Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Transport Osmosis - Mrs Bruno Biology Homework
Uploaded by
api-276944265Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Transport Osmosis - Mrs Bruno Biology Homework
Uploaded by
api-276944265Copyright:
Available Formats
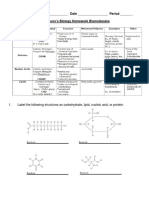
Name _______________________________________
Date _________________ Period _______
Mrs. Brunos Biology Homework: Cell Transport & Osmosis
Directions: Use your journal as a reference tool in addition to the information provided below. Circle your
answer choices and justify your answers.
Plasma (cell) membrane This is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It controls entry of
nutrients and removal of wastes and maintains homeostasis.
***Homeostasis- balance; a stable, internal environment ***
Selective permeability - The cell membrane is picky. Some molecules are allowed to enter
a cell while others are kept out.
Passive Transport
Some substances can move without using energy. This is
called passive transport. The movement of solute
(dissolved substance) from an area of greater
concentration to an area of less concentration is called
diffusion. Water molecules can also diffuse. They move
from where there is more water to where there is less
water. Diffusion of water is called osmosis.
Active Transport
Some molecules are too large to enter or exit the cell, or
their charges prohibit them from passing through the
plasma membrane. If this is the case, the cell can still move them, but it must use energy. Movement of
substances that requires energy is called active transport. Sometimes proteins in the plasma membrane are
used to pump materials out. Sometimes, materials enter and exit the cell using vesicles (pockets of the cell
membrane).Endocytosis uses vesicles to bring materials (like nutrients) into the cell. Exocytosis uses vesicles
to move materials (like waste products) out of the cell.
1. A thermostat maintains an ideal temperature of a
room. What cell process is similar to this?
a. food storage
b. protein synthesis
c. active transport
d. homeostasis
3. What process allows large molecules to enter a
2. Passive transport (circle one) requires energy /
4. Facilitated diffusion is
does not require energy, while active transport
(circle one) requires energy / does not require
energy.
5. Identify the cell transport in each diagram to the right as
active or passive.
cell?
a. endocytosis
b. exocytosis
c. osmosis
d. facilitated diffusion
a.
b.
c.
d.
the same as endocytosis
a special kind of osmosis
a process that requires the cells energy
a type of passive transport
6.
Explain how the cell membrane maintains homeostasis.
7. Which of the following is not a part of a prokaryotic cell?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
cytoplasm
cell membrane
ribosomes
DNA
membrane bound organelles
8. A student filled a plastic bag with a starch solution and placed the bag into a beaker filled with distilled water to
soak overnight. The next day, the student observed that the plastic bag had gained mass. The student tested for
starch in the beaker by adding a few drops of iodine. No color change occurred. The results of this experiment
demonstrate that the plastic bag is
a. permeable
b. impermeable
c. selectively permeable
d. a proton pump
A.
osmosis
B.
maintains a stable internal environment
9. Vocabulary. Match the following
words with its
C.
Movement of water from high concentration to
correct definition.
low concentration
_____homeostasis
_____ osmosis
_____ passive transport
Osmosis
You might also like
- Dna Vocabulary Frayer Models HomeworkDocument4 pagesDna Vocabulary Frayer Models Homeworkapi-276944265No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Homework - Bruno BiologyDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Homework - Bruno Biologyapi-2769442650% (1)
- Cells and Cell Organelles Homework - Bruno BiologyDocument2 pagesCells and Cell Organelles Homework - Bruno Biologyapi-276944265No ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Bruno Biology HomeworkDocument2 pagesBiomolecules - Bruno Biology Homeworkapi-276944265No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- G. James Glass Handbook Part ADocument34 pagesG. James Glass Handbook Part AOvidio CalvoNo ratings yet
- Detergent 1Document4 pagesDetergent 1Muhammad Zubair SharifNo ratings yet
- 7 Stream Gauging-2Document54 pages7 Stream Gauging-2ChampNo ratings yet
- ENGR 313 - Chapter 4 - DislocationsDocument48 pagesENGR 313 - Chapter 4 - DislocationsMelissa LaraNo ratings yet
- Boehm Titration ExcelDocument8 pagesBoehm Titration ExcelAbraham Joel Mendoza FloresNo ratings yet
- Manual Tissue ProcessingDocument48 pagesManual Tissue ProcessingKim RuizNo ratings yet
- T040032 00Document17 pagesT040032 00Doanh HoangNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modelling of Arch Dams PDFDocument137 pagesDynamic Modelling of Arch Dams PDFSanjay SibalNo ratings yet
- Wopq Asme Section IxDocument2 pagesWopq Asme Section IxkanchanabalajiNo ratings yet
- fsd35 Technical Information 6845 PDFDocument6 pagesfsd35 Technical Information 6845 PDFAndani RafikaNo ratings yet
- Suspension ExamplesDocument6 pagesSuspension ExamplesDivaan Raj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- 122 HCD408Z Tech SheetDocument1 page122 HCD408Z Tech SheetpendexxNo ratings yet
- Conostan STD Brochure For AAS or ICPDocument14 pagesConostan STD Brochure For AAS or ICPDewi WulandhariNo ratings yet
- PCARE Calculation NotesDocument10 pagesPCARE Calculation NotesToni Sy EncinaresNo ratings yet
- Che 520L: Prelim Exam: Calculations 1Document4 pagesChe 520L: Prelim Exam: Calculations 1Nicole Anne BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Mathlinks8 CH 10textbookDocument30 pagesMathlinks8 CH 10textbookapi-171445363No ratings yet
- Supramolecular ChemistryDocument48 pagesSupramolecular ChemistryKhalid SirajNo ratings yet
- RT Procedure 10.09.16Document9 pagesRT Procedure 10.09.16mukeshsingh6No ratings yet
- Lead Removal Mechanism Using MgO NpsDocument11 pagesLead Removal Mechanism Using MgO NpsKarthikeyan SNo ratings yet
- Ianswer: Bps 4125/Chm 4123 Medicinal Chemistry Midterm 1 (October 5, 2018)Document7 pagesIanswer: Bps 4125/Chm 4123 Medicinal Chemistry Midterm 1 (October 5, 2018)Halima AdenNo ratings yet
- UNECE-Units of MeasureDocument14 pagesUNECE-Units of MeasurexynicNo ratings yet
- Sceng 818Document25 pagesSceng 818Arslan UmarNo ratings yet
- What Is 21 CFR Part 11Document26 pagesWhat Is 21 CFR Part 11chemtabNo ratings yet
- Memoria Estabilidad Del Talud IxiamasDocument5 pagesMemoria Estabilidad Del Talud IxiamasMarco Antonio TorrezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Selection Guide PosterDocument1 pageAntibiotic Selection Guide PosterjbenedicNo ratings yet
- 2012-3 National Chemistry OlympiadDocument14 pages2012-3 National Chemistry OlympiadRSLNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity WorksheetDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity WorksheetRohan ChackoNo ratings yet
- Escaid 110 Fluid Product Safety SummarypdfDocument3 pagesEscaid 110 Fluid Product Safety SummarypdfLuiS EduardO P.100% (1)
- Ial WCH05 01 Nov19 PDFDocument28 pagesIal WCH05 01 Nov19 PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- 1314 Lab - Single Replacement Lab As Inquiry BasedDocument2 pages1314 Lab - Single Replacement Lab As Inquiry Basedapi-239433858No ratings yet