Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effect of Frequency and Velocity On The Apparent Change of Frequency of Wave Motion
Uploaded by
Lee SeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effect of Frequency and Velocity On The Apparent Change of Frequency of Wave Motion
Uploaded by
Lee SeeCopyright:
Available Formats
EFFECT OF FREQUENCY AND VELOCITY ON THE APPARENT CHANGE
OF FREQUENCY OF SOUND WAVE
ABSTRACT
The propagation of sound wave are affected by several factors, among them
are density of medium, temperature, direction of wind and humidity. In the
case of Doppler effect, the apparent frequency of sound wave are affected
mainly by speed of sound and actual frequency of sound wave. Doppler effect
is a change in frequency and wavelength of a wave. It is caused by the
change in distance between the thing creating the wave (causer) and
whatever is measuring (observer), seeing or hearing the wave.
Another word for "causer" is source. Another word for "change in distance" is
"speed" or "relative velocity". A common example is sitting in a car while
another car goes by the observer. The observer will hear a change in pitch,
while the source will not.
INTRODUCTION
Theory
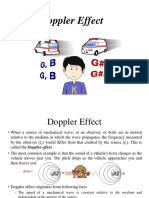
Source moving , Observer stationary
1. Source, S moving towards stationary observer, O
S
O (stationary)
Comparatively ,
S stationary
v
O ( stationary)
S moving
(v-u)
Due to movement of S with speed u, in one second, the wave fronts are
compressed with a distance (v-u).
speed =
Distance
1
Therefore, in this case, speed = distance
The effect thus appear to be a decrease in wavelength.
i.e.
(v u)
f
Using v = f,
f'=
v
v
=
'
vu
f
( )
Therefore,
( vuv ) f
f '=
where
f ' : apparent frequency
f:
actual frequency
2. Source, S moving away from stationary observer, O
v
u
Comparatively,
O( stationary)
S
v+u
O (stationary)
S
Due to movement of S with speed u, in one second, the wave fronts seem to
be rarefied with a distance (v+u). The effect thus appear to be an increase in
wavelength.
i.e.
(v +u)
f
Using v = f,
f'=
v
v
=
'
v +u
f
( )
Therefore,
In general,
( v+v u ) f
f '=
( v v u ) f
f '=
Observer moving , Source stationary
1. Observer,O moving towards stationary source, S
S
speed of observer, u
Stationary
remains unchanged but velocity of wave relative to O varies
i.e. v-(-u) = v+u
Using v = f ,
f'=
But
f'=
v+ u'
v
f
v+ u'
v
f
()
Therefore ,
( v+vu' ) f
f '=
2. Observer, O moving away from stationary source, S
S
Stationary
remains unchanged but velocity of wave relative to O varies
i.e. v-u
Using v = f ,
'
f =
But
f'=
vu '
v
f
vu '
v
f
()
Therefore ,
In general,
( vuv ' ) f
f '=
( v vu ' ) f
f '=
Source and Observer moving
1. Source, S and Observer, O moving towards each other
S
u
u
O
v
Since movement of S causes the change in whereas movement of O cause
the change in relative velocity.
Using v =f ,
We have
f'=
v'
'
But v=v+ u ,
=
vu
f
f '=
v +u '
vu
f
( )
Therefore,
( v+v uu' ) f
f=
2. Source, S and Observer, O moving away from each other
v
u
Since movement of S causes the change in whereas movement of O cause
the change in relative velocity.
