Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 17 1 - Equilibrium Exam Questions
Uploaded by
GytgtCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 17 1 - Equilibrium Exam Questions
Uploaded by
GytgtCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 17.
1 Equilibrium Law
1.
0.50 mol of I2(g) and 0.50 mol of Br2(g) are placed in a closed flask. The following equilibrium
is established.
I2(g) + Br2(g)
IBr(g)
The equilibrium mixture contains 0.80 mol of IBr(g). What is the value of Kc?
A.
0.64
B.
1.3
C.
2.6
D.
64
(Total 1 mark)
2.
For the reaction below:
H2(g) + I2(g)
2HI(g)
3
at a certain temperature, the equilibrium concentrations, in mol dm , are
[H2(g)] = 0.30, [I2(g)] = 0.30, [HI(g)] = 3.0
What is the value of Kc?
A.
1.010
B.
10
C.
33
D.
1.010
(Total 1 mark)
3.
Consider the following equilibrium reaction.
Cl2(g) + SO2(g)
SO2Cl2(g)
H = 84.5 kJ
In a 1.00 dm closed container, at 375 C, 8.60 10 mol of SO2 and 8.60 10 mol of Cl2
4
were introduced. At equilibrium, 7.65 10 mol of SO2Cl2 was formed.
(i)
Deduce the equilibrium constant expression, Kc, for the reaction.
(1)
(ii)
Determine the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc.
IB Questionbank Chemistry
(3)
(iii)
If the temperature of the reaction is changed to 300 C, predict, stating a reason in each
case, whether the equilibrium concentration of SO2Cl2 and the value of Kc will increase
or decrease.
(3)
(iv)
If the volume of the container is changed to 1.50 dm , predict, stating a reason in each
case, how this will affect the equilibrium concentration of SO 2Cl2 and the value of Kc.
(3)
(v)
Suggest, stating a reason, how the addition of a catalyst at constant pressure and
temperature will affect the equilibrium concentration of SO 2Cl2.
(2)
(Total 12 marks)
4.
(a)
The production of ammonia is an important industrial process.
N2(g) + 3H2(g)
(i)
2NH3(g)
Using the average bond enthalpy values in Table 10 of the Data Booklet, determine
the standard enthalpy change for this reaction.
(3)
(ii)
The standard entropy values, S, at 298 K for N2(g), H2(g) and NH3(g) are 193, 131
1
and 192 JK mol respectively. Calculate S for the reaction and with reference
O
to the equation above, explain the sign of S .
(4)
(iii)
Calculate G for the reaction at 298 K.
(1)
(iv)
Describe and explain the effect of increasing temperature on the spontaneity of the
reaction.
(2)
IB Questionbank Chemistry
(b)
The reaction used in the production of ammonia is an equilibrium reaction. Outline the
characteristics of a system at equilibrium.
(2)
(c)
Deduce the equilibrium constant expression, Kc, for the production of ammonia.
(1)
(d)
(i)
0.20 mol of N2(g) and 0.20 mol of H2(g) were allowed to reach equilibrium in a
3
1 dm closed container. At equilibrium the concentration of NH3(g) was
3
0.060 mol dm . Determine the equilibrium concentrations of N2(g) and H2(g) and
calculate the value of Kc.
(3)
(ii)
Predict and explain how increasing the temperature will affect the value of Kc.
(2)
(e)
Describe how increasing the pressure affects the yield of ammonia.
(2)
(f)
In practice, typical conditions used in the Haber process are a temperature of 500 C and
a pressure of 200 atmospheres. Outline why these conditions are used rather than those
that give the highest yield.
(2)
(g)
A catalyst of iron is used in the Haber process. State and explain how the catalyst affects
Kc and the position of equilibrium.
