Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unicellular Organisms: No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY
Uploaded by
Abir OmarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unicellular Organisms: No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY
Uploaded by
Abir OmarCopyright:
Available Formats
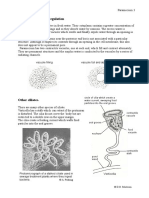
Unicellular Organisms
Unicellular organisms are found almost anywhere there is water. Some are autotropic and produce their own food by photosynthesis, while others are
heterotrophic and must eat food produced by other organisms. The structures within a unicellular organism tells us a lot about their way of life.
flagellum
Contractile vacuole - regulates
amount of water in organism
Chloroplastssite
of
photosynthesis
Chloroplastssite of
of photosynthesis
photosynthesis
Chloroplast - site
heterotrophic
autotrophic
It lives in most moist
Environments water is
continually entering
cell by osmosis, so it
has contractile
vacuoles to pump out
excess water and
prevent the cell exploding.
Anal pore - waste material
exits the organism
Oral groove - food enters
organism and forms a food
vacuole
Cilia - hair like structures
It lives in fresh water
which beat to move the
water is
organism
continually entering
cell by osmosis, so it
has contractile vacuoles to pump out excess water and prevent the cell exploding.
Chlamydomonas
Food - food is ingested by
phagocytosis
Contractile vacuole regulates amount of water
in organism
Food vacuole - contains
digesting food
Autotrophic: it has an
eyespot to sense light,
a flagellum to help it
move towards the light
and chloroplasts for
photosynthesis.
It lives in fresh water
water is
continually entering
cell by osmosis, so it
has contractile
vacuoles to pump out
excess water and
prevent the cell exploding.
Flagellum - beats for movement
Eye spot - senses light
Contractile vacuole regulates amount of
water in organism
Chloroplast - site of
photosynthesis
pseudopodium
Heterotrophic: moves by
pseudopodium - a
temporary protrusion or
retractile process of the
cytoplasm and feeds by
phagocytosis.
Contractile vacuole - regulates
amount of water in organism
phagocytosis
Amoeba
Heterotrophic: it has cilia
which pulsate, moving the
organism towards food.
The food moves into the
oral groove, forming a food
vacuole, which enters the
organism where food is
digested. The waste leaves
the organism via an anal
pore.
food vacuole
It lives in fresh water
water is
continually entering
cell by osmosis, so it
has contractile
vacuoles to pump out
excess water and
prevent the cell
exploding.
Eye spot - senses light
Paramecium
cilia
eye spot
Autotrophic: it has an
eyespot to sense light,
a flagellum to help it
move towards the light
and chloroplasts for
photosynthesis.
Flagellum - beats for movement
oral groove
contractile vacuole
Euglena
anal pore
chloroplast
No Brain Too Small BIOLOGY
You might also like
- English Skills BookDocument49 pagesEnglish Skills BookAngela SpadeNo ratings yet
- Biology Questions and AnswersDocument472 pagesBiology Questions and Answersbusybeefreedom100% (1)
- LLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety TrendsDocument23 pagesLLoyd's Register Marine - Global Marine Safety Trendssuvabrata_das01100% (1)
- Mechanical Questions & AnswersDocument161 pagesMechanical Questions & AnswersTobaNo ratings yet
- Which Stats TestDocument2 pagesWhich Stats Testaby251188No ratings yet
- Drawing Skills Booklet For A Level BiologyDocument16 pagesDrawing Skills Booklet For A Level BiologyRaShid KhAn100% (1)
- Filter Feeding in Mpolychatete, Molluscs and EchinodermataDocument14 pagesFilter Feeding in Mpolychatete, Molluscs and EchinodermataSuchitra Sharma100% (1)
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Reaction rate determination and simulation of hydrogenation processDocument3 pagesReaction rate determination and simulation of hydrogenation processToMemNo ratings yet
- Mixed Questions Genetics1Document11 pagesMixed Questions Genetics1Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Zoology CH 8 Animal Like Pro TistsDocument103 pagesZoology CH 8 Animal Like Pro TistsTHUNDERCLASH_SILVEREYES139100% (3)
- Egg Membrane Project For 12Document18 pagesEgg Membrane Project For 12Hemanth Kumar100% (1)
