Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Map of Biases
Uploaded by
Turchin AlexeiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Map of Biases
Uploaded by
Turchin AlexeiCopyright:
Available Formats
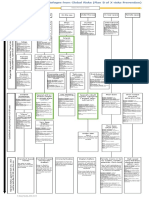
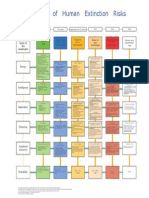
The map of cognitive biases, errors and obstacles affecting judgment and management of global catastrophic risks
Timeline
of risk
prevention
Ignoring
of the risk
Underestimation
Cognitive biases concerning only
global catastrophic risks
Wrong
actions
during
risk prevention
3-1.
Overconfidence
5. A false
7. Bias connected
equivocation of
with the fact that
global catastrophe global catastrophe
with the death of is by definition a
all individual
unique event
humans (value of More...
future generations)
31. Cognitive
32. Cognitive
36. Approaching 37. Religious outbiases based on the biases based on the life in the spirit of looks and eschaidea: It is too bad idea: It is too im- the proverb: af- tological cults,
to be true or It probable to be the ter us the deluge, More...
couldnt happen to truth, More...
More...
me, More...
1. Confusion regarding
the difference between
catastrophes causing
human extinction and
catastrophies non-fatal
to our species
Link
10. Global risks
receive less
attention than
small-scale risks
More...
11. Representations 14. Fear
that thinking about More...
global risks is
pessimistic
More...
83. Overestimate of
own possibilities in
general and
22. Humor
26. Weariness
survival rate in
It is possible to
from catastrophe
particular
misinterpret a gen- expectation
uine threat as a
More...
joke,
or
interpret
a
Overestimation
joke as a genuine
in any particular
threat.
More...
judjement;
69. Need for
86. Curiosity can
calibration
closure
be stronger than
EY, More...
More...
fear of death
More...
2. Underestimating 8. Underestimat- 26. Erroneous repnon-obvious risks ing global risks be- resentation that
cause of emotional people as a whole
More...
reluctance to
do not want caconsider your per- tastrophe and a
sonal demise, more doomsday, More...
19. Intuition as a
source of errors in
thinking about global
risks:
Intuition works good
only for repeatable
things, More...
Brain biology
Emotional
3. Bystander effect: 4. Bias connected
global risks have to psychologization of the probless perceived
national security lem
More...
importance,
EY, More...More...
15. Erroneous
24. Scope neglect,
representation that EY
global risks are in More...
the far future and
not relevant today
More...
Wrong
model
of risks
How universal cognitive biases influence estimates of global risks
56. DunningKruger effect
overconfidence in
ones professional
skills
wiki
More...
25. Exaggeration of
prognostic values
of extrapolation
More...
3.2. Excessive
attention to slow
processes and
underestimation
of fast processes,
More...
40. Generalizing
from fictional
evidence
More
18. Beliefs
More...
30. Stockholm
syndrome desire to
extinction
More...
19. Congenital
fears
More...
39. Use of the
theme of global
risks as a plot for
entertaining
movies
20. Shooting the
messenger,
Discussion of risks can trigger discontent. This discontent
may be directed towards the
bearer of the message rather
than addressing the threat itself.
68. Bystander effect
More...
73. Confusion
between
objective and
subjective threat
More...
47. Availability
bias
LWwiki
EY
More
84. Aspiration to
the wonderful
future, masking
perception of risks
More...
49. Hindsight bias
EY
LWwiki
More
64. Propensity of
72. Mind
people to offer simple projection fallacy
and obvious decisions More...
in difficult situations
not having thought
them though
More...
76. Clear catastrophe
90. Influence of
can be more attractive emotional
than an uncertain future reactions to
More...
catastrophe
More...
15. Underestimating importance
of remote events
(temporal discounting)
More...
42. Excessive
intellectual
criticism or
skepticism
More...
54. Overconfidence of the young
professional
More...
89. Minimum
78. The upper lim- 81. Refusal to
it of possible ca- consider a certain perceived risk
scenario because of More...
tastrophe is
formed on the ba- its incredibility
sis of past experi- More...
ence
More...
99. Dependence of
reaction on speed
of change
A frog may be boiled to death
in a pot, since if the heat is
only turned up a little bit at a
time, it does not notice.
More...
32. A group of
33. Working
people can make memory limits
worse decisions
More...
than each person
separately, More...
