Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AM f4 c10 Solution of Triangle New 2
Uploaded by
Noelle LimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AM f4 c10 Solution of Triangle New 2
Uploaded by
Noelle LimCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
FORM 4
PAPER 2
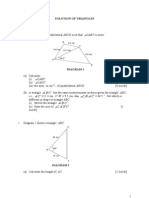
1.
Diagram 1 shows a
quadrilateral ABCD such that
ABC is acute.
a ) Calculate
i ) ABC
ADC
ii )
iii ) the area, in cm2, of the
quadrilateral ABCD
[ 8 marks]
Diagram 1
b ) A triangle ABC has the
same measurements as those given for triangle ABC but it is
different in shape to triangle ABC. Sketch the triangle ABC
[ 2 marks ]
2.
P
R
12cm
65
10cm
Diagram 2
Q
The Diagram 2 shows a triangle PQR.
(a) Calculate the length, in cm, of PR
[ 2 marks ]
PR is a diagonal, PRS = 30 and PS = 8.2 cm.
(b) A quadrilateral PQRS is then formed so that
Calculate the two possible values of PSR.
[2 marks ]
(c) Using the acute PSR from ( b ) , calculate
i ) the length, in cm, of RS
ii ) the area, in cm2, of quadrilateral PQRS.
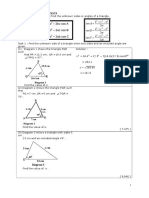
3.
6cm
[ 6 marks]
53
7cm
58
A
D
10cm
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
FORM 4
Diagram 3
Diagram 3 shows a quadrilateral ABCD.
The area of BCD is 20cm2 and BCD is acute. Calculate
(a) BCD
[ 2 marks]
(b) the length in cm, of BD.
(c) ADB
(d) the area, in cm2 , of quadrilateral ABCD
[ 2 marks]
[ 3 marks]
[ 3 marks]
4.
5cm
5cm
80 48'
120
10cm
C
Diagram 4
Diagram 4 shows quadrilateral ABCD.
(a) Calculate
(i ) the length, in cm. of AC,
(ii) ACB
(b) Point A lies on AC such that AB = AB
(i ) Sketch ABC
(ii) Calculate the area, in cm2, of ABC
( 4 marks )
( 6 marks )
59
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
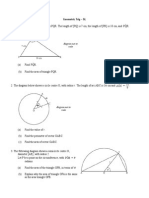
5.
FORM 4
Diagram 1
Diagram 1 shows a pyramid PQRS with triangle PQR as the horizontal base. S is the vertex of the
pyramid and the angle between the inclined plane QRS and the base PQR is 50. Given that PQ
and PR =5.6 cm and SQ = SR = 4.2 cm, calculate
(a) the length of RQ if the area of the base PQR is 12.4 cm2
(b) the length of SP,
(c) the area of the triangle PQS.
[ 3 marks ]
[ 3 marks ]
[ 4 marks ]
ANSWER(PAPER2)
60
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
1. ( a ) ( i ) =
FORM 4
10.8
8.5
sin
sin42.5
ABC
ABC =59.14
1
1
(ii) 10.82=6.52 +5.22- 2(6.5)(5.2)
cosADC
1
ADC = 134.46
1
(iii) Total area
=(10.8)(8.5)sin(180- 42.5 -59.14 ) + 1 (6.5)(5.2)sin134.46
= 57.02 cm2
2
(b)
3
1
42.5
10.8 cm
2
8.5 cm
A
61
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
FORM 4
2.
( a ) PR2 =122 +102- 2(12)(10)cos65
= 142.6
PR = 11.94cm
_
(b)
1
1
S
S'
P
30
12 cm
10 cm
65
sin
sin30
PSR
=
11.94
8.2
PSR = 46.72 or 180 - 46.72
=133.28
( c) ( i ) RPS = 180 - 30 - 46.72
= 103.28
1
8.2
RS
sin103.28
sin 30
( ii) Area = (10)(12)(sin65 ) + (11.94)
=102.02cm2
1 (15.96)(sin30 )
2
=
RS = 15.96cm
1
1
2
1
3.
