Professional Documents
Culture Documents
End Stage Renal Failure
Uploaded by
GerardLum100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
366 views2 pagesEnd Stage Renal Failure
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnd Stage Renal Failure
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
366 views2 pagesEnd Stage Renal Failure
Uploaded by
GerardLumEnd Stage Renal Failure
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
jslum.
com | Medicine
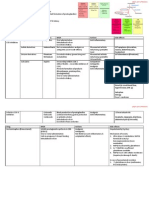
End-Stage Renal Failure (=Terminal Renal Failure)
Definition
Kidney Function is so poor
Patient requires Lifelong Dialysis or Renal Transplantation for survival
Due to underlying Chronic Renal Disease, receive inadequate therapy
Renal Replacement Therapy
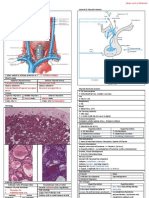
Haemodialysis CAPD/ IPD Renal Transplantation
(Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis)
Provide blood a ccess to Haemodialysis Require permanent catheter insertion “Cure” for Chronic Renal Failure
Arteriovenous Fistula (through which dialysis fluid infused & drained out)
Temporary Venous access/ shunt
Diffusion Using Peritoneal Membrane as Dialysis Membrane Forms of Transplant
Solutes at ↑ concentration in blood pass to Allows Mobility while dialysis is being performed Cadaveric Live Donor
↓ concentration in dialysis fluid across membrane Brain Death 1st Degree Blood Relative
Convection (Blood group
As Solutes move, surrounding Solvents are dragged compatibility)
Ultrafiltration (created by machine) Died from 2nd Degree Relative
Excess water moves into dialysis fluid Accident/ (Aunts, Uncles, Nephew)
Blood from patient passed through Extracorporeal circuit Suicide
Blood is expose d to dialysis fluid in Artificial Kidney Died Donors Unrelated Live Donor
Electrolytes, Water exchanges take place without (Developing countries)
ventilator but
functional CVS
Living donor
Nephrectomy does not
cause Renal Failure
Procedures
Transplant Kidneys are placed in Iliac Fossa
Assessment of Graft Function depends on
• Urine Output
• Electrolytes
Require Immun osuppressive Drugs
(Prednisolone, Azathioprine, Cyclosporin A,
IVIG)
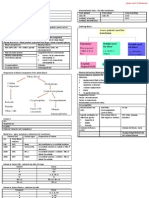
Complications Complications Complications
Hypotension / Hypertension Infection Infections
Anaemia Catheter displacement / Obstruction Acute Rejection (usually within 3 months)
Renal Osteodystrophy Loss of Ultrafiltration 2° Malignancy
Dialysis Athropathy Hyperlipidaemia worsen Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Heads
Hyperlipidaemia Worsen Diabetic control ↑ Incidence of CAD
Cystic Renal Disease Recurrent of Original Disease
Aluminium Toxicity
Prognosis
↓ Life expectan cy (due to CVS disease,
Malignancy)
Graft Survival
• 80-85% - 1st year
• 50-60% - 5th year
jslum.com | Medicine
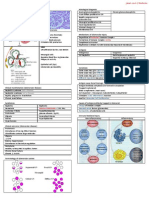
Ethics in Dialysis & Renal Transplantation
Dialysis Renal Transplantation
Availability Live Donor selection
Shortage of Facilities (expansion requires Money) Prospective Donor interviewed without Family Members/ Recipient present
(done at other expense of other medi cal services) Ensure Donor is a Volunteer (no Financial inducement, Coercion)
Initiating Dialysis (Understand Nature of Act & Risk)
Explain Nature of Illness & Prognosis if Treatment not given Donor Informed – Operation is not free from risk
Treatment available must be described Risk of Death of Donor (1:1600 Donor Operation)
Waiting for Government Facilities (clear guideline for selection criteria) Donor can change his mind
• 1st come 1st served basis (Right up to the moment of commen cement of s urgery)
• Not having debilitating illness other than Kidney failure Unrelated Living Donor
• Breadwinner of family Spouse considered (i f no related donor)
Ensure true Volunteer
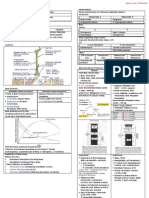
In China – Convicts become Don or
In India – Kidney bought from Poor
(without appropriate medical prep & protection for Donor & Recipient)
Cadaveric Transplantation
Religions, Races – Consider view
Japan – Brain Death is not accepted as Death
Jews – Accept Brain Death as Death (obligated to donate)
Islam – Transgressing a Death Body is not allowed (validity need conformation)
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDocument1 pagePosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Vesico Ureteral RefluxDocument1 pageVesico Ureteral RefluxGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument1 pageUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDocument4 pagesPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument6 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- ThalassaemiaDocument4 pagesThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 pagesThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- ThrombophiliaDocument3 pagesThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDocument2 pagesRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390No ratings yet
