Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Process Dynamics and Control, and Instrumentation Laboratory y
Uploaded by
carlette11Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Process Dynamics and Control, and Instrumentation Laboratory y
Uploaded by
carlette11Copyright:
Available Formats
10/6/2015
Introduction to
Process Dynamics and Control,
y
and Instrumentation Laboratory
WhatshouldIcontrol?Whereonthe
processdoIputmycontrolloops?
d I t
t ll
? AsI
A I
proceedwiththedesignofaprocess,
whataspectsofcontrolshouldIconsider
atwhichstages?
10/6/2015
Process Control
and Instrumentation
Instrumentation
Controllers
Sensors
Transmitters
Final Control Elements
P
Process
Analysis
A l i
Process Model
Development/Solution
Process Dynamics
1st, 2nd, higher order
Analysis
A
l i and
dD
Design
i
of Control Systems
Time/Laplace Domain
Frequency Domain
Advanced Control Methods
Definitions
What is Control?
methods to force parameters in the environment
to have specific values
e.g. controlling of room temp
Control System
elements necessary to accomplish the control
objective
10/6/2015
Definitions
Process Control
study of automatic control principles
applied to chemical processes
applies principles of mathematics and
engineering science to the regulation of the
dynamic operation of process systems
Definitions
Process Control
study of elements and methods of control
system operation used in industry to
control industrial processes
any condition, natural or artificial, by
which a physical quantity is regulated
10/6/2015
Main Functions
Set point tracking
the ability to shift from one desired
operating point to another
Disturbance rejection
the ability to maintain an operating point
despite fluctuating conditions and external
forces
Hierarchy of Control Objectives
1. Safety
2. Environmental
Protection
3. Equipment Protection
4. Smooth Plant Operation
5. Product Quality
6 Profit Optimization
6.
7. Monitoring and
Diagnosis
10/6/2015
Advantages of Process Control
allows basic operation by product tracking and
inventory
ensures safety
y byy preventing
p
g dangerous
g
situations
guides startup, shutdown, and setpoint tracking
saves energy, material, and time
reduces waste and maintains product quality
Applications of Control Systems
industrial processes, manufacturing, robotics
consumer g
goods,, home appliances
pp
10/6/2015
Applications of Control Systems
computers, networks, communications systems
transportation
p
systems,
y
, cars,, planes,
p
, aircraft
Simple Process Control
10/6/2015
Ancestor of Automatic Control
10/6/2015
Process Control Principles
The main objective of process control is to
regulate the value of a certain quantity
To regulate means to maintain a certain
quantity at some desired value
The desired value is called the setpoint or the
reference value
The actual value of the variable is called the
control point
Self-Regulation
10/6/2015
Human-Aided (Manual) Control
Controlled Variable
Setpoint
Manipulated Variable
Inthecontrolsystem,weadjustthe
manipulatedvariable
i l t d
i bl tomaintainthe
t
i t i th
controlledvariable atitssetpoint.
10/6/2015
Automatic Control System
Automatic Control
Sensor
measures the value of the level and
converts it to a signal
Controller
a machine, electronic circuit, or a
computer that accepts the signal
Actuator
receives the output signal to change the
valve settings
10
10/6/2015
Identification of Elements
The Process
flow of liquid in and out of the tank
the tank and the liquid
all the are under control with respect to fluid
level
could be single or multivariable
Identification of Elements
1. Measurement
used to get some information about the variable
being controlled
refers to conversion of a variable into some
corresponding analog of the variable (pneumatic
pressure, electrical voltage or current)
a sensor is used to perform the initial
measurement
a transducer converts one signal to another
further transformation of the signal to an
information that can be used by other elements in
the system is called signal conditioning
11
10/6/2015
Identification of Elements
2. Controller
examines the error presented by the detector
determines the appropriate action that should
be undertaken by an operator
computers are widely used in process controls
because of the capability of decision-making and
handling multi-variables
requires input of controlled variable and set
point
Error Detector
part of the controller device that determines the
kind of error in the system
Identification of Elements
3. Control Element
the final element in the process control that
exerts direct influence on the process
provides the required changes to bring the
controlled variable to the set point
the valve adjust the liquid outflow from the tank
Final Control Element
12
10/6/2015
What is a loop?
