Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics Gas Power Cycles
Uploaded by
Al Farabi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views6 pagesThermodynamics Gas Power Cycles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThermodynamics Gas Power Cycles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views6 pagesThermodynamics Gas Power Cycles
Uploaded by
Al FarabiThermodynamics Gas Power Cycles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
CH # 09
GAS POWER CYCLES
Lecture # 11
DIESEL CYCLE: THE IDEAL CYCLE
FOR COMPRESSION-IGNITION ENGINES
In diesel engines, only air is compressed during the
compression stroke, eliminating the possibility of
autoignition (engine knock).
Therefore, diesel engines can be designed to operate at
much higher compression ratios than SI engines, typically
between 12 and 24.
1-2 isentropic
compression
2-3 constantvolume heat
addition
3-4 isentropic
expansion
4-1 constantvolume heat
rejection.
In diesel engines, the spark plug is replaced
by a fuel injector, and only air is compressed
during the compression process.
Cutoff
ratio
for the same compression ratio
Thermal
efficiency of
the ideal Diesel
cycle as a
function of
compression
and cutoff
ratios (k=1.4).
Comparison between Otto & Diesel Cycles
Otto Cycle
Diesel Cycle
Dual cycle: A more realistic
ideal cycle model for modern,
high-speed compression ignition
engine.
P-v diagram of an ideal dual cycle.
How Stuff Works (link)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Web based version and Apps (iOS and Android)
How Automobiles work (link)
How Car Engine works (link)
How Diesel Engine work? (link)
How 2-Stroke Engine works (link)
How Gasoline Works (link)
Why do most cars have gasoline engines (link)
Fuel Injection System (link)
5 New Engine Technologies (link)
Gasoline Direct Injection Engines (link)
Compression Ratio and Octane number (link)
Alternative Fuels (link)
Hybrid Technology (link)
You might also like
- Byoyancy Flow in Free Fluids PDFDocument12 pagesByoyancy Flow in Free Fluids PDFAl Farabi100% (1)
- ME Design Report for Assignment 4Document3 pagesME Design Report for Assignment 4Al FarabiNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation PrinciplesDocument7 pagesInstrumentation PrinciplesAl FarabiNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics and Probability For Engineers, 5th EditionDocument23 pagesApplied Statistics and Probability For Engineers, 5th EditionMuhammadHazmiMokhtar75% (4)
- Thermodynamics Exergy LecturesDocument11 pagesThermodynamics Exergy LecturesAl FarabiNo ratings yet
- Douglus Chap 8Document41 pagesDouglus Chap 8Al Farabi0% (1)
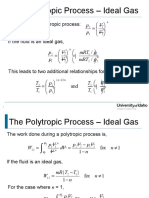
- Polytropic RelationsDocument4 pagesPolytropic RelationsAl Farabi100% (1)
- StratificationDocument109 pagesStratificationAl FarabiNo ratings yet
- Applied statistics and probability textbook chapter on hypothesis testingDocument84 pagesApplied statistics and probability textbook chapter on hypothesis testingFarah Fazlin JamilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Design Chapter 14 SolutionsDocument39 pagesMechanical Engineering Design Chapter 14 SolutionsJeffDavis91205100% (3)
- Gruber's Complete GRE Guide 2012Document746 pagesGruber's Complete GRE Guide 2012naveen_m01100% (4)
- Solution CH # 5Document39 pagesSolution CH # 5Al FarabiNo ratings yet
- 09 01ChapGereDocument12 pages09 01ChapGereChristina Buckle100% (1)
- Probability and Stochastic Processes SolutionsDocument3 pagesProbability and Stochastic Processes SolutionsaeshabanaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solutions - Chapter 6: Yates and Goodman: Probability and Stochastic Processes Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesProblem Solutions - Chapter 6: Yates and Goodman: Probability and Stochastic Processes Solutions ManualAl FarabiNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic Processes: Second EditionDocument22 pagesProbability and Stochastic Processes: Second Editionenchanting_diceNo ratings yet
- Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction For Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J. GoodmanDocument6 pagesProbability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction For Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J. GoodmanAl FarabiNo ratings yet
- Problem Solutions - Chapter 4: Yates and Goodman: Probability and Stochastic Processes Solutions ManualDocument37 pagesProblem Solutions - Chapter 4: Yates and Goodman: Probability and Stochastic Processes Solutions ManualAl FarabiNo ratings yet
- Making The Most Of: ©2016, Jen JonesDocument64 pagesMaking The Most Of: ©2016, Jen JonesYousee IskandarNo ratings yet
- 09 01ChapGereDocument12 pages09 01ChapGereChristina Buckle100% (1)
- Engineering 245: The Lean LaunchpadDocument86 pagesEngineering 245: The Lean LaunchpadAl FarabiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)