Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment No. 1: Theory
Uploaded by
Azrul Ikhwan ZulkifliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No. 1: Theory
Uploaded by
Azrul Ikhwan ZulkifliCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No.
1
AIM: To study about transmission Mediums in Computer Networks
Theory:
Data is represented by computers and other telecommunication devices using signals. Signals are
transmitted in the form of electromagnetic energy from one device to another. Electromagnetic
signals travel through vacuum, air or other transmission mediums to travel between one point to
another(from source to receiver).
Electromagnetic energy (includes electrical and magnetic fields) includes power, voice, visible
light, radio waves, ultraviolet light, gamma rays etc.
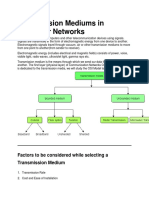
Transmission medium is the means through which we send our data from one place to another.
The first layer (physical layer) of Communication Networks OSI Seven layer model is dedicated to
the transmission media, we will study the OSI Model later.
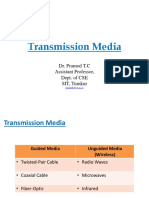
Bounded/Guided Transmission Media
It is the transmission media in which signals are confined to a specific path using wire or cable.
The types of Bounded/ Guided are discussed below.
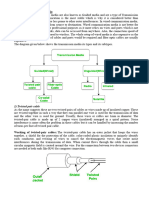
Twisted Pair Cable
This cable is the most commonly used and is cheaper than others. It is lightweight, cheap, can
be installed easily, and they support many different types of network. Some important points :
Its frequency range is 0 to 3.5 kHz.
Typical attenuation is 0.2 dB/Km @ 1kHz.
Typical delay is 50 s/km.
Repeater spacing is 2km.
Twisted Pair is of two types :
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable
It is the most common type of telecommunication when compared with Shielded Twisted Pair
Cable which consists of two conductors usually copper, each with its own colour plastic insulator.
Identification is the reason behind coloured plastic insulation.
UTP cables consist of 2 or 4 pairs of twisted cable. Cable with 2 pair use RJ-11 connector and 4
pair cable useRJ-45 connector.
Advantages :
Installation is easy
Flexible
Cheap
It has high speed capacity,
100 meter limit
Higher grades of UTP are used in LAN technologies like Ethernet.
It consists of two insulating copper wires (1mm thick). The wires are twisted together in a helical
form to reduce electrical interference from similar pair.
Disadvantages :
Bandwidth is low when compared with Coaxial Cable
Provides less protection from interference.
Shielded Twisted Pair Cable
This cable has a metal foil or braided-mesh covering which encases each pair of insulated
conductors. Electromagnetic noise penetration is prevented by metal casing. Shielding also
eliminates crosstalk (explained in KEY TERMS Chapter).
It has same attenuation as unshielded twisted pair. It is faster the unshielded and coaxial cable. It
is more expensive than coaxial and unshielded twisted pair.
Advantages :
Easy to install
Performance is adequate
Can be used for Analog or Digital transmission
Increases the signalling rate
Higher capacity than unshielded twisted pair
Eliminates crosstalk
Disadvantages :
Difficult to manufacture
Heavy
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial is called by this name because it contains two conductors that are parallel to each other.
Copper is used in this as centre conductor which can be a solid wire or a standard one. It is
surrounded by PVC installation, a sheath which is encased in an outer conductor of metal foil,
barid or both.
Outer metallic wrapping is used as a shield against noise and as the second conductor which
completes the circuit. The outer conductor is also encased in an insulating sheath. The
outermost part is the plastic cover which protects the whole cable.
Here the most common coaxial standards.
50-Ohm RG-7 or RG-11 : used with thick Ethernet.
50-Ohm RG-58 : used with thin Ethernet
75-Ohm RG-59 : used with cable television
93-Ohm RG-62 : used with ARCNET.
There are two types of Coaxial cables :
BaseBand
This is a 50 ohm () coaxial cable which is used for digital transmission. It is mostly used for
LANs. Baseband transmits a single signal at a time with very high speed. The major drawback is
that it needs amplification after every 1000 feet.
BroadBand
This uses analog transmission on standard cable television cabling. It transmits several
simultaneous signal using different frequencies. It covers large area when compared with
Baseband Coaxial Cable.
Advantages :
Bandwidth is high
Used in long distance telephone lines.
Transmits digital signals at a very high rate of 10Mbps.
Much higher noise immunity
Data transmission without distortion.
The can span to longer distance at higher speeds as they have better shielding when
compared to twisted pair cable
Disadvantages :
Single cable failure can fail the entire network.