the loop is the complete circuit formed when a signal
flows through measurement, error detection, controller,
and final controlling
Open Loop (Command)
there is no feedback mechanism
13
10/6/2015
Open Loop
non-feedback controller
computes inputs by comparing the current
state and its model
does not observe the output of the
process that it controls
cannot correct errors and may be affected
by disturbances in the system
Open Loop
used in well-defined systems where the
relationship between the input and the
resultant state can be modeled by a
mathematical formula
e.g. irrigation sprinkler, washing machines
14
10/6/2015
Disturbance
Input
Process
Output
Closed Loop (Regulation)
there is a repeating series of actions
15
10/6/2015
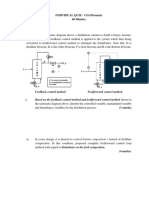
Feedback Control
a controller reacts to the error between the
setpoint and the process value
Low Cost Operation
its structure and algorithm are independent of
the process since it only reacts to the error
Poor Performance
an error is always present
Easy and Simple
tuning methods are always the same
Disturbance
Output
Input
Process
Adjustment
Measurement
Controller
Setpoint
16
10/6/2015
Two-knob Faucet Shower
Disadvantages of Feedback
Large magnitude disturbance
Large time delay
http://www.see.ed.ac.uk
17
10/6/2015
Feedforward Control
designed to compute the output of the
controller to ensure the process variable is
unaffected by any predictable disturbances
in the process
process conditions are monitored and
compared with a model system
if conditions deviate from the model they
are altered
e.g. regulation of heartbeat, heater
systems
Feedforward Control
Expensive Solution
the solution is unique and each controller
is different
algorithms are expensive and it cannot be
tuned easily
Good Performance
since the error is predicted, almost no
error is present
18
10/6/2015
Disturbance
Feedforward
Input
Process
Output
Block Diagrams
the block diagram of a control loop defines
all the basic elements and signals involved in the
process
Setpoint, r
Controlled Variable, c
Measured Representation, b
19
10/6/2015
Process Flow Diagrams (PFD)
simple illustration that describes the
primary flow path to a unit
includes primary equipment and flows of
chemicals through the unit
Sections: Feed, preheating, the process, and final products. Left-toright approach.
20
10/6/2015
A process flow diagram of an amine treating system for the removal
of gaseous hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. It is widely used in oil
refineries and chemical plants.
Piping and Instrumentation
Diagrams (P&ID)
analogous to circuits schematics
graphic representation of equipment,
piping, and instrumentation
uses symbols to represent elements in a
process-control system
developed
p by
y Instrument Society
y of
America (ISA)
21
10/6/2015
Purpose of using P&ID
to have a common language for
instrument technicians, process engineers,
and suppliers
to properly document plant designs for
installation in a graphical format
to help in equipment maintenance, failure
analysis,
a
a ys s, a
and
d troubleshooting
oub es oo g
systematic illustration of functional relationships of piping,
instrumentation, and system equipment components
22
10/6/2015
P&ID Symbols and Guidelines
identify process lines from instrument
lines
identify the location of the instrument
identify the function of the instrument
provide other relevant information
23
10/6/2015
P&ID Signal and Process Lines
uses lines that denotes the particular nature of the signal
P&ID Symbols
for Sensors
and Elements
24
10/6/2015
Balloon Symbols
/ Instrument Tags
denotes the actual instruments used in processcontrol
uses circles called balloon
FC means Flow Controller (nature,function)
117 denotes the loop it represents
Balloon Symbols
/ Instrument Tags
e.g. PRC 143
1. Process variable
2. Function
3. Function Modifier/
Instrument
PRC
143
PRC: pressure recording controller on loop #143
25
10/6/2015
P&ID Symbols for Transducers
and other Elements
26
10/6/2015
Constructing an
Instrument Flow Sheet
1.
2
2.
3.
4.
