Deflection of beams given by,
P = Force acting on the beam
L= support span
B= seal span
E = modulus of elasticity 200 GPa
I = moment of inertia of the section
Design limitation of deflection is, it should be lower than the value of 1/800.
Design Supporting
Beam
Load
Span
No
N
L mm
1
2
3
4
3188
16407
19810
24650
2700
2700
2700
2700
Seal
Span
B
mm
2400
2400
2400
2400
E
modulus
of
Elasticity
N/mm2
200,000.00
200,000.00
200,000.00
200,000.00
Moment of
Inertia
mm4
Deflection
mm
10,600,000.00
10,600,000.00
10,600,000.00
10,600,000.00
0.427
2.198
2.654
3.303
Deflection accepted
ratio
def.ratio
1/800
Difference
(1/800 )
0.0001582
0.0008142
0.0009831
0.0012233
0.00109179
0.000435777
0.000266898
2.6705E-05
0.00125
0.00125
0.00125
0.00125
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
2.6 Skin Plate
For this steel made sliding gate selected skin plate thickness as the lowest
recommended value, 8mm. Then checked stresses acting on the skin plate.
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
L mm
(vertical
beam
pitch)
900
900
700
1.2857143
900
700
0.77777778
15.201
30.9
59.45
168.64
900
450
900
450
0.5
17.4
30.9
68.05
168.64
Bay
b/a
P kN/m
850
0.94444444
8.33
t skin
plate
thickness
mm
8
l mm
(Beam
space)
L/l
a mm
b
mm
850
1.0588235
900
stress
MPa
a allowable
stress
MPa
30.9
32.58
168.64
Gate Lifting Forces Calculation
The gate hoist designs to overcome the resistance forces arising during the gate
movements. In general following forces are to be considered.
Gate weight
Buoyancy of submerged part
Friction forces on supports
Friction forces on seals
Down-pull/uplift forces
3.1 Gate weight
Gate Weight
weight of structure
7251 N
weight of mechanical parts
(wheels,pins,seals etc.)
0N
Total weight with debris &
paint
7.61 kN
3.2 Buoyancy of submerged parts
10
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
Wr = Buoyancy force
Wg = Weight of Gate
7.85 = Specific gravity of steel
Wg
Wr
Weight of
the gate
Buoyancy
force
7.61 kN
0.96 kN
(maximum)
** Minimum buoyancy force = 0 kN
3.3 Friction forces on sliding surfaces
Friction coefficient (steel to steel) = 0.4
Reaction force N = (Total Hydraulic Force on the Gate) X (Friction Coefficient)
= 25.628 kN
3.4 Combined operating load
During Lifting (kN)
During Lowering(kN)
Gate weight
7.61 (+)
7.61 (-)
Buoyancy force
0 (min.)
0.96(max.)(+)
25.628 (+)
0-25.628(+)
1.85 (+)
1.85 (-)
52.63 (+)
17.128 (+)
Friction force (due to sealing)
Weight of the Spindle
Friction force (hinges, rollers, etc)
Total Force
11
Design Note on Level Crossing Inlet 2014
Then we have to select self- locked gear box for the gate operation. Otherwise gate will
be closed due to its self weight automatically.
