Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2013 Pembungaan
Uploaded by
Chariot TigatiganolOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2013 Pembungaan
Uploaded by
Chariot TigatiganolCopyright:
Available Formats
17/05/2013
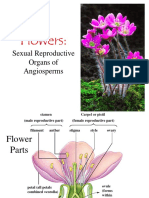
Floral organs
Berdasarkan hipotesis ABC, bagaimanakah struktur bunga yang
dihasilkan (dari karangan paling luar) oleh tumbuhan yang memiliki
ekspresi gen A dan C tetapi tidak terjadi ekspresi gen B pada
keempat karangan bunganya?
A. carpel-petal-petal-carpel
B. Petal-petal-stamen-stamen
C. sepal-carpel-carpel-sepal
D. sepal-sepal-carpel-carpel
E. carpel-carpel-carpel-carpel
Floral architecture
B
A
Floral Organ Organization
Floral organ whorls replace the meristem
Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels
Floral organs are:
ABC model explains determination
- initiated sequentially by of floral organ identity
the floral meristem
- A alone sepals
- produced as successive
- A+B petals
whorls (concentric circles)
- B+C stamen
- C alone carpels
Floral organ identity is specified by five MADS box genes:
APETALA1 (AP1)
APETALA2 (AP2)
PISTELLATA (PI)
AGAMOUS (AG)
APETALA3 (AP3)
MADS box genes control flower development
Whorl
1
2
3
4
ABC Model of Floral Organ Identity
A genes: APETALA1*, APETALA2
B genes: APETALA3*, PISTILLATA*
C gene: AGAMOUS*
*Produce MADS box transcription factors.
Loss of A function ->
spread of C function
Loss of B function ->
only expression of
A and C
Loss of C function ->
spread of A function
Cadastral
genes
17/05/2013
Summary
Floral Organ Identity Genes
Vegetative
Apical
Meristem
Inflorescence
Meristem
Floral
Meristem
Floral
Organs
1. Give organs their identity
2. Homeotic genes: Major developmental switches
3. Transcription factors
4. Some are Cadastral genes boundary genes that
mutually repress each other.
Homeotic floral gene mutations: apetala2
Wild type
apetala2-2
No sepals
No petals
Floral Organ Identity Genes
1.
Give floral organs their identity
2.
Major developmental switches
3.
Originally determined through homeotic mutations
Mutations: Floral organs appeared in the wrong place
Encode transcription factors
4.
Determine location at which specific floral organs develop
Belong to class of related DNA sequences having MADS box
gene domains encode protein structures known as MADS
domains.
Three classes: A, B & C
Homeotic floral organ gene
mutations: agamous
1. No stamens
2. No carpels
3. Whorls of petals
or sepals
Quadruple Mutant in Arabidopsis Flowers
Whats the
phenotype of a
ap1, ap2, pi, ag
mutant flower?
1.No sepals
2.No petals
3.No stamens
4.No carpels
5.All Leaf-like appendages
17/05/2013
Fotoperiode
Fenomena pd berbagai jenis tumbuhan dimana panjang hari
menentukan apakah meristem pucuk /lateral mampu membentuk
bunga atau tidak
* obligate fotoperiod : tetap vegetatif jika
panjang hari tak sesuai
* facultative fotoperiod : dpt berbunga pada
kondisi panjang hari yg tak sesuai, tetapi
pembungaan tetap diinduksi oleh LD atau SD
Shade avoidance (phytochromes)
Perception of light
Plants have specific photoreceptors
Different photoreceptors detect
different wavelengths of light
- Phytochromes (red and far-red light)
- Cryptochromes (blue, green, UV-A light)
- Phototropin (blue light)
- UV-B receptor (still not identified)
Sensor panjang hari (day length)
Terletak pada daun
*satu daun yang menerima fotoperiod yang tepat
mampu menginduksi terbentuknya bunga
Vegetation absorbs/reflects
light of wavelengths below
700nm
Between 700 and 800nm
transmitted
Plants in shade receive more
far-red light than red light
Results in increase in rate of
internode elongation
Grow beyond shading
plants, growth slows as red
light perceived
* stimulus pembungaan dapat ditransmisikan
melalui sambung pucuk pada tanaman yang
sama atau bahkan berbeda spesiesnya
Key regulatory interactions in the leaf and at the shoot apex
Direct interactions are indicated
by bold lines (regulation of
mRNA levels refers to
transcriptional control)
Photoperiodism
The ability of an organism to
detect day length
Kobayashi and Weigel 2007