Identify your process
Define your control objective/s
Create a process flow diagram
Identify the needed equipment and process
lines
5. Determine the instrument and connecting lines
needed
6. Extract information with ISA symbology
convention
7. Apply the ISA codes to identify instrument and
functions
27
You might also like
- Lecture1, Process Control and AnalysisDocument60 pagesLecture1, Process Control and AnalysisPaul RwomwijhuNo ratings yet
- Process Control & Automation: Sobukola, O.P. (PHD) /kajihausa, O.E. (MRS)Document24 pagesProcess Control & Automation: Sobukola, O.P. (PHD) /kajihausa, O.E. (MRS)gobra senNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Process ControlDocument35 pages01 Introduction To Process ControlJohn DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 InstrumentationDocument14 pagesChapter-3 InstrumentationIrtiza RasulNo ratings yet
- 271 Introduction To Process Control Course DescriptionDocument2 pages271 Introduction To Process Control Course DescriptionAdrian Reyes100% (1)
- Introducation To Linear Control SystemsDocument23 pagesIntroducation To Linear Control SystemsJahan ZaibNo ratings yet
- PC-Hardware of A Process Control SystemDocument22 pagesPC-Hardware of A Process Control SystemSafyan Manzoor0% (1)
- Process Control CHP 1Document53 pagesProcess Control CHP 1kishoreprithikaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12 Instrumentation and Control LabDocument17 pagesExperiment 12 Instrumentation and Control LabAyesha KhurramNo ratings yet
- 1.topic 1 - Ind ControlDocument52 pages1.topic 1 - Ind ControlLoga HSNo ratings yet
- CSC Unit 1Document22 pagesCSC Unit 1aviitharu2472No ratings yet
- CH 1 - Intro J5800Document54 pagesCH 1 - Intro J5800mohd_mizanNo ratings yet
- ECNG3004 Control System ApplicationsDocument7 pagesECNG3004 Control System ApplicationsMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Process Control B.SDocument437 pagesProcess Control B.Sram uo100% (1)
- ELEC3320 - Lecture Notes 1Document36 pagesELEC3320 - Lecture Notes 1Aneketh GurumurthiNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation & Pro. Cont.Document140 pagesInstrumentation & Pro. Cont.maria neneng bulakNo ratings yet
- Application of Scada For Water Treatment Plant: - by Shraddha Malve MT19ENV017Document34 pagesApplication of Scada For Water Treatment Plant: - by Shraddha Malve MT19ENV017Shraddha Malve100% (1)
- Lecture1 PDFDocument9 pagesLecture1 PDFLokesh JenaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionMr YERRYBBNo ratings yet
- 2023 PCI360S Introductory ConceptsDocument19 pages2023 PCI360S Introductory ConceptsSifanele PotwanaNo ratings yet
- Components of Control Loops1Document19 pagesComponents of Control Loops1May Ann BontoNo ratings yet
- Control Lab Project ReportDocument28 pagesControl Lab Project ReportDanyal QamarNo ratings yet
- Scada SystemDocument18 pagesScada SystemAxcel HelsingNo ratings yet
- The PROCON PH Process Control System Is Based Around The PH Rig and Is A SelfDocument10 pagesThe PROCON PH Process Control System Is Based Around The PH Rig and Is A Selfmiantahir89No ratings yet
- Pertemuan 01Document16 pagesPertemuan 01I Komang Ari Satya WibawaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Control System.Document24 pagesOverview of Control System.la.wajeehakhurshidNo ratings yet
- ProcesscontrolDocument58 pagesProcesscontrolzakariareal623No ratings yet
- Contact Details: Name: Dr. Srinivasa Rao P Office: 17-03-02 Phone: 05-368 7207 Email: Srinivasa - Pedapati@utp - Edu.myDocument45 pagesContact Details: Name: Dr. Srinivasa Rao P Office: 17-03-02 Phone: 05-368 7207 Email: Srinivasa - Pedapati@utp - Edu.myRetneshwaaran GanesanNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document73 pagesModule 5Achsah K VijuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Anonymous tytJlPojNo ratings yet
