Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PP Limits 1516
Uploaded by
Amirul FadlinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PP Limits 1516
Uploaded by
Amirul FadlinCopyright:
Available Formats
6/29/2015
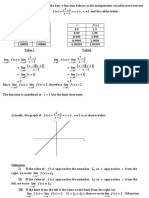
Limits
Limits are used to describe how a function behave as the independent variable move toward
2
a certain value. Consider a funtion f ( x ) x 1 x 1 , x 1 and the tables below .
x 1
x
1.1
1.01
1,001
1.0001
1.00001
f ( x)
2.1
2.01
2.001
2.0001
2.00001
x
0.9
0.99
0.999
0.9999
0.99999
Table 1
f ( x)
1.9
1.99
1.999
1.9999
1.99999
Table2
2
lim f ( x ) lim x 1
x 1 x 1
x 1 x 1
lim
x 1
x 1
lim x 1
2
lim f ( x ) lim x 1
x 1 x 1
x 1 x 1
lim
x 1
x 1
lim x 1
x 1
x 1
x 1
x 1
2
2
Since lim f ( x ) lim f ( x ) 2 , therefore lim f ( x ) 2 .
x 1
x 1
x 1
The function is undefined at x 1 but the limit does exist.
2
Actually, the graph of f ( x ) x 1 x 1 , x 1 is as shown below.
x 1
y
Definition
I) If the value of f ( x ) approaches the numnber L1 as x approaches c from the
right, we write lim f ( x ) L1 .
xc
II) If the value of f ( x ) approaches the numnber L2 as x approaches c from the
left, we write lim f ( x ) L2 .
xc
III) If the limit from the left is the same as the limit from the right say
lim f ( x ) lim f ( x ) L ( L L2 L1 ) , then we write lim f ( x ) L . Otherwise,
xc
xc
xc
the limit does not exist.
Note : The limit of a function as independent variable approaches a value, actually not the
value of the function at the value of independent variable.
6/29/2015
Example
2x 4
f ( x ) 4
x2 7
if
if
if
x3
x3
x3
lim f ( x ) lim x 2 7 2
x 3
x3
x3
x3
lim f ( x ) lim 2 x 4 2
lim f ( x ) 2
x3
Example
2
f ( x) x
2 x 2
x0
if
x0
if
lim f ( x ) lim 2( x 2) 2
x 0
x0
lim f ( x ) lim 2
x 0
x0 x
lim f ( x ) does not exist
x 0
Example
f ( x)
1
x3
lim 1
x 3
lim f ( x )
x 3
lim x 3
x 3
x 3
lim f ( x )
x 3
-3
lim 1
lim
x 3
x 3
lim f ( x ) does not exist
x 3
Example
f ( x)
lim 1
x 2
lim f ( x )
x2
lim x 2 2
x2
lim 1
x 2
lim f ( x )
x2
x 22
lim x 2 2
x 2
lim f ( x )
x2
6/29/2015
Example { lim f ( x ) and lim f ( x ) }
x
y
4
lim f ( x ) 1
lim f ( x ) 4
-1
Example { lim f ( x ) and lim f ( x ) }
x
y
6
lim f ( x ) 6
lim f ( x )
-3
Example { lim f ( x ) and lim f ( x ) }
x
lim f ( x )
lim f ( x )
-3
Limit (Computational techniques)
lim k k , where k is a constant.
xc
lim k lim k k
lim x c
xc
6/29/2015
Example lim x 3
x3
lim x
x
lim x 0
lim x
x 0
lim 1 1
x 3
x 2
lim 1 0
x
x 3
x 2
lim 1
x
x 0
lim x 2
x0
lim 1 does not exist
x
lim 1
x
x 0
lim 1 1
x
2
lim 1 0
x
Theorem
Let lim stand for one of the limits lim , lim , lim , lim or lim .
x c
lim f ( x ) L2 both exist, then
x c
x c
a)
lim f ( x ) g ( x ) lim f ( x ) lim g ( x ) L1 L2 .
b)
lim f ( x ) g ( x ) lim f ( x ) lim g ( x ) L1 L2 .
c)
lim f ( x ) g ( x ) lim f ( x ) lim g ( x ) L1 L2 .
d)
f ( x ) lim f ( x ) L1
lim
, if L2 0 .
g ( x ) lim g ( x ) L2
e)
lim n f ( x ) n lim f ( x ) n L1 , provided L1 0 if n is even .
