Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hypothyroidism
Uploaded by
GerardLumCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypothyroidism
Uploaded by
GerardLumCopyright:
Available Formats
jslum.
com | Medicine
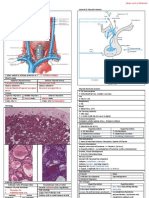
Hypothyroidism
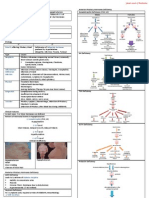
Definition Atrophic (Autoimmune) Hypothyroidism
Deficiency in Thyroid Activity Associated with Autoantibodies leading to Lymphoid Infiltration of Gland
↓ Thyroid Hormone Production Eventually lead to
Characteristics • Atrophy
↓ BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate) • Fibrosis
Fatigue Female ↑
Lethargy Incidence ↑ with Age
Women ↑
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Pathophysiol ogy Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Normally, Thyroid release • Lymphocytic Infiltration of Gland
• T4 (100-125 nmol) • Circulating Antithyroid Antibodies
• T3 Lead to
Half-Life T4 – 7-10 days • Atrophic changes with Regeneration
T4 → T3 (5’-deiodination) • Goitre formation
Deficiency of Thyroid Hormone has wide range of systemic effe cts Common in
• Due to derangements of Metabolic Processes • Women
• Direct Effects by Myxedematous infiltration • Late Middle Age
Myxedematous changes in Heart
• ↓ Contractility Postpartum Thyroiditis
• Cardiac Enlargement A type of Autoimmune Thyroiditis occurring in Women after Childbirth
• Pericardial Effusion May Cause
• ↓ Pulse • Hyperthyroidism
• ↓ Cardiac Output • Hypothyroidism
GIT • Both (Sequentially)
• Achlorhydria (Absence of HCl secretion)
• ↓ Intestinal Transit with Gastric Stasis Dyshormonogenesis
GU Rare condition
• Delayed Puberty Due to Genetic Defects in Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones
• Anovulation Develop Hypothyroidism with a goitre
• Menstrual Irregularities
• Infertility Iodine Deficiency
↓ Thyroid Hormone Dietary Deficiency of Iodine
• ↑ Total Cholesterol Endemic Goitre
• ↑ LDL May be (depend on Severity)
• ↓ HDL (due to Metabolic clearance) • Euthyroid
(Hypothyroidism – result in ↑ Insulin Resistance) • Hypothyroid
Problem in
Etiology • Netherlands
Primary (1°) Secondary (2°) • Western Pacific
Autoimmune Hypothyroidism Hypopituitarism • South East Asia
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Tumours • Africa
Atrophic Thyroiditis Pituitary Surgery, Irradiation Overcome Deficiency
Postpartum Thyroiditis Isolated TSH Deficiency Iodine Salt
Iatrogenic Peripheral Resistance to Thyroid
Drugs Hormone
Congenital Hypothyroidism
(eg. Dyshormonogenesis)
Iodine Deficiency
Infiltrative Disorders
jslum.com | Medicine
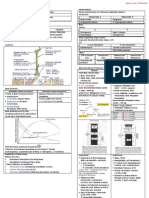
Symptoms, Signs (Descending order of Frequency) Investigations
Symptoms Signs Serum TSH
Tiredness, Weakness Dry Coarse Skin ↑ TSH – Confirm 1° Hypothyroidism
Dry Skin Cool Peripheral Extremities Free T4
Feeling Cold Puff Face, Hands, Feet (Myxedema) ↓ Free T4 – Confirm Hypothyroid State
Hair Loss Diffuse Allopecia TPO Antibodies (Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies)
Difficulty Concentrating Bradycardia Present in 90% patients of Hypothyroidism
Poor Memory Peripheral Edema Present in 80% patients of Grave’s Disease
Constipation Delayed Tendon Reflex Relaxation Anaemia (Menorrhagia)
Weight Gain, Poor Appetite Carpal Tunnel Syndrome ↑ Serum Aspartate Transferase Levels
Dyspnea Serous Cavity Effusions ↑ Serum CreaDnine Kinase Levels (Myopathy)
Hoarse Voice Hypercholesterolaemia, Hypertriglyceridaemia
Menorrhagia Hyponatraemia (↑ ADH, Impaired H2O clearance)
Paresthesia
Impaired Hearing
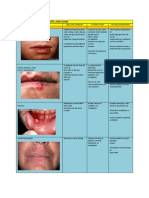
Hypothyroidism
Puff Eyes
Thickened, Pale Skin
Management
Replacement Therapy
Levothyroxine (Thyroxine, eg. T4) is given for life
Monitoring
Aim – Restore T4, TSH to well within Normal range
Assessment – Thyroid Function Tests
Complications
Myxoedema Coma
Rare
Fatal Complication of Long-Term Hypothyroidism
Patient is Comatose with
• Hypothermia
• Depression of Respiration
• Bradycardia
• Hypotension
Usually seen in Elderly patient during Cold weather
Physical Examination
Thyroid