Mundane egocentrism may
cause people to overestimate
the influence they can have
over a certain situation, indirectly making them powerless
to influence it. More...
17. The representa- 18. Views that global risks 6. Perceptive
20. Scientific research of global risks also
tion that books and are either inevitable, destereotype of
faces a number of problems:
articles about glob- pend entirely on casual fac- catastrophes from - no experiment
al risks can change tors not subject to human mass media cover- - no probability
a situation consid- influence, or depend on
age of prior risks, - no statistic
erably
the highest-level politicians More...
- no falsifiability , More...
More...
who are unreachable
22. Methods applica- 23. Erroneous conception 16. The idea that 28. Representa27. Future Shock: 30. Underestible to management of that global risks threaten global catastrophe tion that global ca- Cognitive biases mate of pre-critical
economic and other people only while we are will be personally tastrophe will be connected with fu- events as elements
risks are not applicable Earthbound, and resettle- painless
caused by only one turistic horizons, of coming global
to global catastrophic ment in space will auto- More...
reason, More...
More...
catastrophe
risks, More...
matically solve the probMore...
lem More...
35. Inability of a 38. Uncertainty 34. Representations 29. Underestimat- 21. The errors connected 57. The error connectsystem to simulate and ambiguity of that human adapt- ing systemic factors with unawareness of lit- ed with concentrating
itself, More...
novel terminology, ability is high and of global risk
tle-known logical argu- on prevention of small
More...
continues to grow More...
ments for global risk:
catastrophes instead of
- Doomsday Argument
beyond all bounds
prevention of the great- Observation selection
thanks to new
est possible catastrophe
More...
technologies, More
More...
35. A situation
when a bigger
problem follows
a smaller one, but
we are incapable of
noticing it
More...
53. Aspiration of 58. Weariness
people to establish of researchers
a certain risk level More...
acceptable to them
More
The Affect
Heuristic
Good or bad?
EY
97. Egocentrism
13. Poor translation between the
theoretical and
practical
More...
16. Effect of
displacement of
attention
More...
Evolutionary
37. Subconscious
desire for
catastrophe
More
36. Selectivity
of attention
More...
3.3. Age features in
perception of global risks, More...
In the ancestral environment
of mankind, the external threat
we were exposed to most frequently would be rival human
tribes with malignant intent.
More...
The Conjunction
Fallacy
EY
LWwiki
Anchoring ,
Adjustment, and
Contamination
EY
74. Predictions or 75. Fear of loss of
dreams of
identity because of
catastrophe, caused change
by envy
More...
More...
98. Excessive focus
on needing a villain
Statistical
46. Statistics as a
source of possible
errors
More...
4.1. Mess between
different type of
probability
More...
55. Sensation of
invulnerability
through survival
More...
11. Trading off a 33. Ideas about selective
relinquishment, deliberslight risk to
humanity for some ately deciding not to deperceived benefit velop certain technolo(e.g. genetic engi- gies as a way of dealing
with global risks, More
neering)
More...
Confirmation bias
EY
50. False positives 7. The burden of
More...
proof is on a designer to prove that
a system is safe,
not on the users
to prove that a catastrophe is likely
27. An experts estimates which are
not based on strict
calculations
cannot serve as a
measure of real
probability, More...
3.4. Polarization
through discussion, More...
6. Excessively conservative thinking
about risk possibilities associated with
memetic selection effects (Semmelweis),
More
5. Skill at arguing is 10. Specific risks are
harmful, More... perceived as more
dangerous than more
general risks
More
10. An error in a
choice of a neutral
position More...
More...
3. The incorrect use of
inductive logic of a following kind: if something did not occur for
a long time, it will not
occur the same long
period. More...
4.11. Confidence as
a source of errors
The more human doubts his
point of view, the more is often
he changes it under the influence of the new facts, and the it
is more than chances, that it will
get to more authentic knowledge.
4. The thinking
caused by desire to
prove something
(whiful thinking)
More...
14. Predisposal to
risk-taking and
aggression
More...
12. Use completely
the erroneous logic
The situation when human in
the reasoning makes mistakes
in each line is possible. In
this case he could not find errors even if he would like.
More...
18. The error
connected with
representation that
each each event has
only one cause
More...
4.19. Necessity of
a choice between
equally proved options on the basis
of belief
More...