62
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
(6)(7)sinBCD = 20
2
BCD =72 15
(a)
FORM 4
1
1
( b ) BD2 = 6 2 + 7 2 2(6)(7)cos 72 15
=59.39
BD = 7.706
(c ) =
1
sinsin
53
BAD
7.10
706
BAD =37 59
ADB =180- 3759-53
=89 1
1
1
1
(d) Area = (7)(6)(sin72 15 ) + (7.706)(10)
=58.52cm2
1
2 (sin89 1)
2
1
4.
( a ) ( i ) AC2 = 5 2 + 10 2 2(5)(10)cos 80 48
AC = 10.44
sin
sin120
ACB
10.44
5
( ii ) =
ACB = 24 30
1
1
1
1
( b) ( i)
( ii ) BAC = 180 -120 - 24 30
=35 30
5cm
ABA = 180 - 2 (35 B 30) 5cm
=109
A'
63
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
Area of ABC =(5)(10.4408)(sin35
=15.1575
Area of ABA =(5)(5)(sin109 )
=11.8190
FORM 4
1 30 )
2
1
2
Area of ABC =15.1575 - 11.8190
=3.3385 cm2
1
1
1
5.
( a ) Area of PQR = 12.4
(5.6) (5.6)sinQPR = 12.4
sinQPR = 0.7908
QPR=52.26
1
2
RQ2 = 5.6 2 + 5.6 2 2(5.6)(5.6)cos 52.26
=24.33
RQ = 4.933cm
1
1
(b) QM = QR where M is the midpoint of
= (4.933)
= 2.466
1 RQ
12
2
SM2 = 4.22- 2.4662
=11.56
SM =3.4 cm
PM2 = 5.62- 2.4662
PM = 5.028
SP2 = 3.42 + 5.0282 2(3.4)( 5.028) cos 50
1
1
64
CHAPTER 10
SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
SP =3.855 cm
(c) cos SQP =
=0.7257
SQP = 43.47
Area of PQS
=(5.6) (4.2)sin 43.47
=8.091 cm2
FORM 4
1
5.62 4.22 3.8552
2(5.6)(4.2)
V
1
2
1
1
1
65
You might also like
- f4 c10 Solution of TriangleDocument8 pagesf4 c10 Solution of TrianglerajhiniNo ratings yet
- Module 10B - Solution of TrianglesDocument9 pagesModule 10B - Solution of TrianglesHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Triangles Past SPM QuestionsDocument6 pagesSolutions of Triangles Past SPM QuestionsHo Yen SzeNo ratings yet
- f4 Solution of TrianglesDocument0 pagesf4 Solution of TrianglesvioletgohNo ratings yet
- f4 c10 Solution of TrianglenewDocument8 pagesf4 c10 Solution of Trianglenewnor fazlinaNo ratings yet
- 10 Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pages10 Solution of TrianglesDa-teen Sabreena BernoulliNo ratings yet
- ABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pagesABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesSyafiqah RedzwanNo ratings yet
- DIAGRAM SOLVINGDocument5 pagesDIAGRAM SOLVINGSabariah OsmanNo ratings yet
- HRT-3 For 9th Test MathDocument10 pagesHRT-3 For 9th Test Mathsudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Solution of TriangleDocument5 pagesSolution of TriangleSpike ChingyenNo ratings yet
- ABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pagesABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesNazatulsyima MursalinNo ratings yet
- ABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pagesABC Is Acute.: Solution of Trianglesjhjhtan99No ratings yet
- ABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pagesABC Is Acute.: Solution of TrianglesMK Joey ThamNo ratings yet
- Solution of Triangles 3.2 Task: Answer All The Questions Below.Document23 pagesSolution of Triangles 3.2 Task: Answer All The Questions Below.Karmen ThumNo ratings yet
- 10 Solution of TrianglesDocument5 pages10 Solution of Trianglesbjkhaw75No ratings yet
- Ssc-Geometry Questions PDFDocument13 pagesSsc-Geometry Questions PDFShobhit Mishra0% (1)
- Solution of Triangles: 2 Cos Cos CosDocument4 pagesSolution of Triangles: 2 Cos Cos CosakuesukaNo ratings yet
- PPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre ODocument17 pagesPPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre OakuesukaNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Document22 pagesSine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Rudi Berlian100% (2)
- Solutions of Triangle - Set 2Document2 pagesSolutions of Triangle - Set 2Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument21 pagesSolution of TrianglesAnonymous YcxEABNo ratings yet