Size
Consistency
Nodularity
Tenderness
Fixation
Lymphadenopathy
Supraclavicular
Cervical Regions of Neck
You might also like
- HyperthyroidismDocument3 pagesHyperthyroidismGerardLum100% (2)
- HypopituitarismDocument2 pagesHypopituitarismGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Endocrine - BoardsDocument9 pagesEndocrine - BoardsSoojung Nam100% (4)
- HyperthyroidismDocument11 pagesHyperthyroidismKaraLyn HatcherNo ratings yet
- Management of Thyroid DisordersDocument53 pagesManagement of Thyroid DisordersAnityo S AthmadjaNo ratings yet
- Investigations in An Unconscious PatientDocument16 pagesInvestigations in An Unconscious Patientcyphochilus0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Hypothyroidism Signs and ManagementDocument17 pagesHypothyroidism Signs and ManagementBinbinbabu BinuNo ratings yet
- Hematologic Diseases OverviewDocument11 pagesHematologic Diseases OverviewPerrilyn Perey100% (2)
- Obgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONDocument94 pagesObgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONvalentinemusa218100% (1)
- Endometrial HyperplasiaDocument21 pagesEndometrial HyperplasiaEggyDs100% (2)
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument2 pagesAntihypertensive DrugsJillary LlagunoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine SystemDocument64 pagesPathophysiology of Endocrine SystemTess MohamedNo ratings yet
- Causes and Symptoms of Nontoxic GoiterDocument17 pagesCauses and Symptoms of Nontoxic Goiterabigaille chua100% (1)
- Thyroid DisordersDocument21 pagesThyroid DisordersSuliman GarallehNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument5 pagesHypothyroidismlikeaquarianNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument9 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionTom Mallinson100% (1)
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDocument3 pagesLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathology of Thyroid DiseasesNur Kamalia KamalNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument43 pagesHypothyroidismRama Krishnan100% (2)
- Hypothyroidism Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument59 pagesHypothyroidism Diagnosis and TreatmentAmir Mahmoud100% (1)
- Hyperthyroidism: DR Rajeshwar ReddyDocument59 pagesHyperthyroidism: DR Rajeshwar ReddyRajeshwarreddy RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DiseasesDocument52 pagesThyroid DiseasesNurul Sakinah Rosli100% (3)
- The clinical value of blood testsDocument35 pagesThe clinical value of blood testsAgus SyaifudinNo ratings yet
- The Detailed Neurologic Examination in Adults - UpToDate PDFDocument29 pagesThe Detailed Neurologic Examination in Adults - UpToDate PDFMiguel GarciaNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument51 pagesThyroid3rd yrsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NursingDocument2 pagesEndocrine Nursingsurviving nursing school100% (2)
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsSheral Aida100% (2)
- DDX - Gastrointestinal Disorders ChartDocument21 pagesDDX - Gastrointestinal Disorders Chartapi-26938624100% (2)
- Cardiomyopathy and MyocarditisDocument8 pagesCardiomyopathy and Myocarditisoddone_out100% (1)
- AmenorrheaDocument41 pagesAmenorrheaBonitavanyNo ratings yet
- STI Chart (Maternity-Nursing)Document4 pagesSTI Chart (Maternity-Nursing)brittney bradyNo ratings yet
- Management of Neonatal JaundiceDocument22 pagesManagement of Neonatal JaundiceSuhazeli Abdullah100% (1)
- Cholinergic Drugs - TablesDocument7 pagesCholinergic Drugs - TablesThuan Tăng NguyenNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Eclampsia and Hellp SyndromeDocument24 pagesPreeclampsia Eclampsia and Hellp Syndromeapi-403416350100% (1)
- Pediatric Vital Signs MeasurementsDocument3 pagesPediatric Vital Signs MeasurementsJheDelaPazValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsDocument3 pagesLecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Vital Sign Normal RangesDocument5 pagesPediatric Vital Sign Normal Rangestinea nigraNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Lips, Mouth and GumsDocument5 pagesDisorders of The Lips, Mouth and GumstheglobalnursingNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument2 pagesAntihypertensive Agentskryscae nacarNo ratings yet