Genes Dev 21: 2371-2384
17/05/2013
Seleksi olimpiade tingkat propinsi 2009
Tim olimpiade biologi indonesia 2008
Sistem Fitokrom
Pada waktu tengah malam, suatu tumbuhan berbunga didedahkan
kepada cahaya merah dan merah jauh dengan urutan sebagai berikut:
merah, merah jauh, merah. Pernyataan berikut ini benar, KECUALI;
A. Bentuk aktif dari fitokrom adalah Pfr
B. Pfr dalam jumlah besar akan terdapat pada akhir perlakuan
C. Pr dalam jumlah kecil akan terdapat pada akhir perlakuan
D. Pada tumbuhan hari pendek, pembungaan akan terinduksi
E. Pada tumbuhan panjang hari netral, pembungaan tidak akan
terinduksi
Red light
660 nm
Pr
Pfr
Response
730 nm
Far red light
long dark
period
Photoperiodic regulation of flowering
Photoperiodic induction of flowering (phytochromes)
Short-day plant: light period shorter than a critical length to flower (flower in
late summer, fall, or winter: poinsettias, chrysanthemums)
Long-day plant: light period longer than a critical length to flower (flower in
late spring or early summer: spinach, radish, lettuce, iris)
Day-neutral plant: unaffected by photoperiod (tomatoes, rice, dandelions)
Critical night length controls flowering (genetic factor), it varies widely
between species
Short-day plants flower when the day length
is less than (or the night length exceeds) a
certain critical duration in a 24-h cycle.
Short-day (long-night) plants flower
when night length exceeds a critical
dark period. Interruption of the dark by
brief light treatment prevents flowering.
Effects of the duration of the dark period on flowering
Treating short- and longday plants with different
photoperiods shows that
the length of the dark
period is critical.
Chrysanthemum
Rice, Kalanchoe
Poinsettias
Morning glory (Pharbitis)
Cocklebur (Xanthium)
Soybean
Day-neutral plants
Hibiscus
Fuchsia
Spinach
Arabidopsis
Sugar beet
Radish
Kidney bean
Desert plants
Cucumber
Tomato
Long-day plants flower when the day length
exceeds (or the night length is less than) a
certain critical duration in a 24-h cycle.
Long-day (short-night) plants flower if
the night length is shorter than a critical
period. In some long-day plants,
shortening the night with a night break
induces flowering.
Phytochrome is the primary photoreceptor in photoperiodism
Short-day
(long night) plant
Long-day
(short night) plant
A flash of red light during the dark period induces flowering in a long-day plant, and
effect is reversed by far-red light. involvement of phytochrome
In a short-day plant, red light prevents flowering, and effect is reversed by flash of
far-red light.
17/05/2013
How does an oscillation with a 24-h period
measure a critical duration of darkness?
Short-day
(long night) plant
Example:
Plant Reproduction
How does Chrysanthemum know
that it needs 10-12 hrs to induce
flowering?
Long-day
(short night) plant
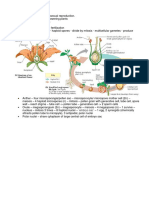
The life cycle of a flowering plant with emphasis on egg cell formation
and seed development
Pada Angiospermae, setiap butir pollen menghasilkan dua sperma.
Apa yang dilakukan oleh kedua sperma ini?
A. Masing-masing memfertilisasi sel telur yang terpisah
B. Salah satu memfertilisasi satu sel telur dan yang lain
memfertilisasi buah
C. Salah satu memfertilisasi satu sel telur dan yang lain tetap
dipertahankan
D. Keduanya memfertilisasi satu sel telur
E. Salah satu memfertilisasi satu sel telur dan yang lain
memfertilisasi suatu sel yang akan berkembang menjadi tempat
cadangan makanan
Life circle of Angiosperm
Pada angiosperma,
fase sporofit
dominan :
Menghasilkan
spora yang
berkembang
menjadi gamet
jantan
Menghasilkan
gametofit betina
(kantung embrio)
Stigma
Carpel
Anther
Style
Stamen
Filament
Ovary
Petal
Ovule
Sepal
17/05/2013
Polinasi
Polinasi : melekatnya serbuk sari ke
kepala putik
Setelah terjadi pembuahan (fertilisasi)
ovulum akan berkembang menjadi biji
dan ovarium akan menjadi buah
Banyak tumbuhan angiospermae
melakukan perkembangbiakan vegetatif
Fertilization
Male gametogenesis
Diploid pollen mother cells undergo meiosis to
produce a tetrad of haploid microspores.