Difficult to install and expensive when compared with twisted pair.
If the shield is imperfect, it can lead to grounded loop.
Fiber Optic Cable
These are similar to coaxial cable. It uses electric signals to transmit data. At the centre is the
glass core through which light propagates.
In multimode fibres, the core is 50microns, and In single mode fibres, the thickness is 8 to 10
microns.
The core in fiber optic cable is surrounded by glass cladding with lower index of refraction as
compared to core to keep all the light in core. This is covered with a thin plastic jacket to protect
the cladding. The fibers are grouped together in bundles protected by an outer shield.
Fiber optic cable has bandwidth more than 2 gbps (Gigabytes per Second)
Advantages :
Provides high quality transmission of signals at very high speed.
These are not affected by electromagnetic interference, so noise and distortion is very less.
Used for both analog and digital signals.
Disadvantages :
It is expensive
Difficult to install.
Maintenance is expensive and difficult.
Do not allow complete routing of light signa
Unbounded/Unguided Transmission Media
Unguided or wireless media sends the data through air (or water), which is available to anyone
who has a device capable of receiving them. Types of unguided/ unbounded media are
discussed below :
Radio Transmission
Microwave Transmission
Radio Transmission
Its frequency is between 10 kHz to 1GHz. It is simple to install and has high attenuation. These
waves are used for multicast communications.
Microwave Transmission
It travels at high frequency than the radio waves. It requires the sender to be inside of the
receiver. It operates in a system with a low gigahertz range. It is mostly used for unicast
communication.
Advantages of Microwave Transmission
Used for long distance telephone communication
Carries 1000s of voice channels at the same time
Disadvantages of Microwave Transmission
It is Very costly
Reference: http://www.studytonight.com/
You might also like
- Transmission MediumDocument12 pagesTransmission MediumSuryanshuNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument14 pagesTransmission MediaCONSTANTINOSNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 CCNDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 CCNsajjadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Transmission MediaDocument9 pagesLesson 3 Transmission MediaKevin SambuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Computer NetworksDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Computer Networkspratyay dhondNo ratings yet
- Transmission Mediums in Computer Networks: Factors To Be Considered While Selecting A Transmission MediumDocument24 pagesTransmission Mediums in Computer Networks: Factors To Be Considered While Selecting A Transmission MediumRaj SriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Transmission MediaDocument9 pagesLesson 3 Transmission MediateddykigiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Transmission MediaDocument22 pages3 Transmission MediaRashad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Notes-Transmission MediaDocument22 pagesNotes-Transmission MediaRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Bounded or Guided Transmission Media: Twisted Pair CableDocument15 pagesBounded or Guided Transmission Media: Twisted Pair Cablevany tagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-: Physical LayerDocument26 pagesChapter 2-: Physical Layeralish shrsethaNo ratings yet
- Idresss sir#6OKDocument17 pagesIdresss sir#6OKDil NawazNo ratings yet
- Medi-Caps University Indore: Computer Network Lab File Department of Computer Science Engineering Session: 2019-23Document46 pagesMedi-Caps University Indore: Computer Network Lab File Department of Computer Science Engineering Session: 2019-23Harsh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Ambo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDocument27 pagesAmbo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaNo ratings yet
- Ambo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDocument27 pagesAmbo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document70 pagesUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNo ratings yet
- CableDocument26 pagesCableHrithik ReignsNo ratings yet
- MediaDocument19 pagesMediaDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Transmission MediaDocument24 pagesChapter 3 - Transmission MediaTawanda MukuteNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document84 pagesUnit 2Gaytri HogaleNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media and Network Cabling: Transmission Medium Is The Physical Path Between The Transmitter and ReceiverDocument68 pagesTransmission Media and Network Cabling: Transmission Medium Is The Physical Path Between The Transmitter and ReceiversaadbinsamiNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media ProjectDocument10 pagesTransmission Media ProjectSahil Aggarwal60% (5)
- Transmission Media: By: Kapil Rishi Yadav 37-DDocument25 pagesTransmission Media: By: Kapil Rishi Yadav 37-DkapilryadavNo ratings yet
