Professional Documents
Culture Documents
24-Hr Chick Embryo
Uploaded by
pau0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
752 views8 pages24-Hr Chick Embryo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document24-Hr Chick Embryo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
752 views8 pages24-Hr Chick Embryo
Uploaded by
pau24-Hr Chick Embryo
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
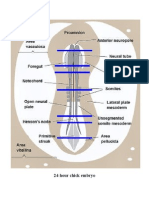
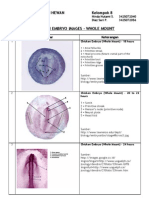
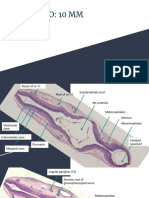
EMBRYO. LAB. 4.
3 DEVELOPMENT OF CHICK EMBRYO
(Part 1 24 HR CHICK EMBRYO)
(WHOLE MOUNT)
1) Area Opaca periphery of blastodisc
- surround area pellucida
- in direct contact with yolk (makes it opaque)
- (during early devt) 3 zones:
1. Margin of Growth (MoG) peripheral; where cells proliferate without adhering to yolk
2. Zone Junction (ZJ) intermediate region; where cells cut free from yolk
3. Germ Wall (GW) inner; its cells are from ZJ (thus, has yolk); marks transition from area
opaca to area pellucida
a. Area Opaca Vasculosa inner; where splanchnic mesoderm thicken into blood
islands
b. Area Opaca Vitellina outer; initially lacks blood islands
2) Area Pellucida center of blastodisc
- where primitive streak forms
- lies over subgerminal cavity
- appears transluscent (due to thinness of blastoderm)
Blastoderm consist of:
Epiblast outer; differentiates into ectoderm and mesoderm
Hypoblast inner
3) Primitive Streak longitudinal cleft on surface of amniote blastodisc
- formed by cell convergence
- gastrulation begins when epiblast cells migrate into the streak
1. Primitive Groove central furrow
2. Primitive Ridges margins of primitive streak @ sides of primitive groove
3. Primitive Pit indented region @ anterior end of primitive streak
4. Hensens Node / Primitive Knot named after Viktor Hensen (1835-1924)
- thickened area @ anterior end of primitive streak
- thru it, cells invaginate, forming notochord
- homologous to dorsal lip of blastopore of amphibians
4) Proamnion anterior to avian embryo
- surrounds head
- contains endoderm and ectoderm
- later involved with mesoderm, then with amnion
- amnion is the membrane around the fetus
5) Neural Folds margins of neural plate
- about to fuse @ mid-dorsal region
6) Neural Groove median longitudinal groove
- formed by rolling up neural plate
7) Head Fold folded part of blastoderm
- dark crescentic line (boundary of head)
8) Notochord longitudinal band of cells
- extends from neural folds to Hensens node
9) Foregut 1st part of digestive tract
- w/ definite floor
- endodermal
- dome-shaped
- lies inside the head
10) Anterior Intestinal Portal (AIP) opening of foregut
- prominent arched line beneath neural folds
- continuous with lateral walls of foregut
- moves posteriorly as gut elongates
- ultimately becomes part of yolk stalk
11) Mesenchyme of Head loose network of cells
- found between foregut and heads ectoderm
12) Mesoderm
1. Anterior Border of Mesoderm faint line across area pellucida
- @ level of anterior end of notochord
2. Thickened Splanchnic Mesoderm dark lines @ lateral borders of anterior intestinal portal
- formed by delamination of lateral plate mesoderm
- becomes heart, part of circulatory system, etc.
