Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sotalol
Uploaded by
Jashim JumliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sotalol
Uploaded by
Jashim JumliCopyright:
Available Formats
Sotalol
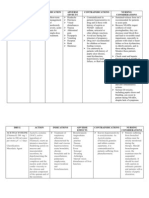
Drug Type Anti-arrhythmic
Indication
Action
Beta adrenergic blocking with type 3 anti arrhythmic activity for the treatment of supra
ventricular arrhythmia (SVT) after consultation with a cardiologist.
Its beta adrenergic activity causes a reduction in heart rate and a limited reduction in the force of
contraction. This leads to a decrease in myocardial oxygen consumption and cardiac work. The
anti arrhythmic activity of sotolol causes a prolongation of the action potential in cardiac tissue
by delaying repolarisation.
Presentation Oral suspension: 5mg/ml suspension (prepared by pharmacy)
Intravenous ampoule: 10mg / ml
Oral suspension: 1 to 2mg /kg/dose 12th hourly.
If necessary, can increase to maximum of 4mg/kg/dose 12th hourly.
Dose
Intravenous: 0.5 to 1.5mg/kg/dose 12th hourly by slow IV infusion over 10 minutes.
Dilution For intravenous preparation dilute 10mg / ml with normal saline 0.9% to make a 5ml solution that
is a concentration of 2mg/ml
Administration
Oral: The medication should preferably be administered on an empty stomach at least 30
minutes before feeding. This practice can vary according to the frequency of feeding and
practical issues relating to some problematic feeders. Intravenous: via peripheral or central
cannula.
Compatible
The cannula should be flushed with normal saline pre and post administration of sotolol.
Interactions
Sotolol can exacerbate existing arrhythmias or cause new arrhythmias including: Torsades de
Pointes, AV block, and ventricular ectopic beats. Other adverse effects include: hypertension,
bradycardia, rash and dyspnoea. Vomiting and diarrhoea have been reported. Signs of
hypoglycaemia may be masked by sotolol.
Side Effects Elimination is primarily by the kidneys with 75% of a dose excreted unchanged in the urine. As
sotalol is primarily excreted by the kidneys, dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with
moderate renal impairment. Severe renal impairment is a contraindication.
Sotolol should not be used when there is shock (cardiogenic or hypovolaemia), congestive
cardiac failure, sinus bradycardia, heart block, congenital or acquired long QT syndromes,
hypokalaemia or hypomagnesaemia.
Consultation with a paediatric cardiologist should be sought before concomitant therapy with
amiodarone (cordarone X), diuretics, flecainide or chlorpromazine (largactil)
Contraindications
Other Considerations Special Considerations:
Infant should be on cardio respiratory monitor. During intra venous administration observe for
return of sinus rhythm. Observe QT interval. Caution if QT becomes prolonged especially with
increased dosage
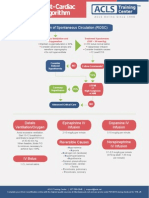
During intravenous administration have the resuscitation equipment nearby and atropine should
be available for profound bradycardia
Atropine
1. 10-30 micrograms/kg/dose IV over 1 minute.
2. Dose may be repeated every 10-15 minutes to achieve desired effect, with a maximum total
dose of 40 micrograms/kg.
Also monitor: electrolytes, especially potassium and magnesium
References
References King Edward memorial Hospital (2011). Neonatal Medication Protocols
http://www.kemh.health.wa.gov.au/services/nccu/guidelines/drug_protocols/Sotalol.pdf.
Accessed June 2011
National Womens Hospital Newborn Services (2005). Drug Protocols Sotolol hydrochloride.
Auckland http://www.adhb.govt.nz/newborn/DrugProtocols/AdenosinePharmacology.htm
Accessed June 2011
NSW Health (2010) Clinical Information Access Programme MIMS Online Sotolol
hydrochloride. Accessed June 2011
Saul JP, Schaffer MS, karpawich PP, Erickson CC, Epstein MR et al. Single dose
pharmacokinetics of sotolol in a pediatric population with supra ventricular and / or ventricular
tachyarrythmia. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2001: 41,1;35. http://jcp.sagepub.com
Accessed July 2011.