- Running Head: NETWORK MEDIA: Case Study: Types of Network Media SCT 121-C004-0454/2019 DITDocument7 pagesRunning Head: NETWORK MEDIA: Case Study: Types of Network Media SCT 121-C004-0454/2019 DITIANNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Notes: What Is Communication Media?Document18 pagesData Communication Notes: What Is Communication Media?ychokhatNo ratings yet
- CN Pract-2Document13 pagesCN Pract-2Ur MnNo ratings yet
- Assignment of NetworkingDocument13 pagesAssignment of NetworkingJyoti BhanotNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Computer NetworkDocument46 pagesLab Manual Computer Networkmeghana09No ratings yet
- Example: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneDocument33 pagesExample: For A Written Message, The Transmission Medium Might Be A Mail Carrier, A Truck, or An AirplaneAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document27 pagesChapter 3yayatarekegn123No ratings yet
- Network Media-70413Document37 pagesNetwork Media-70413hanaNo ratings yet
- 02b Transmission Media and Their CharacteristicsDocument44 pages02b Transmission Media and Their CharacteristicsBenson MugaNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer: Twisted-Pair CableDocument6 pagesPhysical Layer: Twisted-Pair CableNeenu PrasannanNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document17 pagesDocument 3Night FuryNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument12 pagesTransmission MediaJatin RajputNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument5 pagesResearchNicole BernalNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument33 pagesTransmission MediaAshish ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Guided MediaDocument23 pagesGuided MediaJohn Ellonye AckahNo ratings yet
- Media Types: Dr. Ajantha Atukorale University of Colombo School of Computing (UCSC)Document53 pagesMedia Types: Dr. Ajantha Atukorale University of Colombo School of Computing (UCSC)jasonNo ratings yet
- Mbalenhle Ndaba ICT1532: The Advantages of The Twisted Pair Cable AreDocument4 pagesMbalenhle Ndaba ICT1532: The Advantages of The Twisted Pair Cable AreMbali NdabaNo ratings yet
- DC Module3 - Transmission MediaDocument35 pagesDC Module3 - Transmission MediaMayank RajNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & Networks (CS-628)Document27 pagesData Communication & Networks (CS-628)abdul rehman juttNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Transmission MediaDocument43 pages1.3 Transmission MediaDiimu AfarNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Wired NetworkDocument10 pagesDifferent Types of Wired NetworkGagan DeepNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document33 pagesLecture 3Mstafa MhamadNo ratings yet
- Basis For Comparison Guided Media Unguided MediaDocument19 pagesBasis For Comparison Guided Media Unguided MediaFikru TesefayeNo ratings yet
- Networking 1.5Document13 pagesNetworking 1.5Echo greenNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Wired MediaDocument5 pages1.5 Wired Mediayabocew846No ratings yet
- Delivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItDocument52 pagesDelivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItjoelanandrajNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media - Project ReportDocument15 pagesTransmission Media - Project ReportShahin Sha Z0% (1)
- Wired/Guided Media: Chapter No: 2 Transmission Media Transmission MediaDocument18 pagesWired/Guided Media: Chapter No: 2 Transmission Media Transmission MediaWidimongar JarqueNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument73 pagesTransmission Mediahardcore85No ratings yet
- Industrial Technology - Electronics Cable Types Cable Types Description/Application Advantage/DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesIndustrial Technology - Electronics Cable Types Cable Types Description/Application Advantage/Disadvantagesmaxiboy239No ratings yet
- Transmission Media: Guided: Transmission Capacity Depends Critically On The Medium, The Length, andDocument10 pagesTransmission Media: Guided: Transmission Capacity Depends Critically On The Medium, The Length, andMONEER THAMEERNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibre Communication With Overview 1.pdf 2Document97 pagesOptical Fibre Communication With Overview 1.pdf 2ahmedNo ratings yet
- Transmisson InfrastructureDocument11 pagesTransmisson Infrastructuresrbehera2022No ratings yet
- Communication Medias and TopologiesDocument49 pagesCommunication Medias and TopologiesAmjad IrshadNo ratings yet