- TRIANGLESDocument6 pagesTRIANGLESSweety SharmaNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF PAST YEAR QUESTIONS FORM 4 MATHEMATICSDocument8 pagesANALYSIS OF PAST YEAR QUESTIONS FORM 4 MATHEMATICSJarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- SPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesDocument8 pagesSPM 1993-2021 PAST YEARS Solutions of TrianglesTIME DIDA滴答No ratings yet
- GeomeDocument13 pagesGeomesomu646No ratings yet
- Solution of Triangle 2Document5 pagesSolution of Triangle 2Iman ZaiNo ratings yet
- AMATH Solution of TriangleDocument12 pagesAMATH Solution of TriangleLeneNo ratings yet
- Weebly - 3d TrigDocument4 pagesWeebly - 3d Trigapi-200177496No ratings yet
- SPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 + AnsDocument3 pagesSPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 + AnsSim Kwang Yaw46% (13)
- Solution of Triangle FinalDocument4 pagesSolution of Triangle FinalAkma FekhruzieNo ratings yet
- X-STB-Geomerty - Prelim - I - SET A - QPDocument5 pagesX-STB-Geomerty - Prelim - I - SET A - QPSAID SAYALINo ratings yet
- MODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimeterDocument14 pagesMODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimetersyarelNo ratings yet
- SPM QUESTION FORM 4 SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES AND QUADRILATERALSDocument6 pagesSPM QUESTION FORM 4 SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES AND QUADRILATERALSTee Pei LengNo ratings yet
- Geometric Trig - SLDocument15 pagesGeometric Trig - SLNatNo ratings yet
- Properties of TrianglesDocument8 pagesProperties of TrianglesaayushcooolzNo ratings yet
- Trig WorksheetDocument19 pagesTrig WorksheetRottenHelloNo ratings yet
- Lines, Angles & TrianglesDocument25 pagesLines, Angles & TrianglesBalachandra MallyaNo ratings yet
- Complete Geometry Class - 1 SSC Specail BatchDocument11 pagesComplete Geometry Class - 1 SSC Specail BatchChiranjibee BhoiNo ratings yet
- Circle geometry word problemsDocument7 pagesCircle geometry word problemsSurvivor UBNo ratings yet
- Math AP ProblemsDocument7 pagesMath AP ProblemsSUKUMAR GUCHHAITNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry Word ProblemsDocument9 pagesCircle Geometry Word Problemsidaman2905No ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument10 pagesSolution of TrianglesMohd HarrisNo ratings yet
- DocDocument41 pagesDocDeepankar Sadhan BanikNo ratings yet
- 4024 w04 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w04 QP 2mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Solution of Triangle 1Document7 pagesSolution of Triangle 1Iman ZaiNo ratings yet
- Acs I Y4 Prelim Em1 2010Document15 pagesAcs I Y4 Prelim Em1 2010math3matics3No ratings yet
- Congruency Worksheet SolutionsDocument6 pagesCongruency Worksheet SolutionsBurhan AzharNo ratings yet
- Congruency Worksheet SolutionsDocument6 pagesCongruency Worksheet SolutionsBurhan AzharNo ratings yet
- Nsejs Geometry Sa2Document6 pagesNsejs Geometry Sa2gobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- Similar Triangles Problems and SolutionsDocument13 pagesSimilar Triangles Problems and Solutionssudhir_kumar_33100% (1)
- Properties of Triangles - Maths IADocument3 pagesProperties of Triangles - Maths IAavsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Solution of TrianglesDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Solution of TrianglesHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- 09 O Level Jan 68 - Paper 2Document5 pages09 O Level Jan 68 - Paper 2deepheat_008No ratings yet
- Math ChapterDocument6 pagesMath ChapterRavi AutiNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument3 pagesGeometrysamina shaikhNo ratings yet
- Microsoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures NewDocument10 pagesMicrosoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures Newuzai88No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Trigonometric Functions: Graphing The Trigonometric FunctionDocument55 pagesUnit 7: Trigonometric Functions: Graphing The Trigonometric FunctionNoli NogaNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument27 pagesTrigonometryChetna DhingraNo ratings yet
- Triangles Mind Maps + Top 10 QsDocument46 pagesTriangles Mind Maps + Top 10 QsnirikdhaNo ratings yet
- 30 60 90 Triangle Practice 1w3mynuDocument4 pages30 60 90 Triangle Practice 1w3mynuIrish Serdeña - Sigue0% (1)
- Trigonometry Guide for Angles, Ratios and FormulasDocument15 pagesTrigonometry Guide for Angles, Ratios and FormulasQasim TariqNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Unit Circle and TrigonometryDocument4 pagesModule 2 The Unit Circle and TrigonometryRodante P Hernandez Jr.100% (1)
- Circles (XYZ)Document12 pagesCircles (XYZ)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Triangle IneqDocument14 pagesTriangle IneqTRUE SAMuraiNo ratings yet
- Summative Pre-Calc.Document6 pagesSummative Pre-Calc.SerjohnRapsingNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities With SolutionsDocument35 pagesTrigonometric Identities With SolutionsDhrushiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Trigonometric Ratios: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Trigonometric Ratios: Multiple Choice QuestionshiiiiNo ratings yet
- Trig Quiz Reference Angles Radians OddEven FunctionsDocument4 pagesTrig Quiz Reference Angles Radians OddEven FunctionsAnonymous dq3zN9SkNo ratings yet
- Section 13 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Worksheet 2Document5 pagesSection 13 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Worksheet 2Patrick Junther SazonNo ratings yet
- Activity: Find The Missing Side and Evaluate The Remaining Trigonometric RatiosDocument1 pageActivity: Find The Missing Side and Evaluate The Remaining Trigonometric RatiosJessa Lou Liba CapapasNo ratings yet
- 3D Trig PPT 1Document31 pages3D Trig PPT 1Kulsum KhanNo ratings yet
- PACE Final Lap (Co-Ordinate Geometry)Document84 pagesPACE Final Lap (Co-Ordinate Geometry)Anwesh SahaNo ratings yet
- O LEVEL (P1) TRIGONOMETRY QUESTION'SDocument16 pagesO LEVEL (P1) TRIGONOMETRY QUESTION'SDua LatifNo ratings yet
- Siop Lesson Plan PDFDocument13 pagesSiop Lesson Plan PDFKarly Sachs100% (2)
- NapoleonDocument15 pagesNapoleonAdithya NarayananNo ratings yet
- A Powerpoin Presentation On CircleDocument26 pagesA Powerpoin Presentation On CircleNitesh BhuraNo ratings yet
- Law of Sines and Cosines PresentationDocument44 pagesLaw of Sines and Cosines PresentationJuneReyArgawanonNo ratings yet
- Percentile: ClassesDocument27 pagesPercentile: ClassesVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- HW Arc and Central AnglesDocument4 pagesHW Arc and Central Anglesjennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesDocument2 pagesGrade 5 Geometry: Choose Correct Answer(s) From The Given ChoicesAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- M2 Module 6 Newsletter Similarity and Right Triangle TrigDocument6 pagesM2 Module 6 Newsletter Similarity and Right Triangle TrigHuan HuanNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself TrigonometryDocument210 pagesTeach Yourself Trigonometrylukas100% (2)
- StudenttextDocument26 pagesStudenttextapi-195130729No ratings yet
- Angle Chasing - Junior: Thanom Shaw March 31 & April 1, 2021Document5 pagesAngle Chasing - Junior: Thanom Shaw March 31 & April 1, 2021BobNo ratings yet
- Chapter II IntroductionDocument18 pagesChapter II IntroductionMark Jason DuganNo ratings yet
- QA Geometry TriangleDocument43 pagesQA Geometry TriangleKshitij KumarNo ratings yet