Using v =f ,
We have
'
f =
But v=v-u ,
=
'
f =
vu '
v +u
f
( )
Therefore,
'
f
( vu
v +u )
f=
v +u
f
v'
'
You might also like
- DopplerEffect PDFDocument5 pagesDopplerEffect PDFNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect: WavelengthDocument6 pagesDoppler Effect: WavelengthshohobiNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect: Roy D. Tipones, EceDocument20 pagesDoppler Effect: Roy D. Tipones, EceErica May ReyesNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect - OkDocument66 pagesDoppler Effect - OkAntonioNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect T HarishDocument26 pagesDoppler Effect T HarishLoverboy6556No ratings yet
- Unit 02-Lecture 03Document6 pagesUnit 02-Lecture 03Harshan SNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics ProjectFrooti DubeyNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument7 pagesDoppler EffectYugandhar VeeramachaneniNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument2 pagesDoppler Effectapi-323795755No ratings yet
- The Doppler Effect (Or The Doppler Shift) Is The: Page 1 of 27Document27 pagesThe Doppler Effect (Or The Doppler Shift) Is The: Page 1 of 27Mohamed Aswir AswirNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument1 pageDoppler EffectMaybe Daily GamingNo ratings yet
- Doppler PDFDocument19 pagesDoppler PDFSam lama100% (1)
- The Doppler EffectDocument7 pagesThe Doppler Effectdharul khairNo ratings yet
- Genius PHYSICS: Doppler EffectDocument4 pagesGenius PHYSICS: Doppler EffectAman BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect: On The Coloured Light of The Binary Stars and Some Other Stars of The HeavensDocument10 pagesDoppler Effect: On The Coloured Light of The Binary Stars and Some Other Stars of The Heavensharshit tiwariNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument38 pagesDoppler EffectIhtisham Ahmad ButtNo ratings yet
- Topic 9.5 - Doppler Effect - AHLDocument41 pagesTopic 9.5 - Doppler Effect - AHLPaul Amezquita100% (1)
- Ao Mte Report (05 & 46)Document28 pagesAo Mte Report (05 & 46)Anshu GangwarNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesDoppler Effect: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument8 pagesDoppler EffectJemimah MpofuNo ratings yet
- DopplerDocument13 pagesDopplerkobioguadinmaNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument1 pageDoppler EffectQuazi Rafquat HossainNo ratings yet
- Doppler's Effect and Its ApplicatonDocument18 pagesDoppler's Effect and Its ApplicatonUmer ManzoorNo ratings yet
- DopplerDocument9 pagesDopplerlhen26No ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument11 pagesDoppler Effect5G (15) Chuang Hui Hua VeraNo ratings yet
- What Are Derivatives of DisplacementDocument10 pagesWhat Are Derivatives of DisplacementMichael MargoleseNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument31 pagesSound Wavesvirginiajuma812No ratings yet
- Free Space May Refer To: A Perfect Vacuum, That Is, A Space Free of All Matter. in Electrical Engineering, Free Space Means AirDocument5 pagesFree Space May Refer To: A Perfect Vacuum, That Is, A Space Free of All Matter. in Electrical Engineering, Free Space Means AirCarl Angelo MartinNo ratings yet
- Doppler LogDocument10 pagesDoppler Logiris2326100% (1)
- Amplitude Intensity SoundwavesDocument23 pagesAmplitude Intensity SoundwavesJason LuNo ratings yet
- Physics IADocument15 pagesPhysics IAManishNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument8 pagesLab ManualDavinder KakkarNo ratings yet
- Stephan J.G. Gift - The Luminiferous Ether DetectedDocument6 pagesStephan J.G. Gift - The Luminiferous Ether DetectedOppekee0% (1)
- Doppler EffectDocument16 pagesDoppler EffectRamya RNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves:: Doppler EffectDocument7 pagesSound Waves:: Doppler EffectDadan HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument8 pagesSound WavesAliyu MuhammadNo ratings yet
- DoplerDocument4 pagesDoplerJorge Ivan ZsNo ratings yet
- Range & DopplerDocument11 pagesRange & DopplerRamya RNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect:: (I) Observer (Detector) Moving, Source at RestDocument3 pagesDoppler Effect:: (I) Observer (Detector) Moving, Source at RestMishkat Ahmed NaoshadNo ratings yet
- Doppler EffectDocument8 pagesDoppler EffectkrawczybNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Waves & Sound-StudentDocument65 pagesChapter 14 - Waves & Sound-StudentMuhammad ZuhilmiNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument15 pagesMotionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Ch11 PhysicsDocument34 pagesCh11 Physicsthe_truth_94No ratings yet
- Physics Project On Doppler's EffectDocument26 pagesPhysics Project On Doppler's EffectJayant Chandra74% (27)
- Doppler Effect: V Speed of Wave VDocument10 pagesDoppler Effect: V Speed of Wave Vjoe0% (1)
- Lecture Notes 01 - The Doppler Effect and Special Relativity - Ebln1-1Document18 pagesLecture Notes 01 - The Doppler Effect and Special Relativity - Ebln1-1Andres FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect: 1 DevelopmentsDocument8 pagesDoppler Effect: 1 DevelopmentsVinayak NadirNo ratings yet
- Special RelativityDocument31 pagesSpecial RelativityzcqsmcmNo ratings yet