- Jahid 1Document24 pagesJahid 1Nazmul AhsanNo ratings yet
- Report ControlDocument33 pagesReport Controlajwadalfatani100% (5)
- Mechatronic ApplicationsDocument31 pagesMechatronic ApplicationsDevice SamsungNo ratings yet
- C TLL HD Control Loop HardwareDocument20 pagesC TLL HD Control Loop Hardwareenigmaticmind23No ratings yet
- Model Reference Adaptive ControlDocument57 pagesModel Reference Adaptive ControlmervebayrakNo ratings yet
- What Is Automation?: - Automatic Assembly MachinesDocument24 pagesWhat Is Automation?: - Automatic Assembly MachinesNazmul AhsanNo ratings yet
- What Is Instrument Hook Up Diagram ? Instrument Hook Up Diagram Is Also Called Installation Drawing, Specifies The ScopeDocument31 pagesWhat Is Instrument Hook Up Diagram ? Instrument Hook Up Diagram Is Also Called Installation Drawing, Specifies The ScopevrajakisoriDasiNo ratings yet
- Automation 2 Topic 1: Design A Simple Process Control SystemDocument12 pagesAutomation 2 Topic 1: Design A Simple Process Control SystemChriscarl De LimaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument28 pagesAssignmentfaisal58650No ratings yet
- Temperature Control LabDocument16 pagesTemperature Control Labhoocheeleong234100% (1)
- Sugar Corporation Sugar AcademyDocument110 pagesSugar Corporation Sugar AcademyMesafint kassieNo ratings yet
- Cc&a - 4Document51 pagesCc&a - 4Gauri SinghNo ratings yet
- QDocument27 pagesQHassanAhmedNo ratings yet
- L1 - Introduction To ControlDocument28 pagesL1 - Introduction To ControlOmer Ahmed100% (1)
- Mechatronics: Notes by Arulsahayabeni, M.E.Document125 pagesMechatronics: Notes by Arulsahayabeni, M.E.beniNo ratings yet
- Concept of Process Control - Multiserve Session 1 PDFDocument67 pagesConcept of Process Control - Multiserve Session 1 PDFAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Ia&c Unit - IiiDocument23 pagesIa&c Unit - IiiPradhunya KambleNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Liquid Level SensorDocument24 pagesUltrasonic Liquid Level Sensormadhuri12345678No ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Process ControlDocument30 pages1-Introduction To Process ControlRazif Metta100% (4)
- PDF Document eDocument31 pagesPDF Document eア ムNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and ControlDocument53 pagesInstrumentation and ControlDaniel D Danso100% (1)
- Automatic Controllers: (ME 572/571L Instrumentation and Control Systems)Document15 pagesAutomatic Controllers: (ME 572/571L Instrumentation and Control Systems)Vanessa M. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and ControlDocument32 pagesProcess Dynamics and ControlJohn Ray Clarin100% (1)
- EEIB413 Chapter 1 - StudentDocument84 pagesEEIB413 Chapter 1 - StudentSanjanaLakshmi50% (2)
- Manufacturing Automation Lecture 2Document38 pagesManufacturing Automation Lecture 2Kashan Aamir Aamir IshaqNo ratings yet
- Architecture of Industrial Automation Systems: Unit-1 ECE361Document20 pagesArchitecture of Industrial Automation Systems: Unit-1 ECE361anuj jainNo ratings yet
- PARUL UNIVERSITY - Faculty of Engineering and Technology Parul Institute of TechnologyDocument4 pagesPARUL UNIVERSITY - Faculty of Engineering and Technology Parul Institute of TechnologySmit ChristianNo ratings yet
- Keys To On-Line Monitoring in Steam Generating SystemsDocument9 pagesKeys To On-Line Monitoring in Steam Generating SystemsShameer MajeedNo ratings yet
- Tsim Sha Tsui Symphony of Lights: 8 PM: Macau Day Tour-Outer HarborDocument11 pagesTsim Sha Tsui Symphony of Lights: 8 PM: Macau Day Tour-Outer Harborcarlette11No ratings yet
- WritingaResearchAbstract CompI-BDocument2 pagesWritingaResearchAbstract CompI-Bcarlette11No ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics: Intended Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics: Intended Learning Outcomescarlette11No ratings yet