- The Coral Reef Aquarium: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishFrom EverandThe Coral Reef Aquarium: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- IEC-60721-3-3-2019 (Enviromental Conditions)Document12 pagesIEC-60721-3-3-2019 (Enviromental Conditions)Electrical DistributionNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument18 pagesCellsapi-272901382No ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of Marketing Marketing ManagementDocument51 pagesNature and Scope of Marketing Marketing ManagementFeker H. MariamNo ratings yet
- Storytelling ScriptDocument2 pagesStorytelling ScriptAnjalai Ganasan100% (1)
- MKT-case StudyDocument7 pagesMKT-case StudyJoe Thampi KuruppumadhomNo ratings yet
- Aquaponics Algae: How to Control, Combat and Get Rid of Algae in Aquaponics SystemFrom EverandAquaponics Algae: How to Control, Combat and Get Rid of Algae in Aquaponics SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Regulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsDocument16 pagesRegulation of Body Fluids: Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsPaopao Macalalad100% (3)
- Understand Azure Event HubsDocument12 pagesUnderstand Azure Event HubselisaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista NotesDocument3 pagesKingdom Protista Noteshafizhusain0% (1)
- Why Cell Specialization Is Necessary in Multicellular OrganismsDocument20 pagesWhy Cell Specialization Is Necessary in Multicellular OrganismsNITIASSWARENo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista ClassificationDocument2 pagesKingdom Protista ClassificationRei Diaz ApallaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Guide: The 7 Steps of NutritionDocument17 pagesNutrition Guide: The 7 Steps of NutritionAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Protists: Four Phyla of Animal-Like ProtistsDocument3 pagesProtists: Four Phyla of Animal-Like ProtistsalivNo ratings yet
- Vacuole 1Document14 pagesVacuole 1nadia riaz100% (1)
- ProtistsDocument3 pagesProtistsJeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- Animals ChartDocument2 pagesAnimals ChartShervin MortazaviNo ratings yet
- Unicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaDocument3 pagesUnicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaEGSRHEtjykudli.u;No ratings yet
- Life Processes of Living ThingsDocument25 pagesLife Processes of Living Thingszanu winfred kwame100% (1)
- Insect Digestive System OverviewDocument3 pagesInsect Digestive System OverviewjamNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation: Biology (../index - HTML) / Oc-Ph (Index - HTML) / OsmoregulationDocument7 pagesOsmoregulation: Biology (../index - HTML) / Oc-Ph (Index - HTML) / Osmoregulationdr_swaralipiNo ratings yet
- 2.2.1 Cell OrganisationDocument15 pages2.2.1 Cell Organisationche salNo ratings yet
- The Functions of Vacuoles in Plant and Animal Cells (39 charactersDocument3 pagesThe Functions of Vacuoles in Plant and Animal Cells (39 charactersAmber L.No ratings yet
- Unicellular OrganismsDocument3 pagesUnicellular Organisms362730558No ratings yet
- Discover Diverse Microorganisms in a Homemade Hay InfusionDocument3 pagesDiscover Diverse Microorganisms in a Homemade Hay InfusionMark Louie DolotaNo ratings yet
- Paramecium: Classification, Structure, Function and CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesParamecium: Classification, Structure, Function and CharacteristicsGail EmbudoNo ratings yet
- 0 Bryozoa PDFDocument4 pages0 Bryozoa PDFMark Robert MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Protists 8Document46 pagesProtists 8api-235185802No ratings yet
- Life Process Part 1Document49 pagesLife Process Part 1Jyoti AsatiNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista: - Sometimes Called The "Junk Drawer" - Contains Animal-Like, Plant-Like andDocument76 pagesKingdom Protista: - Sometimes Called The "Junk Drawer" - Contains Animal-Like, Plant-Like andRahul KushwahaNo ratings yet
- How Does An Amoeba Obtain FoodsDocument5 pagesHow Does An Amoeba Obtain FoodsnidhiNo ratings yet
- ProtistsDocument27 pagesProtistsapi-234472684No ratings yet
- Nutrition in ProtozoaDocument6 pagesNutrition in Protozoaapi-481318101100% (3)
- Zoology (Book)Document26 pagesZoology (Book)sme olaplNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Excretory SystemguranjanNo ratings yet
- Science: Life ProcessesDocument94 pagesScience: Life ProcessesNandhaKumarSNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate Biology: by Jane YaweDocument42 pagesInvertebrate Biology: by Jane YaweANYWAR SIMONNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument25 pagesPoriferaAmelia MeiriskaNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument28 pagesLife ProcessesNithyasri RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Parts and movement of amoeba and parameciumDocument5 pagesParts and movement of amoeba and parameciumlyka_manzano_1No ratings yet