13) Somite division of dorsal mesoderm
- 3 or 4 pairs of somites lateral to neural folds
14) Unsegmented Mesoderm undivided part of mesoderm
- posterior to somites
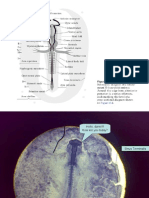
(TRANSVERSE SECTION thru Pharyngeal Membrane)
1) Head Ectoderm cuboidal cells (cuboidal in origin also); encloses head
2) Neural Folds neural epithelium margins
- have NOT fused @ midline yet
3) Anterior Neuropore - temporary external opening of neurocoel
4) Neural Groove median longitudinal groove
- formed by rolling up neural plate
5) Prechordal Plate mass of chordamesodermal cells
- anterior to notochord
- forms head mesenchyme
6) Notochord small medial cell mass; between foregut and neural plate
7) Foregut dorsoventral flattened tube
- endodermal cells
- beneath neural plate
8) Oral Plate / Oropharyngeal Membrane foregut floor is in contact w/ neural ectoderm of head
- (in lateral devt) breaks open to form mouth
9) Mesenchyme loosely scattered cells
- fill up spaces between foregut and neural plate
10) Proamnion - blastoderm beneath head; ectoderm + endoderm
11) Subcephalic Pocket cavity beneath head as head fold develops
12) Somatopleure membrane (ectoderm + somatic mesoderm)
- forms part of body wall, chorion, and amnion
13) Splanchnopleure splanchnic mesoderm + endoderm
- forms into part of body wall, yolk sac, and allantois
14) Coelom cavity formed when somatic mesoderm and mesoderm separates
15) Subgeminal Cavity space beneath hypoblast, w/in area pellucida
- gives rise to midgut
(TRANSVERSE SECTION thru Intestinal Portal)
Neural tube formed
@ level of open foregut
Endoderm of foregut is continuous w/ rest of endoderm
Anterior Intestinal Portal (AIP) opening of closed foregut
Prospective Cardiac Mesoderm - thickened splanchnic mesoderm @ sides of AIP
1) Neural Tube formed by thickening & rolling up of neural plate (during neurulation)
- forms into brain and spinal cord of animal
2) Neural Crest - @ edges of neural plate
- lies above neural tube
- form ganglia, pigment cells, part of gill arches, etc. (by migration thru the embryo)
3) Head Fold marked by downward bend of membranes around the head
4) Anterior Intestinal Portal opening of foregut
- moves posteriorly as gut elongates
- ultimately becomes part of yolk stalk
5) Amnio-Cardiac Vesicle (ACV) part of coelom
- gives rise to amnion and heart
Amnion formed by dorsal wall of ACV, composed of somatopleure
Heart formed by thickened splanchnic mesoderm making up proximal wall of SCV
(TRANSVERSE SECTION thru Midgut)
1) Midgut middle part of gut w/ yolky floor (yolk removed due to fixation)
- floorless region of gut posterior to AIP
(TRANSVERSE SECTION thru a Pair of Somites)
Neural folds not yet closed
Somites - from dorsal mesoderm (D)
- located on sides of neural folds and notochord
Intermediate Mesoderm (I) lateral and adjacent to somites
- small region of mesoderm
- becomes kidneys
Lateral Plate Mesoderm (L) lateral to I
- delaminates to form somatic and splanchnic mesodermal layers
1) Somites segmented mesodermal blocks
- @ sides of spinal cord
- arise from dorsal mesoderm
2) Nephrotome / Intermediate Mesoderm / Mesomere / Nephromere
- stalk-like connection between somites and L
- anteriorly forms pronephros
- posteriorly forms mesenchyme w/c develops into mesonephros and metanephros
3) Hypomere part of mesoderm distal to nephrotome
- 2 layers: somatic and splanchnic mesoderm
(TRANSVERSE SECTION thru the Primitive Streak)
Note the ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
1) Primitive Streak longitudinal cleft
- @ surface of amniote blastodisc
- formed by convergence of cells
- gastrulation begins as epiblast migrates into the streak
1. Hensens Node (HN) / Primitive Knot named after Viktor Hensen (1835-1924)
- thickened area @ anterior end of primitive streak
- thru it, cells invaginate, forming notochord
- homologous to dorsal lip of blastopore of amphibians
2. Primitive Pit depression, a bit deeper than primitive groove
- posterior to HN
3. Primitive Groove (PG) central furrow
- Posterior to primitive pit
4. Primitive Ridges thickened margins on each side of PG
You might also like
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDocument5 pages33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceNo ratings yet
- 72 HR ReviewerDocument8 pages72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- EmbryoLab 10mm FrogDocument13 pagesEmbryoLab 10mm FrogpauNo ratings yet
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocument3 pages24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Document17 pagesEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosNo ratings yet
- 24 Hour Chick EmbryoDocument27 pages24 Hour Chick Embryoaa6280% (1)
- Development of The Pig EmbryoDocument12 pagesDevelopment of The Pig EmbryoKarmina SantosNo ratings yet