(3)
(Total 25 marks)
IB Questionbank Chemistry
You might also like
- IB Chemistry - HL Equilibrium Constant QuestionsDocument5 pagesIB Chemistry - HL Equilibrium Constant QuestionsPisosNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Past Paper QuestionsDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry Past Paper QuestionsDanelia GordonNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Practice Test: (A) Loses ElectronsDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry Practice Test: (A) Loses ElectronsElla Canonigo CanteroNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagent WorksheetDocument2 pagesLimiting Reagent WorksheetKamariah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDocument63 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Reversible Reactions 1 QPDocument12 pagesReversible Reactions 1 QPAbed AymanNo ratings yet
- Exam Chew 1Document7 pagesExam Chew 1ThilagaNo ratings yet
- F2 Is 003 AcidDocument4 pagesF2 Is 003 AcidLorraine TsoiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesUnit - 9 Ionic Equilbrium: Multiple Choice QuestionsSAMBASIVA RAO YEMINENINo ratings yet
- Test 1 As Chemistry Unit 2 - KineticsDocument10 pagesTest 1 As Chemistry Unit 2 - KineticsKajana Sivarasa Shenthan100% (1)
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNo ratings yet
- Chem G12 FiveYearsNationalExamDocument75 pagesChem G12 FiveYearsNationalExamTeklay NegasiNo ratings yet
- STPM Johor Chemistry Paper 2 2011 Trial From (Edu - Joshuatly)Document13 pagesSTPM Johor Chemistry Paper 2 2011 Trial From (Edu - Joshuatly)kokpin100100% (1)
- Common Foundation Organic Q in A LevelDocument21 pagesCommon Foundation Organic Q in A Level黄维燕No ratings yet
- Workbk 10Document177 pagesWorkbk 10Manushree NayakNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems in ElectrochemistryDocument19 pagesSample Problems in ElectrochemistrygiyagirlsNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry Topic 3 MCQs on Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesAS Chemistry Topic 3 MCQs on Chemical BondingAijaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl Compounds Tutorial 6 Key ConceptsDocument21 pagesHydroxyl Compounds Tutorial 6 Key ConceptsJohnNo ratings yet
- Kinetics and EquilibriumDocument26 pagesKinetics and EquilibriumBrian Smith100% (18)
- Organic ChemDocument113 pagesOrganic ChemTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 HLQDocument23 pagesTopic 10 HLQVũ Đức DuyNo ratings yet
- f2 Chemistry TopicalsDocument36 pagesf2 Chemistry TopicalsEvansOmoiNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 22 - Answer SchemeDocument20 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 22 - Answer SchemeNicholas Ow50% (2)
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیNo ratings yet
- Organic C CCCC CCCCDocument88 pagesOrganic C CCCC CCCCKugan KishurNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- Chemistry VII 1st Term 2014-154563Document6 pagesChemistry VII 1st Term 2014-154563JoannNo ratings yet
- 3 - Redox and Electrolysis (Pp2)Document36 pages3 - Redox and Electrolysis (Pp2)api-3700944100% (1)
- Chemsheets GCSE 1147 General Electrolysis 3 1Document1 pageChemsheets GCSE 1147 General Electrolysis 3 1Sumaiya Iqbal78No ratings yet
- 12 Regular Question BankDocument5 pages12 Regular Question BankJava WalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 and 6 Questions: (58 Marks)Document21 pagesChapter 5 and 6 Questions: (58 Marks)aurennosNo ratings yet
- Chem Topic 4 QuestionsDocument19 pagesChem Topic 4 QuestionsOscarHigson-SpenceNo ratings yet
- Practice StoichiometryDocument5 pagesPractice StoichiometryYohanes BAgus ChristiantNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Shailendra KRDocument6 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Shailendra KR1harshikaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Derivatives TutorialDocument18 pagesAcids and Derivatives TutorialChen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding 1Document2 pagesCovalent Bonding 1Vina Octavia AzzahraNo ratings yet