- AACE and ATA 2012 Clinical Practice Guidelines for HypothyroidismDocument63 pagesAACE and ATA 2012 Clinical Practice Guidelines for HypothyroidismNur Rakhma AkmaliaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Hypothyroidism Causes, Signs, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument15 pagesThyroid Hormone Synthesis, Hypothyroidism Causes, Signs, Diagnosis and TreatmentfachrulmirzaNo ratings yet
- Onco PharmacologyDocument9 pagesOnco Pharmacologyarn0ld21No ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesAssessment of Fetal Growth and Developmentaracelisurat100% (1)
- Psych Drugs NursingDocument7 pagesPsych Drugs Nursinglisa100% (2)
- Endocrine Disorders: Adrenal Gland and Thyroid DiseaseDocument27 pagesEndocrine Disorders: Adrenal Gland and Thyroid Diseaseasdfgrttt100% (4)
- Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Thyroid Nodules, and CancerDocument77 pagesHypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Thyroid Nodules, and CancerDann San AntonioNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics and Acronyms For Nursing SchoolDocument20 pagesMnemonics and Acronyms For Nursing SchoolFaye G.100% (3)
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsJoyVee Pillagara-De LeonNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument9 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (1)
- Thyroid: By: RickyDocument116 pagesThyroid: By: Rickyricky hutagalungNo ratings yet
- Thyroid: By: RickyDocument48 pagesThyroid: By: Rickyricky hutagalungNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Patients with Endocrine DisordersDocument50 pagesNursing Care for Patients with Endocrine Disordersعمر حليم omar haleemNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorders ComparisonDocument56 pagesMetabolic Disorders ComparisonRoselily Flores CoquillaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders 22 April 2019Document105 pagesThyroid Disorders 22 April 2019jialeongNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument10 pagesDisorders of The Thyroid Gland PDFNadia Abdurasid100% (1)
- GMS Thyroid Lect 2011Document43 pagesGMS Thyroid Lect 2011Scott YeeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and ParathyroidDocument33 pagesThyroid and Parathyroidkhaled alahmadNo ratings yet
- Hashimoto Thyroiditis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHashimoto Thyroiditis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument1 pageUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Vesico Ureteral RefluxDocument1 pageVesico Ureteral RefluxGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument1 pageSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- ThalassaemiaDocument4 pagesThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- ThrombophiliaDocument3 pagesThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 pagesThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 pagesSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument3 pagesRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument6 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Renal Function in Disease StateDocument2 pagesRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390No ratings yet
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument3 pagesSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDocument1 pagePosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDocument4 pagesPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDocument4 pagesPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Nocturnal EnuresisDocument1 pageNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 pagesPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Pituitary DysfunctionDocument2 pagesPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDocument5 pagesPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Obstructive UropathyDocument3 pagesObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Nsaids DrugsDocument2 pagesNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoNo ratings yet