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 pagesEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- Early Chick EmbryoDocument74 pagesEarly Chick EmbryoMinette EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- 4 MM FrogDocument5 pages4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDocument48 pagesChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvNo ratings yet
- 18 Hour Chick EmbryoDocument7 pages18 Hour Chick Embryoaa628100% (2)
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Document9 pagesChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsDocument22 pages48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsNathan Bantayan100% (1)
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocument5 pages48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNo ratings yet
- Chick 33 HRDocument14 pagesChick 33 HRaa628No ratings yet
- Chick Embryo WMDocument6 pagesChick Embryo WMdhyan_ajjah67% (3)
- ANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Document6 pagesANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Junko TsukudaNo ratings yet
- 10mm Frog TadpoleDocument30 pages10mm Frog TadpoleSarah Margaret Chong33% (3)
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDocument7 pagesEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Chick 72 HR DDocument35 pagesChick 72 HR Daa628No ratings yet
- Chick EmbryoDocument24 pagesChick Embryonabilalk100% (1)
- 10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansDocument9 pages10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- 33 Hour Chick Embryo Transverse SectionDocument36 pages33 Hour Chick Embryo Transverse SectionSasha GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Parts of Frog HistologyDocument6 pagesParts of Frog HistologyVanessa RebancosNo ratings yet
- Frog EmbryosDocument43 pagesFrog EmbryosNics Martinez100% (7)
- Chick Serial SectionsDocument74 pagesChick Serial SectionsKazuki FuchoinNo ratings yet
- PigDocument34 pagesPigVanessa CarinoNo ratings yet
- 24hr Chick Cross SectionsDocument16 pages24hr Chick Cross Sectionsaa628100% (9)
- Serial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoDocument41 pagesSerial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoChristalie Bea FernandezNo ratings yet
- 72 HrsDocument35 pages72 HrsChristalie Bea FernandezNo ratings yet
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDocument9 pagesBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyNo ratings yet
- 72 Hours Chick EmbryoDocument18 pages72 Hours Chick EmbryoZhairra Marie DionsonNo ratings yet
- BIO 30 LAB: Pattens 72-hr Chick SummaryDocument19 pagesBIO 30 LAB: Pattens 72-hr Chick SummaryFaith VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- 48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyDocument34 pages48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyChristalie Bea Fernandez100% (2)
- Science Diliman TemplateDocument3 pagesScience Diliman TemplateKeesha MoranteNo ratings yet
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDocument4 pages10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Histo Ra 3 - Barbosa, Azenith VincentDocument7 pagesHisto Ra 3 - Barbosa, Azenith VincentMinamiSapphire BarbosaNo ratings yet
- 7 MM FrogDocument28 pages7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04No ratings yet
- 33.48,72 From 2011Document63 pages33.48,72 From 2011aa628No ratings yet
- Lbybio4 PDFDocument8 pagesLbybio4 PDFstudent10100No ratings yet
- Exercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Document16 pagesExercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Gail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- 48-Hour Chick ReviewerDocument5 pages48-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatrice100% (1)
- Early DevelopmentDocument5 pagesEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenDocument28 pagesHistology of Glands: Dr. Zana TahseenAhmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- Exercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument8 pagesExercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- LBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity20 Solidum TanDocument13 pagesLBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity20 Solidum TanFernando Martin BarbaNo ratings yet
- 48 Hour ChickDocument13 pages48 Hour ChickJowi SalNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 4.1 1Document11 pagesExp 2 4.1 1Carlo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 Serial Transverse Section of An 18 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 13 Serial Transverse Section of An 18 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela Faye100% (1)
