Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Dualnature of Matter
Uploaded by
Ron HartCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Dualnature of Matter
Uploaded by
Ron HartCopyright:
Available Formats
www.sakshieducation.
com
Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
1.
The work function of a certain metal is 3.31 1019 J . Then the maximum
kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted by incident radiation of wavelength
co
m
5000 A is1) 2.48 eV
2.
2) 0.41 eV
3) 2.07 eV
4) 0.82 ev
An electron beam travels with a velocity of 1.6 x 107 ms1 perpendicular to
(me = 9 x1031 kg)
1) 9 x 105 m
3) 9 x 104 m
4) 9 x 103 m
The work function of nickel is 5eV. When light of wavelength 2000A0 falls on
ed
uc
3.
2) 9 x 102 m
at
io
n.
magnetic field of intensity 0.1 T. The radius of the path of the electron beam
it, it emits photoelectrons in the circuit. Then the potential difference
necessary to stop the fastest electrons emitted is (given h=6.6710-34Js)
1) 1.0V
3) 1.2V
4) 0.75V
In an experiment on photoelectric emission from a metallic surface,
sh
i
4.
2) 1.75V
wavelength of incident light is 2 x 107 m and stopping potential is 2.5V. The
ak
threshold frequency of the metal (in Hz) approximately (charge of electron
e = 1.6 x 1019C, Planks constant h = 6.6 x 1034 JS)
5.
w
.s
1) 12 x 1015
2) 9x 1015
3) 9 x 1014
4) 12 x 1013
A particle of mass 1 x 1026 kg and charge 1.6 x 1019C travelling with a
velocity 1.28 x 106 ms1 along the positive X-axis enters a region in which a
uniform electric field E and a uniform magnetic field of induction B are
1 and B = 8 102 jWbm2 , the direction of motion
present. If E = 102.4 103 kNC
of the particles is
1) Along the positive X-axis
2) Along the negative X-axis
3) At 45 to the positive X-axis
4) At 135 to the positive X-axis
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
6.
Light rays of wavelengths 6000 A and of photon intensity 39.6 watts/m2 is
incident on a metal surface. If only one percent of photons incident on the
surface emit photo electrons, then the number of electrons emitted per second
per unit area from the surface will be
1) 12 x 1018
7.
2) 10 x 1018
co
m
[Planck constant = 6.64 x 10-34 J - S; Velocity of light = 3 x 108 ms-1]
3) 12 x 1017
4) 12 x 1015
Electrons ejected from the surface of a metal, when light of certain frequency
n.
is incident on it, are stopped fully by a retarding potential of 3 volts. Photo
electric effect in this metallic surface begins at a frequency 6 x 1014s-1. The
electron = 1.6 x 10-19C]
8.
2) 13.5 x 1013
3) 14 x 1014
ed
uc
1) 7.5 x 1013
at
io
frequency of the incident light in s-1 is [h=6 x 10-34J-sec; charge on the
4) 7.5 x 1015
Consider the two following statements A and B and identify the correct choice
given in the answers
sh
i
A) In photovoltaic cells, the photoelectric current produced is not proportional
to the intensity of incident light.
B) In gas filled photo emissive cells, the velocity of photoelectrons depends on
1) Both A and B are true
2) Both A and B are false
w
.s
ak
the wavelength of the incident radiation.
4) A is false but B is true
3) A is true but B is false
9.
When radiation of wavelength is incident on a metallic surface, the
stopping potential is 4.8 volts. If the same surface is illuminated with
radiation of double the wavelength, then the stopping potential becomes 1.6
volts. Then the threshold wavelength for the surface is
1) 2
2) 4
3) 6
www.sakshieducation.com
4) 8
www.sakshieducation.com
10.
Two photons of energies twice and thrice the work function of a metal are
incident on the metal surface. Then the ratio of maximum velocities of the
photoelectrons emitted in the two cases respectively is
1)
2)
1
4
3)
1
3
4)
1
2
If 0 is the de Broglie wavelength for a proton accelerated through a
co
m
11.
1
2
potential difference of 100 V, the de Broglie wavelength for particle
12.
2)
0
2
3)
0
2 2
4)
0
2
at
io
1) 2 2 0
n.
accelerated through the same potential difference is
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies v1
and v2 of the incident light rays ( 1 > 2 ) . If the maximum values of kinetic
ed
uc
energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the two cases are in ratio of 1: k, then
the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is
1)
2)
k1 2
k 1
3)
k1 + 2
k 1
4) 0
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron having 80 eV of energy is nearly
(1eV =
1.6x
sh
i
13.
k 2 1
k 1
1019 J), mass of
the electron
= 9
x 1031
kg),
ak
Plancks constant = 6.6 x 1034 Js)
14.
2) 0.14 A
3) 14 A
4) 1.4 A
w
.s
1) 140 A
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250
nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v
respectively.
The work function of the metal is (h = Planks constant,
c = velocity of light in air)
1) 2hc 106 J
2) 1.5hc 106 J
3) hc 106 J
www.sakshieducation.com
4) 0.5hc 106 J
www.sakshieducation.com
15.
A photon of energy E ejects a photo electron from a metal surface whose
work function is W0. If this electron enters into a uniform magnetic field of
induction B in a direction perpendicular to the field and describes a circular
path of radius r, then the radius r is given by (in the usual notation):
16.
2m ( E W0 )
mB
2m ( E W0 ) eB 3)
2)
2m ( E W0 )
co
m
2m ( E + W0 )
eB
1)
4)
Be
In Millikans oil drop experiment, a charged oil drop of mass 3.2 1014 kg is
n.
held stationary between two parallel plates 6 mm apart, by applying a
at
io
potential difference of 1200V between them. How many electrons does the oil
drop carry? (g=10ms-2)
1) 7
3) 9
4) 10
An oil drop having a charge was kept between two plates having a potential
ed
uc
17.