Each microspore develops into a pollen grain
containing two haploid cells (mitosis I):
the generative cell (small)
The vegetative cell (large)
generative
cell
Pollen tubes grow, by tip growth, down through the stigma and
style and into the ovary, toward the ovules.
The pollen tube navigates to the micropyle and discharges the
two sperm cells.
the vegetative cell grows to produce the pollen tube
the generative cell produce 2 sperm cells (mitosis II)
17/05/2013
Double fertilization
Ovule
One sperm fertilizes
the egg cell to develop
into the embryo.
Antipodal cells
Central cell
nuclei
the other sperm
fertilizes the diploid
central cell nucleus to
develop into the
endosperm.
Egg
Synergids
Micropyle
Sperms
Manakah dari aktivitas bakteri tanah berikut ini yang
tidak berkontribusi untuk menghasilkan persediaan
nitrogen yang dapat digunakan untuk tumbuhan
A. Fiksasi nitrogen atmosfer
B. Pengubahan ion amonium menjadi nitrat
C. Dekomposisi hewan yang mati
D. Penyusunan asam amino menjadi protein
E. Pemprosesan amonium dari protein pada daun mati
Pollen
tube
Siklus Nitrogen
You might also like
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument80 pagesChapter 23 Plant Reproductionmain.15001068No ratings yet
- Mechanism of Flowering: What Makes Plants FlowerDocument40 pagesMechanism of Flowering: What Makes Plants FlowerIrdatul WardahNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesDocument76 pagesFlowering Plant Reproduction and Development Lecture SlidesRaja InaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument45 pagesChapter 23 Plant ReproductionMárk SerfőzőNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Development-1Document8 pagesPlant Growth and Development-1Sseruwo JohnsonNo ratings yet
- LSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument64 pagesLSM3261 - Lecture 5 - Reproduction in PlantsAbraham KangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Plant ReproductionDocument45 pagesChapter 23 Plant ReproductionSara SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - PERPETUATION OF LIFEDocument15 pagesModule 6 - PERPETUATION OF LIFEMharcjhefferson RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Reproductive SystemsDocument35 pagesChapter 4. Reproductive Systemsalemneh bayehNo ratings yet
- Flowers: Sexual Reproduction in AngiospermsDocument106 pagesFlowers: Sexual Reproduction in AngiospermsAlfonso PlantillaNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Reproduction ExplainedDocument53 pagesAnimal and Plant Reproduction ExplainedSheryl Osorio100% (1)
- 3.2 Plant Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionDocument79 pages3.2 Plant Reproduction - Sexual ReproductionJuanero, Reyean IñigoNo ratings yet
- Flowers and reproduction life cyclesDocument16 pagesFlowers and reproduction life cyclesCat100% (1)
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsdarkadainNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Gr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryDocument9 pagesGr11 LS PlantDiversity TheoryLutendo Assurance MadzivhaaNo ratings yet
- #2 AngiospermDocument65 pages#2 AngiospermrandelNo ratings yet
- CH # 9 Kingdom Plantae Class 11THDocument37 pagesCH # 9 Kingdom Plantae Class 11THJansher Ali ChohanNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionExceil Matthew Carpio100% (1)
- Plant ReproductionDocument25 pagesPlant ReproductionRAENA MARIE PENDRAS100% (1)
- Angiosperms PPT RevisedDocument55 pagesAngiosperms PPT RevisedJohn Philip Neri Besedillas100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument51 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsbarunmahto001No ratings yet
- General Biology II Q4 Week 1Document36 pagesGeneral Biology II Q4 Week 1Katrina Nicole LomoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSDocument76 pagesReproduction PPT 3 ANGIOSPERMSlisanames.23No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Plants1Document5 pagesChapter 4 Plants1Gabbie CruzNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Reproduction Processes ComparedDocument16 pagesPlant and Animal Reproduction Processes Comparedhellohelloworld100% (1)
- Bio 2Document39 pagesBio 2caezstNo ratings yet
- Genetics of flower development in Arabidopsis thalianaDocument40 pagesGenetics of flower development in Arabidopsis thalianaSanthoshNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument22 pagesPlantsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument19 pagesSexual ReproductionjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Document10 pagesReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesNo ratings yet
- Flowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityDocument4 pagesFlowers, fruits and seeds: A morphological continuityJobadzNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Biology Biology50Document4 pagesSci10 Biology Biology50Nurul NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesSexual ReproductionMasrat AmirNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsShan PMCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasDocument26 pagesChapter 3: Plant Growth and Reproduction: 5 Grade Science Teacher Imarlys CajigasSNOWCHILL VINESNo ratings yet
- Plant reproduction guideDocument9 pagesPlant reproduction guidenanaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument73 pagesReproduction in PlantsCharmaine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Plants Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesPlants Reproduction and DevelopmentAlwìn GarciaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelNo ratings yet
- Plant reproduction: Asexual vs sexual processesDocument9 pagesPlant reproduction: Asexual vs sexual processesregine gamaleNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes on Energy, Plant Systems & Flower StructureDocument3 pagesBiology Notes on Energy, Plant Systems & Flower StructureDivy PurswaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 11C Biology Notes-1Document100 pagesGrade 11C Biology Notes-1Lily PotterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document79 pagesLecture 4Brian Ngugi KamandeNo ratings yet
- Lec7. Plant ReproductionDocument51 pagesLec7. Plant ReproductionJohn Lawrence YbanezNo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument11 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual Reproductionmalicaymichelle20No ratings yet
- Bio 12 First Long Exam ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio 12 First Long Exam ReviewerKyla JavierNo ratings yet
- Bio2 - 4.01 - Plant Reproduction, Nutrition & Devt - CondensedDocument151 pagesBio2 - 4.01 - Plant Reproduction, Nutrition & Devt - CondensedMARKIEL JUSTINE DOMOSMOGNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction: Biology For MajorsDocument35 pagesPlant Reproduction: Biology For MajorsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in VegetablesDocument46 pagesModes of Reproduction and Pollination Types in Vegetablessyamkavitha100% (4)
- Plant Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesPlant Reproduction and Developmentits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction of PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction of PlantsJohn Nowell DiestroNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi UniDocument28 pagesNota Biologi UniMuhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- Lab Report BiologyDocument8 pagesLab Report BiologyFatin NabilahNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDocument15 pagesModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- Plant developmentDocument18 pagesPlant developmentjohn frebNo ratings yet
- 3. Reproduciton in crops Plant 2023Document68 pages3. Reproduciton in crops Plant 2023lemma4aNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Reproduction in Plants – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science Chapter 2 PhotosynthesisDocument38 pages7th Grade Science Chapter 2 Photosynthesisapi-235404570100% (4)
- Fotosintesis ProsesDocument66 pagesFotosintesis ProsesChariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- Osn Bio 2012Document17 pagesOsn Bio 2012Chariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetChariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- Fotosintesis ProsesDocument66 pagesFotosintesis ProsesChariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- OpheliaDocument1 pageOpheliaChariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- Chemosynthesis 1Document48 pagesChemosynthesis 1Chariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- Trigger Finger Anatomy, Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument9 pagesTrigger Finger Anatomy, Causes, Diagnosis and TreatmentChariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- Cant Stop Believing TetsuDocument1 pageCant Stop Believing TetsuChariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- 20-Congestive Heart FailureDocument15 pages20-Congestive Heart FailureGheavita Chandra DewiNo ratings yet