4.20. Effect of first
and last read book
More...
26. The error connected with idea
that if probability of some events
is not computable,
it is believed to be
zero. More...
4.27. Omission of
the fact that safety
of system is defined
by its weakest link
More...
4.28. Denial of
hypotheses without
consideration
More...
5. The logic error
arising at attempts
to prove what it is
necessary to do,
proceeding only
from the description of the facts
13. Pre-science and
pseudo-science
mixture
More...
23. Panic
More...
6. The errors connected
with substitution of the
analysis of risks by the
analysis of commercial
motives of those who
speaks about them
More...
14. The error connected with wrong
definition of the
status of
universalis
Is AI object or class?
4.21. Exaggeration
of a role of computer modeling
More...
29.Noncomputability
More...
More...
4.22. The proof by
analogy as a source
of possible errors
More...
4.9 Perception of
the new information through a
prism of the old
More...
Wrong ideas
9. Erroneous rep- 13. Errors connectresentation that
ed with the conflawhen the
tion of short-term,
problem arises
intermediate term
there will be time and long-term
to prepare for it, forecasts
More...
More...
43. The false belief 34. Futurology is
that it is possible to split across differprove safety con- ent disciplines
clusively
as though the unMore...
derlying processes occur independently, More...
8. Dangerous
research tends to
be self-preserving,
More...
17. The Internet as 44. Underestimate
a source of possible of the human
errors
factor
More...
More...
80. Ambiguity
and a polysemy of
any statement as a
source of a possible
error
More...
45. The false idea
that it is possible
to create a faultless
system
More...
77. Incorrect application of Occams
razor, More...
12. Conspiracy
61. Neglect of
theories as an ob- economic risks
stacle for the sci- More...
entific analysis of
global risks
More...
Occams razor can simply be
used to exclude ideas that are
too complicated to understand,
but nonetheless valid failure
modes
95. Search terms
A scientific concept may have
different systems of terminology associated with it, such that
an internet or journal search
for a given term misses important results associated with
other terms that the searcher
did not know about. More...
79. Underestimating the fragility of
complex systems
More...
65. Error
connected with
incorrect correlation of force and
safety
More...
24. Drowsiness and 67. Planning fallacy 85. Filters between
other mundane
and optimism bias information
human failings
More...
reception and
More...
management
More...
The universal logical errors and problems in reasoning on global risks
4.2. Substitution
of the analysis of
possibilities by the
analysis of the purposes
More...
21. Difficulty in
delimitation of
own knowledge
More...
Mess between
probability and
bets. Some times
we must bey more.
66. Premature
investments
More...
96. Errors connected
with the conscious and
unconscious unwillingness of people to recognize the fault and scale of
catastrophe, More...
12. Absence of
9. Too many cooks
clear understand- in the kitchen:
ing of to whom in- decision paralysis
structions on glob- More...
al risks are directed
More...
Logical
7. Use of so-called
authoritative
knowledge
More...
15. Statements
about possibility
of something and
about impossibility
are not equal
More...
23. The error connected with discrepancy of extrapolation exponential
probability function by means of
the linear,
4.16. Evidence as a
source of error
More...
8. Wrong application of idea that the
theory should be
considered as true,
only if it is proved
(opposite for risks)
More...
16. Logical
conclusion as a
source of errors
More...
4.24. The
St.-Petersburg
paradox
More...
t infinitely big damage from
the extremely rare events has
bigger weight, than all other
events,
4.17. Underestimate of own
inaccuracy
More...
87. Systematic
regulatory failure
More...
92. Fault and
responsibility as
factors in the prevention of risks
More...
Meta-biases
Social games
38. Use of risk
warnings to attract
attention or social
status
More...
41. Privacy as a
source of errors
in management of
risks
More
52. Misuse of apocalyptic scenarios to draw attention and financing
to projects
More...
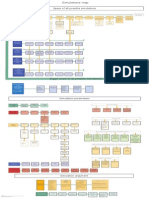
Meta-biases
Some cognitive biases dont allow a person to see and cure his other biases. It results in biases accumulation and strongly
distorted world picture. I tried to draw out a list of main meta-biases.
59. Fear of loss of
the social status by
researchers
More...
60. The quantity of 62. The errors connectthe attention which ed with overestimating,
society can give to underestimating, or
risks is limited
failing to appreciate the
More...
moral condition of a
society and its elite
More...
