Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounting Equations: Subject
Uploaded by
Henry CaoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounting Equations: Subject
Uploaded by
Henry CaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Monday, 1 June 2015
Accounting Equations
Subject
1. Assets = Liability + Share Capital
2. Assets = Liability + (Share Capital + Retained Profit)
3. Assets = Liability + {Share Capital +(Retained Profit at the beginning period +
Revenue - Expenses -Dividends)}
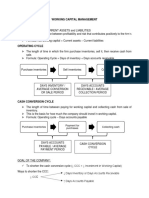
low or negative working capital indicate short-term
4. Working Capital = CA - CL financial difficulties
5. Opening retained profits + Net profit for the period - Distributions (Dividends
declared) = Closing retained profits
6. Perpetual Method: Beginning inventory cost + Inventory acquired during the period Cost of inventory sold = Ending inventory cost
7. Periodic Method: Beginning inventory + Purchases - Ending inventory = Inventory
Sold (COGS)
8. Total cost = Ending Inventory + COGS
9. Depreciable amount = Asset Cost - Residual value
10. Straight-line depreciation: Depreciation expenses = (Cost - Residual value)/ Useful
life
11. Reducing Balance Depreciation: Depreciation expenses = Carrying Amount *
Depreciation value
12. Units of Production Depreciation: Depreciation per unit = (Cost - Residual value)/
Assessing the
Estimated total # of units of prod over life
effectiveness of
Profitability Ratio
(ability to earn
13. Return
profits)
14. Return
asset
utilisation
on Assets (ROA) = Operating Profit After Tax/ Total assets
How much return the
ROE = ROA * Leverage Ratio
company is generating
on Equity (ROE) = Operating Profit After Tax/ Shareholders Equity on the shareholder's
investment
ROA: Profit Margin * Asset Turnover
15. Profit Margin = Operating Profit After Tax/ Sales Revenue
16. Gross Margin = Gross Profit/ Sales
Further indication
Revenue of product pricing
and product mix
Indication of: Pricing
Strategy and competition
intensity in the industry
17. Earning Per Share = (Net operating profit - Dividends on preferred shares)/ Weighted
average number of ordinary share outstanding
18. Assets Turnover = Sales/ Total Assets
Indication of operating efficiency
19. Inventory Turnover = COGS/Average Inventory
Days in inventory: 365/Inventory
Activity
(turnover) Ratios
[efficiency of
operation]1
Efficiency of inventory management
Monday, 1 June 2015
20. Debits Turnover = Credit Sales/ Average Accounts Receivable
Days in Debtor= 365/Debtors turnovers
Efficiency of the company
to collect the amount due
from debtors
21. ROA = Profit Margin * Asset Turnover
enough CA to pay off CL?
to working capital=CA-CL
Liquidity Ratios
(ability pay
short term
debts)
22. Current Ratio = CA/CL Relating
23. Quick Ratio = (Cash + Accounts Receivable + Short-term investment)/ Current
CA without inventory as it needs to
Liabilities
be sold
24. Leverage Ratio = Total assets/ Shareholders Equity
Financial
Structure
Ratios
(ability
to
continue
operating
in long
term)
25. ROE = ROA * Leverage Ratio
how much of assets is financed by equity
indicate company's policy regarding financing
of its assets
>1, too high ratio is a warning about risk
26. Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Liabilities/ Total Shareholders Equity
27. Debt-to-Assets Ratio = Total Liabilities/ Total Assets
higher ratio, greater risk
28. Contribution Margin (CM) = Revenue - Variable Cost
29. Contribution Margin per unit = Unit selling price - Unit variable cost
30. Contribution Margin Ratio = CM per unit/ Unit selling price
31. Break-Even Analysis - Unit-sold Approach
Profit(BT) = (S - V)X - F => X = [F + Profit(BT)]/ (S - V)
- S = unit selling price
X = F + ProfitBT
(S V)
CM
- X = number of units
- V = unit variable cost
- F = fixed cost
32. Profit(AT) = Profit(BT) * (1 - ) => Profit(BT) = Profit(AT)/ (1-)
- = tax rate
33. Break-Even Analysis - Sales Revenue Approach
Profit(BT) = R - F - (vr)R
Sales dollar = [F+Profit(BT)]/ CM Ratio
- R = SX
- vr = V/S