- BY: Marisa Alfianty 03011178Document6 pagesBY: Marisa Alfianty 03011178Chariot TigatiganolNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penambahan Limbah Plastik Kresek Sebagai Subsitusi Aspal Pen 60/70 Terhadap Karakteristik Campuran Laston Ac - BCDocument12 pagesPengaruh Penambahan Limbah Plastik Kresek Sebagai Subsitusi Aspal Pen 60/70 Terhadap Karakteristik Campuran Laston Ac - BCAngga DideNo ratings yet
- How Underground Life Creates Healthy Soil and PlantsDocument31 pagesHow Underground Life Creates Healthy Soil and PlantsscribdanonimoNo ratings yet
- 03 Sherry ViticultureDocument33 pages03 Sherry ViticultureAna Belen PradasNo ratings yet
- How To Plant PeoniesDocument4 pagesHow To Plant PeoniesCamelia M CamiNo ratings yet
- Drainage CoefficientDocument4 pagesDrainage CoefficientJan Dave100% (2)
- Standards interaction highway asphaltDocument7 pagesStandards interaction highway asphaltjoe briffaNo ratings yet
- Horticulture: DefinitionsDocument9 pagesHorticulture: Definitionssatwik bisaryaNo ratings yet
- GeotechData Bearing CapacityDocument1 pageGeotechData Bearing CapacityShridhar BabuNo ratings yet
- Estimate Fence CHBDocument42 pagesEstimate Fence CHBDarren Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Embryo and Seed Coat Factors Produce Seed Dormancy in Capeweed (Arctotheca Calendula)Document8 pagesEmbryo and Seed Coat Factors Produce Seed Dormancy in Capeweed (Arctotheca Calendula)indiNo ratings yet
- Ceng 6102 Concrete Construction Laboratory Report For Production of Self Compacting Concrete and C-70Mpa ConcreteDocument61 pagesCeng 6102 Concrete Construction Laboratory Report For Production of Self Compacting Concrete and C-70Mpa Concreteyared kebedeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of SoilDocument74 pagesChemistry of SoilOmosay Gap ElgyzonNo ratings yet
- Beam Longitudinal Section: Moment DiagramDocument1 pageBeam Longitudinal Section: Moment DiagramLove JoeyNo ratings yet
- Trans Gulf Electro-Mechanical L.L.C: Pricing SheetDocument16 pagesTrans Gulf Electro-Mechanical L.L.C: Pricing SheetJason SecretNo ratings yet
- The Creative Gardener S Guide To Blues and PurplesDocument97 pagesThe Creative Gardener S Guide To Blues and PurplescurarmadretierraNo ratings yet
- High Density Planting System in Fruit CropsDocument5 pagesHigh Density Planting System in Fruit Cropsarid132No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentLoai Al-moqayadNo ratings yet
- Necessity of Harvesting RobotDocument6 pagesNecessity of Harvesting RobotbabgrNo ratings yet
- Underpinning, Shotcreting and GroutingDocument47 pagesUnderpinning, Shotcreting and GroutingMehta ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Rabi Field Crops Manual Provides Comprehensive GuideDocument109 pagesRabi Field Crops Manual Provides Comprehensive GuideGarima Chawla WaliaNo ratings yet
- AllocationDocument1 pageAllocationOmar Ossama MahmoudNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT BUREAU BAMBOO PROPAGATIONDocument24 pagesECOSYSTEMS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT BUREAU BAMBOO PROPAGATIONRoel BrionesNo ratings yet
- IJMFM&AP Vol 2 1 2016Document73 pagesIJMFM&AP Vol 2 1 2016KalkameNo ratings yet
- Blackleg of Canola: Steve Marcroft, Marcroft Grains Pathology, Horsham, Chris Bluett DPI BallaratDocument2 pagesBlackleg of Canola: Steve Marcroft, Marcroft Grains Pathology, Horsham, Chris Bluett DPI BallaratsushantNo ratings yet
- FAS Plant WalkDocument16 pagesFAS Plant Walkapi-26891612No ratings yet
- Effect of Tillage and Staking On The Production of Fluted PumpkinDocument8 pagesEffect of Tillage and Staking On The Production of Fluted PumpkinAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Thru Index PDFDocument446 pagesChapter 14 Thru Index PDFMita PutriNo ratings yet
- Anthesis International: Seminte Profesionale Si Bulbi de FloriDocument38 pagesAnthesis International: Seminte Profesionale Si Bulbi de FloriGrecu ValiNo ratings yet
- Growth and yield of pechay applied with different levels of compost fertilizerDocument4 pagesGrowth and yield of pechay applied with different levels of compost fertilizerSannie Ong MonoyNo ratings yet
- Admixtur PDFDocument19 pagesAdmixtur PDFÖmer ErcanNo ratings yet