2) 8
difference of 400V is in equilibrium. Now another drop of same oil with same
charge but double the radius is introduced between the plates. Then the
1) 200 V
2) 800 V
3) 1600 V
4) 3200 V
The threshold frequency for a certain metal is v0 . When a certain radiation of
ak
18.
sh
i
potential difference necessary to keep the drop in equilibrium is
frequency 2 v0 is incident on this metal surface the maximum velocity of the
w
.s
photoelectrons emitted is 2x106 ms1. If a radiation of frequency 3 v0 is
incident on the same metal surface the maximum velocity of the
photoelectrons emitted (in ms1) is
2) 2 2 106
3) 4 2 106
4) 4 3 106
1) 2 106
19.
The velocity of the most energetic electron emitted from a metallic surface is
doubled when the frequency v of the incident radiation is doubled. The
work function of this metal is
1)
h
4
2)
h
3
3)
h
2
www.sakshieducation.com
4)
2h
3
www.sakshieducation.com
20.
A proton and an alpha particle are accelerated through the same potential
difference. The ratio of the wavelength associated with proton and alpha
particle respectively is
2) 2: 1
1) 1: 2 2
21.
3) 2 2 :1
4) 4: 1
The de-Broglie wavelength of an electron and the wavelength of a photon are
co
m
the same. The ratio between the energy of that photon and the momentum of
that electron is
1) h
3) 1/h
4) 1/C
A proton is projected with a velocity 107 ms1 at right angles to a uniform
n.
22.
2) C
to traverse 90 arc is
at
io
magnetic field of induction 100mT. The time (in seconds) taken by the proton
(Mass of proton= 1.65 x 1027 kg and charge of proton = 1.6 x 1019C)
23.
2) 1.62 x 107
3) 2.43 x 107
ed
uc
1) 0.81 x 107
4) 3.24 x 107
The incident photon involved in the photoelectric effect experiment
1) Completely disappears
sh
i
2) Comes out with increased frequency
3) Comes out with a decreased frequency
24.
ak
4) Comes out without change in frequency
k1 and k2 are the maximum kinetic energies of the photoelectrons emitted
w
.s
when light of wave length 1 and 2 respectively are incident on a metallic
surface. If 1 = 3 2 then
1) k1 >
2) k1 <
k2
3
3) k1 = 3k 2
4) k 2 = 3k1
The de-Broglie wavelength of a particle moving with a velocity
25.
k2
3
2.25 x 108 ms-1is equal to the wavelength of photon. The ratio of kinetic
energy of the particle to the energy of the photon is
[velocity of light = 3 x 108 ms-1]
1) 1/8
2) 3/8
3) 5/8
www.sakshieducation.com
4) 7/8
www.sakshieducation.com
26.
The value of de Broglie wavelength of an electron moving with a speed of
6.6 x 105 ms-1 is approximately
1) 11 Ao
27.
2) 111Ao
3) 211 Ao
4) 311 Ao
The maximum wavelength of light that can be used to produce photoelectric
co
m
effect on a metal is 250nm. The maximum K.E of the electrons in joule,
emitted from the surface of the metal when a beam of light of wavelength 200
nm is used:
28.
2) 69.81 x 10-22
3) 18.96 x 10-20
4) 19.86 x 10-20
n.
1) 89 .61 x 10-22
The work function of Potassium is 2.0 eV. When it is illuminated by light of
photoelectrons is
29.
2) 1.75 V
3) 2.5 V
4) 3.75 V
ed
uc
1) 0.75 V
at
io
wavelength 3300 Ao, photoelectrons are emitted. The stopping potential of
A positron and a proton are accelerated by the same accelerating potential.
Then the ratio of the associated wavelength of positron and proton will be
(M-mass of proton, m=mass of positron)
2)
M
m
3)
m
M
4)
m
M
The work function of metals A and B are in the ratio 1:2.
ak
30.
M
m
sh
i
1)
If light of
frequencies f and 2f are incident on metal surfaces A and B respectively, the
w
.s
ratio of the maximum kinetic energies of the photo electrons emitted is
1) 1:1
3) 1:3
1) Work function of surface
3) Wave length of incident light
32.
4) 1:4
The process of photo electric emission depends on
31.
2) 1:2
2) Nature of surface
4) All of these
If the intensity of incident light is made double, then the maximum number of
emitted electrons will become
1) Double
2) Four times
3) Eight times
www.sakshieducation.com
4) Half
www.sakshieducation.com
33.
The threshold wavelength for photo electric emission from a photo sensitive
surface is 5200 . Which out of the following can start photo electric
emission?
1) 10 watt infrared bulb
2) 1 watt infrared bulb
34.
4) 50 watt ultraviolet bulb
On decreasing the intensity of incident light
1) The photo electric current will increase.
3) The number of emitted electrons will decrease.
35.
at
io
4) All of these.
n.
2) The number of photoelectrons emitted will increase.
co
m
3) 50 watt infrared bulb
When green light is made incident on a metal, photo electrons are emitted by
it but no photo electrons are obtained by yellow light. If red light is made
1) No electrons will be emitted
2) Less electrons will be emitted
3) More electrons will be emitted
4) All of these
The threshold frequency for a metal is 1015 Hz. When light of wavelength
sh
i
36.
ed
uc
incident on that metal then
4000 is made incident on it, them
ak
1) Photo electrons will be emitted from it with zero speed
2) Photoelectric emission will not be started by it
w
.s
3) Photo electrons will be emitted with speed 105 m/s
4) Photo electrons will be emitted with speed 103 m/s
37.
The necessary condition of photo electric emission is
h h 0
1)
1) hc0
39.
h h 0
3) Ek> h 0
4) Ek< h 0
If the work function of a metal is 0, then its threshold wavelength will be
38.
2)
2) c0/h
3) h0/c
4) hc/0
The photo electric equation is
1)
h = h 0 E k
2)
h = h 0 +
Ek
3)
h = h 0 + E k
www.sakshieducation.com
4)
h = h 0
www.sakshieducation.com
40.