Then total lifting force with the factor of safety 1.5,
= 52.63 kN
3.5 Selected Lifting Apparatus technical details
Screw Dia = 2 inch
No. of Spindles = 02
Load capacity of the gear box = 2800 kg/ per gear box
Motor Speed = 600 rpm
Output shaft speed = 28 rpm
Power of the Motor = 1.5 kW
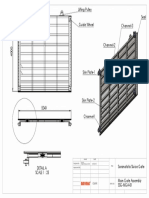
3.6 Arrangement of the Gate
12
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryFrom EverandThe Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryNo ratings yet
- Verticaal Gate DesignDocument12 pagesVerticaal Gate Designsuranga dadallageNo ratings yet
- Design of The Low Head Slide Gate: A) Structural SteelDocument17 pagesDesign of The Low Head Slide Gate: A) Structural SteelAlok Sarkar100% (2)
- Gate CalculationDocument17 pagesGate CalculationWAN CHAND100% (4)
- Design of Vertical Lift GATESDocument31 pagesDesign of Vertical Lift GATESDheeraj Verma90% (39)
- Design of Hydraulic GateDocument20 pagesDesign of Hydraulic GateTarunPatra100% (1)
- Design of Vertical Lift Service Gates of Budaun Irrigation ProjectDocument33 pagesDesign of Vertical Lift Service Gates of Budaun Irrigation ProjectVikash Yadav83% (6)
- Gate Design ProcedureDocument42 pagesGate Design ProcedureNoppadol Ariyakrua92% (13)
- Design Calculations of Trash RackDocument3 pagesDesign Calculations of Trash RackDheeraj Thakur100% (4)
- Gate and Hoist DesignDocument15 pagesGate and Hoist DesignRajivNo ratings yet
- Vertical Lift Hydraulic Gate DesignDocument40 pagesVertical Lift Hydraulic Gate Designmesam100% (3)
- Design of Vertical Lift Service Gates Salarond Barrage: 1.0 Technical DetailsDocument23 pagesDesign of Vertical Lift Service Gates Salarond Barrage: 1.0 Technical DetailsRanjeet Singh MoreyNo ratings yet
- 3D Hydro Mechanical (Gates)Document52 pages3D Hydro Mechanical (Gates)api-19871259100% (2)
- EM 1110-2-2701 - Vertical Lift Gates 1Document61 pagesEM 1110-2-2701 - Vertical Lift Gates 1PDHLibrary50% (2)
- Design of GateDocument29 pagesDesign of Gateramkumar121No ratings yet
- Is 4622 2003Document27 pagesIs 4622 2003Apurba Haldar100% (1)
- Vetical Dam Hoist MechanismDocument38 pagesVetical Dam Hoist Mechanismkrishnan_selvaNo ratings yet
- Radial Gate AnalysisDocument16 pagesRadial Gate AnalysisAkshay Badhani100% (1)
- Weir Intake Gate PDFDocument12 pagesWeir Intake Gate PDFIchwan RachmantoNo ratings yet
- Section 9.0 - CulvertsDocument11 pagesSection 9.0 - CulvertsOMANAKUTTAN100% (1)
- Radial GateDocument47 pagesRadial Gatenidhisasidharan100% (2)
- Sample Calculation - CR GateDocument5 pagesSample Calculation - CR GateRose Mary100% (1)
- 16 Screw Hoist For Sluice Gate PDFDocument10 pages16 Screw Hoist For Sluice Gate PDFsamNo ratings yet
- Design of The Low Head Slide GateDocument15 pagesDesign of The Low Head Slide GateAlok Sarkar100% (1)
- 1offtake Gates DesignDocument26 pages1offtake Gates Designprasadnn2001No ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of Gate Operating SystemsDocument6 pages1 - Overview of Gate Operating SystemsPradeep VM100% (1)
- Vertical Gates Design PDF FreeDocument33 pagesVertical Gates Design PDF FreeAbdul wahid ButtNo ratings yet
- Bifurcation Design PDFDocument51 pagesBifurcation Design PDFMadhav BaralNo ratings yet
- Radial Gate Design ProcedureDocument2 pagesRadial Gate Design ProcedureSangyt Karna100% (2)
- Design of Slide Gate Size 1.6 X 2 MDocument4 pagesDesign of Slide Gate Size 1.6 X 2 MTarunPatraNo ratings yet
- Trashrack DesignDocument12 pagesTrashrack DesignAnonymous b9DIaPTq6BNo ratings yet
- 4 Skin Plate Form Work PDFDocument4 pages4 Skin Plate Form Work PDFraghuveer11No ratings yet
- Gates and HoistsDocument184 pagesGates and HoistsVikas Shrimali86% (7)
- Hydro Dynamic ForcesDocument34 pagesHydro Dynamic Forcesvikasgahlyan100% (1)
- Branch CalcDocument111 pagesBranch CalcAnonymous 6S9tcbh100% (2)
- Sickle PlateDocument24 pagesSickle PlateanjnaNo ratings yet
- Gates, Hoisting ArrangementsDocument21 pagesGates, Hoisting ArrangementsArjun M KumarNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of Penstock Indian StandardDocument24 pagesStructural Design of Penstock Indian StandardPEJU0007100% (2)
- Hydraulics and Design of TrashrackDocument25 pagesHydraulics and Design of TrashracksapkotamonishNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Gate SealsDocument35 pagesHydraulic Gate SealsZohaib AnserNo ratings yet
- DLT 5039-95 Specification For Design of Steel Gate in Hydropower and Water Conservancy ProjectsDocument64 pagesDLT 5039-95 Specification For Design of Steel Gate in Hydropower and Water Conservancy Projectssaliyarumesh2292No ratings yet
- Draft Tube GateDocument23 pagesDraft Tube GateAnonymous sfkedkymNo ratings yet
- Radial+Gate+With+Arm+ +6+m.+++Haji+ShaherDocument65 pagesRadial+Gate+With+Arm+ +6+m.+++Haji+ShaherMuhammed Wahid100% (3)
- 10.2 Erection & Maintenance of Gates & HoistsDocument22 pages10.2 Erection & Maintenance of Gates & Hoistsharry100% (1)
- 1 Steel Penstock: 1.1 Location and ArrangementDocument7 pages1 Steel Penstock: 1.1 Location and ArrangementDangol RupeshNo ratings yet
- ANCHOR BLOCK Design SheetDocument5 pagesANCHOR BLOCK Design SheetMohanSharma0% (1)
- Kodaikanal Weir GateDocument32 pagesKodaikanal Weir GateHarish Kumar MahavarNo ratings yet
- EM 1110-2-2701-Vertical Lift GateDocument61 pagesEM 1110-2-2701-Vertical Lift Gatebasilecoq100% (2)
- Guide Lines For Erection of Verticallift GatesDocument46 pagesGuide Lines For Erection of Verticallift GatesMahipal Reddy100% (1)
- Design of Intake Stoplog R0Document25 pagesDesign of Intake Stoplog R0Sujeet Kumar50% (2)
- Design of Dogging BeamDocument1 pageDesign of Dogging BeamSujeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Jack Lewin-Hydraulic Gates and Valves in Free Surface Flow and Submerged Outlets-T. Telford (1995) PDFDocument301 pagesJack Lewin-Hydraulic Gates and Valves in Free Surface Flow and Submerged Outlets-T. Telford (1995) PDFJoão Paulo FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Considerations in Radial Gate Design ICOLDDocument27 pagesConsiderations in Radial Gate Design ICOLDkamal167100% (1)
- Design As Per APIDocument82 pagesDesign As Per APINeeraj BhallaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculations For Light MastDocument23 pagesDesign Calculations For Light Mastjobees7850No ratings yet
- Pipe Support Columns at Bridge CrossingDocument9 pagesPipe Support Columns at Bridge CrossingChamil Mahagamage100% (1)
- Process Water Tank (LCP703-TK-001)Document44 pagesProcess Water Tank (LCP703-TK-001)hgag selimNo ratings yet
- Design Computation Penstock 3Document26 pagesDesign Computation Penstock 3Roland TagufaNo ratings yet
- Calculation Note (Rev0)Document17 pagesCalculation Note (Rev0)metoo21588% (8)
- Time Sheet/Weekly Report. Consultant's Name: Suranga DadallageDocument1 pageTime Sheet/Weekly Report. Consultant's Name: Suranga Dadallagesuranga dadallageNo ratings yet
- Form Tech-6 (Continued) Curriculum Vitae (CV)Document3 pagesForm Tech-6 (Continued) Curriculum Vitae (CV)suranga dadallageNo ratings yet
- Portable Gantry Cranes: For Sustainable Engineering SolutionsDocument2 pagesPortable Gantry Cranes: For Sustainable Engineering Solutionssuranga dadallageNo ratings yet
- Radial Gate ReviewDocument7 pagesRadial Gate Reviewsuranga dadallageNo ratings yet
- Lifting Pulley Guide Wheel Channel-3 Seal: ClientDocument1 pageLifting Pulley Guide Wheel Channel-3 Seal: Clientsuranga dadallageNo ratings yet
- Radial Gate-Design CheckDocument5 pagesRadial Gate-Design Checksuranga dadallage100% (1)
- Channel GapsDocument1 pageChannel Gapssuranga dadallageNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument8 pagesRetaining WallChetanNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsDocument3 pagesExcellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsGlaiza MarieNo ratings yet