- A. Strong Acid, Weak Base, Salt: Final Examination Subject: General Chemistry A. Subject Code: 604001Document6 pagesA. Strong Acid, Weak Base, Salt: Final Examination Subject: General Chemistry A. Subject Code: 604001TanNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy WorksheetDocument24 pagesSpectroscopy Worksheetpokemon goNo ratings yet
- 2012 Redox Tutorial-TutorDocument11 pages2012 Redox Tutorial-TutorKarunya NarayanamurthyNo ratings yet
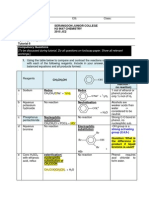
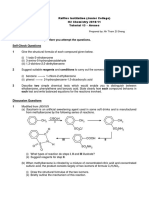
- Raffles Institution Chemistry Tutorial on ArenesDocument2 pagesRaffles Institution Chemistry Tutorial on ArenesDomNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Homework 3 Reaction RatesDocument4 pagesKinetics Homework 3 Reaction RatesRizkiNo ratings yet
- SL Topic 3. PeriodicityDocument7 pagesSL Topic 3. PeriodicityWayne LeungNo ratings yet
- HL9Q&ADocument28 pagesHL9Q&ABrianNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Practice TestDocument13 pagesEquilibrium Practice Testdeckbyte865No ratings yet
- Pioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsDocument31 pagesPioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Document10 pagesPractice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Arianne Foster100% (1)
- Hsslive-XI-Chemistry-Simplified Notes For 1 Improvement ExamDocument35 pagesHsslive-XI-Chemistry-Simplified Notes For 1 Improvement ExamLingesh Waran100% (3)
- BondingDocument52 pagesBondingArian CoenNo ratings yet
- 70 Practice Problems For CH 7Document10 pages70 Practice Problems For CH 7ULFA TUFFAHATINo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 4Document9 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 4Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
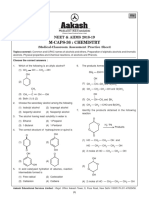
- Chemistry Theory Sample Paper (2022-23) on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument8 pagesChemistry Theory Sample Paper (2022-23) on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsJems Chaudhary100% (1)
- Calculating Moles and Mass in Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesCalculating Moles and Mass in Chemical ReactionsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- NEET & AIIMS 2018 Chemistry MCQ on Alcohols and PhenolsDocument6 pagesNEET & AIIMS 2018 Chemistry MCQ on Alcohols and PhenolsVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Redox Practice HLDocument5 pagesRedox Practice HLSere FernandezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Acid Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesWorksheet Acid Bases and SaltswardaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (Question) PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 (Question) PDFhaziq ajizNo ratings yet
- CH 6 PracticeDocument11 pagesCH 6 PracticeMichel zakhariaNo ratings yet
- Psi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Document30 pagesPsi-Ap-Chemistry-Equilibrium-Multiple-Choice 3Tricyver ChienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document20 pagesChapter 14Angelica UyNo ratings yet
- Economics For The IB Diploma: Help NotesDocument5 pagesEconomics For The IB Diploma: Help NotesGytgtNo ratings yet
- Topic 17 1 - Equilibrium Exam SolutionsDocument3 pagesTopic 17 1 - Equilibrium Exam SolutionsGytgtNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 1 - Equilibrium Exam SolutionsDocument2 pagesTopic 7 1 - Equilibrium Exam SolutionsGytgtNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Past Paper Questions and Mark Schemes 2009 - 2011SORTEDDocument16 pagesMacroeconomic Past Paper Questions and Mark Schemes 2009 - 2011SORTEDSandyKwongNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 1 - Equilibrium Exam QuestionsDocument7 pagesTopic 7 1 - Equilibrium Exam QuestionsGytgtNo ratings yet
- The Equilibrium Law (17.1) : Concentrations For The Reaction Mixture ComponentsDocument5 pagesThe Equilibrium Law (17.1) : Concentrations For The Reaction Mixture ComponentsGytgtNo ratings yet
- SynonymsDocument2 pagesSynonymsGytgtNo ratings yet