Light of frequency 2.50 is incident on a metal surface of threshold frequency
20. If it s frequency is halved and intensity is made three times then the new
value of photo electric current will be
1) Zero
41.
2) Double
3) Four times
4) Six times
In a photo electric cell, the cathode with work function W1 is replaced by
co
m
another one with work function W2 (W2 > W1). If the current before this
change is I1 and that after the change in I2 and other circumstances remain
same and if h >W2, then
3) I1=I2
4) I1<I2<2I1
If the frequency of light incident on metal surface is doubled, then kinetic
at
io
42.
2) I1<I2
n.
1) I1>I2
energy of emitted electrons will become
2) Less than double
3) More than double
4) Nothing can be said
ed
uc
43.
1) Doubled
The work function of a metal is X eV. When light of energy 2X is made
incident on it then the maximum kinetic energy of emitted photo electron will
sh
i
be
1) 2 eV
3) XeV
4) 3 XeV
W1 and W2 are the work functions of two different photo metals (W2 > W1).
ak
44.
2) 2 XeV
The same radiation falls on the two metals separately. i1 and i2 are the photo
w
.s
currents and K1, K2 are the maximum. K.E of the ejected electrons in these
two cases, then
1) i1 = i2 & K1 > K2
3) i1 = i2 & K1 = K2
4) None
When light is made incident on a surface then photo electrons are emitted
45.
2) i1 > i2 & K1 = K2
from it. The kinetic energy of photo electrons
1) Depends on the wavelength of incident light 2) Is same
3) Is more than a certain minimum value
4) None of these
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
46.
The function of photo electric cell is
1) To convert electrical energy into light energy
2) To convert light energy into electrical energy
3) To convert mechanical energy into electric energy
4) To convert ac to dc
If the energy of photo is 10 eV and work function is 5 eV then the value of
co
m
47.
stopping potential will be
1) 15 V
4) 50 V
n.
At stopping potential, the photoelectric current becomes
1) Minimum
49.
3) 2 V
2) Maximum
3) Zero
4) Infinity
at
io
48.
2) 5 V
When the photo electric cell is kept at a distance r from the light source, the
made 3r, will be
1) V
50.
2) 3V
4) The size of electron
ak
The rest mass of a photon is
1)
2) 0
3)
h / c 2
4)
hc 2
w
.s
Electron behaves like a wave because it
1) Ionizes the gas
2) Is affected by an electric field
3) Is affected by a magnetic field
4) Diffracted by a crystal
The graph between the de Broglie wavelength and the momentum of photon
53.
4) 1/9V
2) Size of cathode ray tube
sh
i
3) Variation of g
52.
3) 9V
The mass of electron varies with
1) Its velocity
51.
ed
uc
stopping potential is V. The value of stopping potential, when the distance is
is a
54.
1) Rectangular Hyperbola
2) Circle
3) Parabola
4) Straight Line
The wavelength of a proton and a photon are same then
1) Their velocities are same
2) Their moment are equal
3) Their energies are same
4) None
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
55.
The de Broglie wavelength associated with a charged particle in electric and
magnetic fields are 1 and 2 , then
1) 1 = 2
56.
3) 1 < 2
4) None
The energy of a photon is E and its momentum is p. The speed of light will be
1) E/p
3) (p/E) 2
2) Ep
4) (E/p) 2
De-Broglie wavelength associated with an electron of mass m and accelerated
co
m
57.
2) 1 > 2
through a potential difference V is. Then wavelength associated with a
58.
m
M
2)
M
( )
m
3)
m
M
at
io
1)
n.
proton of mass M and accelerated through the potential difference V will be
4)
m
M
The relation between the length of circumference of a stable orbit of an atom
and the wavelength of stationary wave associated with the electron will be
59.
2r
2)
2r2
3)
ed
uc
1)
2r
4)
2r
The curve between current (i) and potential difference (v) for a photo cells
2)
w
.s
ak
1)
sh
i
will be
4)
3)
The curve between the frequency ( ) and stopping potential (V) in a photo
60.
electric cell will be
1)
2)
3)
4)
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
61.
A graph is drawn between frequency of the incident radiation (on-X axis)
and stopping potential (on Y-axis) then the slope of the straight line indicates
1) he
3) e/h
The correct curve between the stopping potential (V) and intensity of incident
light (I) is
V0
V0
V0
1)
V0
3)
2)
l
4)
l
n.
The stopping potential (V0) as a function of
at
io
63.
4) (e-h)
co
m
62.
2) h/e
V0
frequency of the incident radiation () is plotted for
two different photoelectric surfaces A and B. The
1) Is greater than that of B
2) Is smaller than that of B
3) Is equal to that of B
4) Cannot be compared from graph.
A) In Thomson experiment to determine
sh
i
64.
ed
uc
graph shows that work function of A
an electron, when deflection of
=E
B
ak
beam is zero, velocity of electron
e
of
m
B) Specific charge of cathode rays is independent of applied voltage, and
1) Only A is correct
2) Only B is correct
3) A and B are correct
4) A and B are false
Of the following
65.
w
.s
material of the gas.
A) Photo cell is also called as magic eye.
B) Photo voltaic cell does not require any external source of emf (i.e. battery)
1) A is true B is false
2) B is true A is false.
3) Both A and B are true
4) Both A and B are false.
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
66.
Of the following
A) Photo multiplier is also called electron multiplier.
B) In photo multiplier dynodes are coated with silver oxide-cesium layer.
2) B is true A is false.
3) Both A and B are true
4) Both A and B are false.
Of the following
co
m
67.
1) A is true B is false
A) Photo cells are used as counting devices.
B) Photo cells are used in the reproduction of the sound in cinematography.
3) Both A and B are true
4) Both A and B are false.
n.
2) B is true A is false.
at
io
68.
1) A is true B is false
Of the following
ed
uc
A) de-Broglie waves are electromagnetic waves.
B) de-Broglie waves are produced only when particles are charged.