- Amoeba, Paramecium EuglenaDocument5 pagesAmoeba, Paramecium Euglenalyka_manzano_1No ratings yet
- Life Process Class 10 Science NotesDocument19 pagesLife Process Class 10 Science NotesPranav PatilNo ratings yet
- Protozoa General CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesProtozoa General Characteristicsvasundhara ayyagariNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOLOGYSungdeok MinNo ratings yet
- Vacuoles 1Document19 pagesVacuoles 1anjalyNo ratings yet
- Lec No 5Document6 pagesLec No 5Pratibha ChNo ratings yet
- Who Discovered Protozoa?Document8 pagesWho Discovered Protozoa?arunNo ratings yet
- Kingdom ProtozoaDocument13 pagesKingdom ProtozoaAlyssa Gail de VeraNo ratings yet
- Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument3 pagesExcretion and OsmoregulationAmutuhaire RobertNo ratings yet
- 1 - Cell MembraneDocument60 pages1 - Cell MembraneAlifia Amalia PandaNo ratings yet
- (S.C. Rastogi) Essentials of Animal Physiology, 4t (BookSee - Org) 238Document1 page(S.C. Rastogi) Essentials of Animal Physiology, 4t (BookSee - Org) 238Indah Rizka AprilianiNo ratings yet
- CH 22 Amoeba-Euglena Questions 1Document2 pagesCH 22 Amoeba-Euglena Questions 1api-444439435No ratings yet
- Words To Know: Amoeba Proteus. (Reproduced by Permission ofDocument3 pagesWords To Know: Amoeba Proteus. (Reproduced by Permission ofMary JinuNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 6Document24 pagesLife Processes Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 6Nongpok SinghaNo ratings yet
- Paramecium Osmoregulation and Contractile VacuolesDocument1 pageParamecium Osmoregulation and Contractile VacuolesElijah PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Name That OrganismDocument11 pagesName That Organismapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals: by Sanjana R 7 BDocument33 pagesNutrition in Animals: by Sanjana R 7 BSohan TriceyNo ratings yet
- The Rise of The AnimalsDocument21 pagesThe Rise of The AnimalsJessica ChavezNo ratings yet
- Life Process Class 10 Science NotesDocument26 pagesLife Process Class 10 Science NotesAnmol SudanNo ratings yet
- Digestive System of BranchiostomaDocument6 pagesDigestive System of BranchiostomaAnuradha DasNo ratings yet
- E Pathshala File 801642381308Document48 pagesE Pathshala File 801642381308Aijaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Circulatory System2Document5 pagesWorksheet Circulatory System2Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Revision Grade 9 American Division Miss AlaaDocument14 pagesRevision Grade 9 American Division Miss AlaaAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- June 2003 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEDocument12 pagesJune 2003 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- 5-10 - Grasshopper - Dissection AsDocument7 pages5-10 - Grasshopper - Dissection AsAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument4 pagesMeasurementAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Aies Trial Multiple Choice MsDocument2 pagesAies Trial Multiple Choice MsAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Steven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefDocument8 pagesSteven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Steven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefDocument8 pagesSteven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- June 2005 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument12 pagesJune 2005 QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSE PDFAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A Biology A-Level Determine Tensile Strength Plant FibresDocument2 pagesEdexcel A Biology A-Level Determine Tensile Strength Plant FibresAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- CP 03 - Calculating Mitotic IndexDocument3 pagesCP 03 - Calculating Mitotic IndexAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Behavior Chapter NotesDocument27 pagesBehavior Chapter NotesAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Cycle & Division 1 MSDocument6 pagesEukaryotic Cell Cycle & Division 1 MSAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Infection Grades 7 9Document19 pagesSet 1 