If lim f ( x ) L1 and
6/29/2015
Example
a)
b)
lim x 2 4 x 3 lim x 2 4 lim x lim 3 3 2 4( 3) 3 0
x 3
x3
x3
x3
lim 5 x 4
5( 4) 4
lim 5 x 4 x 4
8
lim x 2
4 2
x 4 x 2
x 4
c)
d)
2
x 2 x 2 lim x 2 4
lim x 4 lim
x 2 x2
x2
x2
x2
lim
x 2
1 x
x 2 x 1 does not exist.
because
lim
x 2
1 x
x 2 x 1
1 x
lim
x 2
x 2 x 1
Example Find
3
lim x 8
x2
a)
c)
x 2
b)
lim
x0
3 x 1
lim f ( x ) if f ( x )
2
3( x 1) 2
x 3
x
x 1 1
if
x3
if
x3
Solution
a)
b)
c)
3
x 2 x 2 2 x 22 lim x 2 2 x 22 12
lim x 8 lim
x 2 x 2
x2
x 2
x 2
lim
x 0
x
x
x
lim
x 1 1 lim
x 1 1 x 0 x 1 1
x 1 1 x 0
x11
lim
x
x0
x11 2
lim f ( x ) lim ( 3 x 1) 3( 3) 1 10
x 3
x3
lim f ( x ) lim 3( x 1) 2 2 3( 2) 2 2 10
x 3
x3
lim f ( x ) 10
x3
10
6/29/2015
Example Find
a)
b)
2 3x
lim f ( x ) if f ( x ) 2
4x 3x 1
x 2
x3 - 1
a if f ( x ) 2
ax 2
if
x2
if
x2
if
x 2
if
x 2
and lim f ( x ) exists.
x 2
lim f ( x ) lim (4 x 2 3 x 1) 4( 2) 2 3( 2) 1 9
Solution a)
x 2
x 2
lim f ( x ) lim 2 3 x 2 3( 2) 8 2 2
x 2
x 2
lim f ( x ) does not exist.
x 2
b)
lim f ( x ) exists lim f ( x ) lim f ( x )
x2
x 2
x2
lim (ax 2 2) lim ( x 3 1)
x2
x2
a ( 2) 2 2 ( 2) 3 1
4a 5
a5
4
11
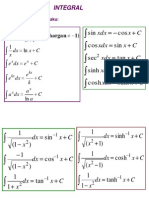
Limits for trigonometric functions
Let c is a real number.
a)
d)
lim sin x sin c
b)
lim csc x csc c
e)
xc
xc
lim cos x cos c
c)
lim sec x sec c
f)
xc
xc
lim tan x tan c
xc
lim cot x cot c
xc
Example
a)
lim sin x sin 1
2
x
2
b)
tan
4 1 4
lim tan x
1 1 4
x x 1
4
4
4
c)
sin x cos x
tan x 1 lim
cos x
lim 1 1 2
x sin x cos x
x sin x cos x
x cos x
cos
4
4
4
4
lim
12
6/29/2015
Special Limits
I.
lim sin x 1
x
lim 1 cos x 0
x
II.