- Gastrulation (20-10-2019)Document16 pagesGastrulation (20-10-2019)kashif manzoorNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 Postlab Frog External AnaDocument8 pagesActivity 7 Postlab Frog External Anaapi-3836574100% (1)
- 13 Respiratory SystemDocument5 pages13 Respiratory Systemvada_soNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Comparative Anatomy of VertebratesDocument7 pagesRespiratory System - Comparative Anatomy of VertebratesAlyssa Gail de Vera0% (1)
- Chick 48 HRDocument50 pagesChick 48 HRaa628No ratings yet
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerClarebelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dumaguit (2021)Document12 pagesDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- 24 33 Hour ChickDocument9 pages24 33 Hour ChickMary Grace Tuazon100% (1)
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Ice 3101: Modern Control THEORY (3 1 0 4) : State Space AnalysisDocument15 pagesIce 3101: Modern Control THEORY (3 1 0 4) : State Space AnalysisBipin KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Health Management Information SystemDocument14 pagesLecture 12 Health Management Information SystemKamran SheikhNo ratings yet
- O'Dell v. Medallia, Inc. Et Al, 1 - 21-cv-07475, No. 1 (S.D.N.Y. Sep. 7, 2021)Document15 pagesO'Dell v. Medallia, Inc. Et Al, 1 - 21-cv-07475, No. 1 (S.D.N.Y. Sep. 7, 2021)yehuditgoldbergNo ratings yet
- Integrator Windup and How To Avoid ItDocument6 pagesIntegrator Windup and How To Avoid ItHermogensNo ratings yet
- Percentage and Profit & Loss: Aptitude AdvancedDocument8 pagesPercentage and Profit & Loss: Aptitude AdvancedshreyaNo ratings yet
- Allegro Delivery Shipping Company Employment Application FormDocument3 pagesAllegro Delivery Shipping Company Employment Application FormshiveshNo ratings yet
- Ankle Injury EvaluationDocument7 pagesAnkle Injury EvaluationManiDeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Java SlidesDocument134 pagesAdvanced Java SlidesDeepa SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- ANS145 - Beef Cattle ProductionDocument52 pagesANS145 - Beef Cattle ProductionEgie BulawinNo ratings yet
- April 2021 BDA Case Study - GroupDocument4 pagesApril 2021 BDA Case Study - GroupTinashe Chirume1No ratings yet
- The Serious Student of HistoryDocument5 pagesThe Serious Student of HistoryCrisanto King CortezNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 2 - Corporate Governance MechanismDocument19 pages02 Chapter 2 - Corporate Governance MechanismHanis ZahiraNo ratings yet
- Route Clearence TeamDocument41 pagesRoute Clearence Teamctenar2No ratings yet
- SAP HR - Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW)Document5 pagesSAP HR - Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW)Bharathk KldNo ratings yet
- Lifting PermanentmagnetDocument6 pagesLifting PermanentmagnetShekh Muhsen Uddin Ahmed100% (1)
- VLT 6000 HVAC Introduction To HVAC: MG.60.C7.02 - VLT Is A Registered Danfoss TrademarkDocument27 pagesVLT 6000 HVAC Introduction To HVAC: MG.60.C7.02 - VLT Is A Registered Danfoss TrademarkSamir SabicNo ratings yet
- Uh 60 ManualDocument241 pagesUh 60 ManualAnonymous ddjwf1dqpNo ratings yet
- Assignment-For-Final of-Supply-Chain - Management of Courses PSC 545 & 565 PDFDocument18 pagesAssignment-For-Final of-Supply-Chain - Management of Courses PSC 545 & 565 PDFRAKIB HOWLADERNo ratings yet
- Design Practical Eden Swithenbank Graded PeDocument7 pagesDesign Practical Eden Swithenbank Graded Peapi-429329398No ratings yet
- Phy Mock SolDocument17 pagesPhy Mock SolA PersonNo ratings yet
- Nyambe African Adventures An Introduction To African AdventuresDocument5 pagesNyambe African Adventures An Introduction To African AdventuresKaren LeongNo ratings yet
- Islamiyat ProjectDocument21 pagesIslamiyat ProjectSubhan Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- ATS2017 ProspectusDocument13 pagesATS2017 ProspectusGiri WakshanNo ratings yet
- 16 Personalities ResultsDocument9 pages16 Personalities Resultsapi-605848036No ratings yet
- Rin Case StudyDocument4 pagesRin Case StudyReha Nayyar100% (1)
- Saif Powertec Limited Project "Standard Operating Process" As-Is DocumentDocument7 pagesSaif Powertec Limited Project "Standard Operating Process" As-Is DocumentAbhishekChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionDocument4 pagesComparitive Study of Fifty Cases of Open Pyelolithotomy and Ureterolithotomy With or Without Double J Stent InsertionSuril VithalaniNo ratings yet
- Windows System Shortcut CommandsDocument2 pagesWindows System Shortcut CommandsVenkatesh YerraNo ratings yet
- Flip The Coin - EbookDocument306 pagesFlip The Coin - EbookAjesh Shah100% (1)
- Flowrox Valve Solutions Catalogue E-VersionDocument16 pagesFlowrox Valve Solutions Catalogue E-Versionjavier alvarezNo ratings yet