Infection Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology GCSE Topic 2 NotesDocument10 pagesEdexcel Biology GCSE Topic 2 NotesAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Document19 pagesSet 1 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Set 2 Cell Biology Grades 4 5 PDFDocument18 pagesSet 2 Cell Biology Grades 4 5 PDFAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Specimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme PDFDocument2 pagesSpecimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme PDFAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- CP 07 - Plant Mineral DeficienciesDocument3 pagesCP 07 - Plant Mineral DeficienciesAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function 5 MSDocument7 pagesEukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function 5 MSAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- SAPS - Chromatography of Photosynthetic Pigments - Student NotesDocument5 pagesSAPS - Chromatography of Photosynthetic Pigments - Student NotesHaruka SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Respiration and Nutrient Cycle AnswersDocument14 pagesPhotosynthesis Respiration and Nutrient Cycle AnswersAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Muscles 1Document5 pagesMuscles 1Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Surface Area To Volume Ratio QPDocument3 pagesSurface Area To Volume Ratio QPAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- CP 06 - Water Potential of Plant CellsDocument3 pagesCP 06 - Water Potential of Plant CellsAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Part One Mxed AnswersDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Part One Mxed AnswersAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Raychem Price ListDocument48 pagesRaychem Price ListramshivvermaNo ratings yet
- Manual - Sentron Pac Profibus Do Modul - 2009 02 - en PDFDocument106 pagesManual - Sentron Pac Profibus Do Modul - 2009 02 - en PDFDante Renee Mendoza DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Fiery Training 1Document346 pagesFiery Training 1shamilbasayevNo ratings yet
- France: French HistoryDocument16 pagesFrance: French HistoryMyroslava MaksymtsivNo ratings yet
- Donaldson 004117 PDFDocument6 pagesDonaldson 004117 PDFNSNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToDocument79 pagesPresentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToVidyaNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Hero Final TNDocument8 pagesThe Invisible Hero Final TNKatherine ShenNo ratings yet
- VNC Function Operation InstructionDocument11 pagesVNC Function Operation InstructionArnaldo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge Sensor PDFDocument12 pagesStrain Gauge Sensor PDFMario Eduardo Santos MartinsNo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutenDocument14 pagesElectrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutensecucaNo ratings yet
- Crash Cart - General Checklist For Medical Supplies On Crash CartsDocument3 pagesCrash Cart - General Checklist For Medical Supplies On Crash CartsYassen ManiriNo ratings yet
- About Version ControlDocument6 pagesAbout Version ControlMaria Kristina Cassandra HeukshorstNo ratings yet
- DNT Audit Cash CountDocument2 pagesDNT Audit Cash CountAnonymous Pu7TnbCFC0No ratings yet
- Scholars of Hadith Methodology in Dealing With The Two Sahihs: The Criticized Ahadith As A Model. Ammar Ahmad Al-HaririDocument37 pagesScholars of Hadith Methodology in Dealing With The Two Sahihs: The Criticized Ahadith As A Model. Ammar Ahmad Al-HaririSalah KhanNo ratings yet
- Operation Guide For The Mercedes-Benz GLA/CLADocument5 pagesOperation Guide For The Mercedes-Benz GLA/CLASantosh TalankarNo ratings yet
- Estwani ISO CodesDocument9 pagesEstwani ISO Codesनिपुण कुमारNo ratings yet
- ArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Document14 pagesArtigoPublicado ABR 14360Sultonmurod ZokhidovNo ratings yet
- CHEM206 Answers 1Document3 pagesCHEM206 Answers 1Shiro UchihaNo ratings yet
- BỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO ĐỀ THI HỌC PHẦN KINH TẾ VĨ MÔDocument5 pagesBỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO ĐỀ THI HỌC PHẦN KINH TẾ VĨ MÔPhạm Thu NgaNo ratings yet
- Jesus - The Creator Unleashes Our Creative PotentialDocument1 pageJesus - The Creator Unleashes Our Creative PotentialKear Kyii WongNo ratings yet
- Samsung 55 Inch LCD LED 8000 User ManualDocument290 pagesSamsung 55 Inch LCD LED 8000 User ManuallakedipperNo ratings yet