63. Popularity bias 70. Influence of
82. Transition from
More...
authority and the deliberate deceit to
social pressure of a self-deception
group
More...
More...
1. Psychological group
First and most important of them is overconfidence. Generalized overconfidence also is known as feeling of self-importance. It
prevents a person from searching and indemnifying his own biases. He feels himself perfect. It is also called arrogance.
Lack or reflectivity. Inability to think about own thinking.
Projection of responsibility. If one used to think that others are source of his problems, he is unable to see his own mistakes
and make changes.
Psychopathic traits of character. They often combine many of above mentioned properties.
Learned helplessness. In this case a person may not believe that he is able to debias himself.
Hyperoptimisctic bias. If you want something very much, you will ignore all warnings.
2. Cognitive group
Stupidity. It is not a bias, but a (sort of very general) property of mind. It may include many psychiatric disorders, from dementia to depression.
88. Scapegoating
More...
91. Problems with 94. Bias caused by
selection of experts differences in outlook,
More...
More...
Lack of knowledge in logic, statistic, brain science, scientific method, biases etc.
3. Belief structure items.
Dogmatism: Unchangeable group of believes, often connected with believe in certain text or author.
Lack of motivation to self-improvement.
Obstinacy. A person may want to signal his high status by ignoring good advises and even facts, and try to demonstrate that
he is strong in his believes.
The ability to see others biases as an instrument for effective arguening
Social pressure: Thinking about own fallacies may not be socially acceptable in the peer group.
93. Underestimating inertia as a
factor of stability
More...
Heuristics
25. Propensity of 28. Ignoring a risk
people to struggle because of its insigwith dangers which nificance accordare in the past
ing to an expert,
More...
More...
48. Analysis of
global risks and
making futurist
forecasts are not
identical
More
71. Conflict
between general
research and
applied research
More...
29. Underestimating or overestimating our ability to
resist global risks
More...
31. Behind errors 51. An overly simof the operator
plistic explanation
there is an improp- is the most
er preparation
prominent
More...
More...
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- AI For Immortality MapDocument3 pagesAI For Immortality MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Resurrection of The Dead MapDocument1 pageResurrection of The Dead MapTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- The Map of X-Risk-Preventing Organizations, People and Internet ResourcesDocument1 pageThe Map of X-Risk-Preventing Organizations, People and Internet ResourcesTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Ideas About P-ZombiesDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas About P-ZombiesTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Future SexDocument1 pageFuture SexTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Ideas of Global Warming PreventionDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas of Global Warming PreventionTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Shelters and Refuges From Global Risks (Plan B of X-Risks Prevention)Document1 pageThe Map of Shelters and Refuges From Global Risks (Plan B of X-Risks Prevention)Turchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- AI Safety LevelsDocument1 pageAI Safety LevelsTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Asteroids Risks and DefenceDocument1 pageThe Map of Asteroids Risks and DefenceTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Agents Which May Create X-RisksDocument1 pageThe Map of Agents Which May Create X-RisksTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- The Map of MontenegroDocument1 pageThe Map of MontenegroTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Natural Global Catastrophic RisksDocument1 pageThe Map of Natural Global Catastrophic RisksTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Risks of AliensDocument1 pageThe Map of Risks of AliensTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Ideas About IdentityDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas About IdentityTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Methods of OptimisationDocument1 pageThe Map of Methods of OptimisationTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Bio Risk MapDocument1 pageBio Risk MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Ideas How Universe Appeared From NothingDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas How Universe Appeared From NothingTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Global Catastrophic Risks Connected With Nuclear Weapons and Nuclear