Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE5310/EE3002: Analog Circuits Tutorial 1 Problems 6, 8, 10, 11 Are Optional
Uploaded by
sunilsheelavant0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views6 pagesprob
Original Title
ee3002prob1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentprob
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
182 views6 pagesEE5310/EE3002: Analog Circuits Tutorial 1 Problems 6, 8, 10, 11 Are Optional
Uploaded by
sunilsheelavantprob
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
EE5310/EE3002: Analog Circuits
Tutorial 1
Problems 6, 8, 10, 11 are optional.
EC2010-ANALOG CIRCUITS : PROBLEM SET 2
shanthi@ee.iitm.ac.in
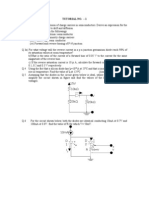
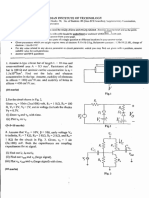
Problem 1
9)
2 k
IX
3V
vi
+
6V
2 k
2 mA
1 k
IX
Vx
Vx
1.9 V
1V
+
1V
Figure 1: Circuit for Problem 1
k = nCox = 100 A/V2, (W/L) = 10, VT = 0.7 V
For the circuit of Figure 1, assume that vi is an incremental voltage source. Determine the operating point of the
network. Find also the small signal voltage across the 1 k
resistor.
Figure 2: Circuit for Problem 3
Problem 210)
In this problem, we delve deeper into the notion of small
signal. Consider two nonlinear ampliers, with inputoutput characteristics given by Vout =
).
VA exp( VVin
A
2
Vin
VA
and Vout =
3V
An incremental gain of 10 is desired of both amplifers.
Determine the operating points so that this gain may be
achieved.
3V
I
We saw in class that the small signal approximation
is valid only when the higher order terms in the Taylor series can be safely neglected in relation to the linear
term. Compare the second order derivative of the two
amplifers around the operating point. What can you say
about the relative magnitudes of the incremental inputs
for each of the ampliers which qualify as small signals
?
I+i
V1
R
V2
V2 + v2
(a)
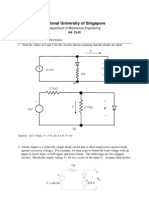
Problem 3
For each of the circuits shown above, plot Ix as Vx varies
from 0-3 V.
(b)
k = nCox = 100 A/V2, (W/L) = 10, VT = 0.7 V
Figure 3: Circuit for Problem 4
Problem 4
For the circuit (a) shown above, determine the minimum
value of I required to make the MOSFET operate at the edge
1
You might also like
- EE5310/EE3002: Analog Circuits Tutorial 1 Problems 6, 8, 10, 11 Are OptionalDocument10 pagesEE5310/EE3002: Analog Circuits Tutorial 1 Problems 6, 8, 10, 11 Are Optionalee12b056No ratings yet
- EE5310/EE3002: Analog Circuits Tutorial 1 Problems 6, 8, 10, 11 Are OptionalDocument10 pagesEE5310/EE3002: Analog Circuits Tutorial 1 Problems 6, 8, 10, 11 Are Optionaldummy1957jNo ratings yet
- Ec201-Analog Circuits: Problem Set 1Document2 pagesEc201-Analog Circuits: Problem Set 1s_subbulakshmiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 08 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial1 08 PDFsanjayr_nittNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document6 pagesTutorial 1soham1994No ratings yet
- Unta BeranakDocument6 pagesUnta Beranakharis kunkunNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated CircuitsDocument14 pagesAnalysis and Design of Digital Integrated CircuitsfjwoemcuNo ratings yet
- A6-7 SolDocument39 pagesA6-7 Solanshikamittal1807No ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- EEB 525 - Assignment 1 2018Document2 pagesEEB 525 - Assignment 1 2018Snr Berel ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Document30 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- 7.sheet OutputstagesDocument6 pages7.sheet OutputstagesAyman ElAshmawyNo ratings yet
- ECD Lab 2 PDFDocument12 pagesECD Lab 2 PDFMaryam MahmoodNo ratings yet
- HW8 PDFDocument2 pagesHW8 PDFGet wNo ratings yet
- CE/EE3311 Electronic Circuits HW3Document2 pagesCE/EE3311 Electronic Circuits HW3Get wNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DiodeDocument15 pagesTutorial DiodeAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- HW4 2023Document2 pagesHW4 2023kunghsiangyuNo ratings yet
- Tut SemiconductDocument3 pagesTut SemiconductLim Chieh ShingNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet No 4 Sti 2054 Enspy May 16 2022Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet No 4 Sti 2054 Enspy May 16 2022Arthur MoloNo ratings yet
- Overhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1Document11 pagesOverhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1e TalalNo ratings yet
- Overhead Line and Substation InsulationDocument11 pagesOverhead Line and Substation InsulationAnkat Rao RaoNo ratings yet
- Homework #3 (Diodes and BJTS) : MicroelectronicsDocument1 pageHomework #3 (Diodes and BJTS) : Microelectronics劉威辰No ratings yet
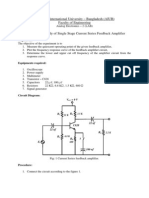
- Experiment Name - Study of Single Stage Current Series Feedback AmplifierDocument3 pagesExperiment Name - Study of Single Stage Current Series Feedback Amplifiermrana_560% (1)
- Exp 3Document5 pagesExp 3MariaNo ratings yet
- Dechassa - Retta - Lemma - 3189815 - 22577354 - BEE 332# Due Nov 2 From Abraham.aDocument33 pagesDechassa - Retta - Lemma - 3189815 - 22577354 - BEE 332# Due Nov 2 From Abraham.ajoe.kurina3194No ratings yet
- Session 3Document10 pagesSession 3hung kungNo ratings yet
- EE210 Midsem 2013Document2 pagesEE210 Midsem 2013egupta1No ratings yet
- Ece3110 HW 3Document7 pagesEce3110 HW 3Apricot BlueberryNo ratings yet
- Eee312 Eee282 HW1 Spring2015Document3 pagesEee312 Eee282 HW1 Spring2015Rüşdi IşlerNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics End Sem Paper PDFDocument4 pagesBasic Electronics End Sem Paper PDFSanket KumarNo ratings yet
- AP UnitI PDFDocument17 pagesAP UnitI PDFPruthvi PutuNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2014-15 CP0267 08-Jan-2015 RM01 Aec2 PDFDocument7 pagesWINSEM2014-15 CP0267 08-Jan-2015 RM01 Aec2 PDFKunal KaushikNo ratings yet
- TAREA 2.6 Ejercicios Con AMP. Operacionales NRC 3417-ComprimidoDocument26 pagesTAREA 2.6 Ejercicios Con AMP. Operacionales NRC 3417-ComprimidoLuis MontesNo ratings yet
- Transitor 2Document22 pagesTransitor 2HpA SaúlNo ratings yet
- Exam Conditions:: Unless Told Otherwise, AssumeDocument5 pagesExam Conditions:: Unless Told Otherwise, AssumekakagoNo ratings yet
- EE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 4: Current Source, Current Mirror, and Differential PairDocument4 pagesEE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 4: Current Source, Current Mirror, and Differential PairSruthiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2006Document45 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2006Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Unit Ix: Electronic Devices Numerical Problems WorksheetDocument8 pagesUnit Ix: Electronic Devices Numerical Problems WorksheetRSNo ratings yet
- ESC201 Assignment 7 SolDocument10 pagesESC201 Assignment 7 Solgarud2221No ratings yet
- Ass 1Document1 pageAss 1Shuvra SahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 3 Due Date: Mar. 3 : EE-341 Microelectronic DesignDocument3 pagesAssignment No. 3 Due Date: Mar. 3 : EE-341 Microelectronic DesignUsama AfzalNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology: Fnian, 3Document2 pagesIndian Institute of Technology: Fnian, 3Sanjay MotwaniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualDocument86 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Circuits Solutions ManualKenneth VogtNo ratings yet
- ) For The Given NMOS. Given: V 1 V, .: ESC201A: Assignment VIII Date: 17 March, 2015Document4 pages) For The Given NMOS. Given: V 1 V, .: ESC201A: Assignment VIII Date: 17 March, 2015Deepak TholiaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Perunit Calculations and Impedance DiagramsDocument3 pagesExperiment 6 Perunit Calculations and Impedance DiagramsJaved Ahmed LaghariNo ratings yet
- Auto Zero Op AmpDocument3 pagesAuto Zero Op AmpAndrei SevcencoNo ratings yet
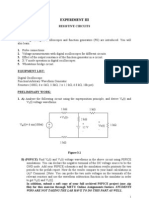
- Experiment 5 (Modified)Document8 pagesExperiment 5 (Modified)Mark Sangalang100% (1)
- BEEI 2383 TutorialDocument3 pagesBEEI 2383 TutorialAIMAN DANIAL BIN SULONGNo ratings yet
- Assi 1 BJT Diff Amp.Document3 pagesAssi 1 BJT Diff Amp.divyangkapadiaNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesHalf Wave RectifierSeski TomabiaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-2 ARFDocument5 pagesAssignment 1-2 ARFPrajwal K SNo ratings yet