- AnswersDocument10 pagesAnswersJulius Erick EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture37 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture37 PDFNico Aumento Jr.No ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity Determination of Small Polymer Samples by Differential Scanning CalorimetryDocument5 pagesThermal Conductivity Determination of Small Polymer Samples by Differential Scanning Calorimetrycarlette11No ratings yet
- Aerogel Drying: Published in "State of The Art Book On Supercritical Fluids", Valencia:AINIA, 2004, Pp. 129-134Document6 pagesAerogel Drying: Published in "State of The Art Book On Supercritical Fluids", Valencia:AINIA, 2004, Pp. 129-134carlette11No ratings yet
- Nanomaterials: Lecture #4 Surface ScienceDocument44 pagesNanomaterials: Lecture #4 Surface Sciencecarlette11No ratings yet
- Technopreneurship Business Plan II. Executive Summary: Mission StatementDocument3 pagesTechnopreneurship Business Plan II. Executive Summary: Mission Statementcarlette11No ratings yet
- Selected LP Apps Handouts 3 PDFDocument88 pagesSelected LP Apps Handouts 3 PDFcarlette110% (1)
- FDSGFDocument5 pagesFDSGFcarlette11No ratings yet
- Unendinggrace Engineering Unendinggrace Engineering Unendinggrace EngineeringDocument87 pagesUnendinggrace Engineering Unendinggrace Engineering Unendinggrace Engineeringcarlette11No ratings yet
- The Design of Pressure Windows: Notes To Calculate Thickness of Optical Windows Used in Vacuum or Pressure ApplicationsDocument2 pagesThe Design of Pressure Windows: Notes To Calculate Thickness of Optical Windows Used in Vacuum or Pressure Applicationscarlette11No ratings yet
- Lect 11 Environ ImpactDocument21 pagesLect 11 Environ ImpactMousumi GhoshNo ratings yet
- FDSFSDDocument7 pagesFDSFSDcarlette11No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: - Organic Chemistry: The Study of The Compounds of CarbonDocument7 pagesBiochemistry: - Organic Chemistry: The Study of The Compounds of Carboncarlette11No ratings yet
- What Is The Integral of CSC U Du A. LN (CSC U - Cot U) + C B. LN (CSC U + Cot U) + C C.LN (Sec U - Tan U) + C D. LN (Sec U + Tan U) + CDocument1 pageWhat Is The Integral of CSC U Du A. LN (CSC U - Cot U) + C B. LN (CSC U + Cot U) + C C.LN (Sec U - Tan U) + C D. LN (Sec U + Tan U) + Ccarlette11No ratings yet
- FdafsfDocument7 pagesFdafsfcarlette11No ratings yet
- DsadaDocument4 pagesDsadacarlette11No ratings yet
- FdafsfDocument9 pagesFdafsfcarlette11No ratings yet
- Process Flow DiagramsDocument47 pagesProcess Flow DiagramsNasi GorengNo ratings yet
- DfafsafsaDocument1 pageDfafsafsacarlette11No ratings yet
- The Three-Dimensional Structure of ProteinsDocument21 pagesThe Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteinscarlette11No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: - Organic Chemistry: The Study of The Compounds of CarbonDocument7 pagesBiochemistry: - Organic Chemistry: The Study of The Compounds of Carboncarlette11No ratings yet
- The Three-Dimensional Structure of ProteinsDocument21 pagesThe Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteinscarlette11No ratings yet
- Unit 11 PDFDocument15 pagesUnit 11 PDFcarlette11No ratings yet
- Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes: What Is A LipidDocument20 pagesLipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes: What Is A Lipidcarlette11No ratings yet
- Unit 9 PDFDocument16 pagesUnit 9 PDFcarlette11No ratings yet
- The Three-Dimensional Structure of ProteinsDocument21 pagesThe Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteinscarlette11No ratings yet
- Sentrifugo 3.0 Performance Appraisal GuideDocument43 pagesSentrifugo 3.0 Performance Appraisal GuideStaceanniNo ratings yet
- Feedback Vs FeedforwardDocument27 pagesFeedback Vs FeedforwardjjhenNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control SystemsDocument25 pagesIndustrial Control SystemsweilingkwayNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Strategic Evaluation and ControlDocument13 pagesModule 5 - Strategic Evaluation and ControlRonald Reagan AlonzoNo ratings yet