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument3 pagesSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Pituitary DysfunctionDocument2 pagesPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 pagesSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument1 pageSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument3 pagesRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 pagesPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDocument5 pagesPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDocument4 pagesPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Nsaids DrugsDocument2 pagesNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoNo ratings yet
- Obstructive UropathyDocument3 pagesObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Nocturnal EnuresisDocument1 pageNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Master Chart Thesis OsaDocument31 pagesMaster Chart Thesis OsaBiradar VijayNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureDocument39 pagesAcute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureMarie MayNo ratings yet
- Dialysis MachineDocument1 pageDialysis MachineMarifer NazNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases IDocument17 pagesRenal Diseases IPoojaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Edward L. Barnes, MD Chief Resident Conference July 5, 2012Document51 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Edward L. Barnes, MD Chief Resident Conference July 5, 2012Nick DanielsNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi HematuriaDocument10 pagesPatofisiologi HematuriaNurunSalamanNo ratings yet
- CKD PDFDocument20 pagesCKD PDFReyhan TarisNo ratings yet
- Journal SubmissionDocument3 pagesJournal SubmissionMaruhum Bonar MarbunNo ratings yet
- Nephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. MowafyDocument64 pagesNephrology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafyrazan moneerNo ratings yet
- Empanelled HospitalsDocument14 pagesEmpanelled HospitalsSwaroopVishnuNo ratings yet
- Nephrology Midt 20 MCQ For StudDocument3 pagesNephrology Midt 20 MCQ For StudMrunal DiveNo ratings yet
- List of Empanelled HCOs - Patna (Nov 2022)Document9 pagesList of Empanelled HCOs - Patna (Nov 2022)Shweta jainNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Acute Kidney Injury.19 PDFDocument14 pagesDrug Induced Acute Kidney Injury.19 PDFJose santos MembreñoNo ratings yet
- Updated ICD 10 Codes 2018Document1 pageUpdated ICD 10 Codes 2018Lucian0691No ratings yet
- Anti-GBM antibody glomerulonephritis diagnosis and treatmentDocument1 pageAnti-GBM antibody glomerulonephritis diagnosis and treatmentDian Putri NingsihNo ratings yet
- Plabable-Gems-30. Nephrology Plabable GemsDocument34 pagesPlabable-Gems-30. Nephrology Plabable GemsHabo HaboNo ratings yet
- Renal Pathology GuideDocument3 pagesRenal Pathology GuideArvinth Guna SegaranNo ratings yet
- Glomerular Diseases: Assistant Professor Dr. Shumaila Rafi MedicineDocument17 pagesGlomerular Diseases: Assistant Professor Dr. Shumaila Rafi MedicineMuhammad MakkiNo ratings yet
- CCHT Examination ApplicationDocument19 pagesCCHT Examination ApplicationAmmar YasserNo ratings yet
- Lupus Nephritis - Treatment of Relapsing Focal or Diffuse Lupus Nephritis - UpToDateDocument16 pagesLupus Nephritis - Treatment of Relapsing Focal or Diffuse Lupus Nephritis - UpToDateOlga BabiiNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in Dialysis PatientsDocument16 pagesHypertension in Dialysis PatientsSaad Anwar GujjarNo ratings yet
- DR Arzoo Nephrology ThesesDocument35 pagesDR Arzoo Nephrology ThesesAzam ArzooNo ratings yet
- Kidney Biopsy Guide to Glomerular PathologyDocument78 pagesKidney Biopsy Guide to Glomerular PathologyGalih AryyagunawanNo ratings yet
- Ar 2015Document159 pagesAr 2015Eric WeintraubNo ratings yet
- RENAP Certification Process Guidelines 2012pdfDocument2 pagesRENAP Certification Process Guidelines 2012pdfHarby Ongbay AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument17 pagesNephrotic Syndrome Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentERICKNo ratings yet
- Nursing Workshop - PediatricDocument27 pagesNursing Workshop - PediatricludiNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) Causes and SymptomsDocument25 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) Causes and SymptomsAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis - UpToDateDocument21 pagesPoststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis - UpToDateHandre Putra100% (1)
- Assessment of Elevated CreatinineDocument10 pagesAssessment of Elevated CreatinineSheryl Ann PedinesNo ratings yet