1) A is true B is false
69.
4) Both A & B are false
sh
i
3) Both A & B are true
2) B is true A is false.
In de-Broglie waves
wave.
ak
A) Moving particle is always associated with a wave packet rather than a
1) A is true B is false
2) B is true A is false
3) A and B are true.
4) A and B are false.
[A]: Matter waves are not electromagnetic waves.
70.
w
.s
B) Velocity of a wave packet is same as that of the particle.
[B]: Electron microscope works on the principle of de-Broglie hypothesis.
1) A is true B is false
2) B is true A is false.
3) Both A and B are true
4) Both A and B are false
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
71.
Statement A: An electron of velocity V and photon of velocity C have same
de-Broglie wave lengths. The ratio of energies of electron and photon is V/2C.
Statement B: The ratio of de-Broglie wavelengths of a photon and an electron
of mass m each with energy E is C
2) A is false, B is true
3) A, B are false
4) A, B are true
Match List I and List II.
co
m
1) A is true, B is false
List II
a) Particle nature of light
e) de-Broglie hypothesis
c) Millikans oil drop experiment
f) Photo electric effect
g) Electromagnetic waves
h) Quantization of charge
ed
uc
d) X rays
n.
List I
b) Dual nature of matter
1) a f, b e, c h, d g
3) a h, b g, c f, d e
2) a e, b f, c g, d e
4) a g, b c, c f, d h
Match List I and List II.
sh
i
73.
at
io
72.
2m
E
List I
List II
e) Rontgen
b) Specific charge of electron
f) Hertz
w
.s
ak
a) Photo electric effect
c) Charge of electron
g) J.J Thomson
d) X rays
h) Millikan
2) a f, b g, c e, d h
3) a f, b g, c h, d e
4) a h, b f, c e, d g
1) a g, b e, c f, d h
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
Assertion & Reason: In each of the following questions, a statement is given
and a corresponding statement or reason is given just below it. In the
statements, marks the correct answer as
1) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is correct explanation of
Assertion.
co
m
2) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation
of Assertion.
3) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
[A]: Though light of single frequency is incident on a metal, the energies of
emitted photo electrons are different.
at
io
74.
n.
4) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
[R]: Due to collision of electron with other atoms in the metal.
[A]: In photo emissive cell inert gas is used.
ed
uc
75.
[R]: Inert gas in the cell gives greater current.
76.
[A]: Photoelectric effect can only be explained by the particle nature of light
sh
i
[R]: For every metal there exists a limiting frequency of the incident light
called, threshold frequency, below which electron emission is not possible.
[A]: Waves associated with moving particles are called matter waves.
ak
77.
[R]: de-Broglie wavelength is inversely proportional to the mass of the
78.
w
.s
particles.
The work function of a surface of a photosensitive material is 6.2 eV. The
wavelength of the incident radiation for which the stopping potential is 5 V
lies in the
1) Infrared region
79.
2) X-ray region 3) Ultraviolet region
4) Visible region
A particle of mass 1 mg has the same wavelength as an electron moving with
a velocity of 3 x 106 ms-1. The velocity of the particle is
1) 3 x 10-31 ms-1
2) 2.7 x 10-21 ms-1
3) 2.7 x 10-18 ms-1
www.sakshieducation.com
4) 9 x 10-2 ms-1
www.sakshieducation.com
80.
In the phenomenon of electric discharge through gases at low pressure, the
coloured glow in the tube appears as a result of
1) Collisions between the charged particles emitted from the cathode and the
atoms of the gas
2) Collision between different electrons of the atoms of the gas
co
m
3) Excitation of electrons in the atoms
4) Collision between the atoms of the gas
The number of photo electrons emitted for light at a frequency (higher than
the threshold frequency 0 ) is proportional to
4) 0
3) Frequency of Light
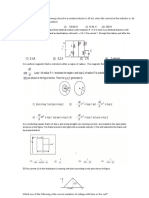
The figure shows a plot of photo current versus anode potential for a photo
ed
uc
82.
2) Intensity of Light
at
io
1) Threshold Frequency (0 )
n.
81.
sensitive surface for three different radiations. Which one of the following is a
sh
i
correct statement?
1) Curves (a) and (b) represent incident radiations of same frequency but of
ak
different intensities.
2) Curves (b) and (c) represent incident radiations of different frequencies and
w
.s
different intensities.
3) Curves (b) and (c) represent incident radiations of same frequency have same
intensity.
4) Curves (a) and (b) represent incident radiations of different frequencies and
different intensities.
83.
Monochromatic light of wavelength 667 nm is produced by a helium neon
laser. The power emitted is 9 mW. The number of photons arriving per sec.
on the average at a target irradiated by this beam is
1) 3 x 1016
2) 9 x 1015
3) 3 x 1019
www.sakshieducation.com
4) 9 x 1017
www.sakshieducation.com
Key
2
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
12)
13)
14)
15)
16)
17)
18)
19)
20)
21)
22)
23)
24)
25)
26)
27)
28)
29)
30)
31)
32)
33)
34)
35)
36)
37)
38)
39)
40)
41)
42)
43)
44)
45)
46)
47)
48)
49)
50)
51)
52)
53)
54)
55)
56)
57)
59)
60)
61)
62)
63)
64)
65)
71)
72)
73)
74)
75)
81)
82)
83)
n.
at
io
2
68)
69)
70)
76)
77)
78)
79)
80)
ed
uc
67)
hc
1
= w 0 + mv 2
w
.s
1 2 hC
mv =
w0
2) Ans: 3
Centripetal force = Magnetic force
Sol:
mv 2
= Bqv
r
r=
58)
sh
i
From photoelectric equation
ak
Sol:
66)
Hints
1) Ans :2
co
m
1)
mv
Bq
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
3). Ans: 3
Sol:
When wavelength is expressed in A then E =
hc
12400
eV
= 0 + eV0
co
m
6.2eV = 5eV + eV0
V0 = 1.2V
hc
= h 0 + ev0
at
io
Sol:
n.