- Analog Digital TransmissionDocument29 pagesAnalog Digital TransmissionImran KeerioNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Week 2Document33 pagesWeek 2Azrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document19 pagesWeek 3Azrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement Specification Vending Machine Component SystemDocument12 pagesSoftware Requirement Specification Vending Machine Component SystemAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & Network 1Document28 pagesData Communication & Network 1Azrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnswerDocument4 pagesChapter 1 AnswerAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterDocument8 pagesLab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Data Com Chapter1-2Document66 pagesData Com Chapter1-2Azrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Storyboarding & Prototyping: IDUS315 - HCI - 1 IDUS315 - HCI - 2Document3 pagesStoryboarding & Prototyping: IDUS315 - HCI - 1 IDUS315 - HCI - 2Azrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnswerDocument4 pagesChapter 1 AnswerAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 01 Class&Object PDFDocument44 pages01 Class&Object PDFAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Queues: Bcs1223: Data Structures & AlgorithmsDocument43 pagesChapter 5: Queues: Bcs1223: Data Structures & AlgorithmsAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Datasheet LMS511-20190 1059529 enDocument10 pagesDatasheet LMS511-20190 1059529 enSlobodan MilosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Wartsila ArtemisDocument2 pagesWartsila ArtemisLuana MarchioriNo ratings yet
- Understanding Wired and Wireless Networks: Lesson 3Document32 pagesUnderstanding Wired and Wireless Networks: Lesson 3Guadalupe SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Decanter BCC VFD Panel Recommendations R0Document7 pagesDecanter BCC VFD Panel Recommendations R0Salomão SouzaNo ratings yet
- DTC Catalog Complete 2012Document40 pagesDTC Catalog Complete 2012Luky HerlambangNo ratings yet
- Tashe DocDocument23 pagesTashe DocOz GNo ratings yet
- Title-Familiarisation With Different Wired Media: DescriptionDocument4 pagesTitle-Familiarisation With Different Wired Media: DescriptionPlaban SarkarNo ratings yet
- L1 Networking BasicsDocument11 pagesL1 Networking BasicsRola HashimNo ratings yet
- Tx6 Cat 6 Utp Copper Cable (Ww-Cosp166) 5-19-11Document2 pagesTx6 Cat 6 Utp Copper Cable (Ww-Cosp166) 5-19-11enigmavjNo ratings yet
- Features: NT50 Series RS485 Modbus RTU Networking LCD Fan Coil ThermostatDocument6 pagesFeatures: NT50 Series RS485 Modbus RTU Networking LCD Fan Coil ThermostatsaddamNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer - Transmission MediaDocument31 pagesPhysical Layer - Transmission Mediaalolmani_oop100% (1)
- Forouzan MCQ in Transmission MediaDocument12 pagesForouzan MCQ in Transmission MediaFroyd WessNo ratings yet
- Installation of Telephone & Data SystemDocument20 pagesInstallation of Telephone & Data SystemvipinkmlNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2-Network-CablingDocument46 pagesLESSON 2-Network-CablingJ A Y T R O NNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DMX PhilipsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To DMX Philipsmile1966No ratings yet
- A6V11272745 - Automations Stations Modular Series PXC..D PXC.. - enDocument14 pagesA6V11272745 - Automations Stations Modular Series PXC..D PXC.. - enMohamed Amine LABIDINo ratings yet
- TIA-862-B Draft 3 Due 2014-12-29Document43 pagesTIA-862-B Draft 3 Due 2014-12-29pabloabelgilsotoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 CSS G11 2nd Sem Week 1 4Document51 pagesModule 6 CSS G11 2nd Sem Week 1 4Kevin LucilaNo ratings yet
- UTP Installation Do's and Don'ts.: Do Do Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not DoDocument3 pagesUTP Installation Do's and Don'ts.: Do Do Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not Do Do Not DoRx FooNo ratings yet
- Boq Mep Bimc Clinic Ubud - BlankDocument16 pagesBoq Mep Bimc Clinic Ubud - BlankFerry WijiantaraNo ratings yet
- Product Guide Metacentre GBHiResenDocument16 pagesProduct Guide Metacentre GBHiResenNihat RustamliNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Network+ Certification Practice Test 4 (Exam N10-006)Document9 pagesCompTIA Network+ Certification Practice Test 4 (Exam N10-006)LostbyondthevoidNo ratings yet
- Subscriber Loop Design LectureDocument79 pagesSubscriber Loop Design LectureReynald BorjaNo ratings yet
- Pcse 100 Et K 003 1 Cables de InstrumentacionDocument38 pagesPcse 100 Et K 003 1 Cables de InstrumentacionEliud RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 10GXE00 TechdataDocument3 pages10GXE00 TechdataSajith AliNo ratings yet
- Desigo™ Ethernet, Tcp/Ip, MS/TP and Bacnet: Technical PrinciplesDocument72 pagesDesigo™ Ethernet, Tcp/Ip, MS/TP and Bacnet: Technical PrinciplesnajibNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification - Section-7Document8 pagesTechnical Specification - Section-7api-25988294No ratings yet
- 1585J M4TBJM 1 PDFDocument1 page1585J M4TBJM 1 PDFsoayNo ratings yet
- NMC-TED300: NIKOMAX Cable Tester With LCD Display, UTP/STP, RJ45, With Length MeasurementDocument2 pagesNMC-TED300: NIKOMAX Cable Tester With LCD Display, UTP/STP, RJ45, With Length MeasurementMaaeglobal ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Computer Systems ServicingDocument18 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Computer Systems ServicingJoshua ConcepcionNo ratings yet