x0
x0
Example
a)
b)
c)
lim tan x lim sin x lim sin x lim 1 1
x
x 0 x cos x
x 0 x x 0 cos x
x0
lim sin 4 x lim sin 4 x 4 4 lim sin 4 x 4
x
x
4 x0 4 x
x0
x0
x sin x lim sin x (1 cos x ) lim sin x lim 1 cos x 0
lim sin x cos
x
x0
x0 x x0
x2
x2
x0
13
Example (Using lim 1 0 and
x x
lim 1 0 )
x
a)
3 5
x 3 1
lim 3 x 5 lim
6
2
x 8 6 x
x 8 6
x
c)
4 1
2
x x2
lim 4 x 3 x lim
0
x 2 x 5
x 2 5
2
x
b)
d)
3 2x3
4
lim 3 2 x lim x
x x 1
x 1 1
x
3 2x3
4
lim 3 2 x lim x
x x 1
x 1 1
x
14
6/29/2015
Definition
A line x c is called a vertical asymptote of a function f ( x ) if f ( x ) or f ( x ) as
x c or x c .
A line y L is called a horizontal asymptote of a function f ( x ) if f ( x ) L as x or
x .
Theorem
A line x c is a vertical asymptote of a rational funtion f ( x )
p x
, if x c is a factor of the
q x
denominator q( x ) and not a common factor for p( x ) and q( x ) .
15
Example Find the vertical and horizontal asymptotes if any for the following functions.
a)
f ( x) x 3
x 1
b)
f ( x)
x
x2 4
c)
3
f ( x) x 2 8
x 4
d)
f ( x)
x 1
x3 x2 x 1
Solution
a)
x 1 is the vertical asymptote.
1 3
x 1.
lim x 3 lim
x x 1
x 1 1
x
b)
f ( x)
lim
y 1 is the horizontal astmptote
x
x
, x 2 and x 2 are the vertical asymptotes.
x 2 4 x 2 x 2
1
x lim
x 0 . y 0 is the horizontal astmptote
x 4 x 1 4
x2
2
16
6/29/2015
c)
3
x 2 x 2 2 x 4
f ( x) x 2 8
x 2 x 2
x 4
x 82
3
x .
lim x 2 8 lim
x x 4
x 1 4
x2
d)
f ( x)
x 2 is the vertical asymptote.
f ( x ) has no horizontal astmptotes
x 1
x 1
x 1
x 3 x 2 x 1 x 2 ( x 1) x 1 ( x 1) x 2 1
f ( x ) has no vertical astmptote
lim
1 1
x 1
x2 x3
lim
0.
x 3 x 2 x 1 x 1 1 1 1
x x2 x3
y 0 is the horizontal astmptote
17
Definition
A function f ( x ) is said to be continuous at x c if the following conditions are satisfied.
a)
b)
c)
f (c ) is defined.
lim f ( x ) exists
x c
lim f ( x ) f (c )
xc
18
6/29/2015
Example Given the graph of f ( x ) .
Determine whether f ( x ) continuous at x c for c 1,4,6 .
Solution
At x 1 , f ( 1) 3 and lim f ( x ) does not exist.
x 1
f ( x ) is discontinuous at x 1 .
At x 4 , f ( 4) 5 and lim f ( x ) 3 .
x4
-1
f ( x ) is discontinuous at x 4 .
-2
-3
At x 6 , f (6) 3 and lim f ( x ) 3 .
x6
f ( x ) is continuous at x 6 .
19
3x 1
2x 6
4 6 x
Example Given f ( x )
3 x 3 2 1
5
21 2 x
x 3
if
if
if
if
if
3 x 2
.
2 x5
x5
x5
Determine whether f ( x ) continuous at x c for c 3,2,5 .
Solution At x 3 , f ( 3) 1 and lim f ( x ) lim 3 x 1 .
x 3
x 3 2 x 6
lim f ( x ) does not exist.
x 3
f ( x ) is discontinuous at x 3 .
At x 2 , f ( 2) 3( 2 3) 2 1 2 ,
x2
lim f ( x ) lim 3( x 3)2 1 2
x 2
x2
lim f ( x ) lim 4 6 x 2 ,
x 2
lim f ( x ) 2 .
x2
f ( x ) is continuous at x 2 .