4) Ans: 3
Sol
ed
uc
5) Ans: 1
: E , B are acting in Z, Y directions
Here
E
gives velocity of charge particle
B
Number of electrons emitted per second per unit area from the surface n =
w
.s
Sol:
ak
6) Ans: 3
sh
i
The charged particle is not deviated
Photon energy, h =
1240
= 2.066eV
600 ( nm )
I = 39.6 W/m2 = 39.6 J/s/m2
39.6
eV / s / m 2
1.6 10 19
Photoelectrons emitted/s/m2
=
39.6
1
1
= 12 1017
19
1.6 10
2.066 100
www.sakshieducation.com
E
hc
www.sakshieducation.com
7) Ans:3
Sol:
According to Einsteins Photo electric equation,
hv = hv0 + K .E = hv0 + ev0
v0 = v0 +
ev0
h
co
m
v0 = 13.5 1014 Js 1
8) Ans: 4
A) According to the laws of photoelectric effect photoelectric current is directly
n.
Sol.
9) Ans: 2
From Einsteins photoelectric equation
: eV0 = h h0
hc
hc
e 1.6 =
e 4.8 =
hc
hc
.(1)
sh
i
ed
uc
Sol
at
io
proportional to intensity of incident light.
hc hc
...(2)
2 0
w
.s
ak
Solving (1) and (2) 0 = 4
10) Ans: 4
Sol:
From Einsteins photoelectric equation hv = w + K .E
K = h W
K1 = 2W W = W
K 2 = 3W W = 2W
But kinetic energy =
1 2
mv
2
1
K1
W
1
=
=
=
2W
K2
2
2
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
11) Ans: 3
de-Broglie wavelength =
p =
=
h
=
2m p k p
h
=
2m k
h
2 m p eV
h
2 4m p 2eV
1
=
= 0
p
8
2 2
at
io
n.
h
=
p
h
h
h
=
=
p mv
2m ( K .E )
co
m
Sol:
12) Ans: 2
Sol:
Let the maximum energy of the photoelectrons be x and Kx
ed
uc
x = h1 h0 = h (1 0 ) .(1)
k x = h2 h0 = h (2 0 ) .(2)
sh
i
( 2 ) = k1 2
0
k 1
(1)
de-Broglie wavelength =
h
2mE
w
.s
Sol:
ak
13) Ans: 4
150
150
= 1.37 A0
80
14) Ans: 1
hc
1
= W0 + mv 2 .(1)
4000
2
w
Sol:
hc
1
= W0 + 4 mv 2 .(2)
2500
2
From (1),
1 2
hc
mv =
W0
2
4000
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
Substituting in equation (2)
hc
hc
hc
= W0 + 4
W0 =
3W0
2500
400
1000
W0 =
hc
= ( 2hc 106 ) J
5000 10 10
1
E = w0 + mv 2
2
2 ( E w0 )
(1)
m
v=
at
io
In the magnetic field,
mv 2
Be v =
r
mv
..(2)
Be
Substituting (1) in (2)
16) Ans: 4
Under equilibrium
w
.s
Sol:
Be
sh
i
2 m ( E w0 )
ak
r=
ed
uc
r=
n.
Sol:
co
m
15) Ans: 4
mg = Eq
V
mg = ( ne )
d
4
3
mgd ( 3.2 10 ) (10 ) ( 6 10 )
n=
=
Ve
(1200 ) (1.6 1019 )
n = 10
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
17) Ans: 4
Sol:
F = Eq = mg but E =
v
d
Vq
= mg
d
co
m
Vq 4
= R3 g
d
3
V R3
V2 = 3200volt
Sol:
ed
uc
18) Ans: 2
at
io
400 R 3
= 3;
V2
8R
n.
V1 R13
=
V2 R23
K .E1 = h ( 2v0 ) hv0 = hv0 .(1)
sh
i
K .E2 = h ( 3v0 ) hv0 = 2hv0 ..(2)
Dividing (1) and (2)
w
.s
ak
1 2
mv1
1
2
=
1 2 2
mv2
2
V2 = 2V1
V2 = 2 2 106 ms 1
19) Ans: 4
Sol:
1
hv = 0 + mV 2 .(1)
2
h2v = 0 + mV 2 4 ..(2)
2
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
(1) 4 4hv = 40 + 4
1 2
mv
2
1
2 hv = 0 + 4 mv 2
2
(2)
-------------------------------------------------2 hv
3
co
m
Subtracting 2hv = 30 0 =
h
2m p q pV
= 2 2 :1
h
2m qV
p
=
Sol:
e =
h
pe
P =
hC
EPh
h hC
=
Pe EPh
w
.s
ak
sh
i
21) Ans: 2
h
h
=
mv
2meV
at
io
From de-Broglie wavelength =
ed
uc
Sol:
n.
20) Ans: 3
EPh
=C
Pe
22) Ans: 2
Sol:
If proton is projected at right angle to the magnetic field it rotates in circular path.
The required centripetal force is supplied by force due to magnetic field.
mr 2 = Bqv =
Bqv
mr
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
T = 2
2 m
mr
=
Bq
Bqv
Time taken to transverse 900 arc is
T
.
4
co
m
T m
=
= 1.6 107 s
4 2 Bq
23) Ans: 1
Sol.