- Basic Tools and Concepts: 2.1 Circular Arcs and Spherical AstronomyDocument21 pagesBasic Tools and Concepts: 2.1 Circular Arcs and Spherical AstronomyGytgtNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Pipe and Fitting ChartDocument12 pagesPipe and Fitting Chartyulianus_sr100% (2)
- Who Took Jerell'S Ipod? - An Organic: Compound MysteryDocument8 pagesWho Took Jerell'S Ipod? - An Organic: Compound Mysteryakm1187No ratings yet
- Astm D 4176 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm D 4176 PDFAlexander Amado QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Membrane Technology: Reverse Osmosis Ultrafiltration MicrofiltrationDocument66 pagesMembrane Technology: Reverse Osmosis Ultrafiltration MicrofiltrationShivani MunishwarNo ratings yet
- Himalaya Health CareDocument38 pagesHimalaya Health Careactive1cafeNo ratings yet
- Acid BassDocument41 pagesAcid BassRobert Edwards100% (1)
- Low Temperature Behavior of Metals: Fracture Toughness and Ductile to Brittle TransitionDocument39 pagesLow Temperature Behavior of Metals: Fracture Toughness and Ductile to Brittle TransitionkoontattNo ratings yet
- 2010 Proportional CatalogDocument16 pages2010 Proportional CatalogjondesousaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Microbial HabitatDocument87 pagesTopic 5 - Microbial Habitatayu80% (5)
- Fishing in Drilling OperationsDocument19 pagesFishing in Drilling Operationsmts1234100% (1)
- Production of Insulating Refractory Bricks From Kankara Kaolin Using AchaDocument150 pagesProduction of Insulating Refractory Bricks From Kankara Kaolin Using AchaSAMUEL PSALMNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black ProcessDocument4 pagesCarbon Black ProcessAnonymous azD9vQD100% (1)
- MSS SP-44-2016 Steel Pipeline FlangesDocument52 pagesMSS SP-44-2016 Steel Pipeline Flangesarnoldbatista55100% (2)
- Final Drawing Hull NB. 151Document154 pagesFinal Drawing Hull NB. 151Nomad100% (2)
- 2023 Liu JCleanerProdDocument14 pages2023 Liu JCleanerProdNgô Ích SơnNo ratings yet
- Well Control Methods PDFDocument10 pagesWell Control Methods PDFrobert5castillo-5No ratings yet
- Catalog Copeland KCLDocument40 pagesCatalog Copeland KCLIsidro MendozaNo ratings yet
- Quick Coupling Products Distribution: Catalogue 3800-DS/UKDocument68 pagesQuick Coupling Products Distribution: Catalogue 3800-DS/UKhoussem houssemNo ratings yet
- Disassembly & Assembly Instructions Multistage Centrifugal PumpsDocument28 pagesDisassembly & Assembly Instructions Multistage Centrifugal Pumpsjalw88100% (1)
- Bio Monitoring of AtmosphericDocument174 pagesBio Monitoring of AtmosphericOluflourish EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- THE THE: Notes Meter Factor ForDocument19 pagesTHE THE: Notes Meter Factor Forjgarcia388No ratings yet
- LCP SpanlockDocument8 pagesLCP SpanlockGarfieldNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Pt. Musim MasDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Pt. Musim MasAydilover AydinousNo ratings yet
- Progress in Polyethylene Terephthalate RecyclingDocument24 pagesProgress in Polyethylene Terephthalate RecyclingyuppeNo ratings yet
- John Franc Angco - AMTE 216 Assignment Nunber 2Document5 pagesJohn Franc Angco - AMTE 216 Assignment Nunber 2john angcoNo ratings yet
- Fisher Paykel Cosycot - Manual de Funcionamiento PDFDocument133 pagesFisher Paykel Cosycot - Manual de Funcionamiento PDFpirihuey1234No ratings yet
- Name: Ridus Haroon Roll No: 21-10884 Course: Commercialization of Biotechnology Course Code: BIOT305 Section: A Instructor: Z. MehmoodDocument8 pagesName: Ridus Haroon Roll No: 21-10884 Course: Commercialization of Biotechnology Course Code: BIOT305 Section: A Instructor: Z. MehmoodAreeba KhanNo ratings yet
- Creatively Using Poo for Fertilizer or EnergyDocument7 pagesCreatively Using Poo for Fertilizer or EnergyprasadjdwNo ratings yet
- SRISAI PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS X CHAPTER 1 PERIODIC TABLEDocument3 pagesSRISAI PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS X CHAPTER 1 PERIODIC TABLENaga VikramNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Bakey's Food Private Limited (Edited)Document7 pagesCase Study of Bakey's Food Private Limited (Edited)Omkar Gholap100% (1)