- PCI QuizDocument4 pagesPCI QuizSaranya DeviNo ratings yet
- Optimum State Space Control of A BLDC MotorDocument18 pagesOptimum State Space Control of A BLDC Motorauralius0% (1)
- Control System PresentationDocument36 pagesControl System PresentationJosh KingNo ratings yet
- Motion Planning and Control For FRCDocument46 pagesMotion Planning and Control For FRCDavidNo ratings yet
- Peer Coaching OverviewDocument15 pagesPeer Coaching OverviewSilvia Regina SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Framework ComparisonsDocument7 pagesFramework Comparisonsarm masudNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Artificial Neural Networks - : IntroductionDocument43 pagesArtificial Intelligence Artificial Neural Networks - : IntroductionRawaz AzizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Principles of Feedback: Topics To Be Covered IncludeDocument40 pagesIntroduction To The Principles of Feedback: Topics To Be Covered IncludeAliNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control Toolbox: User's GuideDocument246 pagesModel Predictive Control Toolbox: User's GuideLệ DuyênNo ratings yet
- Week 12.1Document14 pagesWeek 12.1Faizan RehmanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Supercritical 8404673Document90 pagesBoiler Supercritical 8404673Appleuk SudarNo ratings yet
- 2019 Blanken LearningAndRepetitiveControlForComplexSystems PDFDocument219 pages2019 Blanken LearningAndRepetitiveControlForComplexSystems PDFAyman IsmailNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 SWE2004 ETH VL2021220101016 Reference Material I 21-10-2021 10-Sep-2020 2. Architectural Style 11Document32 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 SWE2004 ETH VL2021220101016 Reference Material I 21-10-2021 10-Sep-2020 2. Architectural Style 11tamilzharasan SNo ratings yet
- Manual McoDocument45 pagesManual McoCearEo AraGonNo ratings yet
- (IFAC Symposia Series) International Federation of Automatic Control, C. McGreavy-Dynamics and Control of Chemical Reactors and Distillation Columns. Selected Papers from the IFAC Symposium, Bournemou.pdfDocument322 pages(IFAC Symposia Series) International Federation of Automatic Control, C. McGreavy-Dynamics and Control of Chemical Reactors and Distillation Columns. Selected Papers from the IFAC Symposium, Bournemou.pdfAmino AcidNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa ControllerDocument4 pagesYokogawa ControllerLaurence MalanumNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management Final RevisionDocument53 pagesFundamentals of Management Final RevisionAntony GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Management Final Paper 27062020 044941pm PDFDocument8 pagesManagement Final Paper 27062020 044941pm PDFHuzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Control Concepts Unit2Document10 pagesBasic Control Concepts Unit2Noyon NoyonNo ratings yet
- Controlling in ManagementDocument45 pagesControlling in Managementrevathi26100% (2)
- Aspen DMCplus Training-CAPC PDFDocument11 pagesAspen DMCplus Training-CAPC PDFKhairatun Nisa0% (1)
- Feedback and Feed ForwardDocument27 pagesFeedback and Feed ForwardEngr. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 CpdicDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Cpdiceja70No ratings yet
- Feedforward and Ratio Control: Isa Mentor Program Presentation By: Gregory K. McmillanDocument24 pagesFeedforward and Ratio Control: Isa Mentor Program Presentation By: Gregory K. McmillanJosé Diogo ForteNo ratings yet
- ScaraDocument7 pagesScaraAnand Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Boiler Drum Level ControlDocument5 pagesBoiler Drum Level ControlAlka KaushikNo ratings yet