As the total incident energy is completely absorbed by the electrons the incident
24) Ans: 2
From Einsteins photo electric equation
hc
K2 =
hc
1
2
W =
hc
X
W = W
32
3
W = X W
Where X =
hc
= w + K .E
ed
uc
K1 =
hc
sh
i
Sol:
at
io
n.
photon completely disappears.
w
.s
ak
X
W X W
K1
= 3
= 3
K2 X W
X W
K1 1
K
< K1 < 2
K2 3
3
Now x>W Hence
25) Ans: 2
Sol:
h c
= [From de-Broglie wavelength]
p
cp=h
k
p2
p2
=
=
h 2mh 2mcp
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
p
v 2.25 108 3
=
=
=
2mc 2c 2 3 108 8
26) Ans: 1
=
h
h
6.63 1034
=
=
p mv 9.11031 6.6 105
co
m
Sol:
= 11 10 10 m = 11A0
W=
1240
= 4.96eV
250
h =
1240
= 6.20eV
200
K =6.20 4.96 = 1.24eV
= 19.84 10 20 J
= 3300 A0 = 330nm
w
.s
Sol:
ak
28) Ans: 2
sh
i
= 1.24 1.6 1019
12400
at
io
When is expressed in A then, W =
ed
uc
Sol:
n.
27) Ans: 4
h =
1240
= 3.757
330
eV0 = h W = 3.757 2 = 1.757eV
V0 = 1.757 V
29) Ans: 4
Sol
Since both proton and positron have the same charge
proton =
h
h
=
2mK
2meV
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
positron =
proton
h
m
=
M
positron
2meV
30) Ans: 2
: W1 : W 2 = 1: 2
co
m
Sol
v1 : v2 = 1:2
1 2
mv2 = h 2 W0 = 2hf 2 = 2 ( hf 1)
2
78.
ed
uc
Ratio of kinetic energies = 1:2
at
io
1 2
mv1 = h1 W0 = hf 1 ..(1)
2
n.
According to photo electric equation,
(3): Work function = 6.2 eV
K.E = eVS = 5e
0
hc 12400 eV
=
= 1107 A
E 11.2 eV
ak
sh
i
Total incident energy = 6.2 + 5= 11.2 eV
79.
w
.s
This wavelength is in the ultraviolet region.
(3)
h
mv
From de-broglie hypothesis =
80
(1) Collisions of the charged particles with the atoms in the gas The colour of the
glow depends upon the nature of the glass.
Eg : Yellowish green for soda glass grayish blue for lead glass.
www.sakshieducation.com
www.sakshieducation.com
81
(2) The number of photoelectrons decide the photocurrent. Assuming that the
number of electrons emitted depends on the number of photons incident, the
number of photoelectrons depend on the intensity of light.
co
m
(1)
n.
82
(a) and (b) represent radiations of the same frequency because their kinetic
at
io
energies are the same. But saturation photocurrents are different. Therefore
83
(1) = 6670 A
ed
uc
intensities are different.
E of a photon =
12400eV A
0
12400
1.6 1019 J
6670
sh
i
6670 A
Energy emitted per second, power P = 9 103 J
ak
Power
P
=
Energy E
9 10 3 6670
= 3 1016
19
12400 1.6 10
w
.s
Number of Photons incident =
www.sakshieducation.com
You might also like
- ATPL Notes - ElectricsDocument23 pagesATPL Notes - ElectricsMoslem Grimaldi100% (3)
- 24-07-2021 SR - Super60 (In Coming) Jee-Main WTM-37 Question PaperDocument23 pages24-07-2021 SR - Super60 (In Coming) Jee-Main WTM-37 Question Paperdasari srinidhiNo ratings yet
- Proceedings CIB W062 2018 SymposiumDocument354 pagesProceedings CIB W062 2018 SymposiumdplumbingNo ratings yet
- AC4251 Group Project Written ReportDocument24 pagesAC4251 Group Project Written ReportranniamokNo ratings yet
- Refrig - Samsung RF23J9011SR - v2 - User ManualDocument108 pagesRefrig - Samsung RF23J9011SR - v2 - User ManualadamsusaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Operación Mantenimiento y Partes P375WCU P250WCUDocument160 pagesManual de Operación Mantenimiento y Partes P375WCU P250WCUPercy Cárdenas100% (2)
- 7 Dualnature of MatterDocument26 pages7 Dualnature of MatterSarvajith KumarNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature Worksheet TUITIONDocument5 pagesDual Nature Worksheet TUITIONAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Problems For Practice - Dual NatutreDocument2 pagesProblems For Practice - Dual NatutreSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Aieee2006 Paper (Key) PDFDocument30 pagesAieee2006 Paper (Key) PDFAnonymous T5Vm4ZIbJt100% (1)
- AIIMS Full Paper 2007Document33 pagesAIIMS Full Paper 2007Sombir Ahlawat100% (1)
- Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument57 pagesDual Nature of Matter and RadiationSyed MuzakkirNo ratings yet
- Electrons and PhotonsDocument3 pagesElectrons and PhotonsAnkit BansalNo ratings yet
- UPSEE - 2000 Full Paper: Section-1 PhysicsDocument50 pagesUPSEE - 2000 Full Paper: Section-1 Physicsramendra100% (1)
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument2 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and MatterMukhil R PillaiNo ratings yet
- UPSEE - 2000 Full Paper: Section-1 PhysicsDocument0 pagesUPSEE - 2000 Full Paper: Section-1 PhysicsAbhay Upadhyay100% (1)
- Electrons & ProtonsDocument31 pagesElectrons & ProtonsBiprodeep14No ratings yet
- Modern Physics 8Document6 pagesModern Physics 8Ramesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 2006 PrelimsDocument34 pagesAipmt 2006 Prelimskajal100% (1)
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India.,: Jee-Main - 1 Year Revision - Chemistry - AssignmentsDocument9 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy, India.,: Jee-Main - 1 Year Revision - Chemistry - AssignmentswanetanishqNo ratings yet
- AIIMS MBBS Entrance Examination 2000 Solved Question PaperDocument35 pagesAIIMS MBBS Entrance Examination 2000 Solved Question PaperChandan Kumar100% (1)
- Modern Phy Assi SubDocument4 pagesModern Phy Assi SubNikhilPrakashNo ratings yet
- PYL100: Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum Mechanics (II Semester, 2016-17) Exercise Sheet # 1Document2 pagesPYL100: Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum Mechanics (II Semester, 2016-17) Exercise Sheet # 1Franklin GarysonNo ratings yet
