Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hi 14.6-2011
Uploaded by
linch1Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hi 14.6-2011
Uploaded by
linch1Copyright:
Available Formats
()
a
~
~.
HI Rotodynamic Pumps for Hydraulic Performance Acceptance Tests -
2011
::T
Cii
a.
3
III
A minimum of five test points shall be taken for all performance tests, regardless of acceptance grade, with one of
the points being within -5% and 0%, and one being within 0% and +5% of the guarantee point flow rate. The other
three points shall be spaced over the allowable operating range of the pump performance curve, with points taken
near the maximum allowable head and flow regions.
Cii
::l.
!l!.
'
::::J
IIIa.
o
c-<
NOTE: Other test procedures apply to NPSH tests. See Appendix F.
Z
I
14.6.5.7.2
m
m
c...
c
Speed of rotation during test
Unless otherwise agreed, tests may be carried out at a speed of rotation within the range of 50 to 120% of the test
point(s) specified speed of rotation to establish rate of flow, pump total head, and power input. The efficiency may
be affected if testing with different speeds. However, if the variation of speed is within 20% of the specified speed,
then the efficiency change is considered negligible.
G)
::::J
For NPSH tests, the speed of rotation should lie within the range of 80 to 120% of the specified speed of rotation,
provided that the rate of flow lies within 50 and 120% of the rate of flow corresponding to the maximum efficiency at
the test speed of rotation.
14.6.5.8
NPSH tests
14.6.5.8.1
Objective of NPSH tests
The objective of the NPSH test is to verify the pump's NPSHR for the guarantee. This test deals only with measurements relating to the hydraulic performance of the pump (variations of head, flow, and power) and not with other
effects that can be caused by cavitation (e.g., noise, vibration, and erosion).
Cavitation effects may be detected as a drop in head or power at a given rate of flow. Unless otherwise specified, a
3% drop in head (the accepted industry practice) will be used to determine NPSHR and defined as NPSH3. In the
case of multistage pumps, the head drop shall be referred to the head of the first stage, which should be measured
if accessible. For very low head pumps, a head drop larger than 3% may be agreed on.
In most cases, cavitation tests will be conducted with deaerated clear water. Cavitation tests in water cannot accurately predict the behavior of the pump with liquids other than clear water.
NOTE: Air content may have a significant effect on measured NPSHR values and should be considered.
14.6.5.8.2
14.6.5.8.2.1
NPSH test types
Type I test: Determination of NPSH3 for multiple flow rates
iii'
In this test NPSHA is reduced progressively until the drop of the total head at constant flow rate reaches 3%. This
value of NPSHA is the NPSH3 (see Table 14.6.5.8.2.1). A minimum of four different suitably spaced flow rates shall
be evaluated within the allowable operation region.
5".
C"
c
a.
Cii
C"
"<
:;!
a
14.6.5.8.2.2 Type II test: Determination of NPSH3 for a single flow rate
In this test NPSHA is reduced progressively until the drop of the total head of 3% at specified constant flow rate can
be determined. This value of NPSHA is NPSH3 (see Table 14.6.5.8.2.1).
14.6.5.8.2.3
NPSHA
Q.
(!)
::::J
S'
5"
Type III test: Verification of limited influence of cavitation on the performance at specified
f'
Verification is made at the specified NPSHA to show that the total head at rated flow of the pump is not affected by
cavitation more than 3%.
Hydraulic Institute Standards, Copyright 1997-2011, All Rights Reserved
::::J
(Jl
19
oo
"0
"<
HI Rotodynamic Pumps for Hydraulic Performance Acceptance Tests -
2011
c.6'
:::T
0-
3
Q)
14.6.3.3.4 Overall measurement uncertainty
The fluctuation due either to the characteristics of the measuring system or to variations of the measured quantity,
or both, appears directly as a scatter of the measurements. Unlike the systematic uncertainty, the fluctuation can
be reduced by increasing the number of measurements of the same quantity under the same conditions.