At x 5 , f ( 5) 5 ,
lim f ( x ) lim 3( x 3) 2 1 11 ,
x 5
x5
lim f ( x ) 11 f (5) .
x 5
lim f ( x ) lim 21 2 x 11.
x 5
x5
f ( x ) is discontinuous at x 5 .
20
10
6/29/2015
Derivative of a function
y
f ( x h)
f ( x h) f ( x )
f ( x)
From the diagram
A
h
Gradiaent AB f ( x h) f ( x )
xh
Gradiaent of the curve at A lim f ( x h) f ( x )
h
h 0
If y f ( x ), then
dy
f ( x h) f ( x )
f , ( x ) lim
.
dx
h
h 0
This process is known as differentiation from the first principles or differentiation using definition.
21
Example Find the derivative of f ( x ) 1 with respect to x from the first principles.
2
x
Solution
dy
f ( x h) f ( x )
f , ( x ) lim
dx
h
h 0
x h2
lim
h 0
12
x
x 2 x h2
lim
h 0 h x h 2 x 2
2
2
h2
lim x x 2 xh
h 0
h x h2 x 2
2
lim 2 xh 2h 2
h 0 h x h x
lim 2 x 2 h 2
h 0 x h x
2 x4 23
x
x
22
11
6/29/2015
Example
Given f ( x ) 2 x 2 x 2 . Find f ' ( x ) from the first principles.
Solution
f , ( x ) lim
h 0
lim
h 0
f ( x h) f ( x )
h
2 x h2 x h 2 2 x 2 x 2
h
2
2
2
lim 2 x 4 xh 2h x h 2 2 x x 2
h
h 0
2
lim 4 xh 2h h
h
h 0
lim 4 x 2h 1
h 0
4x 1
23
Example
1
Given f ( x ) x 2 . Find f ' ( x ) from the first principles.
Solution
f , ( x ) lim
h 0
f ( x h) f ( x )
h
xh x xh x
h
xh x
x
h x
lim
h 0 h x h x
h
lim
h 0 h x h x
1
lim
h 0 x h x
1
2 x
lim
h 0
24
12
6/29/2015
Example Show that d cos x sin x .
dx
Solution
d cos x f ' ( x ) for f ( x ) cos x .
dx
From the first principles
f , ( x ) lim
h 0
f ( x h) f ( x )
h
cos( x h) cos x
h
lim cos x cosh sin x sinh cos x
h
h 0
cos x cosh 1 sin x sinh
lim
h
h 0
cos x cosh 1 sin x sinh
lim
h
h
h 0
cos x cosh 1
sin
x
sinh
lim
lim
h
h
h 0
h 0
cosh 1
cos x lim
sin x lim sinh
h
h 0
h 0 h
cos x (0) sin x (1) sin x
lim
h 0
25
13
You might also like
- Math 1105 (11) Solution Key To Assignment #2: X X X X X X X XDocument3 pagesMath 1105 (11) Solution Key To Assignment #2: X X X X X X X XHasan128No ratings yet
- Finding Limits AnalyticallyDocument63 pagesFinding Limits AnalyticallyKaviarasu SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Differentiation - 2Document164 pagesChapter 3 Differentiation - 2dopeNo ratings yet
- Limits and ContinuityDocument41 pagesLimits and Continuityrofi modiNo ratings yet
- 151 Exam 1 Review AU10Document3 pages151 Exam 1 Review AU10Nathan W. SerafiniNo ratings yet
- Functions, Limits and ContinuityDocument3 pagesFunctions, Limits and ContinuityMohd AfzalNo ratings yet
- Limit Calculus)Document30 pagesLimit Calculus)Muhammad_Syaki_1428No ratings yet
- Find Limits of Functions HomeworkDocument17 pagesFind Limits of Functions HomeworknevinNo ratings yet
- CC Calculus Chapter 2 Answers PDFDocument19 pagesCC Calculus Chapter 2 Answers PDFOliver Ponoy MoncatarNo ratings yet
- Numericals ShimalowDocument118 pagesNumericals ShimalowClyde MaghamilNo ratings yet
- Calculus NoteDocument95 pagesCalculus NoteAfeef Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- 1-2FindingLimitsDocument26 pages1-2FindingLimitsAbu SalmanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Integration TechniquesDocument60 pagesNumerical Integration TechniquesImran ParvezNo ratings yet
- LIMITS AND CONTINUITYDocument41 pagesLIMITS AND CONTINUITYAan SajaNo ratings yet
- Book 18 - Limits and DerivativesDocument13 pagesBook 18 - Limits and Derivativessudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- 2 Differentiation 1 SlidesDocument102 pages2 Differentiation 1 Slidesmseconroy84No ratings yet
- Welcome Back TO Maths' World QS025: Hclim - KMJDocument175 pagesWelcome Back TO Maths' World QS025: Hclim - KMJHaspreet GillNo ratings yet
- Guia2 LimitesDocument5 pagesGuia2 LimitescarlaleivaNo ratings yet
- 03 Chapter 3 Differentiation 5oktDocument38 pages03 Chapter 3 Differentiation 5oktMohd ShahidNo ratings yet
- Numerical Integration FormulasDocument60 pagesNumerical Integration FormulasBeverly PamanNo ratings yet
- INTEGRATION RULES AND TECHNIQUESDocument11 pagesINTEGRATION RULES AND TECHNIQUESahlam_1995No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Limit and ContinuityDocument93 pagesChapter 1 Limit and ContinuityAna ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of Inverse Function - Problems and SolutionsDocument11 pagesDerivatives of Inverse Function - Problems and SolutionsYinkci Heart Entertainment StudioNo ratings yet
- Master differentiation techniquesDocument17 pagesMaster differentiation techniquesMuhamad NazrinNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT - Limits & ContinuityDocument5 pagesASSESSMENT - Limits & ContinuityShannon Burton100% (1)
- Class 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesDocument9 pagesClass 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesRoy67% (6)
- Limites - Profº CarlosDocument12 pagesLimites - Profº CarlosWeriq TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Limit TheoremsDocument3 pagesLimit TheoremsDane SinclairNo ratings yet
- 16.2 Limit TheoremsDocument9 pages16.2 Limit TheoremsGemechis MergaNo ratings yet
- Exercicios Limite FilipeDocument2 pagesExercicios Limite FilipeJulio SousaNo ratings yet
- One Sided Limits and Limits Involving Infinity Examples and SolutionsDocument20 pagesOne Sided Limits and Limits Involving Infinity Examples and SolutionsVencent YoutubeNo ratings yet
- M2 PDFDocument7 pagesM2 PDFabasNo ratings yet
- Calculus I: Advanced Level Pure MathematicsDocument27 pagesCalculus I: Advanced Level Pure Mathematicsmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Integral Bag 1Document10 pagesIntegral Bag 1NayundaBellaMNo ratings yet
- BM Chapter 4Document35 pagesBM Chapter 4nurfatimah473No ratings yet
- Honors Pre Cal Chapter 13 NotesDocument16 pagesHonors Pre Cal Chapter 13 NotesKent MillerNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity: An SEO-Optimized Guide to Key ConceptsDocument33 pagesLimits and Continuity: An SEO-Optimized Guide to Key ConceptsHanani IdrisNo ratings yet
- Limit of A FunctionDocument30 pagesLimit of A FunctionhamZaNo ratings yet
- Limits (Students Study Material & Assignment)Document15 pagesLimits (Students Study Material & Assignment)DAVID ABDULSHUAIB AYEDUNNo ratings yet
- Limits: Calculus Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesLimits: Calculus Cheat SheetPratiksh PatelNo ratings yet
- Handwritten Notes Week 6Document35 pagesHandwritten Notes Week 6Good For NothingNo ratings yet
- By: Jessa Mhaem. ElviñaDocument22 pagesBy: Jessa Mhaem. ElviñaBb-chaii MhenggaiiNo ratings yet
- Rules of Derivative Used in Economics (ECO401)Document8 pagesRules of Derivative Used in Economics (ECO401)Atif MahiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CalculusDocument11 pagesMathematics CalculusAnish NaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0Document30 pagesChapter 0Mc VinothNo ratings yet
- LIMIT OF A SEQUENCE. As Consecutive Points, Given by The Terms of The SequenceDocument13 pagesLIMIT OF A SEQUENCE. As Consecutive Points, Given by The Terms of The SequenceReni KinongNo ratings yet
- Calc Study PDFDocument7 pagesCalc Study PDFRussell FromUpNo ratings yet
- 1 HomCalculo1Document3 pages1 HomCalculo1Ignacio Manzanares EstebanNo ratings yet
- LastDocument107 pagesLastAnonymous XC6BngNo ratings yet
- MATH1151 Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesMATH1151 Final Exam ReviewtravissaronNo ratings yet
- Graphing Polynomials WorksheetDocument2 pagesGraphing Polynomials WorksheetAria JonesNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityDocument57 pagesLimits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityPol EboyNo ratings yet
- Grade (10) Chapter - 12 CalculusDocument33 pagesGrade (10) Chapter - 12 CalculusZakir Amad 32No ratings yet
- Limits and ContinuityDocument4 pagesLimits and ContinuityShoaib ShaikNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 3 Derivative of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Dr. Ghada AbdelhadyDocument32 pagesLecture # 3 Derivative of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Dr. Ghada AbdelhadyEsraa AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Differential and Integral CalculusDocument6 pagesBasic Concepts of Differential and Integral CalculusManoj KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- WEEK MathsDocument22 pagesWEEK Mathsshahmeer sultanNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 SolutionDocument5 pagesTutorial 6 SolutionAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Note - W3 and W4Document19 pagesFluid Note - W3 and W4Amirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Lecture W4Document10 pagesFluid Lecture W4Amirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Deflection 2Document15 pagesDeflection 2Amirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics: Fluid Mechanics Notes Basic Physics 1 (Fmax 0111)Document4 pagesFluid Dynamics: Fluid Mechanics Notes Basic Physics 1 (Fmax 0111)Amirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Deflection TeachingDocument21 pagesDeflection TeachingAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- MOM - Chap 8 PDFDocument25 pagesMOM - Chap 8 PDFAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Takwim Fizik Sem 1 Sesi 2014-2015Document2 pagesTakwim Fizik Sem 1 Sesi 2014-2015Amirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Note - W3 and W4Document8 pagesFluid Note - W3 and W4Amirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- BALANCING REDOX REACTIONS USING METHODSDocument8 pagesBALANCING REDOX REACTIONS USING METHODSAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Note - W3 and W4Document8 pagesFluid Note - W3 and W4Amirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SecretsDocument1 pageTrigonometry SecretsOggy22No ratings yet
- Partial Fraction Decomposition PDFDocument4 pagesPartial Fraction Decomposition PDFAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Kedah-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009Document16 pagesKedah-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Grand Theft Auto San Andreas CheatsDocument1 pageGrand Theft Auto San Andreas CheatsAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- SIGNFIGDocument10 pagesSIGNFIGAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Thanks ScribdDocument1 pageThanks ScribdAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Thanks ScribdDocument1 pageThanks ScribdAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Example Doc For Scribd SharingDocument1 pageExample Doc For Scribd SharingAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Thanks ScribdDocument1 pageThanks ScribdAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Example Doc For Scribd SharingDocument1 pageExample Doc For Scribd SharingAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- Thank YouDocument1 pageThank YouAmirul FadlinNo ratings yet
- GCSE CurvedGraphsDocument15 pagesGCSE CurvedGraphsAdil HafeezNo ratings yet