- SR Neet Star Super Chaina (Cbse) (Pt-1) Q.P Ex - Dt. 17.07.2023Document24 pagesSR Neet Star Super Chaina (Cbse) (Pt-1) Q.P Ex - Dt. 17.07.2023dhruvi.v91No ratings yet
- Dual Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesDual Nature of MatterK_S_Krishna0001No ratings yet
- Homework1Document2 pagesHomework1Anand KumarNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch34 Test BankDocument17 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch34 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- (Questionpaperz - In) UPSEE Previous Paper 2005Document39 pages(Questionpaperz - In) UPSEE Previous Paper 2005Pushpendra ShawNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument19 pagesAtomic Structure PDFggk2013100% (3)
- Screening Test Repeaters 2025 Sample QuestionsDocument27 pagesScreening Test Repeaters 2025 Sample QuestionsAmina sabu06No ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Photoelectric EffectDocument27 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Photoelectric Effectmehalingam nainarNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 2009 Question PaperDocument38 pagesAipmt 2009 Question PaperPooja100% (1)
- Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesPhotoelectric EffectrujintoNo ratings yet
- KCET Sample Paper-8 (Kcet 2013 Physics Paper)Document8 pagesKCET Sample Paper-8 (Kcet 2013 Physics Paper)Firdosh Khan0% (1)
- Paper 2 Atomic and PEEDocument6 pagesPaper 2 Atomic and PEEAnonymous oDx8RFfZNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Assignment 5Document3 pagesAtomic Structure Assignment 5iamrockyNo ratings yet
- Tut-sheet-1-PHL120-13 With Final Answers PDFDocument3 pagesTut-sheet-1-PHL120-13 With Final Answers PDFjgrgpt33No ratings yet
- Which One of The Following Statement Is NOT True About PhotoelectricDocument11 pagesWhich One of The Following Statement Is NOT True About PhotoelectricVidhi ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- EEN2056 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesEEN2056 Tutorial 1Paramesvaran VeerasingamNo ratings yet
- 18 - Modern Physics-01-TheoryDocument19 pages18 - Modern Physics-01-TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature Dinesh QuestionsDocument3 pagesDual Nature Dinesh QuestionsPankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Physics (Question Bank) - Dual Natutre of Matter and Radiation (Subj) - 04.02.2022Document4 pagesClass Xii - Physics (Question Bank) - Dual Natutre of Matter and Radiation (Subj) - 04.02.2022Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- AIPMT Sample Paper 1Document40 pagesAIPMT Sample Paper 1Yogesh Kadian100% (1)
- Aipmt 2009 Question Paper PDFDocument38 pagesAipmt 2009 Question Paper PDFkajal100% (1)
- Hi NotesDocument4 pagesHi NotesDevansh UppalNo ratings yet
- Physics 2018Document29 pagesPhysics 2018milapdhruvcomputerworkNo ratings yet
- Module 4-QUANTUM-PROBLEMS-SENT-2023Document2 pagesModule 4-QUANTUM-PROBLEMS-SENT-2023tvkhang93182018No ratings yet
- Practice TestDocument0 pagesPractice TestTooba Sardar100% (1)
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument7 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and MatterKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6) Photoelectric Effect and Uncertainity ProblemsDocument4 pages6) Photoelectric Effect and Uncertainity ProblemsGame 1No ratings yet
- Dawn of Modern PhysicsDocument16 pagesDawn of Modern Physicsالفيزيائي MSNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4nitramrkl172No ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 3 Energy Photoelectric Effect Hydrogen AtomDocument12 pages3 Chapter 3 Energy Photoelectric Effect Hydrogen AtomannauuuNo ratings yet
- Physics Test 3Document8 pagesPhysics Test 3Arulkumar MuthuramalingamNo ratings yet
- Aieee-2012 Physics SolutionsDocument5 pagesAieee-2012 Physics SolutionsAman Bhutta100% (1)
- Modern Physics (CPP 1 To 3)Document11 pagesModern Physics (CPP 1 To 3)Priyansh Vaibhav100% (3)
- Dual Nature Assignment1Document2 pagesDual Nature Assignment1hsofficial910No ratings yet
- Physics 104 Long Quiz Sample ADocument4 pagesPhysics 104 Long Quiz Sample AMico de LeonNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics-07-Subjective Unsolved Problems Level-1Document2 pagesModern Physics-07-Subjective Unsolved Problems Level-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mendel GregorDocument5 pagesMendel GregorRon HartNo ratings yet
- UniverseDocument12 pagesUniverseColumbia GomezNo ratings yet
- Abdul K AzadDocument1 pageAbdul K AzadRon HartNo ratings yet
- Al GoreDocument1 pageAl GoreRon HartNo ratings yet
- Abraham LincolnDocument8 pagesAbraham LincolnRon HartNo ratings yet
- Bill ClintonDocument1 pageBill ClintonRon HartNo ratings yet
- Stephen Hawking - Universe - The Teachers' GuideDocument12 pagesStephen Hawking - Universe - The Teachers' GuideBatForNo ratings yet
- The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument27 pagesThe Earth in The Solar SystemsnarendranathNo ratings yet
- Earth Move Link 1Document7 pagesEarth Move Link 1Ron HartNo ratings yet
- AJ Biography PDFDocument22 pagesAJ Biography PDFRon HartNo ratings yet
- The Case of SoftwarDocument8 pagesThe Case of SoftwarRon HartNo ratings yet