2"
:J
~
~
0-
8"
c-<
The overall measurement uncertainty is calculated by the square root of the sum of the squares of the systematic
and random uncertainties (fluctuations).
'-
14.6.3.4 Performance test acceptance grades and tolerances
Gl
o
:J
Six pump performance test acceptance grades: 1B, 1E, 1U, 2B, 2U, and 3B are defined below.
Grade 1 is the most stringent, with acceptance grade 1U having a unilateral tolerance band and 1B having a bilateral tolerance band. Acceptance grade 1E is also bilateral and is important to those concerned with energy efficiency. Grades 2 and 3 have wider tolerance bands, with 2B and 38 being bilateral and 2U unilateral. Note that all
grade 1 tolerances have the same tolerance bandwidth for flow and head; the same is true for grades 2 and 3.
The purchaser and manufacturer can agree to use any grade to judge if a specific pump will meet a guarantee
point. If a guarantee point is given, but no acceptance grade is specified, then this standard reverts to a default test
acceptance grade, as described in Section 14.6.4.
Guarantee point acceptance grades for pump head, flow, power, and efficiency are provided in Table 14.6.3.4.
Table 14.6.3.4 - Pump test acceptance grades and corresponding tolerance band
Grade
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
t. to
10%
16%
18%
t. tH
6%
10%
14%
Acceptance grade
Test
parameter
Guarantee
requirement
Symbol
1B
Rate of flow
Mandatory
to (%)
Total head
Mandatory
tH (%)
Optional
(either/or)
Powerll }
Efficiencya
1E
1U
28
2U
3B
5%
5%
3%
3%
0% to + 10%
8%
0% to +16%
9%
O%to+ 6%
5%
0% to +10%
tp (%)
+4%
+4%
7%
+10%
+8%
+16%
+9%
t(%)
-3%
-0%
-0%
-5%
-5%
-7%
a The power and efficiency tolerances are not the result of an exact calculation using the maximum values of a related column.
They are instead reflecting real life experience. For grade 1E and 1U, no negative tolerance on efficiency is allowed.
NOTE:
CJ
a=
c:
All tolerances are percentages of values guaranteed.
Other specified duty points, including their tolerances, shall be per separate agreement between the supplier and buyer. If other
specified duty points are agreed on, but no tolerance is given for these points, then the default acceptance grade for these
points shall be grade 38.
-I
:::T
U>
:J
en
14.6.3.4.1
Q.
Tolerances for pumps with an input power of 10 kW (13 hp) and below
CD
;a
3i
For pumps with a shaft power input up to 10 kW (13 hp) but larger than 1 kW (1.3 hp), the tolerance factors given in
Table 14.6.3.4 may be too stringent. If not otherwise agreed on between manufacturer and purchaser, the tolerance
factors shall be as follows for pumps falling within this range:
rate of flow
pump total head
to
= 10%
tH = 8%
Hydraulic Institute Standards, Copyright 1997-2011, All Rights Reserved
13
S'
:;-
You might also like
- EXHIBIT 071 (B) - Clearfield Doctrine in Full ForceDocument4 pagesEXHIBIT 071 (B) - Clearfield Doctrine in Full ForceAnthea100% (2)
- Alga AlgasDocument40 pagesAlga AlgasGGUNANo ratings yet
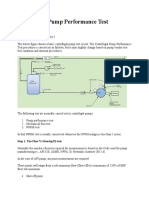
- Centrifugal Pump Performance Test Procedure: Step 1. The Flow Vs Head (Q/H) TestDocument8 pagesCentrifugal Pump Performance Test Procedure: Step 1. The Flow Vs Head (Q/H) TestVinod SaleNo ratings yet