total variable cost/ sales revenue
unit
You might also like
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument10 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisAli Gokhan Kocan100% (1)
- Presentation On Financial ModelingDocument136 pagesPresentation On Financial ModelingMd. Zahedul Ahasan100% (1)
- Business Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsFrom EverandBusiness Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Final - FMVDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet Final - FMVhanifakih100% (2)
- 04 Fs Analysis With StudentDocument10 pages04 Fs Analysis With StudentarianasNo ratings yet
- Ratio FormulasDocument4 pagesRatio FormulasImran SarwarNo ratings yet
- Corporate Financial Analysis NotesDocument19 pagesCorporate Financial Analysis NotesWinston WongNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Summary SheetDocument1 pageFinancial Ratio Summary SheetKeith Tomasson100% (1)
- CMA FORMULA SHEET NEW SYLLABUS-Executive-RevisionDocument7 pagesCMA FORMULA SHEET NEW SYLLABUS-Executive-RevisionGANESH KUNJAPPA POOJARINo ratings yet
- Technician Pilot Papers PDFDocument133 pagesTechnician Pilot Papers PDFCasius Mubamba100% (4)
- Inventory Turnover Cost of Sales / Avg Inventory High Is Effective Inv MGMT Days of Inventory On Hand (DOH) 365/inv TurnoverDocument3 pagesInventory Turnover Cost of Sales / Avg Inventory High Is Effective Inv MGMT Days of Inventory On Hand (DOH) 365/inv Turnoverjoe91bmwNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis: Amerbran Company (BDocument37 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis: Amerbran Company (BZati Ga'in100% (1)
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- ACYAVA1 Comprehensive Examination Quiz Instructions: Started: Jun 4 at 13:00Document37 pagesACYAVA1 Comprehensive Examination Quiz Instructions: Started: Jun 4 at 13:00Joel Kennedy BalanayNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Important FormulaDocument4 pagesRatio Analysis: Important FormulaHarsh Vardhan KatnaNo ratings yet
- Section 1 : Mastering Depreciation Testbank Solutions Depreciation On The Financial Statements V. Tax ReturnDocument4 pagesSection 1 : Mastering Depreciation Testbank Solutions Depreciation On The Financial Statements V. Tax ReturnSamuel ferolinoNo ratings yet
- Bbap2103 Akaun PengurusanDocument10 pagesBbap2103 Akaun PengurusanEima AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer - 28Document30 pagesQuestion and Answer - 28acc-expert33% (3)
- Accounting Equations: SubjectDocument2 pagesAccounting Equations: SubjectYuxuan ChenNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis FormulaeDocument3 pagesRatio Analysis FormulaeKalyani ShindeNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios ListDocument1 pageFinancial Ratios Listbibekmishra8107No ratings yet
- I) Short Term Solvency or Liquidity Ratios: Net IncomeDocument2 pagesI) Short Term Solvency or Liquidity Ratios: Net Incomedude devilNo ratings yet
- I) Short Term Solvency or Liquidity Ratios Or: InterestDocument2 pagesI) Short Term Solvency or Liquidity Ratios Or: InterestSonia DalviNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis FormulaDocument2 pagesRatio Analysis Formulaaceleaf100% (3)
- Ratio - Basics: Liquidity Ratios (Short Term Solvency Ratios)Document5 pagesRatio - Basics: Liquidity Ratios (Short Term Solvency Ratios)Avijash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis Advisory ServicesDocument14 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Advisory ServicesWilsonNo ratings yet
- Accounting Ratios and Formulas GuideDocument6 pagesAccounting Ratios and Formulas GuideRavikumar GandhiNo ratings yet
- Dupont MethodDocument4 pagesDupont MethodgitzNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Key Financial Metrics for Business PerformanceDocument8 pagesRatio Analysis: Key Financial Metrics for Business PerformancezainNo ratings yet