You might also like
- BretyliumDocument4 pagesBretyliumButchay LumbabNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyClarkEstacioNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart Disease With AsthmaDocument31 pagesCoronary Heart Disease With AsthmaEf LablaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyVic MagtotoNo ratings yet
- Emergency MedsDocument24 pagesEmergency MedsNursyNurse100% (1)
- Side Effects:: AtropineDocument7 pagesSide Effects:: AtropinekletadaNo ratings yet
- Normiten Atenolol tablets for hypertension, angina & MIDocument7 pagesNormiten Atenolol tablets for hypertension, angina & MIasdwasdNo ratings yet
- Icu Drug StudyDocument7 pagesIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- DBL Adrenaline 1 in 10,000 InjDocument11 pagesDBL Adrenaline 1 in 10,000 InjKada med kamelNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol IV administration side effects nursing considerationsDocument7 pagesParacetamol IV administration side effects nursing considerationsCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine and other emergency drug doses and indicationsDocument5 pagesEpinephrine and other emergency drug doses and indicationsColette Marie PerezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- RSI Pharmacology For The Emergency Medicine PhysicianDocument2 pagesRSI Pharmacology For The Emergency Medicine PhysicianGuide LPNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Action: Indications:: Drug: Oxygen Class of Medication: Oxidizing Agent (Gas)Document6 pagesAction: Indications:: Drug: Oxygen Class of Medication: Oxidizing Agent (Gas)Andreas100% (2)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsStacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- PEDRIATICDocument17 pagesPEDRIATICMaxxdlc 16No ratings yet
- LI Case 2 (Pharmacological Properties of Propanolol)Document2 pagesLI Case 2 (Pharmacological Properties of Propanolol)adtyadaviaNo ratings yet
- Cloxacillin, Sodium: How Should I Take Cloxacillin?Document7 pagesCloxacillin, Sodium: How Should I Take Cloxacillin?Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- 24 Emergency DrugsDocument7 pages24 Emergency DrugsApple BelicanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Names: Ventolin, Proventil, Accuneb, Vospire, ProairDocument9 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Names: Ventolin, Proventil, Accuneb, Vospire, Proairwasiq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Emergency Pharmacology Drugs GuideDocument5 pagesEmergency Pharmacology Drugs GuideAce RegellanaNo ratings yet
- DuaventDocument9 pagesDuaventAjurs UrsabiaNo ratings yet
- Tenormin Tablet GuideDocument5 pagesTenormin Tablet Guiderizi007No ratings yet
- Drugs Study Neh Jai2xDocument10 pagesDrugs Study Neh Jai2xjai2xNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNo ratings yet
- GelafusalinfDocument5 pagesGelafusalinfToni Dafia PutraNo ratings yet
- Emergency Oxygen Therapy for Cardiac IssuesDocument11 pagesEmergency Oxygen Therapy for Cardiac IssuesMin Hong LuoNo ratings yet
- Opiates (E.g. Codeine, Heroin, Pethidine, Morphine, Methadone)Document7 pagesOpiates (E.g. Codeine, Heroin, Pethidine, Morphine, Methadone)Ali HussnainNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Drug AmiodaroneDocument7 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias Drug AmiodaroneMarie Angeline ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K IV antidote for warfarin bleedingDocument10 pagesVitamin K IV antidote for warfarin bleedingQueennitaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Drug RationaleDocument77 pagesDrug RationaleYolanda WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Poison and Antidote ChartDocument5 pagesPoison and Antidote ChartSusanne Mae Gonzales50% (2)
- Emergency Drugs KathDocument29 pagesEmergency Drugs Kathmajin655No ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- Emergency Cardiac Medications for ArrhythmiasDocument14 pagesEmergency Cardiac Medications for ArrhythmiasRomzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Life SupportDocument33 pagesPediatric Life SupportAndre montolaluNo ratings yet
- Common Drug & Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument50 pagesCommon Drug & Nursing ResponsibilitiesRyanMatira100% (1)
- AcetazolamideDocument4 pagesAcetazolamideAmarnath SahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CARDIODocument17 pagesDrug Study CARDIODiannetotz Morales100% (1)
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drug Review: UHHS BMH Paramedic Training ProgramDocument116 pagesEmergency Drug Review: UHHS BMH Paramedic Training ProgramShailja HanumantaNo ratings yet
- methotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1Document9 pagesmethotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1joonabil29No ratings yet
- PACKAGE LEAFLET - CORDARONE EngDocument17 pagesPACKAGE LEAFLET - CORDARONE Engvaka17No ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Information From American Heart Association, Advanced Cardiac Life Support, 2006Document25 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Information From American Heart Association, Advanced Cardiac Life Support, 2006karento1No ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticDocument9 pagesPiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭No ratings yet
- Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride (Benadryl) 50mg/1mlDocument6 pagesDiphenhydramine Hydrochloride (Benadryl) 50mg/1ml'SheenMarkReal'No ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Ipratropium BromideDocument20 pagesIpratropium BromideAngelique Ramos PascuaNo ratings yet