- Physics Vibrations and Waves: Wave That Follows Behind The Plane in A ConeDocument1 pagePhysics Vibrations and Waves: Wave That Follows Behind The Plane in A ConeJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Doppler S EffectDocument26 pagesPhysics Project On Doppler S EffectNisha AnandNo ratings yet
- ANewDopplerEffect PetrescuDocument81 pagesANewDopplerEffect PetrescuAdryana StefyNo ratings yet
- Topic 9.5 - Doppler Effect - TeacherDocument40 pagesTopic 9.5 - Doppler Effect - TeacherFerit HatipNo ratings yet
- IB - PHYSICS (AHL) - Wave Phenomena: Topic 11.1 Standing WavesDocument8 pagesIB - PHYSICS (AHL) - Wave Phenomena: Topic 11.1 Standing WavesAshisNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves: AccousticsDocument10 pagesSound Waves: AccousticsDiyar KhoshnawNo ratings yet
- Ives - Stilwell Experiment Fundamentally FlawedDocument22 pagesIves - Stilwell Experiment Fundamentally FlawedAymeric FerecNo ratings yet
- Doppler ShiftDocument9 pagesDoppler Shiftkumar1968No ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Beyond the World of Relativity to the World of Invariance: A Journey of Discovery into the Realm of Absolute Space and TimeFrom EverandBeyond the World of Relativity to the World of Invariance: A Journey of Discovery into the Realm of Absolute Space and TimeNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabian Oil Company: Indicates Information To Be Completed by PurchaserDocument2 pagesSaudi Arabian Oil Company: Indicates Information To Be Completed by PurchaserMohamed Wasim ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 300W Single Output Battery Charger: SeriesDocument2 pages300W Single Output Battery Charger: SeriesCsaba WielandNo ratings yet
- P RT/ (V - B) - A/v P RT/V V RT/P: Do Problem 40 in Chapter 1Document45 pagesP RT/ (V - B) - A/v P RT/V V RT/P: Do Problem 40 in Chapter 1AleksaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Motion and Vectors Chapter Test B With AnswersDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Motion and Vectors Chapter Test B With AnswersLiliNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics by M KumarDocument43 pagesApplied Physics by M KumarheloverNo ratings yet
- General Layout of Modern Steam Power PlantDocument15 pagesGeneral Layout of Modern Steam Power PlanttabishkhanaligNo ratings yet
- Liberty Port-ZTE-ZXDU58-B121 Product Description PDFDocument29 pagesLiberty Port-ZTE-ZXDU58-B121 Product Description PDFJCARLOS COLQUENo ratings yet
- MPFM Data SheetDocument2 pagesMPFM Data SheetPedro NuñezNo ratings yet
- Computers & Fluids: Andreas Hölzer, Martin SommerfeldDocument18 pagesComputers & Fluids: Andreas Hölzer, Martin SommerfeldBRANDON ALBERTO QUINTERO CIFUENTESNo ratings yet
- Control Relay: NKG3 Time SwitchDocument2 pagesControl Relay: NKG3 Time SwitchRafatNo ratings yet
- Rotator Baltrotors GR30Document3 pagesRotator Baltrotors GR30Anonymous 80HAPYsoNo ratings yet
- CalculatorDocument4 pagesCalculatorBenedict MadriagaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XI Phy Study-Package-2 SET-2 Chapter-6 PDFDocument58 pagesCLS Aipmt-18-19 XI Phy Study-Package-2 SET-2 Chapter-6 PDFPankaj JakharNo ratings yet
- Applications of Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesApplications of Second Law of Thermodynamicss100% (1)
- 8 Combined Cycle and CogenerationDocument19 pages8 Combined Cycle and CogenerationMuffin Everydays100% (1)
- Experiment 4 Cross Flow Heat ExchangerDocument19 pagesExperiment 4 Cross Flow Heat Exchangerbeasturs1No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Fluid Mechanics ComprehensiveDocument336 pagesComprehensive Fluid Mechanics ComprehensiveOsmr Ramos100% (1)
- Unit 3.1 - Hydrostatic ForcesDocument29 pagesUnit 3.1 - Hydrostatic ForcesIshmael MvunyiswaNo ratings yet
- 3NE13342 Datasheet enDocument4 pages3NE13342 Datasheet enWilber SánchezNo ratings yet
- 9-Drilling Fluids & Rig HydraulicsDocument48 pages9-Drilling Fluids & Rig HydraulicsazizsarshoghNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDocument20 pagesMechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenjjNo ratings yet
- 1SC0 2PF Exam-Paper 20180616Document20 pages1SC0 2PF Exam-Paper 20180616Thasanya AlgamaNo ratings yet
- Surge Filters, Low Current Dinsafe: Technical Information Sheet Sf105Din/ADocument1 pageSurge Filters, Low Current Dinsafe: Technical Information Sheet Sf105Din/AjohnarllanNo ratings yet
- DLP Q1 WK 4 D3 (16) AdelineDocument8 pagesDLP Q1 WK 4 D3 (16) AdelineCathy MoronioNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1 Earthing Systems Basic Constructional AspectsDocument16 pages6.5.1 Earthing Systems Basic Constructional AspectsbehnamatgNo ratings yet
- Si Brochure Draft ch123 PDFDocument29 pagesSi Brochure Draft ch123 PDFJosuè Omar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Ace2 Inverter: User ManualDocument85 pagesAce2 Inverter: User ManualAdam Schwemlein100% (1)
- E-Ce Rh-Rw15-MilltronicsDocument49 pagesE-Ce Rh-Rw15-MilltronicsCesar Miguel Meza RicardoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document10 pagesExperiment 3hellothere100% (1)
- A Novel Concept of Air Blade Rain HatDocument2 pagesA Novel Concept of Air Blade Rain HatNovelty JournalsNo ratings yet