- Important Points 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7Document15 pagesImportant Points 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7RAVI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Guide to Key Liquidity, Leverage, Operating and Profitability RatiosDocument5 pagesGuide to Key Liquidity, Leverage, Operating and Profitability RatiosGyanam SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal College, Goheer Campus,: BahawalpurDocument1 pageAllama Iqbal College, Goheer Campus,: BahawalpurMuhammad Qaisar LatifNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Unit-V Liquidity DecisionDocument24 pagesFinancial Management: Unit-V Liquidity DecisionVinay VinnuNo ratings yet
- Ecnomic Notes 1Document26 pagesEcnomic Notes 1ehnzdhmNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Ratio Analysis: Financial Analysis and InterpretationDocument21 pagesUnit-V Ratio Analysis: Financial Analysis and InterpretationAnusha EnigallaNo ratings yet
- Fsa 2Document15 pagesFsa 2Abinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 BMADocument4 pagesChapter 28 BMAmylittlespammyNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis. A) Liquidity Ratio - 1) Current Ratio Current Asset Current LiabilityDocument6 pagesRatio Analysis. A) Liquidity Ratio - 1) Current Ratio Current Asset Current LiabilitysolomonNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument4 pagesAccountingNicolas LuchmunNo ratings yet
- Butler Lumber Glossary of Financial Ratios and TermsDocument1 pageButler Lumber Glossary of Financial Ratios and TermsBusiness ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Main RatioDocument4 pagesMain RatioJuliette Hamel-GauthierNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance II: Session II 09/06/01 Werner Stanzl Yale School of ManagementDocument24 pagesCorporate Finance II: Session II 09/06/01 Werner Stanzl Yale School of ManagementManoj KhullarNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument23 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisHinata UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Ratio AnalysisDocument1 pageFinancial Management Ratio AnalysisAmrita GhartiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Evaluasi Rasio KeuanganDocument16 pages2 - Evaluasi Rasio KeuanganRophinta ViolytaNo ratings yet
- AfM 8 - Tools For Financial AnalysisDocument12 pagesAfM 8 - Tools For Financial AnalysisjaymursalieNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis Using Ratio AnalysisDocument5 pagesFinancial Analysis Using Ratio AnalysisJiten BendleNo ratings yet
- The Preparation and Analysis of FSs of Sole TraderDocument5 pagesThe Preparation and Analysis of FSs of Sole TraderSangeeta SadeoNo ratings yet
- Cma Formula SheetDocument7 pagesCma Formula Sheetanushkamohanan0No ratings yet
- Accounting ReviewerDocument2 pagesAccounting Reviewerjoshua korylle mahinayNo ratings yet
- Capital Employed Ordinary Share Capital + Reserves + Non-Current Liabilities or Capital Employed Total Liabilities - Current LiabilitiesDocument6 pagesCapital Employed Ordinary Share Capital + Reserves + Non-Current Liabilities or Capital Employed Total Liabilities - Current Liabilitiesbinder8640No ratings yet
- CFA RatiosDocument11 pagesCFA RatiosrooptejaNo ratings yet
- GMR Operating Revenue Operating Expense Sales N MR Net Profit Sales Roa Profit Assets DE Total Debt Total Equity Liabilities EquityDocument4 pagesGMR Operating Revenue Operating Expense Sales N MR Net Profit Sales Roa Profit Assets DE Total Debt Total Equity Liabilities EquityShahreyar YawarNo ratings yet
- Fin Stat AnalysisDocument23 pagesFin Stat AnalysisSadiabcdNo ratings yet
- Key Terms For Prelim ExamDocument8 pagesKey Terms For Prelim ExamArnold LuayonNo ratings yet
- Acc ExamDocument3 pagesAcc ExamKhanim RzaevaNo ratings yet
- 4 Financial Statement AnalysisDocument13 pages4 Financial Statement AnalysisAdnan RizviNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance & International Controlling (BPO) : Home Work 2 On The Balance Sheet and The Important RatiosDocument7 pagesCorporate Finance & International Controlling (BPO) : Home Work 2 On The Balance Sheet and The Important RatiosNitish RawatNo ratings yet
- Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology111Document11 pagesBapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology111UmeshNo ratings yet
- UNDERSTANDING FINANCIAL STATEMENTSDocument53 pagesUNDERSTANDING FINANCIAL STATEMENTSRashmi KhatriNo ratings yet
- Investment Analysis FormulasDocument2 pagesInvestment Analysis FormulasNESIBE ERBASNo ratings yet
- Accounting Formulas: Short Term Solvency or Liquidity RatiosDocument2 pagesAccounting Formulas: Short Term Solvency or Liquidity RatiosTambro IsbNo ratings yet
- InsyncDocument6 pagesInsyncVivek AdateNo ratings yet
- Accounting Formulas and ConceptsDocument10 pagesAccounting Formulas and ConceptsDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- RATIO ANALYSIS INSIGHTSDocument31 pagesRATIO ANALYSIS INSIGHTSRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial RatiosDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Financial Ratiospv12356No ratings yet
- Applied Auditing Perando PatriciaDocument32 pagesApplied Auditing Perando PatriciamaurNo ratings yet
- RAK Ceramics PJSC CFS Q2 2020 EnglishDocument34 pagesRAK Ceramics PJSC CFS Q2 2020 Englishahme farNo ratings yet
- XYZ TagumDocument8 pagesXYZ TagumBSA3Tagum MariletNo ratings yet
- Beximco Pharma-Financial AnalysisDocument26 pagesBeximco Pharma-Financial AnalysisIffat Binte Rabbani100% (1)
- Acca f9 and p4 Answers To Reinforcing Questions p4Document80 pagesAcca f9 and p4 Answers To Reinforcing Questions p4Calvince OumaNo ratings yet
- Asset Revaluation or Impairment Understanding The Accounting For Fixed Assets in Release 12 White PaperDocument7 pagesAsset Revaluation or Impairment Understanding The Accounting For Fixed Assets in Release 12 White Papervarachartered283No ratings yet
- Module 3 Chapter 15 DCF ModelDocument2 pagesModule 3 Chapter 15 DCF ModelMaulik JainNo ratings yet
- FAC4764 Study Pack 2Document41 pagesFAC4764 Study Pack 2Muvhusi NethonondaNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 Quarter1 Module 6.2 Week 6Document22 pagesFabm1 Quarter1 Module 6.2 Week 6Danny BulacsoNo ratings yet
- Calculate Payback Period, NPV-Chapter 2Document13 pagesCalculate Payback Period, NPV-Chapter 2Khuetu NguyenhoangNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Dewan Mushtaq GroupDocument26 pagesFinancial Analysis of Dewan Mushtaq Groupسید نیر سجاد البخاري100% (2)
- Capital Budgeting V2 - Click Read Only To View DocumentDocument40 pagesCapital Budgeting V2 - Click Read Only To View DocumentSamantha Meril PandithaNo ratings yet
- CFAS Reviewer - Module 3Document8 pagesCFAS Reviewer - Module 3Lizette Janiya SumantingNo ratings yet
- RHB Sports Club Financial Statements 2012Document11 pagesRHB Sports Club Financial Statements 2012Pranava Gurukul SamaajNo ratings yet
- Advanced aCCOUNTING 2 SOLMAN PDFDocument418 pagesAdvanced aCCOUNTING 2 SOLMAN PDF杉山未来100% (1)
- AFS MCQsDocument43 pagesAFS MCQsNayab KhanNo ratings yet
- MTQS Investment Appraisal Test AnsDocument5 pagesMTQS Investment Appraisal Test AnsChoudhristNo ratings yet
- The Other Side of Value: The Gross Profitability Premium: Robert Novy-Marx June, 2012Document73 pagesThe Other Side of Value: The Gross Profitability Premium: Robert Novy-Marx June, 2012Rohit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Cost of Capital for Capital Budgeting DecisionsDocument2 pagesCalculating Cost of Capital for Capital Budgeting DecisionsAnonymous wSXoP5aaNo ratings yet
- Unit 03Document69 pagesUnit 03Shah Maqsumul Masrur TanviNo ratings yet
- Pénzügyi Számviteli Angol Teljes Könyv Megoldásokkal KitöltveDocument60 pagesPénzügyi Számviteli Angol Teljes Könyv Megoldásokkal KitöltveJudit FehérnéNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation: Fundamentals of ABM 1Document97 pagesAccounting Equation: Fundamentals of ABM 1ediwowNo ratings yet
- QUIZ BEE AUDITING THEORYDocument12 pagesQUIZ BEE AUDITING THEORYErica Sophia KwanNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument7 pagesHandoutSalma AbdullahNo ratings yet