- TYFTY Qs BankDocument7 pagesTYFTY Qs BankgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Comparison of LRFD With WSDDocument11 pagesComparison of LRFD With WSDGerry RyanNo ratings yet
- Tekla Structural Designer To BS CodesDocument135 pagesTekla Structural Designer To BS CodesReader of Down Hill100% (1)
- Numerical Analyses of Steel Beam-Column Joints Subjected To Catenary ActionDocument11 pagesNumerical Analyses of Steel Beam-Column Joints Subjected To Catenary ActionSohini MishraNo ratings yet
- Diaphragms For Timber Framed Buildings Vol 17 No1 2004Document8 pagesDiaphragms For Timber Framed Buildings Vol 17 No1 2004Tiago Lamy SilvaNo ratings yet
- GFRG Panels ManualDocument108 pagesGFRG Panels ManualGANGA RSNo ratings yet
- TesiDocument159 pagesTesiSudip ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lec3 - Ce131p-2 - Double Integration Method PDFDocument26 pagesLec3 - Ce131p-2 - Double Integration Method PDFThe BluemanNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of BridgesDocument45 pagesVibration Analysis of Bridgesmedic009No ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument7 pagesStructural AnalysiscustomerxNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Stiffened Raft FoundationDocument270 pagesAnalysis and Design of Stiffened Raft FoundationKemoH0% (1)
- Intro, Bending, Composite Sections & Combined Loading StressDocument31 pagesIntro, Bending, Composite Sections & Combined Loading StressKavish DayaNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration of A Functionally Graded Rotating Timoshenko Beam Using FEM PDFDocument14 pagesFree Vibration of A Functionally Graded Rotating Timoshenko Beam Using FEM PDFtengzcNo ratings yet
- ShipStr II - Assign3 - HullBeamLoads-2 PDFDocument1 pageShipStr II - Assign3 - HullBeamLoads-2 PDFJorge Ricardo AlcivarNo ratings yet
- Cven9806 Prestressed Concrete: School of Civil and Environmental EngineeringDocument7 pagesCven9806 Prestressed Concrete: School of Civil and Environmental EngineeringSuman.SNo ratings yet
- Formulas To RememberDocument6 pagesFormulas To Remembermr.xinbombayNo ratings yet
- Mechanical System Design Project (Me 4131) : Design of E.O.T CraneDocument42 pagesMechanical System Design Project (Me 4131) : Design of E.O.T CraneHemant KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Reinforced Concrete BeamsDocument87 pagesAnalysis of Reinforced Concrete BeamsJomarie Alcano50% (2)
- TRB - 2017 - Final Key - Pyramid IAS Academy-1Document10 pagesTRB - 2017 - Final Key - Pyramid IAS Academy-1Er Jeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument46 pagesBuilding Construction'Izzad AfifNo ratings yet
- 22f-UC Runway Beam DesignDocument2 pages22f-UC Runway Beam DesignParthiban ArivazhaganNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia of An AreaDocument8 pagesMoment of Inertia of An AreaEzequiel Guillermo Trejo NavasNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Strength Topics: Castigliano's TheoremDocument5 pagesMiscellaneous Strength Topics: Castigliano's TheoremDeepak Chachra100% (1)
- Solution To Problem 407 - Shear and Moment Diagrams - Strength of Materials ReviewDocument4 pagesSolution To Problem 407 - Shear and Moment Diagrams - Strength of Materials ReviewNagaraj MuniyandiNo ratings yet
- Beam SelectionDocument24 pagesBeam SelectionGustavNo ratings yet
- Composite Metal Decking: Technical ManualDocument80 pagesComposite Metal Decking: Technical Manualdalton wongNo ratings yet
- Example: Fin Plate Beam-To-Column-Flange Connection: Localized Resource For UKDocument247 pagesExample: Fin Plate Beam-To-Column-Flange Connection: Localized Resource For UKfloi dNo ratings yet
- Hidden Beam DesignDocument8 pagesHidden Beam DesignAnil kumar R100% (1)