- LS Furmanite OyMDocument26 pagesLS Furmanite OyMDanny Carrasco Vicharra0% (2)
- Acceptance Tests of Centrifugal PumpsDocument20 pagesAcceptance Tests of Centrifugal PumpsAndrés Barón100% (1)
- Angiomat Illumena MallinkrodtDocument323 pagesAngiomat Illumena Mallinkrodtadrian70% (10)
- Gaps, Pro Versus NoviceDocument2 pagesGaps, Pro Versus Novicertkiyous2947No ratings yet
- Making Sense of Pump Testing Standards - How Understanding Standards Can Impact The Bottom Line PDFDocument24 pagesMaking Sense of Pump Testing Standards - How Understanding Standards Can Impact The Bottom Line PDF1sympatyagaNo ratings yet
- 3-4 HD - Api - 617 PDFDocument8 pages3-4 HD - Api - 617 PDFkagasaw023No ratings yet
- Type SAP Usage / Definition Example Procurement RotablesDocument4 pagesType SAP Usage / Definition Example Procurement Rotablessabya1411No ratings yet
- API Standard 619 - Rotary-Type Displacement Compressors For Petroleum, Chemical, and Gas Industry ServicesDocument2 pagesAPI Standard 619 - Rotary-Type Displacement Compressors For Petroleum, Chemical, and Gas Industry ServicesmishraenggNo ratings yet
- Torque Values RTJ B16 5 PDFDocument3 pagesTorque Values RTJ B16 5 PDFPranpath NarupantawartNo ratings yet
- LabVIEW Core 3 2013 - Course ManualDocument135 pagesLabVIEW Core 3 2013 - Course Manualtalaindio100% (2)
- Man 3779Document2 pagesMan 3779Abrar Hussain100% (14)
- Pump Inspection HandbookDocument16 pagesPump Inspection Handbookyoonchankim0911100% (2)
- Factory Acceptance Test (FAT)Document9 pagesFactory Acceptance Test (FAT)Horas Canman SianiparNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Performance Test ProcedureDocument7 pagesCentrifugal Pump Performance Test Proceduresamuraivicky100% (1)
- ASTM A370 - 97a PDFDocument53 pagesASTM A370 - 97a PDFbaolengocNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operating Manual FMTB 5000 Test Bench: 0.5 - 5000 m3 / HDocument36 pagesInstallation and Operating Manual FMTB 5000 Test Bench: 0.5 - 5000 m3 / HDaniel Oscar100% (1)
- SAUNDERS Industrial Diaphragm ValvesDocument52 pagesSAUNDERS Industrial Diaphragm ValvesGohilakrishnan ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- NPSH 12 PDFDocument5 pagesNPSH 12 PDFJose Luis Ornelas LourithNo ratings yet
- International Standard: Fans - Performance Testing Using Standardized AirwaysDocument19 pagesInternational Standard: Fans - Performance Testing Using Standardized AirwaysviniciusschwabNo ratings yet
- Astm A182-A182m-05Document17 pagesAstm A182-A182m-05NadhiraNo ratings yet
- Astm A254Document4 pagesAstm A254dai.nh100% (2)
- SAEJ110 V 002Document13 pagesSAEJ110 V 002Marcos Verissimo Juca de PaulaNo ratings yet
- Amarex KRT8041eDocument36 pagesAmarex KRT8041eRui Alves da Silva100% (1)
- Norma Astm e 165Document20 pagesNorma Astm e 165joseNo ratings yet
- Properties of Ss410Document5 pagesProperties of Ss410gregkilatonNo ratings yet
- F 876 - 01 - Rjg3ni0wmuuyDocument6 pagesF 876 - 01 - Rjg3ni0wmuuyPrakash MakadiaNo ratings yet
- 612 PDFDocument1 page612 PDFalassy juyNo ratings yet
- Schedule Large Vertical TurbineDocument1 pageSchedule Large Vertical TurbineGodwin ChagotaNo ratings yet
- Is-4696-1 2004Document7 pagesIs-4696-1 2004ofajNo ratings yet
- A485 PDFDocument4 pagesA485 PDFProduction DepartmentNo ratings yet