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 The Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesChapter 34 The Endocrine SystemCarl Agape Davis100% (3)
- Psychology (Psy10) PowerpointDocument134 pagesPsychology (Psy10) PowerpointEdin AbolenciaNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument14 pagesOral RevalidaAyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document9 pagesScience 9Jennifer O. CatubigNo ratings yet
- What Are Human Skeletal System Organs?: 1. BonesDocument5 pagesWhat Are Human Skeletal System Organs?: 1. BonesKiara Denise TamayoNo ratings yet
- Normal Anatomy, Histology, and Spontaneous Pathology of The Nasal Cavity of The Cynomolgus Monkey (Macaca Fascicularis)Document19 pagesNormal Anatomy, Histology, and Spontaneous Pathology of The Nasal Cavity of The Cynomolgus Monkey (Macaca Fascicularis)Dina SartikaNo ratings yet
- Cold Agglutinin Disease Autoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaDocument2 pagesCold Agglutinin Disease Autoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- RectDocument1 pageRectPANNADYNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Practice TestDocument13 pagesEssentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Practice TestDani AnyikaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document12 pagesPresentation 1Rizka FarahinNo ratings yet
- Manifestasi Klinis dan Etiologi Sindrom Koroner AkutDocument4 pagesManifestasi Klinis dan Etiologi Sindrom Koroner AkutFerdinando BaehaNo ratings yet
- 1stsemester CoursesDocument8 pages1stsemester CoursesIzaz UllahNo ratings yet
- CH 15 Excretory-SystemDocument94 pagesCH 15 Excretory-SystemAntonio Calleja II100% (1)
- DriftodonticsDocument2 pagesDriftodonticssweetieNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Renal SystemDocument8 pagesDrugs Affecting The Renal SystemAmandaNo ratings yet
- Questions From DHA ExamDocument3 pagesQuestions From DHA ExamMohsen Saeed OzaibiNo ratings yet
- Membranes and FasciaeDocument18 pagesMembranes and FasciaeBurak KıvırcıkNo ratings yet
- M5 Part 1 Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesM5 Part 1 Assignment PDFJoshua Miguel BunoNo ratings yet
- 21.1 Action PotentialDocument43 pages21.1 Action PotentialNazirah Arba'inNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)Document25 pagesLecture 6 Periapical Periodontitis (Slide)JustDen09No ratings yet
- Biology of The Alveolar Bone - Orthodontic Tissue Regeneration (OTR) PDFDocument5 pagesBiology of The Alveolar Bone - Orthodontic Tissue Regeneration (OTR) PDFDonald FlorezNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesHypothyroidism Case AnalysisKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System OverviewDocument35 pagesAutonomic Nervous System OverviewDr. R. PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell: Kelompok 1 1. Alestya Febrimaharani 2. Iftah Shorayya 3. Lastri Sulastri 4. Siti ShopiaturohmahDocument15 pagesSickle Cell: Kelompok 1 1. Alestya Febrimaharani 2. Iftah Shorayya 3. Lastri Sulastri 4. Siti ShopiaturohmahErnesta Saulina DewiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Review Worksheet KEYDocument7 pagesCirculatory System Review Worksheet KEYJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Mock ExamDocument5 pagesScience 5 Mock ExamReynold Luke PaduaNo ratings yet
- Chap-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument31 pagesChap-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationMANIK CHHABRANo ratings yet
- Neck Anatomy: Lymph NodesDocument5 pagesNeck Anatomy: Lymph NodesKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland DisordersDocument5 pagesAdrenal Gland Disordersdujana rastanawiNo ratings yet
- 01 - Overview of The Cardiovascular Physiology - ACPDocument6 pages01 - Overview of The Cardiovascular Physiology - ACPMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet