Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Linguistics
Uploaded by
Đỗ Thanh ThảoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Linguistics
Uploaded by
Đỗ Thanh ThảoCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition
Larynx: a tube-shaped organ in the neck that contains the vocal chords (located btw the pharynx and the trachea)
Vocal chords: 2 small brands of elastic tissue (2 flat strips or rubber, opposite each other across air passage in larynx)
Pharynx: the pace behind tongue, immediate above the larynx, reaching up towards the nasal cavity
Palate: Forms roof of mouth. Separates mouth/oral cavity from nose/nasal cavity. Font part: hard, back part: soft
Lips: Consists upper, lower lip.
Teeth: lower front teeth not important in speech, upper front teeth: more frequently used
Tongue: greatest variety of movement. 5 parts: tip, blade, front, back (root)
Oral sounds (m mi): production of which soft palate is raised, block off nasal cavity => airstream through mouth only
Nasal sounds (m mig): production of which soft palate is lowered, block off oral cavity => Airstream through nose only
Consonants: 2 articulators come tgther, obstruct airstream (airstream not get out) => stricture or closure of airstream
Vowels: no obstruction to flow or air, passes from larynx to lips (air not get out) => produced with open articulation
Voiced sounds: airstream through vc chords. Vc chords come tgther, obstruct airstream, airstrm not get out => vibrate
Voiceless sounds: airstream through vc chords. Vc chords come apart, theyre open. Airstrm get out freely => not vibrate
Consonants: 2 types: the place and the manner of articulation
Identifying: bng trag 27 (Voicing => Place of articulation => Manner of articulation)
Ex: /s/: voiceless alveolar fricative
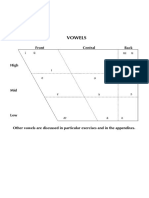
Vowels:
Classification: bg trog slide (tongue height => part of tongue raised => Degree of lip rounding)
Identifying: long/short => high/mid/low => front/central/back => rounded/unrounded
Ex: /e/ => short mid-central unrounded vowel, /u:/ => long high-back rounded vowel
*Diphthongs: a glide from 1 vowel to another, the long simple vowels. 1st part stronger-longer, 2nd part shorter-quieter
Classification: Centring: ending in / /, Closing: ending in / / and / /
Phonemes: the smallest segment of sound distinguishing 2 words
44 phonemes: 24 consonants, 20 vowels
Substituting 1 phoneme for another => different-meaning words (phonemes: meaning-distinguishing sounds)
Substituting allophones => different pronun of same words
Phonemic symbols: symbols for phonemes, phonetic symbols: symbols for allophones
*Phonemic/broad transcription: in which each phoneme is represented by 1 phonemic symbol
Ex: /
/
Phonetic/narrow transcription: contains information about exact quality of the sounds
Ex: [
]
*Minimal pairs: Pair of words which differ by only 1 phoneme in identical environment (Ex: zip-zap, sheep-ship)
Syllable: Onset, nucleus, coda (initial consonant, nuclear, prefinal, final, post final)
Stress: an extra force exerted on a particular syllable or a particular word (word stress: particular syllable, usually fixed;
sentence stress: particular word, not fixed)
Function: distinguish different parts of speech (noun-verb), a word from a phrase (idiom), function and content words, ,
new and given info, contrastive emphasis
Intonation: patterns of pitch variation in a sentence (affect meaning, indicate attitude, show contextual features)
Morphemes: smallest meaningful unit (a class of forms or an abstraction from concrete forms)
*Grammatical morphemes: (function words: pronouns, prepositions, auxiliary verbs, conjunctions, determiners;
inflectional affix: singular/plural, comparison er-est, participle)
*Lexical morphemes: (content word: N, V, adj, adv; derivational affix: prefix, suffix)
Morphs: concrete realization of a morpheme (classification based on form)
Free morph: a root morpheme
Examples: Undressed
Un-dress-ed
(Un-prefix-bound, dress-root-free, ed-suffix-bound)
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- UK EduDocument13 pagesUK EduĐỗ Thanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- TKT Module 3 2007Document15 pagesTKT Module 3 2007Tariq AlMozoghiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Team Peer Evaluation Examples PDFDocument6 pagesTeam Peer Evaluation Examples PDFĐỗ Thanh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- PDF 6099Document1 pagePDF 6099Anonymous xhQTp9No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument32 pagesAspects of Connected SpeechBrendon Jikal100% (2)
- Syllabic ConsonantsDocument3 pagesSyllabic ConsonantsJuan Devoto80% (5)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Introduction To LinguisticDocument12 pagesIntroduction To LinguisticJulia RheintanataNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Determining Phonological Awareness 1Document25 pagesDetermining Phonological Awareness 1Jamie JimenezNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Word Syllables Onset Peak CodaDocument7 pagesWord Syllables Onset Peak CodaMd Muneeruddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Berber DictionaryDocument475 pagesBerber DictionaryvstrohmeNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Looking at Languages - A Workbook in Elementary Linguistics (4th Edition)Document384 pagesLooking at Languages - A Workbook in Elementary Linguistics (4th Edition)Vy Nguyễn Thị Thảo100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Cambridge English: TKT: TKT: Module 1 - Aspects of Pronunciation Think AboutDocument6 pagesCambridge English: TKT: TKT: Module 1 - Aspects of Pronunciation Think AboutVictoria RhadeNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Targum Jonathan On Isaiah.41-42Document8 pagesTargum Jonathan On Isaiah.41-42vagnerxavierNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- BP001 - English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument136 pagesBP001 - English For Academic and Professional Purposesp67kn6kfjvNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Acoustic Effects of Urdu On EngDocument16 pagesAcoustic Effects of Urdu On EngDr Abdus SattarNo ratings yet
- Dosuna - 2012 - Ancient Macedonian As A Greek Dialect - A Critical Survey On Recent WorkDocument13 pagesDosuna - 2012 - Ancient Macedonian As A Greek Dialect - A Critical Survey On Recent WorkMakedonas AkritasNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument16 pagesPhoneticsGulfam AnsariNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Phonetics BasicsDocument84 pagesPhonetics BasicsﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞNo ratings yet
- Pronunciation Worksheet Final - Ed: (T) (D) (/D) : //D/ Adds An Extra SyllableDocument2 pagesPronunciation Worksheet Final - Ed: (T) (D) (/D) : //D/ Adds An Extra Syllableluz alix100% (1)
- Sherpa Dictionary First Edition 2009-LibreDocument303 pagesSherpa Dictionary First Edition 2009-LibreUSergiyu IjikijoloNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- I Found A New Baby Ellen AuditionDocument6 pagesI Found A New Baby Ellen AuditionAnnalise Griswold100% (1)
- Axes Are "The Lifeblood of Government.": National TaxesDocument3 pagesAxes Are "The Lifeblood of Government.": National TaxesYumiNo ratings yet
- لغويات مقارنة 1703Document276 pagesلغويات مقارنة 1703hazemNo ratings yet
- English Phonology:: The Sound Systems of LanguageDocument32 pagesEnglish Phonology:: The Sound Systems of LanguageLili MulyaNo ratings yet
- Íñigo, IsabelDocument127 pagesÍñigo, IsabelBrendaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - ey sound pronunciation guideDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - ey sound pronunciation guideJ-31069No ratings yet
- Holy Quran para 19Document28 pagesHoly Quran para 19Humayun KhanNo ratings yet
- Buka Alal Hussain (A) - UrduDocument140 pagesBuka Alal Hussain (A) - UrduSyed Ali Jaffry100% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- New Generation, English VocabularyDocument158 pagesNew Generation, English VocabularyGaspard de la Nuit100% (2)
- Phonics Assessment For K 3Document6 pagesPhonics Assessment For K 3api-329789525No ratings yet
- Siaton Science High School: Mantuyop, Siaton, Negros OrientalDocument4 pagesSiaton Science High School: Mantuyop, Siaton, Negros OrientalEugene JamandronNo ratings yet
- Phonological Analysis of LoanwordsDocument15 pagesPhonological Analysis of LoanwordsMaha Mahmoud TahaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 206.10 20short Long 20vowels-3Document1 pageLesson 206.10 20short Long 20vowels-3Goryan NikolenkoNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Classical Nahuatl PhonologyDocument31 pagesAspects of Classical Nahuatl Phonologymrtezozomoc100% (2)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)