- PASCAL Check Valves CatalogueDocument19 pagesPASCAL Check Valves Cataloguecrys100% (1)
- HH125 Smanual Completed - Master Updated 30-3-06Document41 pagesHH125 Smanual Completed - Master Updated 30-3-06jacklyn ade putra0% (1)
- Waukesha Knock Index Power CurveDocument1 pageWaukesha Knock Index Power CurveparathasiNo ratings yet
- ASGEpg187 PDFDocument3 pagesASGEpg187 PDFbkprodhNo ratings yet
- TFM 4215Document2 pagesTFM 4215Mohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Model 7600: NDIR Infrared Gas AnalyzerDocument126 pagesModel 7600: NDIR Infrared Gas Analyzerzulfiqar aliNo ratings yet
- SP-P-001 - Specification For StrainerDocument30 pagesSP-P-001 - Specification For Strainervishal bhamreNo ratings yet
- ASTM E 1003 Practica Estandar para PHDocument12 pagesASTM E 1003 Practica Estandar para PHrodoNo ratings yet
- DTW 1239Document16 pagesDTW 1239GANESH GNo ratings yet
- Astm A 335Document8 pagesAstm A 335Ruben Dario Espinoza Vasquez100% (1)
- Leak Detection InspectorDocument41 pagesLeak Detection InspectortonNo ratings yet
- Fisher Type 667 Diaphragm ActuatorDocument32 pagesFisher Type 667 Diaphragm Actuatorimran khanNo ratings yet
- Wellmark PSVDocument6 pagesWellmark PSVHomer SilvaNo ratings yet
- IMIOrton MV SeriesDocument4 pagesIMIOrton MV SeriesFelipe Gamboa GálvezNo ratings yet
- A A 59326 - 1aDocument3 pagesA A 59326 - 1acvz240159No ratings yet
- Astm A217-2001 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm A217-2001 PDFMohammed TariqNo ratings yet
- 16899Document33 pages16899Edson BastoNo ratings yet
- Asme Section Ii A Sa-426 PDFDocument6 pagesAsme Section Ii A Sa-426 PDFAnonymous GhPzn1xNo ratings yet
- 731 AaDocument101 pages731 AaasdasdNo ratings yet
- Grapples CDS 9 5.8 - 43.5 - 53.5Document2 pagesGrapples CDS 9 5.8 - 43.5 - 53.5luis alberto franco rodriguezNo ratings yet
- A1028-03 (2015) Standard Specification For Stainless Steel Bars For Compressor and Turbine AirfoilsDocument4 pagesA1028-03 (2015) Standard Specification For Stainless Steel Bars For Compressor and Turbine Airfoilstjt4779No ratings yet
- Guia de Aplicacion para Potencia HidraulicaDocument62 pagesGuia de Aplicacion para Potencia HidraulicaGeLoRa66No ratings yet
- Grasa para Tuberia Bestolife 2000Document4 pagesGrasa para Tuberia Bestolife 2000Haiber BurgosNo ratings yet
- ASTM A356 A356M - 07 Steel CastingsDocument6 pagesASTM A356 A356M - 07 Steel CastingsMacario LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Secviii Div 2 - 7.5.6Document2 pagesSecviii Div 2 - 7.5.6Bhavin SukhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Sae.j995.1967 Mechanical and Quality Requirements For Steel Nuts PDFDocument5 pagesSae.j995.1967 Mechanical and Quality Requirements For Steel Nuts PDFAlonso Enrique Peña ReyesNo ratings yet
- En1564-1 2017Document4 pagesEn1564-1 2017Dan PopaNo ratings yet
- TEMA FlangesDocument38 pagesTEMA FlangesAshfaq Anwer100% (1)
- Molykote® P-37 Datasheet Eng PDFDocument2 pagesMolykote® P-37 Datasheet Eng PDFBib GmzNo ratings yet
- Installmanual Cotta Arreglado PDFDocument20 pagesInstallmanual Cotta Arreglado PDFCarlos Landeta GarciaNo ratings yet
- 302-Exp7 S13Document10 pages302-Exp7 S13Anurag KashyapNo ratings yet
- Gas Well Deliverability Fetkovich PDFDocument33 pagesGas Well Deliverability Fetkovich PDFBarbara_LFCNo ratings yet