- MCR 3U1 Unit 3 Algebra and Transformations of Functions Part 2 Unit Test Copy 1Document5 pagesMCR 3U1 Unit 3 Algebra and Transformations of Functions Part 2 Unit Test Copy 1benmparker76No ratings yet
- 2008 Acjc Prelims Ma h2 p1 QPDocument5 pages2008 Acjc Prelims Ma h2 p1 QPsimon-leonard-koh-3460No ratings yet
- G11 - General Mathematics - 1st Sem - Midterm NotesDocument5 pagesG11 - General Mathematics - 1st Sem - Midterm NotesaglubatjohngrayNo ratings yet
- X X X X X X FX X X: Group A Find The Vertical Asymptotes and Holes of The FollowingDocument9 pagesX X X X X X FX X X: Group A Find The Vertical Asymptotes and Holes of The Followingapi-262707463No ratings yet
- Asymptotes, Holes, and Graphing Rational FunctionsDocument4 pagesAsymptotes, Holes, and Graphing Rational Functions1DerfulHarrehNo ratings yet
- Iygb Gce: Mathematics MP1 Advanced LevelDocument8 pagesIygb Gce: Mathematics MP1 Advanced LevelEY3SOR3No ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanDocument5 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery PlanRy BargayoNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Formulas SummaryDocument7 pagesDifferential Calculus Formulas SummaryRocelle Andrea BelandresNo ratings yet
- GENMATH SAS Q1 Week 2Document29 pagesGENMATH SAS Q1 Week 2Mannuelle Gacud100% (1)
- Graphs of Rational FunctionsDocument27 pagesGraphs of Rational FunctionsJimmy MagundayaoNo ratings yet
- GVFDocument8 pagesGVFAloke BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Results of 1st Quarter Exam & Item Analysis in English 9Document33 pagesResults of 1st Quarter Exam & Item Analysis in English 9Jen FerrerNo ratings yet
- Core 1 Revision PackDocument28 pagesCore 1 Revision PackSunny AfgNo ratings yet
- SP Las 10Document10 pagesSP Las 10Hevier PasilanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.1 Limit at InfinityDocument19 pagesLesson 4.1 Limit at InfinityYvonne TapanNo ratings yet
- And To Apply Logic To Real-Life SituationsDocument15 pagesAnd To Apply Logic To Real-Life SituationsMatt BarbasaNo ratings yet
- Lui Cheung Kwong Lutheran College F.6 Mathematics Modules 2 MID-TERM EXAMINATION (2021-2022)Document24 pagesLui Cheung Kwong Lutheran College F.6 Mathematics Modules 2 MID-TERM EXAMINATION (2021-2022)Marco LamNo ratings yet
- Skills Practice: Name - DateDocument20 pagesSkills Practice: Name - DateJosephine RowanNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB Study GuideDocument63 pagesAP Calculus AB Study GuideMai Nhiên Lê NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work General Mathematics 2023 24Document3 pagesBudget of Work General Mathematics 2023 24alonaNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Effectiveness Factor for Complex Kinetic ModelsDocument8 pagesCatalyst Effectiveness Factor for Complex Kinetic ModelsnadiaNo ratings yet
- Limits Involving InfinityDocument12 pagesLimits Involving InfinityAde RahmaNo ratings yet
- Arch Anarchy 1Document18 pagesArch Anarchy 1pedrolucas27758No ratings yet
- Ellipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AsDocument18 pagesEllipse: Intercepts. The Endpoints of The Minor Axis Are (0, B) and (0, - B) and Are Referred To AseL LeahNo ratings yet
- H2 Math Paper 1 SolutionsDocument30 pagesH2 Math Paper 1 SolutionsHANSNo ratings yet
- VCE Math Quest - Specialist Maths - Year 11Document96 pagesVCE Math Quest - Specialist Maths - Year 11Anila Jayaraj100% (1)
- Practice: Rational Functions and Their GraphsDocument1 pagePractice: Rational Functions and Their GraphsShammany AlsuwaidiiNo ratings yet
- (MAA 2.13-2.15) RATIONAL AND MODULUS FUNCTIONS - INEQUALITIES - SolutionsDocument11 pages(MAA 2.13-2.15) RATIONAL AND MODULUS FUNCTIONS - INEQUALITIES - SolutionsarmNo ratings yet