- Apo Captopril TabDocument19 pagesApo Captopril TabansenoraNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nurse Technician Exam Blueprint & ReferenceDocument1 pageNurse Technician Exam Blueprint & ReferenceJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Nurse SpecialistDocument1 pageNurse SpecialistJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Lab Technician Exam Content and ReferencesDocument1 pageLab Technician Exam Content and ReferencesJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological ModalitiesDocument9 pagesPharmacological ModalitiesJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Algo PostarrestDocument1 pageAlgo PostarrestMuhammad Rizki ImannudinNo ratings yet
- OmsbexamsfaqsDocument5 pagesOmsbexamsfaqsJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- QCHP FaqDocument3 pagesQCHP FaqJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Bag Physics J PhilipDocument44 pagesReservoir Bag Physics J PhilipJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Professional Classification Manual For Health PractitionersDocument55 pagesProfessional Classification Manual For Health PractitionersMarsFriendNo ratings yet
- E201 Trauma Assessment PDFDocument1 pageE201 Trauma Assessment PDFPrecious Ann Gonzales ReyesNo ratings yet
- ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With ZOLL RBWDocument6 pagesACLS Defibrillation Protocols With ZOLL RBWResa PutraNo ratings yet
- Algo PostarrestDocument1 pageAlgo PostarrestMuhammad Rizki ImannudinNo ratings yet
- ALS Drug SummaryDocument1 pageALS Drug SummaryPramod SharmaNo ratings yet
- BVMDocument17 pagesBVMJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- ACLS Defibrillation Protocols With ZOLL RBWDocument6 pagesACLS Defibrillation Protocols With ZOLL RBWResa PutraNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain: CBT/OTEP 435Document17 pagesAbdominal Pain: CBT/OTEP 435Jashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions About Aeds: Aed FaqsDocument7 pagesFrequently Asked Questions About Aeds: Aed FaqsJashim JumliNo ratings yet
- Algo ArrestDocument2 pagesAlgo ArrestLocomotorica FK UkiNo ratings yet
- ALS Drug SummaryDocument1 pageALS Drug SummaryPramod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Algo ArrestDocument2 pagesAlgo ArrestLocomotorica FK UkiNo ratings yet
- ALS Drug SummaryDocument1 pageALS Drug SummaryPramod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Indication Def.Document11 pagesClinical Indication Def.Anish H DaveNo ratings yet
- 9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXDocument1 page9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Atrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Document2 pagesAtrial-Rhythm 230518 191520-1Maxinne GorospeNo ratings yet
- Almostadoctor - co.Uk-Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesDocument8 pagesAlmostadoctor - co.Uk-Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesAnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Myocardial InfarctionDocument50 pagesComplications of Myocardial InfarctionAli Baker Algelane50% (2)
- Lippincott Antiarrhythmics 7Document2 pagesLippincott Antiarrhythmics 7Wijdan HatemNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cardiac Arrhythmias: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Cardiac Arrhythmias: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSharan MurugaboopathyNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia and Med Compromised Pts JCDA 2000 PDFDocument13 pagesLocal Anesthesia and Med Compromised Pts JCDA 2000 PDFBeatrice Intan KNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StripDocument7 pagesChapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StriptellyNo ratings yet
- Palpitation:evaluation, Ambulatory Monitoring, Mobile Telemetry Eg - MCOT@2012Document19 pagesPalpitation:evaluation, Ambulatory Monitoring, Mobile Telemetry Eg - MCOT@2012Navojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Treadmill Stress TestDocument16 pagesTreadmill Stress TestMuhammad Yasir WahabNo ratings yet
- ECG Quiz 1Document22 pagesECG Quiz 1EINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia and TachycardiaDocument50 pagesBradycardia and Tachycardialiu_owen17No ratings yet
- Incessant VT VFDocument9 pagesIncessant VT VFTor JaNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia and Conduction Disturbance-AAL-UPH2020Document100 pagesArrhythmia and Conduction Disturbance-AAL-UPH2020Ammar GalihNo ratings yet
- ECG .DR Ayalew EthiopiaDocument60 pagesECG .DR Ayalew EthiopiaAyalew Zewdie100% (2)
- Atrial Flutter & Fibrillation GuideDocument8 pagesAtrial Flutter & Fibrillation Guidejamaliganteng88No ratings yet
- ACLS Appendix 3Document32 pagesACLS Appendix 3tostc100% (1)
- Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideDocument7 pagesCardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Normal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial NodeDocument80 pagesNormal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Nodesiusiuwidyanto100% (2)
- Show Questions One by OneDocument12 pagesShow Questions One by OneCharlie Cheng-Ying HsiehNo ratings yet
- Kalnirnay 2023 Marathi CalendarDocument24 pagesKalnirnay 2023 Marathi CalendarAparna Sachin Tembulkar67% (3)
- Teknik AuskultasiDocument23 pagesTeknik AuskultasiIndana Lazulfa NoviaNo ratings yet
- VT Vs SVT AberrantDocument41 pagesVT Vs SVT AberrantAl Hijjah FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Nursing ProcessDocument1 pageNursing ProcessMelissaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentalof Ventilation & PacemakerDocument22 pagesFundamentalof Ventilation & PacemakerLucila Lugo100% (1)
- ECGDocument154 pagesECGSandeep BansalNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Fibrillation Contraction Heart Muscles.: Is A Serious Cardiac Emergency Resulting From Asynchronous of TheDocument28 pagesVentricular Fibrillation Contraction Heart Muscles.: Is A Serious Cardiac Emergency Resulting From Asynchronous of ThechanlalNo ratings yet
- Nursing School EKGDocument43 pagesNursing School EKGRob Dickerson100% (1)
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument5 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasHohl LuminitaNo ratings yet