- Linux Internet Web Server and Domain Configuration TutorialDocument59 pagesLinux Internet Web Server and Domain Configuration Tutorialrajnishmishra2488No ratings yet
- BEVERAGE SERVICE INDUSTRY Lesson 1Document18 pagesBEVERAGE SERVICE INDUSTRY Lesson 1milyn maramagNo ratings yet
- Warman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q PDocument2 pagesWarman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q Pyoel cueva arquinigoNo ratings yet
- Ashik KP - Windows Engineer - 6 00 - Yrs - Bangalore LocationDocument4 pagesAshik KP - Windows Engineer - 6 00 - Yrs - Bangalore LocationmanitejaNo ratings yet
- 5 GR No. 93468 December 29, 1994 NATU Vs TorresDocument9 pages5 GR No. 93468 December 29, 1994 NATU Vs Torresrodolfoverdidajr100% (1)
- Mamba Vs Lara, 608 SCRA 149 (2009) Case DigestsDocument1 pageMamba Vs Lara, 608 SCRA 149 (2009) Case DigestsAce Lawrence AntazoNo ratings yet
- P443 OrderForm - v43 - 122020Document14 pagesP443 OrderForm - v43 - 122020Tuan Dang AnhNo ratings yet
- Is LNG Still Competitive With Other Liquid Fuels?: Proceedings, Ascope'97 ConferenceDocument18 pagesIs LNG Still Competitive With Other Liquid Fuels?: Proceedings, Ascope'97 Conferencemanolo8catalanNo ratings yet
- Art Research Paper OutlineDocument8 pagesArt Research Paper Outlinefyr90d7m100% (1)
- Avimator Beginners GuideDocument13 pagesAvimator Beginners GuideluluzichaNo ratings yet
- Java 9 Real - TimeDocument57 pagesJava 9 Real - TimeDiego AmayaNo ratings yet
- Safurex - Sandvik Materials TechnologyDocument14 pagesSafurex - Sandvik Materials TechnologyGhulam AhmadNo ratings yet
- A Cost Estimation Approach For IoT Projects PDFDocument9 pagesA Cost Estimation Approach For IoT Projects PDFGuru VelmathiNo ratings yet
- Violence Against NursesDocument22 pagesViolence Against NursesQuality Assurance Officer Total Quality ManagementNo ratings yet
- Types of TrianglesDocument5 pagesTypes of Trianglesguru198319No ratings yet
- 2019 Specimen Paper 3 Mark SchemeDocument6 pages2019 Specimen Paper 3 Mark SchemeProjeck HendraNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Management - Midterm ReviewerDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurial Management - Midterm ReviewerAudrey IyayaNo ratings yet
- Project Human Resource Management Group PresentationDocument21 pagesProject Human Resource Management Group Presentationjuh1515100% (1)
- Indian - Origin Girls Bag Google Science Honour - Yahoo! India EducationDocument3 pagesIndian - Origin Girls Bag Google Science Honour - Yahoo! India EducationRiyaz RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of Regula Falsi MethodDocument12 pagesAdvantages, Disadvantages and Applications of Regula Falsi MethodMd Nahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Iata 2008 - Annex ADocument11 pagesIata 2008 - Annex Agurungbhim100% (1)
- Literature Review On Climate Change in NigeriaDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Climate Change in Nigeriac5rn3sbr100% (1)
- Edu 637 Lesson Plan Gallivan TerryDocument11 pagesEdu 637 Lesson Plan Gallivan Terryapi-161680522No ratings yet
- Atex ExplainedDocument3 pagesAtex ExplainedErica LindseyNo ratings yet
- April 24, 2008Document80 pagesApril 24, 2008Reynaldo EstomataNo ratings yet