EnergyDocument5 pagesGlobal Catastrophic Risks Connected With Nuclear Weapons and Nuclear EnergyTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Double Scenarios of A Global Catastrophe.Document1 pageDouble Scenarios of A Global Catastrophe.Turchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Doomsday Argument MapDocument1 pageDoomsday Argument MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Life Extension MapDocument1 pageLife Extension MapTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Simulation MapDocument1 pageSimulation MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- AI Failures Modes and LevelsDocument1 pageAI Failures Modes and LevelsTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Russian Naive and Outsider Art MapDocument1 pageRussian Naive and Outsider Art MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- (Plan C From The Immortality Roadmap) Theory Practical StepsDocument1 page(Plan C From The Immortality Roadmap) Theory Practical StepsTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- The Roadmap To Personal ImmortalityDocument1 pageThe Roadmap To Personal ImmortalityTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Typology of Human Extinction RisksDocument1 pageTypology of Human Extinction RisksTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Civil Disobedience by Henry David ThoreauDocument12 pagesCivil Disobedience by Henry David ThoreauSchubert VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Good Manners by Prof - Varun AryaDocument21 pagesGood Manners by Prof - Varun AryaVarun AryaNo ratings yet
- Possibilities and Paradigms in Education ResearchDocument421 pagesPossibilities and Paradigms in Education ResearchAsis Bellum100% (1)
- Research Methodology Case Study ResearchDocument8 pagesResearch Methodology Case Study ResearchMorita Septi RahayuNo ratings yet
- Pairing and Appresentation in Disproving SolipsismDocument4 pagesPairing and Appresentation in Disproving SolipsismBesoy Legislador BasbañoNo ratings yet
- The Emergence of The Divine PlanDocument3 pagesThe Emergence of The Divine PlanPatrick Mulcahy100% (3)
- Martha C. Nussbaum, Amelie Oksenberg Rorty Essays On Aristotles de Anima 1995Document433 pagesMartha C. Nussbaum, Amelie Oksenberg Rorty Essays On Aristotles de Anima 1995Juan Pedraza100% (2)
- What Is Philosophy - Dietrich Von Hildebrand PDFDocument251 pagesWhat Is Philosophy - Dietrich Von Hildebrand PDFSerennaCTartini100% (2)
- Poetry and ImaginationDocument47 pagesPoetry and ImaginationChrissa Fragiadaki100% (1)
- MAPC Handbook PDF 2014Document28 pagesMAPC Handbook PDF 2014shahban201100% (1)
- CPSC120 UBC Quiz 02-ADocument5 pagesCPSC120 UBC Quiz 02-ARainie FuNo ratings yet
- Communication in Public SectorDocument73 pagesCommunication in Public SectorToaster97100% (1)
- Shining in Plain View John Wheeler Sample PDFDocument28 pagesShining in Plain View John Wheeler Sample PDFPeter CohenNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 MasteryDocument4 pagesPractical Research 1 Masterymalourdes lorca50% (2)
- Grace Chan - Gestalt PDFDocument1 pageGrace Chan - Gestalt PDFGraceNo ratings yet
- AristotleDocument1 pageAristotleShahzadNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk Mains 2016Document12 pagesSBI Clerk Mains 2016BishalNo ratings yet
- Subject Outline: 58102 Language and DiscourseDocument8 pagesSubject Outline: 58102 Language and DiscourseAnonymous 0bkfMCBPaCNo ratings yet
- The Thick and The Thin: On The Interpretive Theoretical Program of Clifford GeertzDocument21 pagesThe Thick and The Thin: On The Interpretive Theoretical Program of Clifford GeertzJoaquin Solano100% (1)
- Johan Huizinga - Conditions For A Recovery of Civilization (Ensaio)Document10 pagesJohan Huizinga - Conditions For A Recovery of Civilization (Ensaio)CydLosekannNo ratings yet
- Are You Ready To Lose Your World PDFDocument20 pagesAre You Ready To Lose Your World PDFChaitanya GaurNo ratings yet
- JurisprudenceDocument22 pagesJurisprudenceDeepashikha0% (1)
- Chomsky's Cognitive TheoryDocument7 pagesChomsky's Cognitive TheoryCamCatimpo100% (1)
- Rationality and RelativismDocument31 pagesRationality and RelativismSamuel Andrés Arias100% (1)
- Yuvraj NotesDocument67 pagesYuvraj NotesSumit PatwaNo ratings yet
- Virtue Ethics Powerpoint JM 09-02-09Document27 pagesVirtue Ethics Powerpoint JM 09-02-09Wotanngare NawaNo ratings yet
- David Myatt and The Quest For Lapis PhilosophicusDocument21 pagesDavid Myatt and The Quest For Lapis Philosophicussliddell_3No ratings yet
- The Art of Effortless PowerDocument5 pagesThe Art of Effortless PowerWangshosanNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Michael of Nebadon, Teachings of Spirit of TruthDocument20 pagesWelcome To Michael of Nebadon, Teachings of Spirit of TruthMichael Of Nebadon100% (2)
- TautologiesDocument3 pagesTautologiesJevenggNo ratings yet