- Democracy and EqualityDocument11 pagesDemocracy and EqualityankurfazilkaNo ratings yet
- Whylabourmex PDFDocument8 pagesWhylabourmex PDFRon HartNo ratings yet
- Manual 1Document6 pagesManual 1Ron HartNo ratings yet
- Education in IndiaDocument3 pagesEducation in IndiaRon HartNo ratings yet
- Amartya Sen - Democracy As A Universal ValueDocument26 pagesAmartya Sen - Democracy As A Universal ValuejoseftsantosNo ratings yet
- Whylabourmex PDFDocument8 pagesWhylabourmex PDFRon HartNo ratings yet
- U.S. Civics TestDocument11 pagesU.S. Civics TestPopeyeKahnNo ratings yet
- Democratic SocialismDocument5 pagesDemocratic SocialismRon HartNo ratings yet
- DemocacyDocument5 pagesDemocacyMawaddah MarjanNo ratings yet
- U.S. Civics TestDocument11 pagesU.S. Civics TestPopeyeKahnNo ratings yet
- Roz Trud Gon Top 10 Market BlockersDocument15 pagesRoz Trud Gon Top 10 Market BlockersRon HartNo ratings yet
- BahumatiDocument3 pagesBahumatisgollavilliNo ratings yet
- Amaravati Kathalu Online Telugu Sahityam-Find More Books at WWW - Telugubooks.tkDocument5 pagesAmaravati Kathalu Online Telugu Sahityam-Find More Books at WWW - Telugubooks.tkkavalirakeshNo ratings yet
- 10th Telugu SLDocument119 pages10th Telugu SLMadhu PriyaNo ratings yet
- A Progressive Grammar of The Telugu LanguageDocument421 pagesA Progressive Grammar of The Telugu LanguageNaveen BejugamNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Maths QuickReviewDocument5 pagesAIEEE Maths QuickReviewSri DNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument5 pagesCircleRon HartNo ratings yet
- SAT Heart of Algebra Practice Test 1 Answer Explanations PDFDocument3 pagesSAT Heart of Algebra Practice Test 1 Answer Explanations PDFRon HartNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formulas For High School and Engineering Examinations (IIT-JEE) by (Charm-Quark) PDFDocument93 pagesMathematics Formulas For High School and Engineering Examinations (IIT-JEE) by (Charm-Quark) PDFRon HartNo ratings yet
- Chart Summary Analysis - Brandon LeeDocument18 pagesChart Summary Analysis - Brandon LeeEyeOfLunaNo ratings yet
- CONSERVATION OF PLANTS AND ANIMALS - NotesDocument3 pagesCONSERVATION OF PLANTS AND ANIMALS - NotesNiraj SethiNo ratings yet
- Capability Statement WGIM Integrity Operating WindowsDocument3 pagesCapability Statement WGIM Integrity Operating WindowsRomainKabs100% (2)
- DNV Maritime Forecast 2050 2021-WebDocument82 pagesDNV Maritime Forecast 2050 2021-WebДмитрий Ганжа100% (1)
- Accident Prevention Program: Thunderstorms - Don't Flirt ... Skirt'EmDocument5 pagesAccident Prevention Program: Thunderstorms - Don't Flirt ... Skirt'EmLohrasp SuraliwalaNo ratings yet
- Braking Capacity of Railway Wheels - State-Of-The-Art SurveyDocument19 pagesBraking Capacity of Railway Wheels - State-Of-The-Art SurveyManjunath AithalNo ratings yet
- Investigation Into The Probable Cause of Failure of Economizer Tube of A Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesInvestigation Into The Probable Cause of Failure of Economizer Tube of A Thermal Power PlantKR PANo ratings yet
- GT ManualDocument10 pagesGT Manualsoldatbr4183No ratings yet
- PPC Zimbabwe Site Visit: Darryll Castle - CEO PPC Limited Kelibone Masiyane - MD PPC ZimbabweDocument38 pagesPPC Zimbabwe Site Visit: Darryll Castle - CEO PPC Limited Kelibone Masiyane - MD PPC ZimbabweBrandon ChinyanduNo ratings yet
- Jurong Junior College: Preliminary Examination 2008Document13 pagesJurong Junior College: Preliminary Examination 2008Ronald McdonaldNo ratings yet
- 2007-08 VodafonecrDocument378 pages2007-08 VodafonecrManisha BishtNo ratings yet
- Cross-Curricular Focus: Life Science: NameDocument2 pagesCross-Curricular Focus: Life Science: NameAndreea Dragomir67% (3)
- Service Station Manual Vespa LX 125 - 150 4t Euro 3Document241 pagesService Station Manual Vespa LX 125 - 150 4t Euro 3Adèle Standard100% (1)
- AEH Company Profile-1Document14 pagesAEH Company Profile-1Hrishikesh RaiNo ratings yet
- Polymers, Natural Polymers, NaturalDocument3 pagesPolymers, Natural Polymers, NaturalPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- W22 Homework #8 AnwsersDocument4 pagesW22 Homework #8 Anwsersiamayesha725No ratings yet
- Biology FolioDocument2 pagesBiology Folio黃將賓No ratings yet
- Magnetic Float Level Switch - KleevDocument2 pagesMagnetic Float Level Switch - KleevRAMZI ALJILANYNo ratings yet
- Bruce E. Depalma: N-Machine: Extraction of Electrical Energy Directly From Space: The N-MachineDocument7 pagesBruce E. Depalma: N-Machine: Extraction of Electrical Energy Directly From Space: The N-MachinebanzailoicNo ratings yet
- BHEL - Agitator Specification PDFDocument68 pagesBHEL - Agitator Specification PDFRiyaz100% (1)
- Learning Module No. 4 - Aircraft Air Conditioning and Pressurization SystemDocument36 pagesLearning Module No. 4 - Aircraft Air Conditioning and Pressurization SystemDavidSamsonNo ratings yet
- Company Profile - Grrsb-SmallDocument2 pagesCompany Profile - Grrsb-Smallmsis81No ratings yet
- OTC 19787 Oil Recovery and Surfactant Adsorption During CO - Foam FloodingDocument14 pagesOTC 19787 Oil Recovery and Surfactant Adsorption During CO - Foam FloodingAseuNo ratings yet
- NACHI Full Catalog Small RevDocument468 pagesNACHI Full Catalog Small RevSombat MahamadNo ratings yet
- Project On Global WarmingDocument22 pagesProject On Global WarmingHilda DsouzaNo ratings yet