- !7374656d5f26736f6c7574696f6e73 PDFDocument12 pages!7374656d5f26736f6c7574696f6e73 PDFluckyNo ratings yet
- Multimedia University WIDocument15 pagesMultimedia University WIGm Fairuz ShahNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuits Formal Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLinear Circuits Formal Lab ReportNishant JalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesFrom EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsFrom EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Exam InstructionDocument1 pageExam InstructionsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 PDFDocument9 pagesExperiment 5 PDFsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- EE619 Lecture08 LNAs Noise CalculationDocument7 pagesEE619 Lecture08 LNAs Noise CalculationsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- MBD Book PDF Version PDFDocument94 pagesMBD Book PDF Version PDFsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Lab3 Pulse ShapingDocument4 pagesLab3 Pulse ShapingsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- An Ultralow Leakage Synaptic Scaling Homeostatic Plasticity Circuit With Configurable Time Scales Up To 100 KsDocument7 pagesAn Ultralow Leakage Synaptic Scaling Homeostatic Plasticity Circuit With Configurable Time Scales Up To 100 KssunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- EE619 Lecture01 OverviewDocument18 pagesEE619 Lecture01 OverviewsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Scanned Lecture14 MidSemDiscussion PDFDocument8 pagesScanned Lecture14 MidSemDiscussion PDFsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Market Survey 2014 PDFDocument7 pagesMarket Survey 2014 PDFsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Brochure 2016 HD PDFDocument34 pagesBrochure 2016 HD PDFAnwesh10000No ratings yet
- Snoa665c PDFDocument18 pagesSnoa665c PDFnaveen reddyNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document24 pagesLec 1Anonymous VASS3z0wTHNo ratings yet
- NoiseDocument5 pagesNoiselokeshbnNo ratings yet
- 2016-17-MTech Shortlist Sem1 PDFDocument1 page2016-17-MTech Shortlist Sem1 PDFsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Team 3 Presentation 2 RF HarvestingDocument16 pagesTeam 3 Presentation 2 RF HarvestingsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Ad 7190Document40 pagesAd 7190erkin1966No ratings yet
- Linux SystemsDocument95 pagesLinux SystemsvijaykumarsinganaNo ratings yet
- Low Noise Amplifier Design Using 0.35 Μm Sige Bicmos Technology For Wlan/Wimax ApplicationsDocument5 pagesLow Noise Amplifier Design Using 0.35 Μm Sige Bicmos Technology For Wlan/Wimax ApplicationssunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Assignment Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAssignment Respiratory SystemsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Lecture AnalogDocument30 pagesLecture AnalogsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- A Broadband Low Noise Amplifier For X-Band ApplicationsDocument3 pagesA Broadband Low Noise Amplifier For X-Band ApplicationsPaul ShineNo ratings yet
- Body ElectricDocument2 pagesBody ElectricsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- An Ultra-Low-Voltage and Ultra-Low-Power 2.4 GHZ Lna Design: Baimei Liu, Chunhua Wang, Minglin Ma, Shengqiang GuoDocument5 pagesAn Ultra-Low-Voltage and Ultra-Low-Power 2.4 GHZ Lna Design: Baimei Liu, Chunhua Wang, Minglin Ma, Shengqiang GuoLaxmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAssignment Respiratory SystemsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- MSC Project ProposalDocument1 pageMSC Project ProposalsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Merit Medical Nis 07aprDocument50 pagesMerit Medical Nis 07aprsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Assignment Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAssignment Respiratory SystemsunilsheelavantNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetSaleem SheikhNo ratings yet
- Intro - CMOS Analog CKT DesignDocument15 pagesIntro - CMOS Analog CKT Designgene_palenciaNo ratings yet